Preface
Code Zoo,这个名字取自于深度学习框架 caffe 中著名的模型集合:Caffe Model Zoo。
就是想把我平时用 Torch 时做深度学习时,写的 Lua 代码,如脚本工具、Lua 和 Torch 中的处理函数、使用过程中跳进去的坑…整理集中起来,供以后参考,也给需要的同学一点线索。
Tensor 逐元素相乘
q=122436
,
w=122436
,则逐元素相乘的意思是,每个对应元素两两相乘:
在 Torch 中,这很容易实现:
th> torch.cmul(q,w)加载保存图片
参考:
1. https://github.com/torch/image/blob/master/doc/saveload.md
2. https://github.com/torch/image
读取图像:
-- To load as byte tensor for rgb imagefile
local img = image.load(imagefile, 3, 'byte')
-- To load as byte tensor for gray imagefile
local img = image.load(imagefile, 1, 'byte')保存图像:
image.save(filename, tensor)返回 Table 前 k 个最小值及其索引
Torch 中数学函数库,可以参考下面:
https://github.com/torch/torch7/blob/master/doc/maths.md
而返回 table 前 K 个最小值,torch.kthvalue():
-- returns the k-th smallest element of x over its last dimension
y = torch.kthvalue(x, k)
-- returns the k-th smallest element in each column (across rows) of x, and a Tensor i of their corresponding indices in x
y, i = torch.kthvalue(x, k, 1)
-- performs the k-th value operation for each row
y, i = torch.kthvalue(x, k, 2)
-- performs the k-th value operation over the dimension n
y, i = torch.kthvalue(x, k, n)我看还可以用 torch.topk() 来求,可参考:
1. http://stackoverflow.com/questions/34750268/extracting-the-top-k-value-indices-from-a-1-d-tensor
2. https://github.com/torch/torch7/blob/03c04c6/doc/maths.md#torchtopkresval-resind-x-k-dim-dir-sort
> t = torch.Tensor{9, 1, 8, 2, 7, 3, 6, 4, 5}
-- obtain the 3 smallest elements
> res = t:topk(3)
> print(res)
1
2
3
[torch.DoubleTensor of size 3]
-- you can also get the indices in addition
> res, ind = t:topk(3)
> print(ind)
2
4
6
[torch.LongTensor of size 3]
-- alternatively you can obtain the k largest elements as follow
-- (see the API documentation for more details)
> res = t:topk(3, true)
> print(res)
9
8
7
[torch.DoubleTensor of size 3]lua 中遍历 table
如果我想知道一个 table 中元素的最小值或者最大值,用 lua 该如何遍历呢?
参考:http://stackoverflow.com/questions/20827259/returning-key-of-maximum-or-minimum-number-in-a-table
local t = {1, 3, 7, 6, 4, 0}
local key, max = 1, t[1]
for k, v in ipairs(t) do
if t[k] > max then
key, max = k, v
end
end
print(key, max)lua 中 string 转 int
lua 中 string 转 数值该怎么做呢,可以使用函数 tonumber(),参考:
http://stackoverflow.com/questions/10962085/lua-string-to-int
>a = "10"
>print(type(a))
string
>b = tonumber(a)
>print(type(b))
numberlua 中转字符串 string
用 tostring(),如下所示:

Torch 中查看 Tensor 的 size 大小
vector = torch.randn(2, 5)
-- 若想查看 Tensor 的 size:
print(vector:size())输出:
2
5
[torch.LongStorage of size 2]若是在 lua 中:
x = {{1, 2, 3},{4, 5, 6}}
print(table.getn(x))输出为:
2lua 中字符串的截取函数 string.sub( )
我在 itorch notebook 中写了例子,很好理解,就不详细叙述了:

Torch 中按行读入 TXT 文件
2016.07.22 更新
今天在用 Torch 组织 Triplet Loss 的数据时,需要用我在 Python Zoo 中用 python 生成的 TXT 文件:
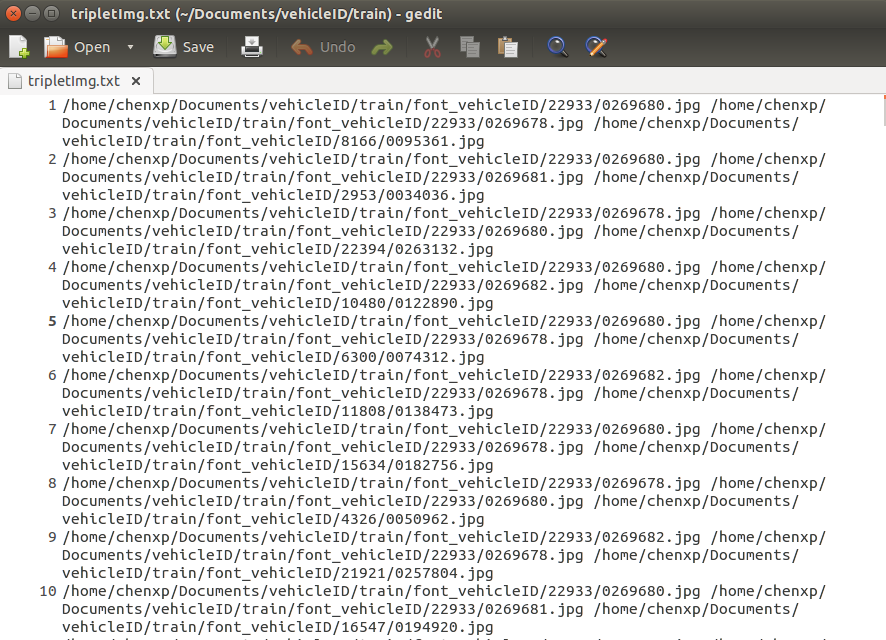
那这样的 TXT 怎么生成 Torch 可读的 .t7 文件呢?
require 'io'
require 'xlua'
require 'image'
batchSize = 49060
imgSize = 128
aImgs = torch.Tensor(batchSize, 3, imgSize, imgSize):zero():float()
pImgs = torch.Tensor(batchSize, 3, imgSize, imgSize):zero():float()
nImgs = torch.Tensor(batchSize, 3, imgSize, imgSize):zero():float()
file = io.open('/home/chenxp/torch/mytorch/tripletVehicle/tripletImg.txt', 'r')
if file then
local count = 1
for line in file:lines() do
xlua.progress(count, batchSize)
imgAnchor, imgPositive, imgNegative = unpack(line:split(" "))
local img1 = image.load(imgAnchor)
local img2 = image.load(imgPositive)
local img3 = image.load(imgNegative)
aImgs[count] = image.scale(img1, imgSize, imgSize):float()
pImgs[count] = image.scale(img2, imgSize, imgSize):float()
nImgs[count] = image.scale(img3, imgSize, imgSize):float()
count = count + 1
end
else
print('File do not exists!')
end
file:close()
print('Save Anchor Images: aImgs.t7: ')
torch.save('aImgs.t7', aImgs)
print('Save Positive Images: pImgs.t7: ')
torch.save('pImgs.t7', pImgs)
print('Save Negative Images: nImgs.t7: ')
torch.save('nImgs.t7', nImgs)Torch 按行读取参考了下面的 stackoverflow 回答:How to load text file into sort of table-like variable in Lua :
local file = io.open("filename.txt")
if file then
for line in file:lines() do
local name, address, email = unpack(line:split(" ")) --unpack turns a table like the one given (if you use the recommended version) into a bunch of separate variables
--do something with that data
end
else
end
--you'll need a split method, i recommend the python-like version at http://lua-users.org/wiki/SplitJoin
--not providing here because of possible license issuesLua 中 collectgarbage 函数
2016.07.25 更新
在阅读 Google 的论文:《FaceNet: A Unified Embedding for Face Recognition and Clustering》,这篇 CVPR2015 的 Paper 的torch 代码 OpenFace ,多次碰到碰到下面一句 lua 代码:
collectgarbage()由于多次碰到,我感觉还是比较重要的,所以 Google 了一下,在这篇网页中找到了函数解释:http://luatut.com/collectgarbage.html
This function is a generic interface to the garbage collector. It performs different functions according to its first argument, opt:
- “collect”: performs a full garbage-collection cycle. This is the default option.
- “stop”: stops the garbage collector.
- “restart”: restarts the garbage collector.
- “count”: returns the total memory in use by Lua (in Kbytes).
- “step”: performs a garbage-collection step. The step “size” is controlled by arg (larger values mean more steps) in a non-specified way. If you want to control the step size you must experimentally tune the value of arg. Returns true if the step finished a collection cycle.
- “setpause”: sets arg as the new value for the pause of the collector. Returns the previous value for pause. “setstepmul”: sets arg as the new value for the step multiplier of the collector. Returns the previous value for step.
根据上面的解释,这个函数是 Lua 中的一个垃圾收集函数,可以输入待选参数,默认为 collectgarbage(“collect”)。这个参数说明函数将要进行一个全面的垃圾收集,在每次循环中都要进行垃圾收集。
有两个参数说明一下。
一个是当参数是 count 的时候,
To find the number of kilobytes currently in use by Lua, you can simply make a call with count.
What you see in the console is the memory usage before and after the assignment. You should see around \sim 21 - 22 bytes of memory used up by the assignment.
即找到目前 Lua 所使用的内存大小,可以使用
count参数。看下面的控制台输出,当进行一个赋值后,增加了 21 - 22 字节的内存使用(但这是在上面网页提供的控制台的输出,我在自己的机子上好像不止这么多…)
collectgarbage("count")的示例如下:
print(collectgarbage("count")*1024)
a = "123"
print(collectgarbage("count")*1024)输出如下:
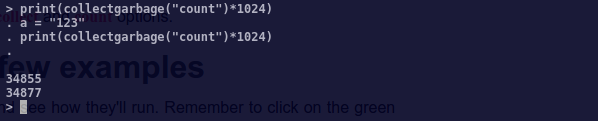
另外一个是默认的 collect,这是要进行一个全面的收集:
a = {1,2,3}
a = nil
collectgarbage()事实上,当我将 print(collectgarbage()),输出的是 0 。
Torch 中生成等差数列
2016.07.26 更新
Torch 中生成等差数列跟 Python 中类似,用如下:
x = torch.range(beginNumber, endNumber [, step])
-- y = torch.range(x, y) returns a Tensor of size:
-- floor((y - x) / step) + 1
-- with values from x to y with step 'step' (default to 1)
>torch.range(2,5)
2
3
4
5
[torch.DoubleTensor of size 4]
>torch.range(2, 5, 1.2)
2.0000
3.2000
4.4000
[torch.DoubleTensor of size 3]更多的数学函数查阅可以看下面的地址:
1. http://torch7.readthedocs.io/en/latest/maths/index.html
2. https://github.com/torch/torch7/blob/master/doc/maths.md
Torch 中遍历文件夹及文件
2016.07.27 更新
有一个文件夹,叫做 tripletTestImgs,其下面有三个子文件夹:aImgs、pImgs、nImgs,三个字文件下各有 5 张图片。用 Tree 命令显示文件目录如下:
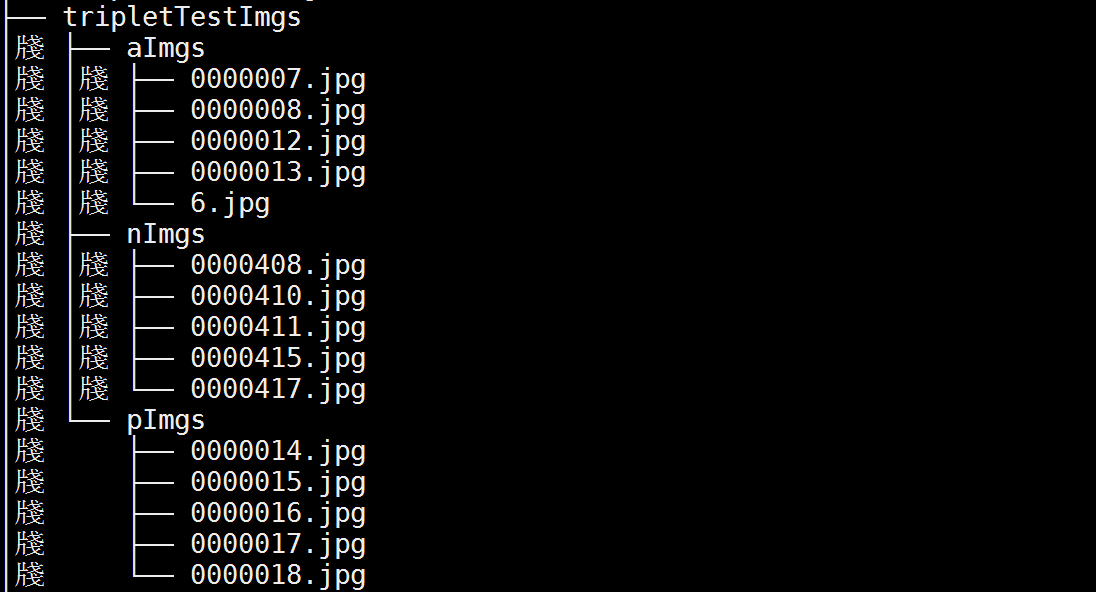
在 Torch 中遍历方法如下:
for d in paths.iterdirs('tripletTestImgs') do
for f in paths.iterfiles('d') do
img = image.load('tripletTestImgs' .. d .. '/' .. f)
......
-- do you want to do --
end
endTorch 中判断字符串是否是 nil 或者为空字符串
2016.07.28 更新
在写 lua 的代码中,经常要判断字符串是否是 nil 或者是空字符串。如果不先判断,写不好的话就很容易报错。
这个总结来自于 Stackoverflow 的一篇回答:http://stackoverflow.com/questions/19664666/check-if-a-string-isnt-nil-or-empty-in-lua
if (foo == nil or foo == '') then
foo = "some default value"
end像上面那样判断本来是不错的,但一旦需要判断的字符串多了。就不如写一个判断函数 isempty() 了:
local function isempty(s)
return s == nil or s == ''
end
if isempty(foo) then
foo = "some default value"
endTorch 中 AlexNet 网络
2016.07.28 更新
Alexnet 是经典的常用网络结构,可以参考下面这个仓库里写的,做了效果更好的初始化:https://gist.github.com/gcr/0bab9929dfee95164a4d
------- AlexNet: Using my own weight initialization
model = nn.Sequential()
model:add(cudnn.SpatialConvolution(3,96,11,11,4,4,2,2))
model.modules[#model.modules].weight:normal(0, 0.01)
model.modules[#model.modules].bias:fill(0)
model:add(cudnn.ReLU())
model:add(inn.SpatialCrossResponseNormalization(5, 0.0001, 0.75, 1))
model:add(nn.SpatialMaxPooling(3,3,2,2))
model:add(cudnn.SpatialConvolution(96,256,5,5,1,1,2,2))
model.modules[#model.modules].weight:normal(0, 0.01)
model.modules[#model.modules].bias:fill(0.1)
model:add(cudnn.ReLU())
model:add(inn.SpatialCrossResponseNormalization(5, 0.0001, 0.75, 1))
model:add(nn.SpatialMaxPooling(3,3,2,2))
model:add(cudnn.SpatialConvolution(256,384,3,3,1,1,1,1))
model.modules[#model.modules].weight:normal(0, 0.01)
model.modules[#model.modules].bias:fill(0)
model:add(cudnn.ReLU())
model:add(cudnn.SpatialConvolution(384,384,3,3,1,1,1,1))
model.modules[#model.modules].weight:normal(0, 0.01)
model.modules[#model.modules].bias:fill(0.1)
model:add(cudnn.ReLU())
model:add(cudnn.SpatialConvolution(384,256,3,3,1,1,1,1))
model.modules[#model.modules].weight:normal(0, 0.01)
model.modules[#model.modules].bias:fill(0.1)
model:add(nn.ReLU())
model:add(nn.SpatialMaxPooling(3,3,2,2))
model:add(nn.View(256*6*6))
model:add(nn.Linear(256*6*6, 4096))
model.modules[#model.modules].weight:normal(0, 0.005)
model.modules[#model.modules].bias:fill(0.1)
model:add(cudnn.ReLU())
model:add(nn.Dropout(0.5))
model:add(nn.Linear(4096, 4096))
model.modules[#model.modules].weight:normal(0, 0.005)
model.modules[#model.modules].bias:fill(0.1)
model:add(cudnn.ReLU())
model:add(nn.Dropout(0.5))
model:add(nn.Linear(4096, 1000))
model.modules[#model.modules].weight:normal(0, 0.01)
model.modules[#model.modules].bias:fill(0)
model:add(nn.LogSoftMax())
model:cuda()未做自己的初始化的结构如下:
------- AlexNet: Using Torch defaults for weight initialization
model = nn.Sequential()
model:add(cudnn.SpatialConvolution(3,96,11,11,4,4,2,2))
model:add(cudnn.ReLU())
model:add(inn.SpatialCrossResponseNormalization(5, 0.0001, 0.75, 1))
model:add(nn.SpatialMaxPooling(3,3,2,2))
model:add(cudnn.SpatialConvolution(96,256,5,5,1,1,2,2))
model:add(cudnn.ReLU())
model:add(inn.SpatialCrossResponseNormalization(5, 0.0001, 0.75, 1))
model:add(nn.SpatialMaxPooling(3,3,2,2))
model:add(cudnn.SpatialConvolution(256,384,3,3,1,1,1,1))
model:add(cudnn.ReLU())
model:add(cudnn.SpatialConvolution(384,384,3,3,1,1,1,1))
model:add(cudnn.ReLU())
model:add(cudnn.SpatialConvolution(384,256,3,3,1,1,1,1))
model:add(nn.ReLU())
model:add(nn.SpatialMaxPooling(3,3,2,2))
model:add(nn.View(256*6*6))
model:add(nn.Linear(256*6*6, 4096))
model:add(cudnn.ReLU())
model:add(nn.Dropout(0.5))
model:add(nn.Linear(4096, 4096))
model:add(cudnn.ReLU())
model:add(nn.Dropout(0.5))
model:add(nn.Linear(4096, 1000))
model:add(nn.LogSoftMax())
model:cuda()Torch 中 norm 函数
2016.07.29 更新
所谓的 norm,就是指大名鼎鼎的 范数,A norm is a way of measuring the length of a vector. 给定一个
n
维 vector:
向量的 p−norm 定义为:
向量的 ∞ 范定义为:
这么多范数中,最常用的应该是 L2−norm 范数了吧( 更通俗的来讲,就是广义上的欧氏距离):
Torch 中提供了求范数的函数:
y=torch.norm(x) -- returns the 2-norm of the tensor x
y=torch.norm(x,p) -- returns the p-norm of the tensor x
y=torch.norm(x,p,dim) -- returns the p-norms of the tensor x computed over the dimension dim.




















 1372
1372

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








