本章我们来深入了解一下string类,模拟实现一下string类,了解string类的底层结构,揭开string类的神奇面纱!
目录
1. string类的模拟实现
1.1 经典的string类问题
之前已经对string类进行了简单的介绍,大家只要能够正常使用即可,但实际面试时面试官的要求可能会更高,最主要是实现string类的构造、拷贝构造、赋值运算符重载以及析构函数。大家看下以 下string类的实现是否有问题?
// 为了和标准库区分,此处使用String
class String
{
public:
/*String()
:_str(new char[1])
{*_str = '\0';}
*/
//String(const char* str = "\0") 错误示范
//String(const char* str = nullptr) 错误示范
String(const char* str = "")
{
// 构造String类对象时,如果传递nullptr指针,可以认为程序非
if (nullptr == str)
{
assert(false);
return;
}
_str = new char[strlen(str) + 1];
strcpy(_str, str);
}
~String()
{
if (_str)
{
delete[] _str;
_str = nullptr;
}
}
private:
char* _str;
};
// 测试
void TestString()
{
String s1("hello bit!!!");
String s2(s1);
} 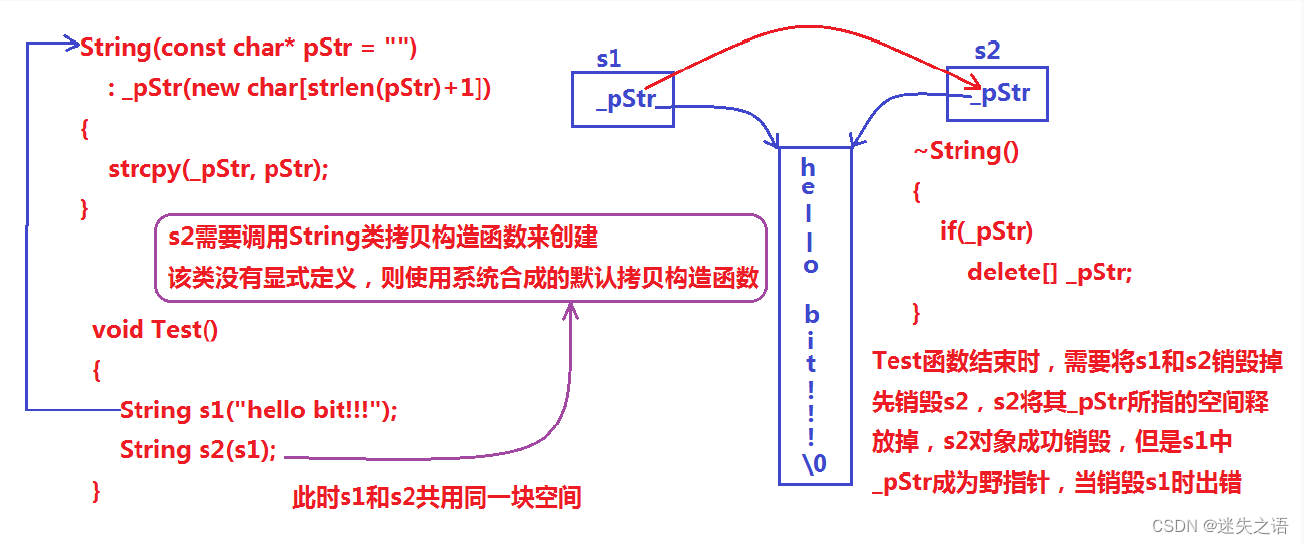
说明:上述String类没有显式定义其拷贝构造函数与赋值运算符重载,此时编译器会合成默认的,当用s1构造s2时,编译器会调用默认的拷贝构造。最终导致的问题是,s1、s2共用同一块内存空间,在释放时同一块空间被释放多次而引起程序崩溃,这种拷贝方式,称为浅拷贝。
1.2 浅拷贝
浅拷贝:也称位拷贝,编译器只是将对象中的值拷贝过来。如果对象中管理资源,最后就会导致多个对象共 享同一份资源,当一个对象销毁时就会将该资源释放掉,而此时另一些对象不知道该资源已经被释放,以为 还有效,所以当继续对资源进项操作时,就会发生发生了访问违规。
就像一个家庭中有两个孩子,但父母只买了一份玩具,两个孩子愿意一块玩,则万事大吉,万一不想分享就 你争我夺,玩具损坏。
可以采用深拷贝解决浅拷贝问题,即: 每个对象都有一份独立的资源,不要和其他对象共享。父母给每个孩子都买一份玩具,各自玩各自的就不会有问题了。
1.3 深拷贝
如果一个类中涉及到资源的管理,其拷贝构造函数、赋值运算符重载以及析构函数必须要显式给出。 一般情况都是按照深拷贝方式提供。

下面笔者将介绍两种常见写法,当然,这两种写法并无优劣之分,
1.3.1 传统版写法的String类
class String
{
public:
String(const char* str = "")
{
// 构造String类对象时,如果传递nullptr指针,可以认为程序非
if (nullptr == str)
{
assert(false);
return;
}
_str = new char[strlen(str) + 1];
strcpy(_str, str);
}
String(const String& s)
: _str(new char[strlen(s._str) + 1])
{
strcpy(_str, s._str);
}
String& operator=(const String& s)
{
if (this != &s)
{
char* pStr = new char[strlen(s._str) + 1];
strcpy(pStr, s._str);
delete[] _str;
_str = pStr;
}
return *this;
}
~String()
{
if (_str)
{
delete[] _str;
_str = nullptr;
}
}
private:
char* _str;
};1.3.2 现代版写法的String类
class String
{
public:
String(const char* str = "")
{
if (nullptr == str)
{
assert(false);
return;
}
_str = new char[strlen(str) + 1];
strcpy(_str, str);
}
String(const String& s)
: _str(nullptr)
{
String strTmp(s._str);
swap(_str, strTmp._str);
}
// 对比下和上面的赋值那个实现比较好?
String& operator=(String s)
{
swap(_str, s._str);
return *this;
}
/*
String& operator=(const String& s)
{
if(this != &s)
{
String strTmp(s);
swap(_str, strTmp._str);
}
return *this;
}
*/
~String()
{
if (_str)
{
delete[] _str;
_str = nullptr;
}
}
private:
char* _str;
};
1.3 写时拷贝(了解)

写时拷贝就是一种拖延症,是在浅拷贝的基础之上增加了引用计数的方式来实现的。
引用计数:用来记录资源使用者的个数。在构造时,将资源的计数给成1,每增加一个对象使用该资源,就给 计数增加1,当某个对象被销毁时,先给该计数减1,然后再检查是否需要释放资源,如果计数为1,说明该 对象时资源的最后一个使用者,将该资源释放;否则就不能释放,因为还有其他对象在使用该资源。
1.4 string类的模拟实现
2. string类模拟实现全代码
#pragma once
#include<assert.h>
namespace mystring
{
class string
{
public:
typedef char* iterator;
typedef const char* const_iterator;
const_iterator begin() const
{
return _str;
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return _str + _size;
}
iterator begin()
{
return _str;
}
iterator end()
{
return _str + _size;
}
/* string()
:_str(new char[1])
,_size(0)
,_capacity(0)
{
_str[0] = '\0';
}
string(const char* str)
:_size(strlen(str))
,_str(new char[strlen(str)+1])
,_capacity(strlen(str))
{
strcpy(_str, str);
}*/
const char* c_str() const
{
return _str;
}
//string(const char* str = "\0")
string(const char* str = "")
:_size(strlen(str))
{
_capacity = _size;
_str = new char[_capacity + 1];
strcpy(_str, str);
}
// s2(s1)
/*string(const string& s)
{
_str = new char[s._capacity + 1];
strcpy(_str, s._str);
_size = s._size;
_capacity = s._capacity;
}*/
// s2(s1)
string(const string& s)
{
string tmp(s._str);
swap(tmp);
}
// s1 = s3
string& operator=(string ss)
{
swap(ss);
return *this;
}
/*string& operator=(const string& s)
{
string ss(s);
swap(ss);
return *this;
}*/
// s1 = s3;
/*string& operator=(const string& s)
{
char* tmp = new char[s._capacity + 1];
strcpy(tmp, s._str);
delete[] _str;
_str = tmp;
_size = s._size;
_capacity = s._capacity;
return *this;
}*/
~string()
{
delete[] _str;
_str = nullptr;
_size = _capacity = 0;
}
// 遍历
size_t size() const
{
return _size;
}
size_t capacity() const
{
return _capacity;
}
char& operator[](size_t pos)
{
assert(pos < _size);
return _str[pos];
}
const char& operator[](size_t pos) const
{
assert(pos < _size);
return _str[pos];
}
void resize(size_t n, char ch = '\0')
{
if (n <= _size)
{
_str[n] = '\0';
_size = n;
}
else
{
reserve(n);
for (size_t i = _size; i < n; i++)
{
_str[i] = ch;
}
_str[n] = '\0';
_size = n;
}
}
void reserve(size_t n)
{
if (n > _capacity)
{
char* tmp = new char[n + 1];
strcpy(tmp, _str);
delete[] _str;
_str = tmp;
_capacity = n;
}
}
void push_back(char ch)
{
// 扩容2倍
/*if (_size == _capacity)
{
reserve(_capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * _capacity);
}
_str[_size] = ch;
++_size;
_str[_size] = '\0';*/
insert(_size, ch);
}
void append(const char* str)
{
// 扩容
/*size_t len = strlen(str);
if (_size + len > _capacity)
{
reserve(_size + len);
}
strcpy(_str + _size, str);
_size += len;*/
insert(_size, str);
}
string& operator+=(char ch)
{
push_back(ch);
return *this;
}
string& operator+=(const char* str)
{
append(str);
return *this;
}
void insert(size_t pos, char ch)
{
assert(pos <= _size);
// 扩容2倍
if (_size == _capacity)
{
reserve(_capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * _capacity);
}
/*int end = _size;
while (end >= (int)pos)
{
_str[end + 1] = _str[end];
--end;
}*/
size_t end = _size + 1;
while (end > pos)
{
_str[end] = _str[end - 1];
--end;
}
_str[pos] = ch;
++_size;
}
void copy_on_write()
{
// ...
}
void insert(size_t pos, const char* str)
{
assert(pos <= _size);
//copy_on_write();
size_t len = strlen(str);
if (_size + len > _capacity)
{
// 扩容
reserve(_size + len);
}
size_t end = _size + len;
while (end > pos + len - 1)
{
_str[end] = _str[end - len];
end--;
}
strncpy(_str + pos, str, len);
_size += len;
}
void erase(size_t pos, size_t len = npos)
{
assert(pos < _size);
if (len == npos || len >= _size - pos)
{
_str[pos] = '\0';
_size = pos;
}
else
{
strcpy(_str + pos, _str + pos + len);
_size -= len;
}
}
void swap(string& s)
{
std::swap(_str, s._str);
std::swap(_size, s._size);
std::swap(_capacity, s._capacity);
}
size_t find(char ch, size_t pos = 0) const
{
assert(pos < _size);
for (size_t i = pos; i < _size; i++)
{
if (_str[i] == ch)
return i;
}
return npos;
}
// 20:15继续
size_t find(const char* sub, size_t pos = 0) const
{
assert(pos < _size);
const char* p = strstr(_str + pos, sub);
if (p)
{
return p - _str;
}
else
{
return npos;
}
}
string substr(size_t pos = 0, size_t len = npos)
{
string sub;
//if (len == npos || len >= _size-pos)
if (len >= _size - pos)
{
for (size_t i = pos; i < _size; i++)
{
sub += _str[i];
}
}
else
{
for (size_t i = pos; i < pos + len; i++)
{
sub += _str[i];
}
}
return sub;
}
void clear()
{
_size = 0;
_str[_size] = '\0';
}
private:
char* _str = nullptr;
size_t _size = 0;
size_t _capacity = 0;
//char _buff[16];
public:
static const int npos;
};
const int string::npos = -1;
void swap(string& x, string& y)
{
x.swap(y);
}
bool operator==(const string& s1, const string& s2)
{
int ret = strcmp(s1.c_str(), s2.c_str());
return ret == 0;
}
bool operator<(const string& s1, const string& s2)
{
int ret = strcmp(s1.c_str(), s2.c_str());
return ret < 0;
}
bool operator<=(const string& s1, const string& s2)
{
return s1 < s2 || s1 == s2;
}
bool operator>(const string& s1, const string& s2)
{
return !(s1 <= s2);
}
bool operator>=(const string& s1, const string& s2)
{
return !(s1 < s2);
}
bool operator!=(const string& s1, const string& s2)
{
return !(s1 == s2);
}
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const string& s)
{
for (auto ch : s)
{
out << ch;
}
return out;
}
// 21:15
istream& operator>>(istream& in, string& s)
{
s.clear();
char ch;
//in >> ch;
ch = in.get();
char buff[128];
size_t i = 0;
while (ch != ' ' && ch != '\n')
{
buff[i++] = ch;
// [0,126]
if (i == 127)
{
buff[127] = '\0';
s += buff;
i = 0;
}
ch = in.get();
}
if (i > 0)
{
buff[i] = '\0';
s += buff;
}
return in;
}
//istream& operator>>(istream& in, string& s)
//{
// s.clear();
// char ch;
// //in >> ch;
// ch = in.get();
// s.reserve(128);
// while (ch != '\n' && ch != ' ')
// {
// s += ch;
// ch = in.get();
// }
// return in;
//}
istream& getline(istream& in, string& s)
{
s.clear();
char ch;
//in >> ch;
ch = in.get();
char buff[128];
size_t i = 0;
while (ch != '\n')
{
buff[i++] = ch;
// [0,126]
if (i == 127)
{
buff[127] = '\0';
s += buff;
i = 0;
}
ch = in.get();
}
if (i > 0)
{
buff[i] = '\0';
s += buff;
}
return in;
}
void test_string1()
{
string s1("hello world");
string s2;
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
cout << s2.c_str() << endl;
for (size_t i = 0; i < s1.size(); i++)
{
s1[i]++;
}
cout << endl;
// s1[100];
for (size_t i = 0; i < s1.size(); i++)
{
cout << s1[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
const string s3("xxxx");
for (size_t i = 0; i < s3.size(); i++)
{
//s3[i]++;
cout << s3[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
// 越界检查是一种抽查
//int a[10];
// a[10];
// a[11];
// //a[10] = 1;
// a[15] = 1;
}
void test_string2()
{
string s3("hello world");
for (auto ch : s3)
{
cout << ch << " ";
}
cout << endl;
string::iterator it3 = s3.begin();
while (it3 != s3.end())
{
*it3 -= 1;
cout << *it3 << " ";
++it3;
}
cout << endl;
const string s4("xxxx");
string::const_iterator it4 = s4.begin();
while (it4 != s4.end())
{
//*it4 += 3;
cout << *it4 << " ";
++it4;
}
cout << endl;
for (auto ch : s4)
{
cout << ch << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test_string3()
{
string s3("hello world");
s3.push_back('1');
s3.push_back('2');
cout << s3.c_str() << endl;
s3 += 'x';
s3 += "yyyyyy";
cout << s3.c_str() << endl;
string s1("hello world");
s1.insert(11, 'x');
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
s1.insert(0, 'x');
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
}
void test_string4()
{
string s1("hello world");
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
s1.erase(6, 3);
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
s1.erase(6, 30);
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
s1.erase(3);
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
string s2("hello world");
cout << s2.c_str() << endl;
s2.resize(5);
cout << s2.c_str() << endl;
s2.resize(20, 'x');
cout << s2.c_str() << endl;
}
void test_string5()
{
string s1("hello world");
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
string s2(s1);
cout << s2.c_str() << endl;
s1[0] = 'x';
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
cout << s2.c_str() << endl;
string s3("xxxxx");
s1 = s3;
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
cout << s3.c_str() << endl;
}
void test_string6()
{
string s1("hello world");
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
s1.insert(6, "xxx");
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
string s2("xxxxxxx");
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
cout << s2.c_str() << endl;
swap(s1, s2);
s1.swap(s2);
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
cout << s2.c_str() << endl;
}
void test_string7()
{
string url1("https://legacy.cplusplus.com/reference/string/string/substr/");
string url2("http://www.baidu.com/s?ie=utf-8&f=8&rsv_bp=1&rsv_idx=1&tn=65081411_1_oem_dg&wd=%E5%90%8E%E7%BC%80%20%E8%8B%B1%E6%96%87&fenlei=256&rsv_pq=0xc17a6c03003ede72&rsv_t=7f6eqaxivkivsW9Zwc41K2mIRleeNXjmiMjOgoAC0UgwLzPyVm%2FtSOeppDv%2F&rqlang=en&rsv_dl=ib&rsv_enter=1&rsv_sug3=4&rsv_sug1=3&rsv_sug7=100&rsv_sug2=0&rsv_btype=i&inputT=1588&rsv_sug4=6786");
string protocol, domain, uri;
size_t i1 = url1.find(':');
if (i1 != string::npos)
{
protocol = url1.substr(0, i1 - 0);
cout << protocol.c_str() << endl;
}
// strchar
size_t i2 = url1.find('/', i1 + 3);
if (i2 != string::npos)
{
domain = url1.substr(i1 + 3, i2 - (i1 + 3));
cout << domain.c_str() << endl;
uri = url1.substr(i2 + 1);
cout << uri.c_str() << endl;
}
// strstr 10:40继续
size_t i3 = url1.find("baidu");
cout << i3 << endl;
}
void test_string8()
{
string s1("hello world");
string s2("hello world");
cout << (s1 == s2) << endl;
cout << ("hello world" == s2) << endl;
cout << (s1 == "hello world") << endl;
cout << s1 << endl;
cout << s2 << endl;
cin >> s1 >> s2;
cout << s1 << endl;
cout << s2 << endl;
getline(cin, s1);
cout << s1 << endl;
}
void test_string9()
{
string s1;
cin >> s1;
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;
}
void test_string10()
{
string s1("hello world");
string s2(s1);
cout << s1 << endl;
cout << s2 << endl;
string s3("xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx");
s1 = s3;
}
}本章完!






















 2442
2442

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








