那就别跟他们比,先跟自己比,争取今天比昨天强一些,明天比今天强一些。
1.包装类
针对八种基本数据类型封装的相应的引用类型。
有了类的特点,就可以调用类中的方法。(为什么要封装)
| 基本数据类型 | 包装类 |
|---|---|
| boolean | Boolean |
| char | Character |
| byte | Byte |
| short | Short |
| int | Integer |
| long | Long |
| float | Float |
| double | Double |
1.1 装箱与拆箱
装箱:基本类型 ——> 包装类型
拆箱:包装类型 ——> 基本类型
JDK5之后,都是自动拆箱与自动装箱,不用手动控制。
自动装箱底层调用的是valueOf方法,如 Integer.valueOf()。
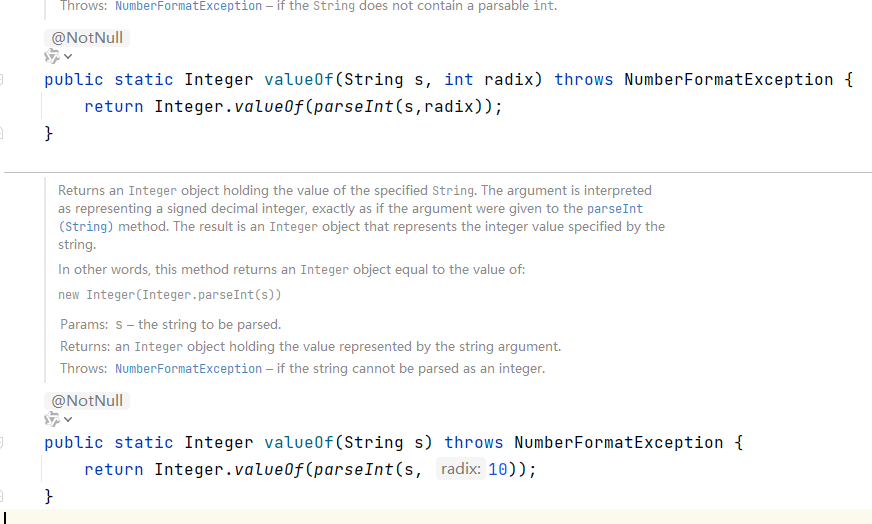
/**
* Parses the string argument as a signed integer in the radix
* specified by the second argument. The characters in the string
* must all be digits of the specified radix (as determined by
* whether {@link java.lang.Character#digit(char, int)} returns a
* nonnegative value), except that the first character may be an
* ASCII minus sign {@code '-'} ({@code '\u005Cu002D'}) to
* indicate a negative value or an ASCII plus sign {@code '+'}
* ({@code '\u005Cu002B'}) to indicate a positive value. The
* resulting integer value is returned.
*
* <p>An exception of type {@code NumberFormatException} is
* thrown if any of the following situations occurs:
* <ul>
* <li>The first argument is {@code null} or is a string of
* length zero.
*
* <li>The radix is either smaller than
* {@link java.lang.Character#MIN_RADIX} or
* larger than {@link java.lang.Character#MAX_RADIX}.
*
* <li>Any character of the string is not a digit of the specified
* radix, except that the first character may be a minus sign
* {@code '-'} ({@code '\u005Cu002D'}) or plus sign
* {@code '+'} ({@code '\u005Cu002B'}) provided that the
* string is longer than length 1.
*
* <li>The value represented by the string is not a value of type
* {@code int}.
* </ul>
*
* <p>Examples:
* <blockquote><pre>
* parseInt("0", 10) returns 0
* parseInt("473", 10) returns 473
* parseInt("+42", 10) returns 42
* parseInt("-0", 10) returns 0
* parseInt("-FF", 16) returns -255
* parseInt("1100110", 2) returns 102
* parseInt("2147483647", 10) returns 2147483647
* parseInt("-2147483648", 10) returns -2147483648
* parseInt("2147483648", 10) throws a NumberFormatException
* parseInt("99", 8) throws a NumberFormatException
* parseInt("Kona", 10) throws a NumberFormatException
* parseInt("Kona", 27) returns 411787
* </pre></blockquote>
*
* @param s the {@code String} containing the integer
* representation to be parsed
* @param radix the radix to be used while parsing {@code s}.
* @return the integer represented by the string argument in the
* specified radix.
* @exception NumberFormatException if the {@code String}
* does not contain a parsable {@code int}.
*/
public static int parseInt(String s, int radix)
throws NumberFormatException
{
/*
* WARNING: This method may be invoked early during VM initialization
* before IntegerCache is initialized. Care must be taken to not use
* the valueOf method.
*/
if (s == null) {
throw new NumberFormatException("null");
}
if (radix < Character.MIN_RADIX) {
throw new NumberFormatException("radix " + radix +
" less than Character.MIN_RADIX");
}
if (radix > Character.MAX_RADIX) {
throw new NumberFormatException("radix " + radix +
" greater than Character.MAX_RADIX");
}
int result = 0;
boolean negative = false;
int i = 0, len = s.length();
int limit = -Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int multmin;
int digit;
if (len > 0) {
char firstChar = s.charAt(0);
if (firstChar < '0') { // Possible leading "+" or "-"
if (firstChar == '-') {
negative = true;
limit = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
} else if (firstChar != '+')
throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);
if (len == 1) // Cannot have lone "+" or "-"
throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);
i++;
}
multmin = limit / radix;
while (i < len) {
// Accumulating negatively avoids surprises near MAX_VALUE
digit = Character.digit(s.charAt(i++),radix);
if (digit < 0) {
throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);
}
if (result < multmin) {
throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);
}
result *= radix;
if (result < limit + digit) {
throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);
}
result -= digit;
}
} else {
throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);
}
return negative ? result : -result;
}代码示例:
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 手动装箱 int->Integer
int n1 = 100;
Integer integer = new Integer(n1);
Integer integer1 = Integer.valueOf(n1);
// 手动拆箱 Integer -> int
int i = integer.intValue();
int n2 = 200;
// 自动装箱 int->Integer
Integer integer2 = n2; //底层使用的是 Integer.valueOf(n2)
// 自动拆箱 Integer->int
int n3 = integer2; //底层仍然使用的是 intValue()方法
}2.String类
保存的是一组字符序列。字符串的字符使用的是 Unicode 字符编码,一个字符(不区分字母还是汉字)占两个字节。
创建 String 对象的两种方式
// 直接赋值
String s = "路明非";
// 调用构造器
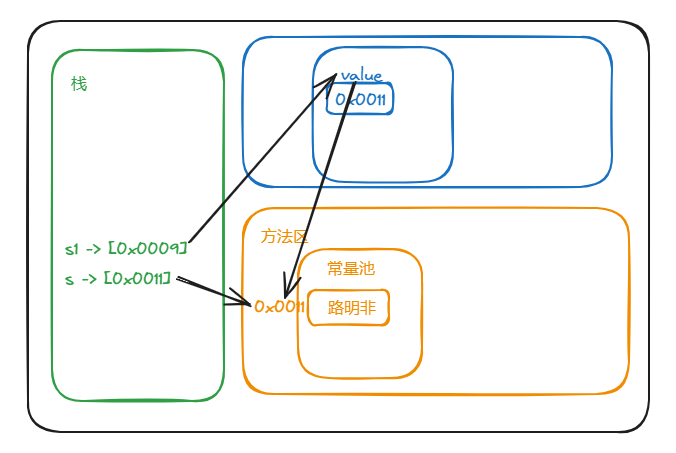
String s1 = new String("路明非");两者有什么不同(通过构造器创建的对象,在堆空间中会创建空间)
- 直接赋值
先从常量池查看是否有 "路明非" 数据空间,如果有,直接指向;
如果没有这重新创建,然后指向,s最终指向的是常量池的空间地址。
- 构造器赋值
先在堆中创建空间,里面维护了value属性,指向常量池的 "路明非" 数据空间。
如果常量池没有 "路明非",创新创建,如果有,直接通过value指向。最终指向的是堆中的空间地址。
内存分布图
注意:
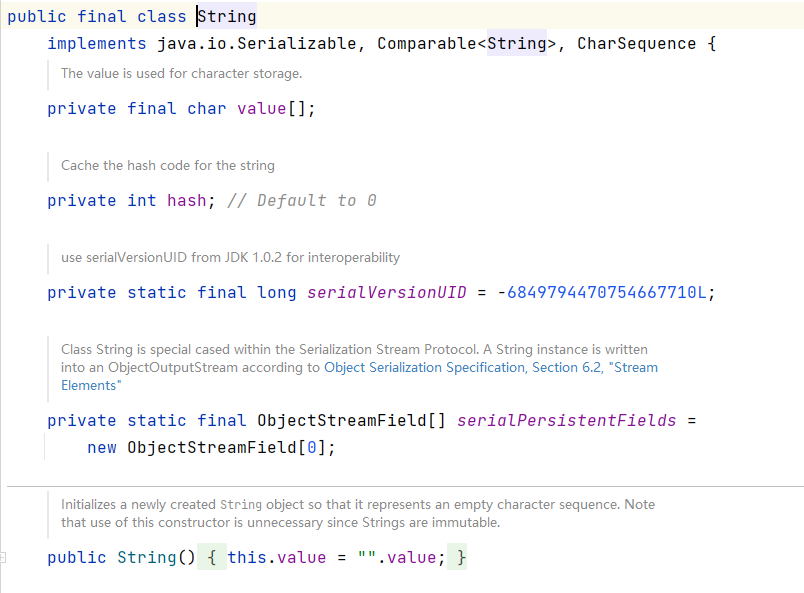
String 是一个 final 类,代表不可变的字符序列。改变赋值,相当于就是再创建了一个对象。
jdk 源码
String类的常见方法
equals // 区分大小写,判断内容是否相等
equalsIgnoreCase // 忽略大小写的判断内容是否相等
length // 获取字符的个数,字符串的长度
indexOf // 获取字符在字符串中第一次出现的索引,索引从0开始,如果找不到,返回-1
lastIndexOf // 获取字符在字符串中最后一次出现的索引,索引从0开始,如果找不到,返回-1
substring // 截取指定范围的子串
trim // 去除空格
charAt // 获取某索引处的字符3.StringBuffer类
String 保存的是字符串常量,里面的值不能更改,每次String类的更新实际上就是更改地址,效率较低。
StringBuffer 保存的是字符串变量,里面的值可以更改,每次StringBuffer的更新实际上可以更新内容,不用每次更新地址,效率较高。(char[] value 这个放在堆中)
代码示例
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1. StringBuffer 的直接父类 是 AbstractStringBuilder
// 2. StringBuffer 实现了 Serializable, 即 StringBuffer 的对象可以串行化
// 3. 在父类中 AbstractStringBuilder 有属性 char[] value,不是 final
// 该 value 数组存放 字符串内容,引出存放在堆中的
// 4. StringBuffer 是一个 final 类,不能被继承
// 5. 因为 StringBuffer 字符内容是存在 char[] value, 所有在变化(增加/删除)
// 不用每次都更换地址(即不是每次创建新对象), 所以效率高于 String
StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer("Hello");
}String 和 StringBuffer 相互转换
public static void main(String[] args) {
// String —> StringBuffer
String str = "Hello world";
// 方式 1 使用构造器
StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer(str);
// 方式 2 使用的是 append 方法
StringBuffer stringBuffer1 = new StringBuffer();
stringBuffer1 = stringBuffer1.append(str);
// StringBuffer -> String
StringBuffer stringBuffer3 = new StringBuffer("路明非");
// 方式 1 使用 StringBuffer 提供的 toString 方法
String s = stringBuffer3.toString();
// 方式 2: 使用构造器来搞定
String s1 = new String(stringBuffer3);
}4.StringBuilder类
一个可变的字符序列。相比于StringBuffer,StringBuilder不是线程安全的,但是速度要比StringBuffer要快。
代码示例
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1. StringBuilder 继承 AbstractStringBuilder 类
// 2. 实现了 Serializable ,说明 StringBuilder 对象是可以串行化(对象可以网络传输,可以保存到文件)
// 3. StringBuilder 是 final 类, 不能被继承
// 4. StringBuilder 对象字符序列仍然是存放在其父类 AbstractStringBuilder 的 char[] value;
// 因此,字符序列是堆中
// 5. StringBuilder 的方法,没有做互斥的处理,即没有 synchronized 关键字,因此在单线程的情况下使用
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
}String、StringBuffer、StringBuilder的比较
- String:不可变字符序列,效率低,但是复用率高。
- StringBuffer:可变字符序列,效率较高,线程安全。
- StringBuilder:可变字符序列,效率最高,线程不安全。
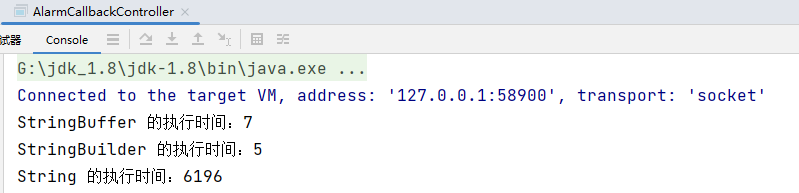
效率测试代码示例
public static void main(String[] args) {
long startTime;
long endTime;
StringBuffer buffer = new StringBuffer("");
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 80000; i++) {
buffer.append(i);
}
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("StringBuffer 的执行时间:" + (endTime - startTime));
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder("");
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 80000; i++) {
builder.append(i);
}
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("StringBuilder 的执行时间:" + (endTime - startTime));
String text = "";
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 80000; i++) {
text = text + i;
}
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("String 的执行时间:" + (endTime - startTime));
}运行结果
如何选择
- 如果字符串存在大量修改操作,一般使用 Stringbuilder 或 StringBuffer
- 如果字符串存在大量修改操作,并在单线程的情况,使用 StringBuilder
- 如果字符串存在大量修改操作,并在多线程的情况,使用 StringBuffer
- 如果字符串很少修改,被多个对象引用,使用 String ,比如配置信息等
5.Math类
Math类包含用于执行基本数学运算的方法。
代码示例
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1.abs 绝对值
int abs = Math.abs(-9);
System.out.println(abs); //9
// 2.pow 求幂
double pow = Math.pow(2, 4); //2 的 4 次方
System.out.println(pow); //16
// 3.ceil 向上取整,返回>=该参数的最小整数(转成 double);
double ceil = Math.ceil(3.9);
System.out.println(ceil); //4.0
// 4.floor 向下取整,返回<=该参数的最大整数(转成 double)
double floor = Math.floor(4.001);
System.out.println(floor); //4.0
// 5.round 四舍五入 Math.floor(该参数+0.5)
long round = Math.round(5.51);
System.out.println(round); //6
// 6.sqrt 求开方
double sqrt = Math.sqrt(9.0);
System.out.println(sqrt); //3.0
// 7.random 求随机数 random 返回的是 0 <= x < 1 之间的一个随机小数
// Math.random()*6 返回的是 0 <= x < 6 小数
// 思考:请写出获取 a-b 之间的一个随机整数,a,b 均为整数 ,比如 a = 2, b=7
// 公式就是 (int)(a + Math.random() * (b - a + 1) )
for(int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.println((int)(2 + Math.random() * (7 - 2 + 1)));
}
// max , min 返回最大值和最小值
int min = Math.min(1, 9);
int max = Math.max(45, 90);
System.out.println("min=" + min);
System.out.println("max=" + max);
}6.Arrays类
Arrays里面包含了一系列静态方法,用于管理和操作数组。
常用方法
toString:返回数组的字符串形式
sort:排序
binarySearch:二分查找、要求是有序列表
copyOf:数组元素的复制
fill:数组元素的填充
equals:比较两个数组元素内容是否完全一致
asList:将一组值,转换成list 7.System类
常用方法
exit:退出当前程序
currentTimeMillens:返回当前时间距离1970-1-1的毫秒数
gc:运行垃圾回收机制
8.BigInteger类 和 BigDecimal类
应用场景
- BigInteger:保存比较大的整形。
- BigDecimal:保存精度更高的浮点数。
常用方法
- add:加
- subtract:减
- multiply:乘
- divide:除
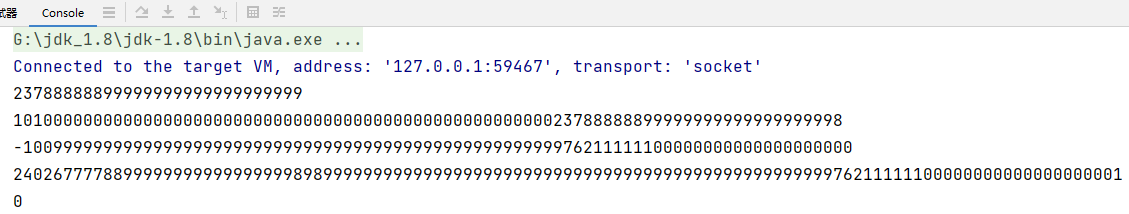
代码示例
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 需要处理很大的整数,long 不够用,可以使用 BigInteger 的类
BigInteger bigInteger = new BigInteger("23788888899999999999999999999");
BigInteger bigInteger2 = new BigInteger("10099999999999999999999999999999999999999999999999999999999999999999999999999999999");
System.out.println(bigInteger);
// 在对 BigInteger 进行加减乘除的时候,需要使用对应的方法,不能直接进行+ - * /
BigInteger add = bigInteger.add(bigInteger2);
System.out.println(add); //加
BigInteger subtract = bigInteger.subtract(bigInteger2);
System.out.println(subtract); //减
BigInteger multiply = bigInteger.multiply(bigInteger2);
System.out.println(multiply); //乘
BigInteger divide = bigInteger.divide(bigInteger2);
System.out.println(divide); //除
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 需要保存一个精度很高的数时,double 不够用,用BigDecimal
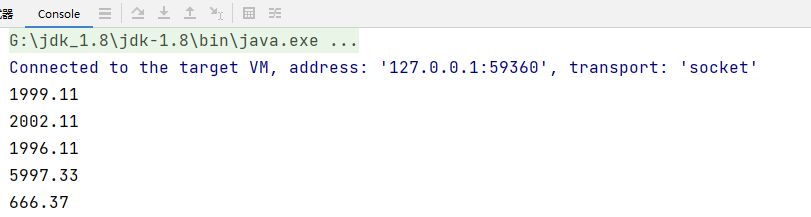
BigDecimal bigDecimal = new BigDecimal("1999.11");
BigDecimal bigDecimal2 = new BigDecimal("3");
System.out.println(bigDecimal);
// 如果对 BigDecimal 进行运算,比如加减乘除,需要使用对应的方法
System.out.println(bigDecimal.add(bigDecimal2));
System.out.println(bigDecimal.subtract(bigDecimal2));
System.out.println(bigDecimal.multiply(bigDecimal2));
//System.out.println(bigDecimal.divide(bigDecimal2));//可能抛出异常 ArithmeticException
// 在调用 divide 方法时,指定精度即可. BigDecimal.ROUND_CEILING
// 如果有无限循环小数,就会保留 分子 的精度
System.out.println(bigDecimal.divide(bigDecimal2, BigDecimal.ROUND_CEILING));
}输出结果
9.日期类
9.1 第一代日期类Date
- Date:精确到毫秒,代表特定的瞬间
- SimpleDateFormat:格式化日期。(日期 -> 文本、文本 -> 日期)
代码示例
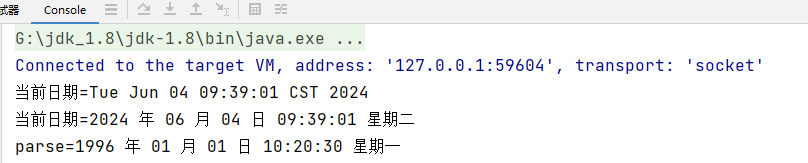
public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {
// Date 类是在 java.util 包
// 默认输出的日期格式是国外的方式, 因此通常需要对格式进行转换
Date d1 = new Date();
System.out.println("当前日期=" + d1);
// 创建 SimpleDateFormat 对象,可以指定相应的格式
// 这里的格式使用的字母是规定好,不能乱写
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy 年 MM 月 dd 日 hh:mm:ss E");
String format = sdf.format(d1);
System.out.println("当前日期=" + format);
// 把 String -> Date , 使用的 sdf 格式需要和你给的 String 的格式一样,否则会抛出转换异常
String s = "1996 年 01 月 01 日 10:20:30 星期一";
Date parse = sdf.parse(s);
System.out.println("parse=" + sdf.format(parse));
}输出结果
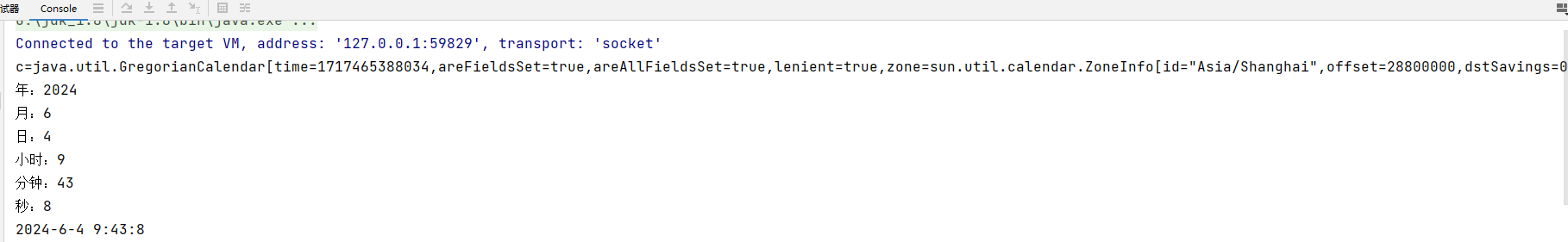
9.2 第二代日期类Calendar
Calendar类是一个抽象类,它为特定瞬间与一组诸如YERA、MONTH、DAY_OF_MONTH、HOUR等日历字段之间的转换提供了一些方法,并为操作日历字段提供了一些方法。
代码示例
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Calendar 是一个抽象类, 并且构造器是 private,通过 getInstance() 来获取实例
// Calendar 没有提供对应的格式化的类,因此需要程序员自己组合来输出(灵活)
// 如果需要按照 24 小时进制来获取时间, Calendar.HOUR ==改成=> Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY
Calendar c = Calendar.getInstance();
System.out.println("c=" + c);
// 获取日历对象的某个日历字段
System.out.println("年:" + c.get(Calendar.YEAR));
// 这里为什么要 + 1, 因为 Calendar 返回月时候,是按照 0 开始编号
System.out.println("月:" + (c.get(Calendar.MONTH) + 1));
System.out.println("日:" + c.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH));
System.out.println("小时:" + c.get(Calendar.HOUR));
System.out.println("分钟:" + c.get(Calendar.MINUTE));
System.out.println("秒:" + c.get(Calendar.SECOND));
// Calender 没有专门的格式化方法,所以需要程序员自己来组合显示
System.out.println(c.get(Calendar.YEAR) + "-" + (c.get(Calendar.MONTH) + 1) + "-" +c.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH) +
" " + c.get(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY) + ":" + c.get(Calendar.MINUTE) + ":" + c.get(Calendar.SECOND) );
}输出结果
9.3 第三代日期类
JDK8新加入的
- LocalDate:获取日期(年月日)
- LocalTime:获取时间(时分秒)
- LocalDateTime:获取日期 + 时间
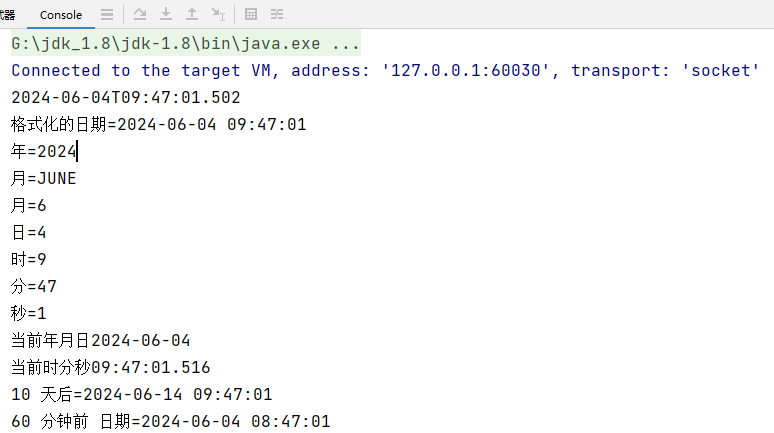
代码示例
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1.使用 now() 返回表示当前日期时间的对象
LocalDateTime ldt = LocalDateTime.now();
System.out.println(ldt);
// 2.使用 DateTimeFormatter 对象来进行格式化
DateTimeFormatter dateTimeFormatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
String format = dateTimeFormatter.format(ldt);
System.out.println("格式化的日期=" + format);
System.out.println("年=" + ldt.getYear());
System.out.println("月=" + ldt.getMonth());
System.out.println("月=" + ldt.getMonthValue());
System.out.println("日=" + ldt.getDayOfMonth());
System.out.println("时=" + ldt.getHour());
System.out.println("分=" + ldt.getMinute());
System.out.println("秒=" + ldt.getSecond());
LocalDate now = LocalDate.now();
System.out.println("当前年月日" + now);
LocalTime now2 = LocalTime.now();
System.out.println("当前时分秒" + now2);
// 提供 plus 和 minus 方法可以对当前时间进行加或者减
// 看看 10 天后,是什么时候 把 年月日-时分秒
LocalDateTime localDateTime = ldt.plusDays(10);
System.out.println("10 天后=" + dateTimeFormatter.format(localDateTime));
// 看看在 60 分钟前是什么时候,把 年月日-时分秒输出
LocalDateTime localDateTime2 = ldt.minusMinutes(60);
System.out.println("60 分钟前 日期=" + dateTimeFormatter.format(localDateTime2));
}输出结果
























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








