16.1.1:访问构造方法
反射:
1.class类
2.获取构造方法
3.获取成员属性
4.获取成员方法
注解
1.内置注解
2.反射注解
3
1.使用getClass()方法
object str = new object();
class c = str.getClass()
Demo1 d1 = new Demo1();
Class c1 = d1.getClass();2.使用.class属性
class c = object.class
Class c2 = Demo1.class;3.使用class类的forname方法
class c = class.forname("全路径")3.使用class类的forname方法
class c = class.forname("全路径")
Class c3 = Class.forName("com.mr.Demo1");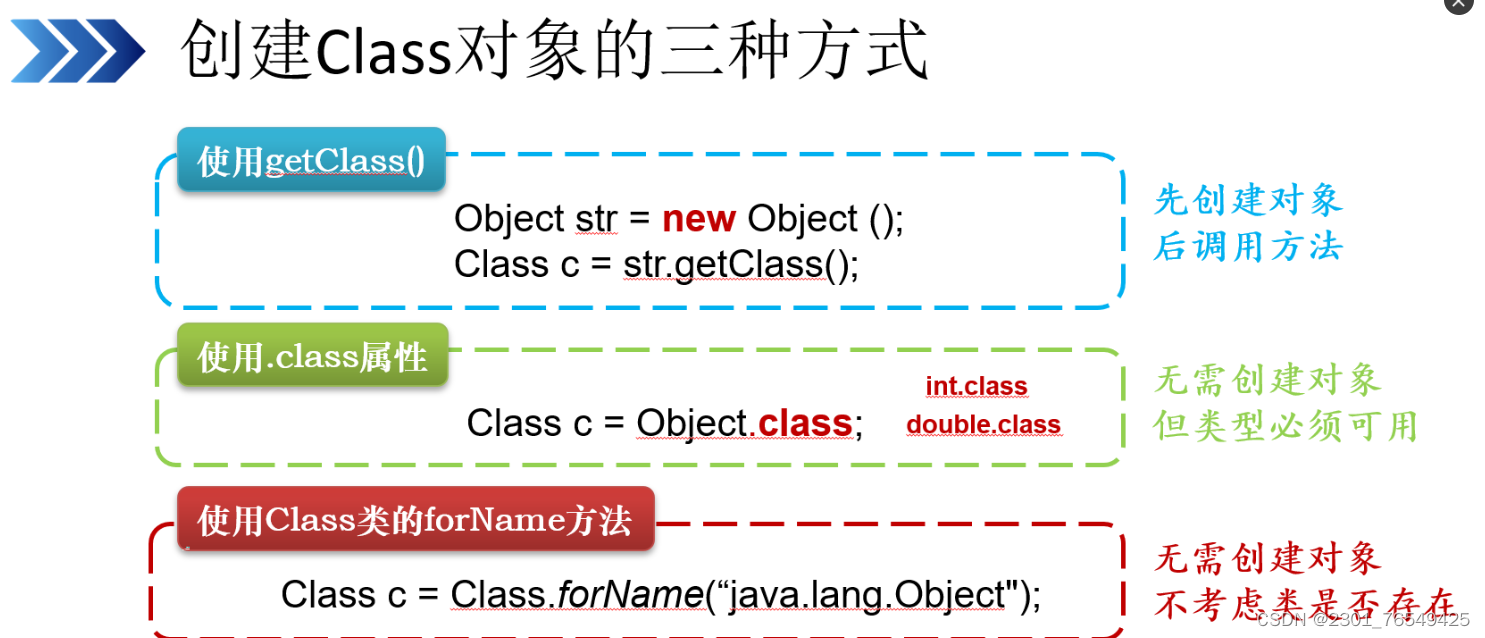
创建class,包会自动创建
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import com.mr.Demo1;
public class ConstructorDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Demo1 d1 = new Demo1("10", "20", "30");
Class<? extends Demo1> demoClass = d1.getClass();
// 获得所有构造方法
Constructor[] declaredConstructors = demoClass.getDeclaredConstructors();
for (int i = 0; i < declaredConstructors.length; i++) { // 遍历构造方法
Constructor<?> constructor = declaredConstructors[i];
System.out.println("查看是否允许带有可变数量的参数:" + constructor.isVarArgs());
System.out.println("该构造方法的入口参数类型依次为:");
Class[] parameterTypes = constructor.getParameterTypes(); // 获取所有参数类型
for (int j = 0; j < parameterTypes.length; j++) {
System.out.println(" " + parameterTypes[j]);
}
System.out.println("该构造方法可能抛出的异常类型为:");
// 获得所有可能抛出的异常信息类型
Class[] exceptionTypes = constructor.getExceptionTypes();
for (int j = 0; j < exceptionTypes.length; j++) {
System.out.println(" " + exceptionTypes[j]);
}
Demo1 d2 = null;
try { // 如果该成员变量的访问权限为private,则抛出异常,即不允许访问
if (i == 2) // 通过执行默认没有参数的构造方法创建对象
d2 = (Demo1) constructor.newInstance();
else if (i == 1)
// 通过执行具有两个参数的构造方法创建对象
d2 = (Demo1) constructor.newInstance("7", 5);
else { // 通过执行具有可变数量参数的构造方法创建对象
Object[] parameters = new Object[] { new String[] { "100", "200", "300" } };
d2 = (Demo1) constructor.newInstance(parameters);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("在创建对象时抛出异常,下面执行setAccessible()方法");
constructor.setAccessible(true); // 设置为允许访问
}
if (d2 != null) {
d2.print();
System.out.println();
}
}
}
}
//例题16.1
package com.mr;
public class Demo1 {
String s;
int i, i2, i3;
private Demo1() {
}
protected Demo1(String s, int i) {
this.s = s;
this.i = i;
}
public Demo1(String... strings) throws NumberFormatException {
if (0 < strings.length)
i = Integer.valueOf(strings[0]);
if (1 < strings.length)
i2 = Integer.valueOf(strings[1]);
if (2 < strings.length)
i3 = Integer.valueOf(strings[2]);
}
public void print() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("s=" + s);
System.out.println("i=" + i);
System.out.println("i2=" + i2);
System.out.println("i3=" + i3);
}
}
//例题16.1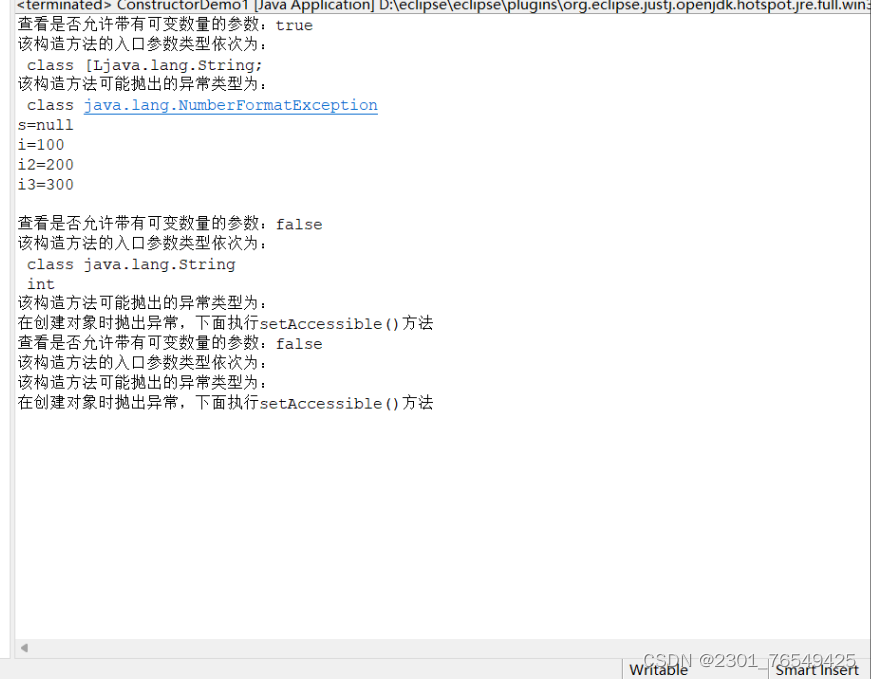
16.1.2:访问成员变量
package com.mr;
public class Demo2 {
int i;
public float f;
protected boolean b;
private String s;
}
//例题16.2import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import com.mr.Demo2;
public class FieldDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Demo2 example = new Demo2();
Class exampleC = example.getClass();
// 获得所有成员变量
Field[] declaredFields = exampleC.getDeclaredFields();
for (int i = 0; i < declaredFields.length; i++) { // 遍历成员变量
Field field = declaredFields[i];
System.out.println("名称为:" + field.getName()); // 获得成员变量名称
Class fieldType = field.getType(); // 获得成员变量类型
System.out.println("类型为:" + fieldType);
boolean isTurn = true;
while (isTurn) {
// 如果该成员变量的访问权限为private,则抛出异常,即不允许访问
try {
isTurn = false;
// 获得成员变量值
System.out.println("修改前的值为:" + field.get(example));
if (fieldType.equals(int.class)) { // 判断成员变量的类型是否为int型
System.out.println("利用方法setInt()修改成员变量的值");
field.setInt(example, 168); // 为int型成员变量赋值
} else if (fieldType.equals(float.class)) { // 判断成员变量的类型是否为float型
System.out.println("利用方法setFloat()修改成员变量的值");
field.setFloat(example, 99.9F); // 为float型成员变量赋值
// 判断成员变量的类型是否为boolean型
} else if (fieldType.equals(boolean.class)) {
System.out.println("利用方法setBoolean()修改成员变量的值");
field.setBoolean(example, true); // 为boolean型成员变量赋值
} else {
System.out.println("利用方法set()修改成员变量的值");
field.set(example, "MWQ"); // 可以为各种类型的成员变量赋值
}
// 获得成员变量值
System.out.println("修改后的值为:" + field.get(example));
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("在设置成员变量值时抛出异常," + "下面执行setAccessible()方法!");
field.setAccessible(true); // 设置为允许访问
isTurn = true;
}
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
//例题16.2
16.1.3:访问成员方法

package com.mr;
public class Demo3 {
static void staticMethod() {
System.out.println("执行staticMethod()方法");
}
public int publicMethod(int i) {
System.out.println("执行publicMethod()方法");
return i * 100;
}
protected int protectedMethod(String s, int i) throws NumberFormatException {
System.out.println("执行protectedMethod()方法");
return Integer.valueOf(s) + i;
}
private String privateMethod(String... strings) {
System.out.println("执行privateMethod()方法");
StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer();
for (int i = 0; i < strings.length; i++) {
stringBuffer.append(strings[i]);
}
return stringBuffer.toString();
}
}
//例题16.3
import java.lang.reflect.*;
import com.mr.Demo3;
public class MethondDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Demo3 demo = new Demo3();
Class demoClass = demo.getClass();
// 获得所有方法
Method[] declaredMethods = demoClass.getDeclaredMethods();
for (int i = 0; i < declaredMethods.length; i++) {
Method method = declaredMethods[i]; // 遍历方法
System.out.println("名称为:" + method.getName()); // 获得方法名称
System.out.println("是否允许带有可变数量的参数:" + method.isVarArgs());
System.out.println("入口参数类型依次为:");
// 获得所有参数类型
Class[] parameterTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
for (int j = 0; j < parameterTypes.length; j++) {
System.out.println(" " + parameterTypes[j]);
}
// 获得方法返回值类型
System.out.println("返回值类型为:" + method.getReturnType());
System.out.println("可能抛出的异常类型有:");
// 获得方法可能抛出的所有异常类型
Class[] exceptionTypes = method.getExceptionTypes();
for (int j = 0; j < exceptionTypes.length; j++) {
System.out.println(" " + exceptionTypes[j]);
}
boolean isTurn = true;
while (isTurn) {
try {// 如果该方法的访问权限为private,则抛出异常,即不允许访问
isTurn = false;
if ("staticMethod".equals(method.getName()))
method.invoke(demo); // 执行没有入口参数的方法
else if ("publicMethod".equals(method.getName()))
System.out.println("返回值为:" + method.invoke(demo, 168)); // 执行方法
else if ("protectedMethod".equals(method.getName()))
System.out.println("返回值为:" + method.invoke(demo, "7", 5)); // 执行方法
else if ("privateMethod".equals(method.getName())) {
Object[] parameters = new Object[] { new String[] { "M", "W", "Q" } }; // 定义二维数组
System.out.println("返回值为:" + method.invoke(demo, parameters));
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("在执行方法时抛出异常," + "下面执行setAccessible()方法!");
method.setAccessible(true); // 设置为允许访问
isTurn = true;
}
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
//例题16.3





















 715
715











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








