头插法和尾插法易错点:
在head==NULL-----头插法和尾插法都是head=p(=tail);
在head!=NULL-------头插法:p->next=head; head=p;
---------尾插法:tail->next=p; tail=p;
头插法是逆序输出
尾插法是顺序输出
头插法
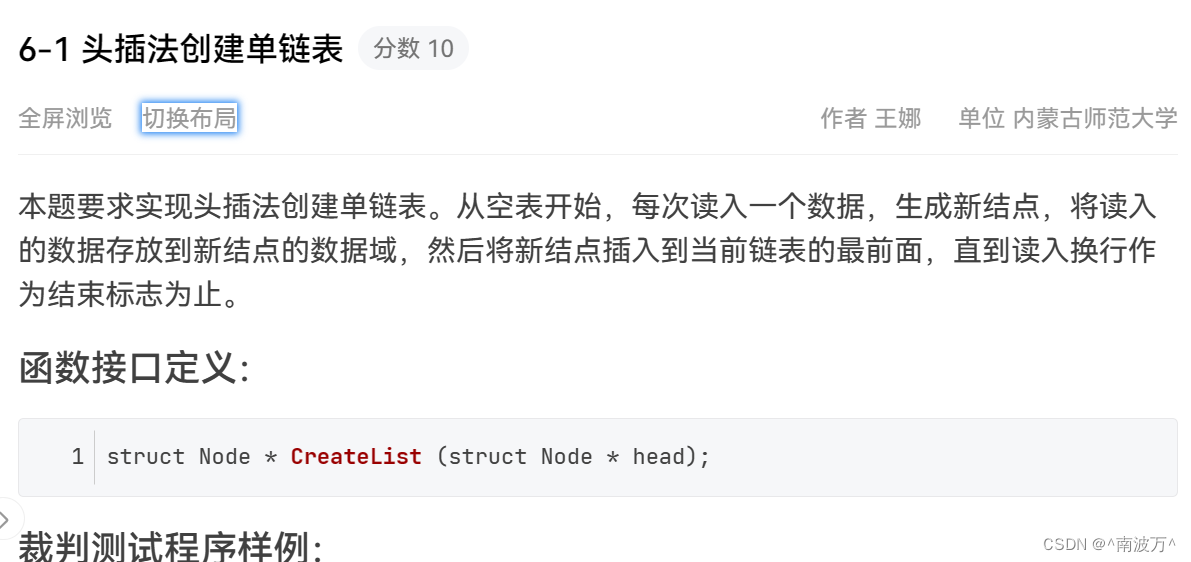
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
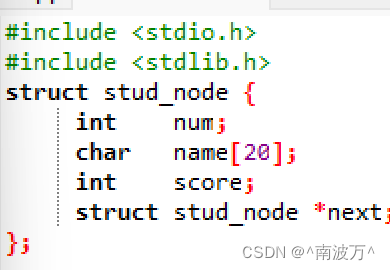
struct Node //定义结构体
{
char data; //数据域
struct Node * next; //指针域
};
/* 请在这里填写答案 */
void PrintList (struct Node * head)
{
struct Node * s;
if(head == NULL)
{
printf("None");
return;
}
for(s=head;s!=NULL;s = s->next)
{
printf("%c ",s->data);
}
}
int main()
{
struct Node * head = NULL;
head = CreateList(head);
PrintList(head);
return 0;
}头插法的步骤
1.新节点 struct Node* p;
2.新节点开空间 p=(struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
3.数据存储 p -> data = ch;
4.头插法重点顺序
p->next = head;
head=p;
5.切记要再scanf("%c",&ch);-------完整循环
struct Node* CreateList (struct Node * head)
{
struct Node* p;
char ch;
scanf("%c",&ch);
while(ch!='\n')
{
p=(struct Node *)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
p->data=ch;
p->next=head;
head=p;
scanf("%c",&ch);
}
return head;
}尾插法:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct Node { // 定义结构体类型,并且用 typedef 简化声明
char data; // 数据域
struct Node * next;// 指针域
} Node;
// 尾插法创建链表
Node * createListTailInsertion()
{
Node *head, *temp, *newnode;
char ch;
head = NULL;
scanf("%c", &ch); // 获取第一个字符
while (ch != '\n') {
newnode = (Node*) malloc(sizeof(Node)); // 创建新节点
newnode->data = ch; // 赋值给新节点的数据域
newnode->next = NULL; // 设置新节点的下一个为null
if (head == NULL) // 如果是第一个节点,则设置头指针指向新节点
head = temp = newnode;
else // 否则将新节点添加到链表末尾
{
temp->next = newnode; // 将最后一个节点的指针域指向新节点
temp = newnode; // 更新最后一个节点指针
}
scanf("%c", &ch); // 获取下一个字符
}
return head; // 返回链表头
}
// 打印链表
void printList(Node * head)
{
Node * s;
if(head == NULL)
{
printf("None\n");
return;
}
for(s=head;s!=NULL;s = s->next)
{
printf("%c ",s->data);
}
printf("\n"); // 输出换行符以使输出更清晰
}
int main()
{
Node * head = NULL;
head = createListTailInsertion(); // 使用尾插法创建链表
printList(head); // 打印链表
return 0;
}
尾插法步骤:
1.比头插法多一个尾结点*tail;
struct Node* head,* tail, * p;
2.头插尾插都需要 char ch;----表示数据
3.scanf("%c",&ch)
4.新指针节点开空间 p = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node))
5.存储数据 p->data = ch;
p->next = NULL;
6.头指针的可能性
head ==NULL-------- head = tail = p; // 头指针是第一个节点,设置头指针指向新节点
head != NULL--------tail -> next = p; tail = p;
7.切记 scanf ("%c",&ch);
返回head;
输出链表:
for (head; head!=NULL; head=head->next)
{
printf("%c",head->data);
}
总结注意易错点:
1.while循环里一定要写成 ch!='\n',循环后面一定要加上 scanf("%c",&ch);---更新数据
不要写成scanf("%c",&ch)!=EOF
否则就不会输出第一个字母
2.头插法和尾插法非常重要的记忆方法:
头插法开始只是struct *head,*p;-------尾插法struct *head,*tail,*p;
头插法开始head=NULL ---------- 尾插法 head = tail =NULL;
头插法循环里 if (head==NULL) ----head = p;
else { p->next = head;
head=p;---更新头结点}
尾插法循环里 if(head==NULL)-------head=tail=p;
else{ tail->next = p;
tail=p;--更新尾结点}
Node * createListTailInsertion()
{
struct Node*head,*p;
char ch;
scanf("%c",&ch);
head=NULL;
while(ch!='\n')
//while(scanf("%c",&ch)!=EOF)
// while(1)
{
//if(scanf("%c",&ch)!=1||ch=='\n')break;
p=(struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
p->data=ch;
p->next=NULL;
if(head==NULL) head=p;
else
{
p->next = head;
head=p;
}
scanf("%c",&ch);
}
return head;
}22届复习链表函数
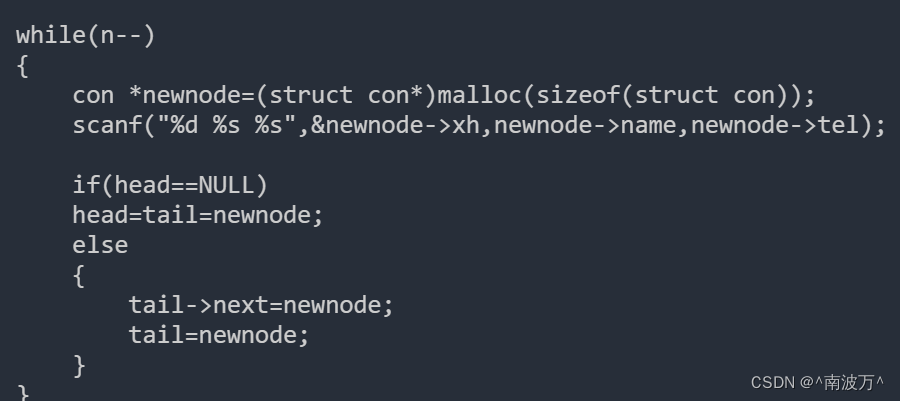
尾插法:

con* creatList()
{
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
struct con*head,*tail;
head=tail=NULL;
while(n--)
{
con *newnode=(struct con*)malloc(sizeof(struct con));
scanf("%d %s %s",&newnode->xh,newnode->name,newnode->tel);
if(head==NULL)
head=tail=newnode;
else
{
tail->next=newnode;
tail=newnode;
}
}
return head;
}头插法:
con* creatList()
{
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
struct con* head=NULL;
int i;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
struct con* newnode = NULL;
newnode=(struct con*)malloc(sizeof(struct con));
scanf("%d %s %s",&newnode->xh,newnode->name,newnode->tel);
if(head==NULL)
head=newnode;
else
{
newnode->next=head;
head=newnode;
}
}
return head;
}新问题新问题新问题!!!!!
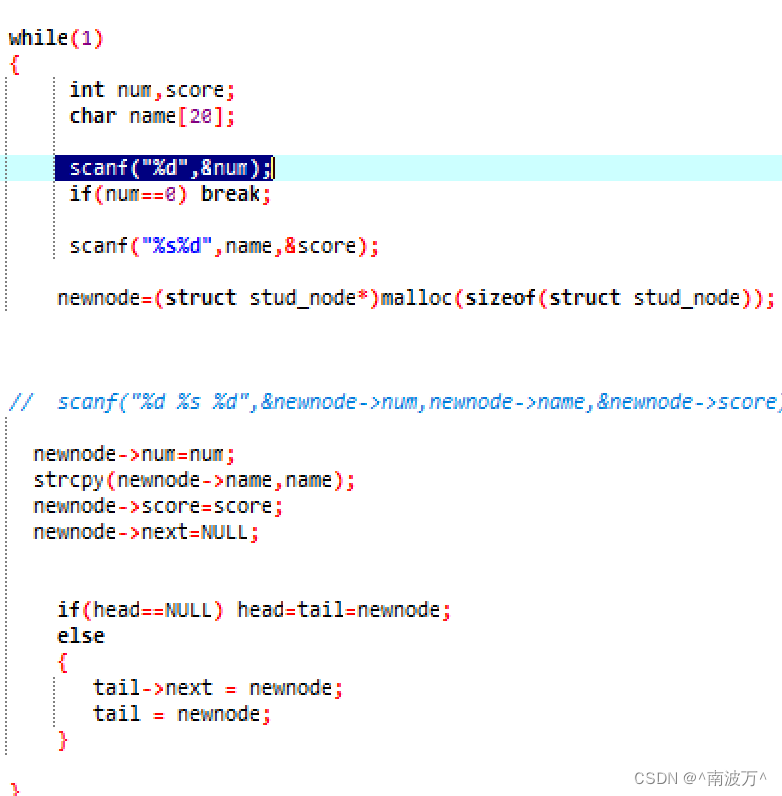
他没有给出循环该怎么结束,也就是上面几个例题中给的案例会先输入 n ,再输入 n 个案例
>>>>这样的循环可以使用两个
1.for (int i=0; i < n; i++)
2.while(n--){---------->最后需要scanf( " ");}
>>>>>>这个是直接输出成员,直到 0 才会结束循环
也就是说需要进行判断
scanf("%d" , &num);
if ( num == 0 ) break;
再输入接下来名字和分数
scanf ( " %s%d ",name,&score);
新问题新问题新问题!!!!!
另外的问题就是:赋值问题!!!!
1.直接先定义新指针后进行开空间
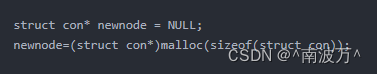
2.先进行定义新的 int 型或者 char 型的新变量
再定义新指针
利用新指针进行指向main中原有的struct结构体里的旧变量
旧变量
新变量

赋值变量之前需要给指针开空间
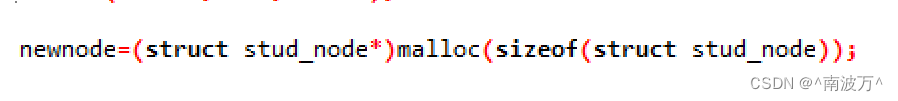
赋值变量: 注意int 型和char 型赋值的不同


总结:
如果案例中
>>>> 先输入n,再输入n个信息
循环>>>>>就利用for 或者while 直接进行即可
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
while( n -- ) {};
信息的描述>>>>>>也可以不用新定义再赋值
先给新指针开空间
再输入scanf("%s%d",newnode->name,&newnode->num)
如果案例中
>>>>直接让输入学生信息>>>>>直到 0 结束循环
循环 >>>>> while(1)
信息描述 >>>>> 先进行 int char 的新变量
>>>>>再进行新旧赋值;>>>>先赋值第一个变量并输入第一个变量
>>>>> 利用 if 语句进行判断 >>>> 如果第一个变量 !=0 >>> 再进行输入其他变量
如果第一个变量 == 0 >>>break
对于循环
while(ch!='\n') >>>>>需要两个scanf

while(n--)
while(1)
























 1190
1190

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








