本文主要摘自CISCO的一篇白皮书.
名词:
NGOSS: Next Generation Operations Systems and Software.
eTom: enhanced Telecommunication Operations Map
ITIL: Information Technology Infrastructure Library
1.什么是NGOSS?
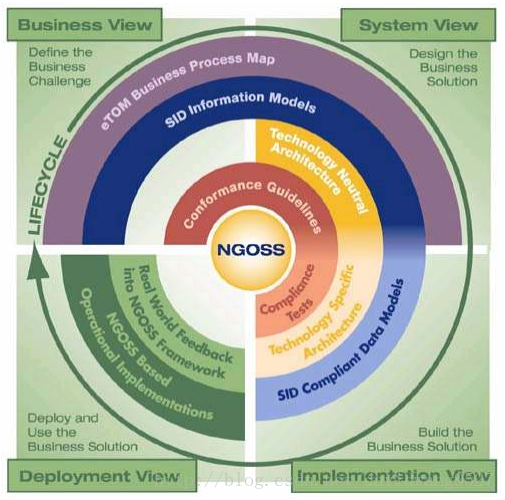
NGOSS (Figure 1) is a comprehensive, integrated framework for developing, procuring, and deploying operations and business support systems (OSSs/BSSs) and software. It is available as a toolkit of industry-agreed specifications and guidelines that cover key business and technical areas including:
● eTOM Business Process Map: An industry-agreed set of integrated business process descriptions, created with today’s customer-centric market in mind, used for mapping and analyzing operational processes. (笔者理解:流程)
● Shared Information/Data (SID) Model: Comprehensive,standardized information definitions acting as the common language for all data to be used in NGOSS-based applications. A common information language is the linchpin in creating easy-to-integrate software solutions.(笔者理解:数据模型与接口)
● Technology Neutral Architecture: Key architectural guidelines and specifications to ensure high levels of flow through amongst diverse systems and components.
● Compliance and Conformance Criteria: Guidelines and tests to ensure that systems defined and developed utilizing NGOSS specifications will interoperate.
● Lifecycle and Methodology: Processes and artifacts that allow developers and integrators to use the toolset to develop NGOSS-based solutions employing a standard approach.
(Figure 1)
这种统一的流程、统一的数据模型、统一的接口、中立的技术架构、兼容性测试、生命周期与方法论,对于运营商与厂商的好处就不言自明了。
2.什么是eTom
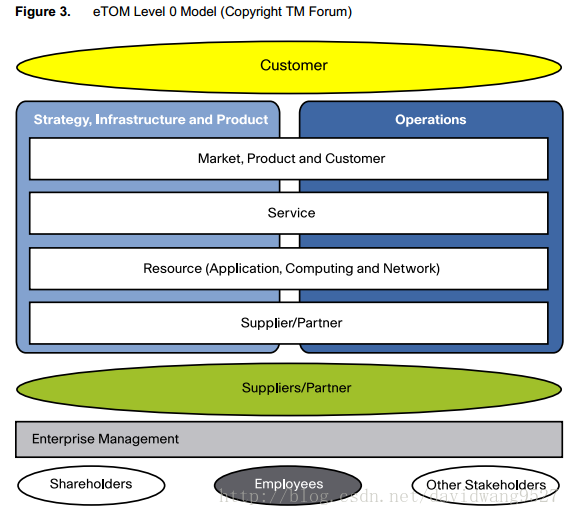
At the overall conceptual level (Figure 3), the Business Process Framework can be viewed as having the following three major process areas:
● Strategy, Infrastructure, and Product (SIP) covering planning and lifecycle management
● Operations covering the core of day-to-day operational management
● Enterprise Management covering corporate or business support management
The Level 0 Framework also includes views of functionality as they span horizontally across an enterprise’s internal organizations:
● Market, Product, and Customer: High-level view of the market and the enterprise’s offerings
● Service: Product components developed by the enterprise
● Resource (Application, Computing, and Network): Consumed in the production of the Service
● Supplier/Partner: Providing products and services to the enterprise for the production of the Service
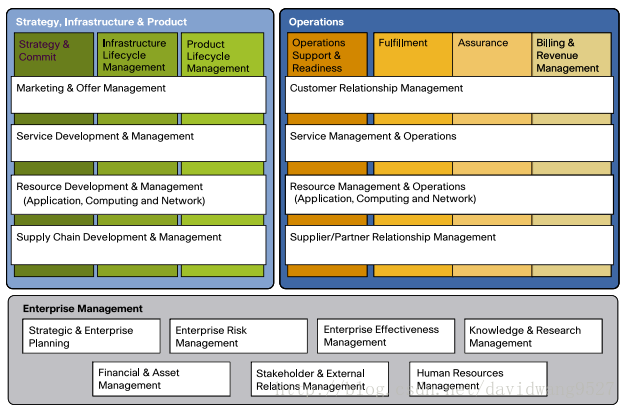
A more detailed view of the Enterprise processes is presented in the Level 1 eTOM model (Figure 4). The model shows seven end-to-end vertical process groupings required to support customers and manage the business.
Among these vertical groupings, the focus of eTOM is on the core customer operational processes of Fulfillment, Assurance, and Billing (FAB).
Operations Support and Readiness (OSR) is the “back-office” environment that enables support and automation for FAB. The SIP processes do not directly support the customer and they include the Strategy and Commit and the two lifecycle process groupings.
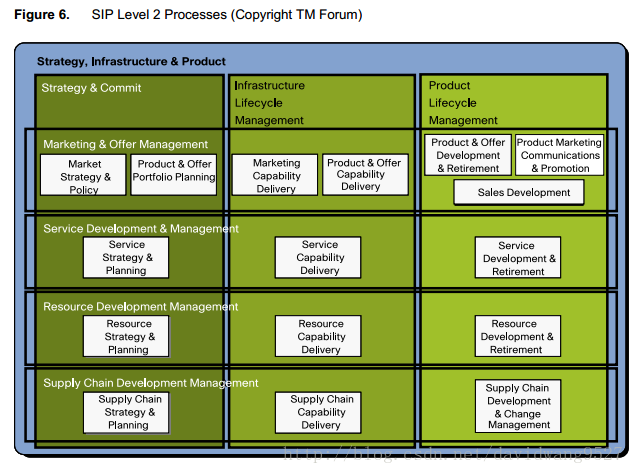
The next three figures show the Level 2 core processes for the Operations, SIP, and Enterprise Management areas.
Each core process is generally part of one verticalLevel 1 grouping and also one horizontal process grouping. In
some cases a Level 2 process is “stretched” across several Level 1 vertical groupings because the process
concerned is needed in several Level 1 verticals.
This procedure can be continued at lower levels as required. The eTOM layers can generally be described as following:
● Level 0: Business Activities that distinguish operational customer-oriented processes from management and
strategic processes
● Level 1: Process Groupings including business functions and standard end-to-end processes
● Level 2: Core Processes that combine together to deliver service streams and other end-to-end processes
● Level 3: Tasks and associated detailed “success model” business process flows
● Level 4: Steps and associated detailed operational process flows with error conditions and product and
geographical variants (where required)
● Level 5: Further decomposition into operations and associated operational process flows where required
3.Using eTom
The focus of eTOM is on the business processes used by service providers, the linkages between these processes,
the identification of interfaces, and the use of customer, service, resource, supplier/partner, and other information by
multiple processes. eTOM represents an industry consensus on the service provider processes, which hasbeen
harmonized across the global scene and is based on TM Forum Member contributions. It is allowable, andindeed
expected, that this will mean that eTOM must be tailored and/or extended for use within an individual company.
and to optimize processes.The two main techniques used to analyze existing organizational processes are through process interaction and process flows, illustrated in Figures 8 and 9.
Figure 8不贴图了,其实process interaction就跟UML的collobration一样,没有次序,只能看出来谁的交互比较多;Process flow就是流程图了,类似于UML的sequence,不过一般用泳道图,这样能够清晰的看出来每个功能点属于哪个模块:
4.eTOM and ITIL
粗浅的理解,ITIL因为整个IT及ICT行业,所以比较宽泛,而eTom更加针对ICT细化,所以eTom可以借鉴部分ICT的流程:
The conclusions of the joint eTOM-ITIL® team are that the two frameworks are compatible, complementary and mutually supportive. eTOM and ITIL® can be integrated by using ITIL® best practices to specialize eTOM processes.






















 1476
1476











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








