题目:压缩感知重构算法之基追踪降噪(Basis Pursuit De-Noising, BPDN)
本篇来探讨基追踪降噪(Basis Pursuit De-Noising, BPDN),与基追踪不同之处在于,基追踪降噪在模型中考虑到了噪声的存在,而这在实际中是非常有意义的。因为考虑到了噪声,所以不同于BP的最优化模型可以转化为线性规划问题,BPDN的最优化模型可以转化为二次规划问题。
1、基追踪降噪的提出
文献【1】为了使基追踪能够适应有噪声的数据,提出了基追踪降噪:

然后将基追踪降噪转化为扰动线性规划(perturbed linear program)问题:

基追踪降噪最优化模型中的参数λ可按如下规划选取:
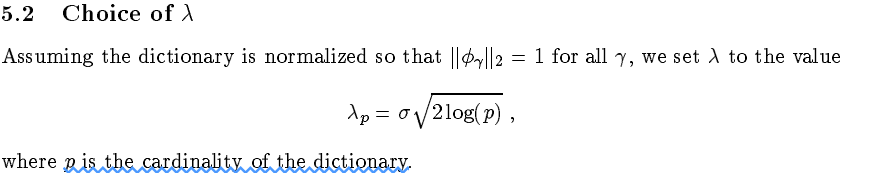
并没有查到简单的MATLAB函数求解扰动线性规划问题。作者发布了文献【1】中的算法MATLAB源代码工具箱Atomizer(下载链接:http://sparselab.stanford.edu/atomizer/),并有一个说明文档,在工具箱\Documentation目录下(AboutAtomizer1208.ps,若想打开需要转换一下格式,不成功者可以参考链接http://download.csdn.net/detail/jbb0523/9583505)
2、利用l1-magic工具箱实现基追踪降噪
在l1-magic工具箱(链接:http://users.ece.gatech.edu/~justin/l1magic/)解决的七类问题中,并没有出现文献【1】式(5.1)类型,但在文献【2】中提到:

即问题(3)与问题(1)等价。下面是l1-magic的(P2)问题:

可以看出文献【2】的问题(3)与l1-magic中的问题(P2)等价,因此,我们完全可以使用l1-magic工具箱中求解(P2)的函数l1qc_logbarrier.m解决基追踪降噪(使用时注意,函数l1qc_logbarrier还调用了工具箱其它的函数)。
3、将基追踪降噪转化为二次规划问题
文献【2】给出了将基追踪降噪转化为二次规划问题的过程:

对于线性代数和矩阵分析基础不好的人,这个过程可能并不是很容易看明白,现详细推导如下:
Step0:
与基追踪推导类似,将变量x变为两个非负变量u和v之差:

Step1:
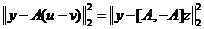
Step2:
Step3:
因为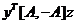
所以
Step4:
因为
所以
令
则
Step5:
Step6:
综合Step3、Step4、Step5的结果,Step2可化为:
Step7:
与基追踪推导类似:
其中, 
Step8:
综合Step6与Step7的结果,Step0可化为:
其中
Step9:
因为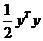
所以Step8可写为标准的二次规划形式:
求得最优化解z0后可得变量x的最优化解x0=z0(1:n)-z0(n+1:2n)。
4、基于quadprog的基追踪降噪MATLAB代码(BPDN_quadprog.m)
根据以上推导结果,可以写出基于MATLAB自带二次规划函数quadprog的代码:
5、基追踪降噪单次重构测试代码
测试代码与OMP测试代码有改动,首先是测量矩阵Phi使用函数orth进行了正交化,其次是观测值y加入了噪声e,可以用比较软件Beyond Compare具体比较不同之处:
运行结果如下:(信号为随机生成,所以每次结果均不一样)
1)图:
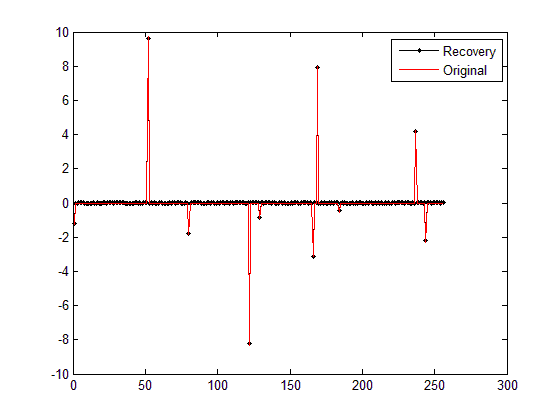
2)Command Windows
Optimization terminated: relative functionvalue changing by less
thansqrt(OPTIONS.TolFun), no negative curvature detected in current
trust region model and the rate of progress(change in f(x)) is slow.
Elapsed time is 8.706162 seconds.
恢复残差:
ans =
0.2723
6、结束语
从Command Windows输出可以看到,本次运行花费了8.706162秒,误差为0.2723。相比于之前的单次重构测试,这个运行时长非常长,误差非常大。为什么呢?
有关运行时间长,是不是由于该二次规划变量只有一个非负约束,故可行域范围比较大,所以时间会很长;而误差大也是可以理解的,因为本来该方法的观测值就是含有噪声的,但问题也就来了,这不是基追踪“降噪”么?为什么没把“噪声”给“降”掉呢?
7、参考文献:
【1】Chen S S, Donoho D L, Saunders MA. Atomicdecomposition by basis pursuit[J]. SIAM review, 2001, 43(1): 129-159.(Available at: http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.37.4272&rep=rep1&type=pdf)
【2】Nowak R D, Wright SJ. Gradientprojection for sparse reconstruction: Application to compressed sensing andother inverse problems[J]. IEEE Journal of selected topics in signalprocessing, 2007, 1(4): 586-597. (Available at: http://pages.cs.wisc.edu/~swright/papers/FigNW07a.pdf)








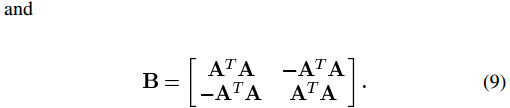


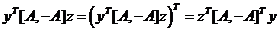
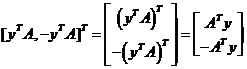
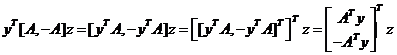
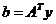
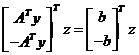
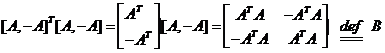
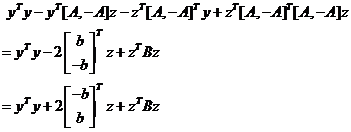
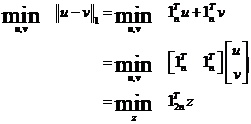
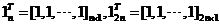
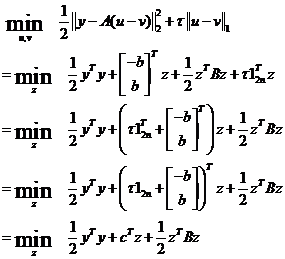
















 2390
2390

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








