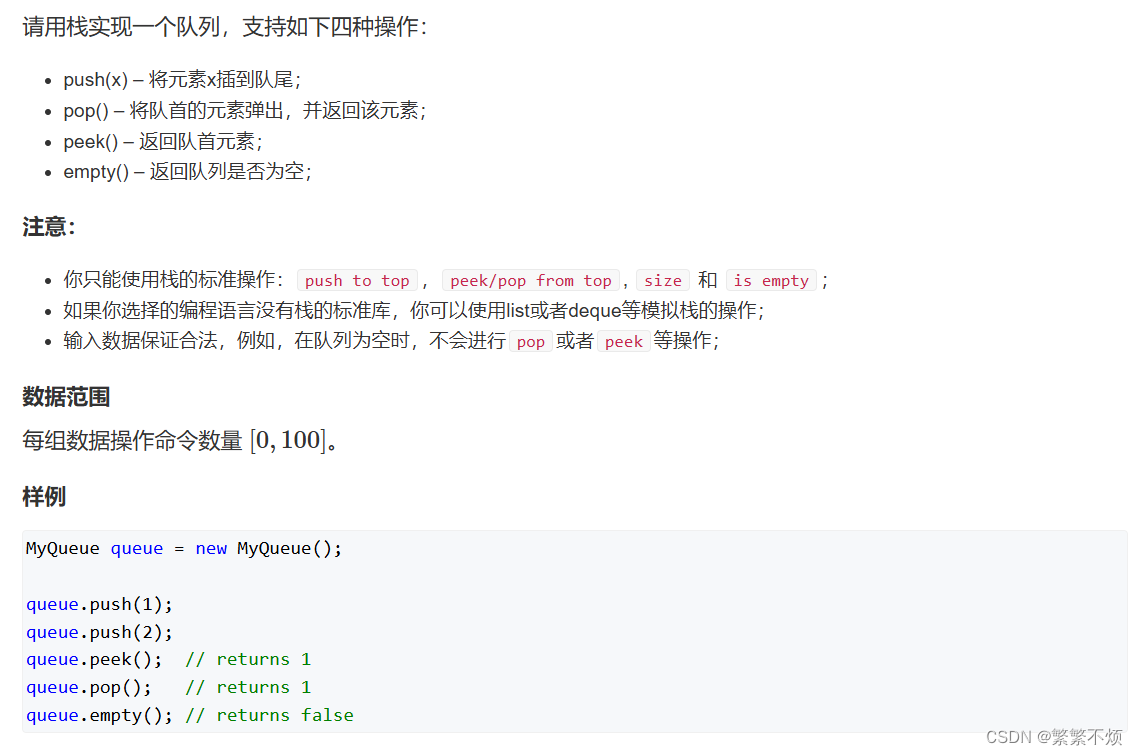
一、题目
栈为先进后出,后进先出,类似于往球桶里放球;队列为先进先出,后进后出,类似于现实生活中的排队。用两个栈就能实现把栈转化为队列,因为一个先进后出的栈,只要按照栈的出栈规则入栈到另外一个栈中,就实现了队列。
二、思路
1、编写一个copy()方法,专门用来将原栈折腾到一个暂存栈中,但是如果这样操作后,原栈就为空了,而且也不只需要折腾一次,因为top()和pop()方法为两个方法,不能保证用户使用pop()方法前就一定会调用top()方法,所以必须在执行完每次折腾到暂存栈后,再折腾回原栈,以便于其他方法对其进行访问。
class MyQueue {
public:
//用两个栈 一个用来存储 一个用来缓存
stack<int> stk,cache;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
MyQueue() {
}
/** Push element x to the back of queue. */
void push(int x) {
stk.push(x);
}
//用一个copy方法 将栈顶的值 放到另外一个栈的栈尾
void copy(stack<int> &a,stack<int> &b)
{
while(a.size())
{
b.push(a.top());
a.pop();
}
}
/** Removes the element from in front of queue and returns that element. */
int pop() {
copy(stk,cache);
int res = cache.top();
cache.pop();
copy(cache,stk);
return res;
}
/** Get the front element. */
int peek() {
copy(stk,cache);
int res = cache.top();
copy(cache,stk);
return res;
}
/** Returns whether the queue is empty. */
bool empty() {
return stk.empty();
}
};
/**
* Your MyQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyQueue obj = MyQueue();
* obj.push(x);
* int param_2 = obj.pop();
* int param_3 = obj.peek();
* bool param_4 = obj.empty();
*/但是这样可能看起来有些冗余操作,因为毕竟如果用户已经调用一个方法,这个方法已经完成了对栈转存的操作,这样下面的 方法直接访问就好了啊,没必要再折腾回去,折腾回来的,所以在评论区看到了这个代码:
2、这个代码思路就是在执行操作前,判断这个暂存栈是否为空,如果不为空,说明已经把栈转为队列了,直接操作就好。
class MyQueue {
public:
//用两个栈 一个用来存储 一个用来缓存
stack<int> stk,cache;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
MyQueue() {
}
/** Push element x to the back of queue. */
void push(int x) {
stk.push(x);
}
/**用一个copy方法 将栈顶的值 放到另外一个栈的栈尾
void copy(stack<int> &a,stack<int> &b)
{
while(a.size())
{
b.push(a.top());
a.pop();
}
}
*/
/** Removes the element from in front of queue and returns that element. */
int pop() {
if(cache.empty())
{
while(!stk.empty())
{
cache.push(stk.top());
stk.pop();
}
}
int res = cache.top();
cache.pop();
return res;
}
/** Get the front element. */
int peek() {
if(cache.empty())
{
while(!stk.empty())
{
cache.push(stk.top());
stk.pop();
}
}
int res = cache.top();
return res;
}
/** Returns whether the queue is empty. */
bool empty() {
return stk.empty()&&cache.empty();
}
};
/**
* Your MyQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyQueue obj = MyQueue();
* obj.push(x);
* int param_2 = obj.pop();
* int param_3 = obj.peek();
* bool param_4 = obj.empty();
*/3、其实可以二者结合,结合copy方法的简洁,再加上一个if。
class MyQueue {
public:
//用两个栈 一个用来存储 一个用来缓存
stack<int> stk,cache;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
MyQueue() {
}
/** Push element x to the back of queue. */
void push(int x) {
stk.push(x);
}
//用一个copy方法 将栈顶的值 放到另外一个栈的栈尾
void copy(stack<int> &a,stack<int> &b)
{
while(a.size())
{
b.push(a.top());
a.pop();
}
}
/** Removes the element from in front of queue and returns that element. */
int pop() {
if(cache.empty())
{
copy(stk,cache);
}
int res = cache.top();
cache.pop();
return res;
}
/** Get the front element. */
int peek() {
if(cache.empty())
{
copy(stk,cache);
}
int res = cache.top();
return res;
}
/** Returns whether the queue is empty. */
bool empty() {
return stk.empty()&&cache.empty();
}
};
/**
* Your MyQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyQueue obj = MyQueue();
* obj.push(x);
* int param_2 = obj.pop();
* int param_3 = obj.peek();
* bool param_4 = obj.empty();
*/三、总结与反思
其实封装成方法是好的,使代码逻辑更清晰。
其实三者的思路都一样,就是把原栈pop,push到新栈,新栈就是原栈的队列形式。
都一样啦





















 145
145











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








