解题思路:
方法一:

1.先判断p或者q 是不是 root当中的一个
2.左子树当中递归査找p或者q
3.右子树当中递归查找p或者q
如何查找:
root 的 left 和 right 都不为空 ->root
root的 left 为空 right 不为空->right这一侧找到的就是公共祖先
root的 left 不为空 right 为空->left这一侧找到的就是公共祖先
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(root==null){
return root;
}
//p或q是root当中的一个
if (root==p || root==q)
{
return root;
}
TreeNode left=lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q);
TreeNode right=lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q);
if(left!=null && right!=null){
//p和q在root的两侧
return root;
}else if(right!=null){
//右树不为空,但左树为空
return right;
}else
//左树不为空,但右树为空
return left;
}
}
方法二:
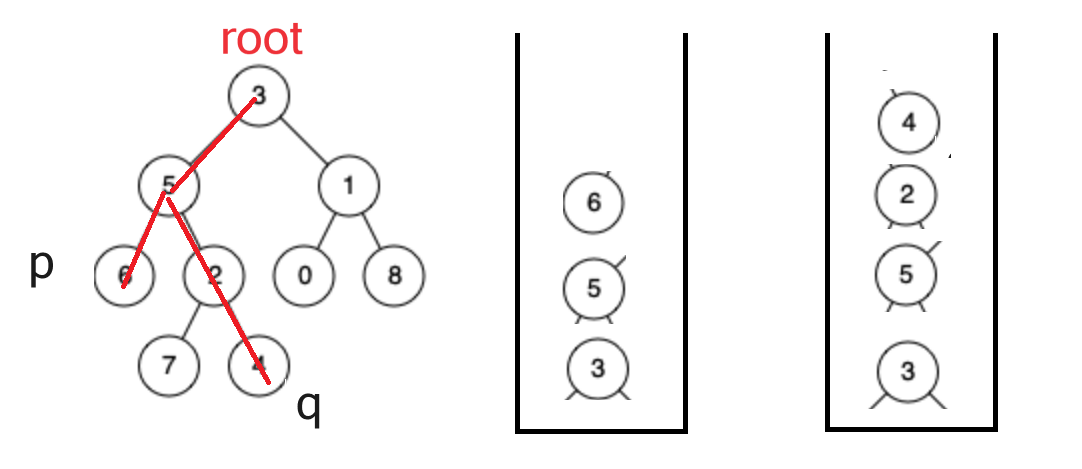
1.得到 root到p 以及 root到q 的路径
2.得到这两条路径之后分别把它们放进两个栈中,然后开始出栈。
3.如何出栈:如果两个栈中的结点数不一样,要先把两个栈中的结点数量变得一样,即size1==size2,再开始两个栈一起出(先看当前栈顶元素是否一样,如果不一样,两个栈一起出;如果一样,随便出一个栈当前的栈顶元素(s1.pop() 或 s2.pop() ),这个出的元素就是公共祖先)。
如何得到路径:
1.只要root不为空 就放在栈中
2.再判断当前节点 左子树 右子树 是不是有要找的节点。如果都没有就出栈。
3. root == node 找到了
public boolean getPath(TreeNode root, TreeNode node,
Stack<TreeNode> stack) {
if(root == null) {
return false;
}
stack.push(root);
if(root == node) {
return true;
}
boolean flgLeft = getPath(root.left,node,stack);
if(flgLeft) {
return true;
}
boolean flgRight = getPath(root.right,node,stack);
if(flgRight) {
return true;
}
stack.pop();
return false;
}
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor2(TreeNode root,
TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(root == null) {
return null;
}
Stack<TreeNode> stack1 = new Stack<>();
Stack<TreeNode> stack2 = new Stack<>();
getPath(root,p,stack1);
getPath(root,q,stack2);
int size1 = stack1.size();
int size2 = stack2.size();
if (size1 > size2) {
int size = size1-size2;
while (size != 0) {
stack1.pop();
size--;
}
}else {
int size = size2-size1;
while (size != 0) {
stack2.pop();
size--;
}
}
while (!stack1.isEmpty() && !stack2.isEmpty()) {
if(stack1.peek().equals(stack2.peek())) {
return stack1.pop();
//return stack2.pop();
}else {
stack1.pop();
stack2.pop();
}
}
return null;
}class Solution {
public String tree2str(TreeNode root) {
StringBuilder sbu = new StringBuilder();
tree2strChild(root,sbu);
return sbu.toString();
}
public void tree2strChild(TreeNode root,StringBuilder sbu) {
if(root == null) {
return;
}
sbu.append(root.val);
//1、先递归左树
if(root.left != null) {
sbu.append("(");
tree2strChild(root.left,sbu);
sbu.append(")");
}else {
if(root.right == null) {
return;
}else {
sbu.append("()");
}
}
//2、递归右树
if(root.right != null) {
sbu.append("(");
tree2strChild(root.right,sbu);
sbu.append(")");
}else {
return;
}
}
}class Solution {
List<Integer> list=new ArrayList<>();
if(root==null){
return list;
}
Stack<TreeNode> stack=new Stack<>();
TreeNode cur=root;
while(cur!=null || !stack.isEmpty())
{
while(cur!=null){
stack.push(cur);
list.add(cur.val);
cur=cur.left;
}
TreeNode top=stack.pop();
cur=top.right;
}
return list;
}
}class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list=new ArrayList<>();
if(root==null){
return list;
}
Stack<TreeNode> stack=new Stack<>();
TreeNode cur=root;
while(cur!=null || !stack.isEmpty())
{
while(cur!=null){
stack.push(cur);
cur=cur.left;
}
TreeNode top=stack.pop();
list.add(top.val);
cur=top.right;
}
return list;
}
} public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null) {
return list;
}
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode cur = root;
TreeNode prev = null;
while (cur != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
while (cur != null) {
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.left;
}
TreeNode top = stack.peek();
if(top.right == null || top.right == prev ) {
stack.pop();
list.add(top.val);
prev = top;
}else {
cur = top.right;
}
}
return list;
}






 文章介绍了在二叉树中寻找最近公共祖先的两种方法,包括递归查找和利用栈实现路径比较。同时提到了二叉树的前序、中序和后序遍历。
文章介绍了在二叉树中寻找最近公共祖先的两种方法,包括递归查找和利用栈实现路径比较。同时提到了二叉树的前序、中序和后序遍历。














 235
235











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








