工厂方法模式:定义了一个创建对象的接口,由子类来决定具体实例化那个对象。工厂方法模式让类的实例化转移到子类中来判断。
Define an interface for creating an object, but let subclasses decide which class to instantiate. Factory Method lets a class defer instantiation to subclasses.
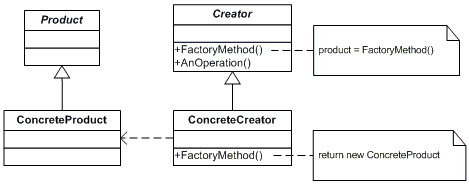
UML图:
主要包括:
- Product(Page):定义了工厂类创建的对象的接口
- ConcreteProduct(SkillPage,EducationPage,ExperiencePage):实现了Product的具体的类
- Creator(Document):声明了一个工厂方法,这个方法返回一个Product类型的对象。
- ConcreteCreator(Report,Resume):重写工厂方法来实例化具体的Product
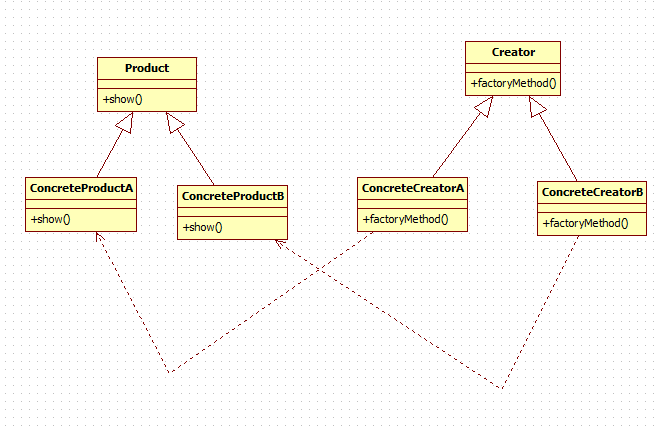
上面的UML是工厂方法模式一般的图例,针对一个具体的有两个ConcreteProductA,ConcreteProductB,以及它们各自工厂类ConcreteCreatorA,ConcreteCreatorB的UML图如下所示:
C++代码如下:
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <iostream>
class Product
{
public:
virtual void show()=0;
};
class ConcreteProductA:public Product
{
public:
void show()
{
std::cout<<"ConcreteProductA:show"<<std::endl;
}
};
class ConcreteProductB:public Product
{
public:
void show()
{
std::cout<<"ConcreteProductB:show"<<std::endl;
}
};
class Creator
{
public:
virtual Product * factoryMethod()=0;
};
class ConcreteCreatorA:public Creator
{
public:
Product* factoryMethod()
{
return new ConcreteProductA();
}
};
class ConcreteCreatorB:public Creator
{
public:
Product* factoryMethod()
{
return new ConcreteProductB();
}
};
int main()
{
std::cout<<"工厂方法模式"<<std::endl;
Creator * creatorA=new ConcreteCreatorA;
Creator * creatorB=new ConcreteCreatorB;
Product * pa=creatorA->factoryMethod();
Product* pb=creatorB->factoryMethod();
pa->show();
pb->show();
delete creatorA;
delete creatorB;
delete pa;
delete pb;
return 0;
}
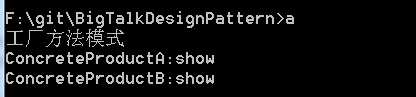
测试输出:
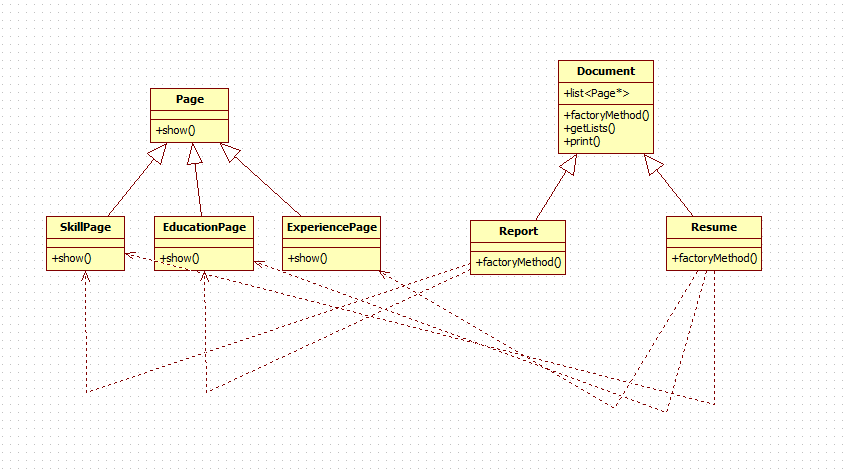
其实还可以一个具体的ConcreteCreator对应多个ConcreteProduct,这里以一个例子为例分析:
- Product为Page
- ConcreteProduct包括SkillPage,EducationPage,ExperiencePage
- Creator为Document(文档)
- ConcreteCreator为Report(报告文档,报告文档中有SkillPage,EducationPage),Resume(简历文档,简历文档中有SkillPage,EducationPage,ExperiencePage)
这也是一个工厂方法模式的例子
UML图为:
C++代码实现如下:
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
class Page
{
public:
virtual void show()=0;
};
class SkillPage:public Page
{
public:
void show()
{
std::cout<<"SkillPage::show"<<std::endl;
}
};
class EducationPage:public Page
{
public:
void show()
{
std::cout<<"Education::show"<<std::endl;
}
};
class ExperiencePage:public Page
{
public:
void show()
{
std::cout<<"Experience::show"<<std::endl;
}
};
class Document
{
public:
virtual void factoryMethod()=0;
list<Page*>& getLists()
{
return lists;
}
void print()
{
list<Page*>::iterator iter;
for(iter=lists.begin();iter!=lists.end();iter++)
(*iter)->show();
}
//注意这里要将list中的指针指向的内存删除掉,不然会造成内存泄露
virtual ~Document(){
list<Page*>::iterator iter;
for(iter=lists.begin();iter!=lists.end();iter++)
{
if(*iter)
delete *iter;
}
}
private:
list<Page*> lists;
};
class Report:public Document
{
public:
void factoryMethod()
{
getLists().push_back(new SkillPage());
getLists().push_back(new EducationPage());
}
};
class Resume:public Document
{
public:
void factoryMethod()
{
getLists().push_back(new SkillPage());
getLists().push_back(new EducationPage());
getLists().push_back(new ExperiencePage());
}
};
int main()
{
std::cout<<"具体的工厂方法模式测试"<<std::endl;
Document * report=new Report();
Document * resume=new Resume();
report->factoryMethod();
resume->factoryMethod();
std::cout<<"report print"<<std::endl;
report->print();
std::cout<<"resume print"<<std::endl;
resume->print();
return 0;
}
测试输出:
























 128
128











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








