1.栈
1.1栈的概念及结构
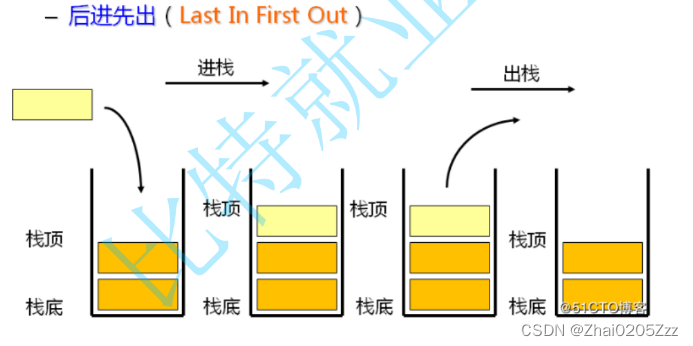
栈:一种特殊的线性表,其只允许在固定的一端进行插入和删除元素操作。进行数据插入和删除操作的一端称为栈顶,另一端称为栈底。栈中的数据元素遵守后进先出LIFO(Last In First Out)的原则。
压栈:栈的插入操作叫做进栈/压栈/入栈,入数据在栈顶。
出栈:栈的删除操作叫做出栈。出数据也在栈顶。
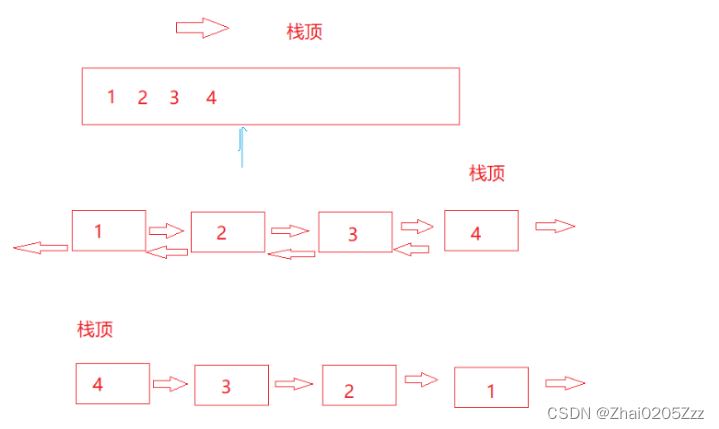
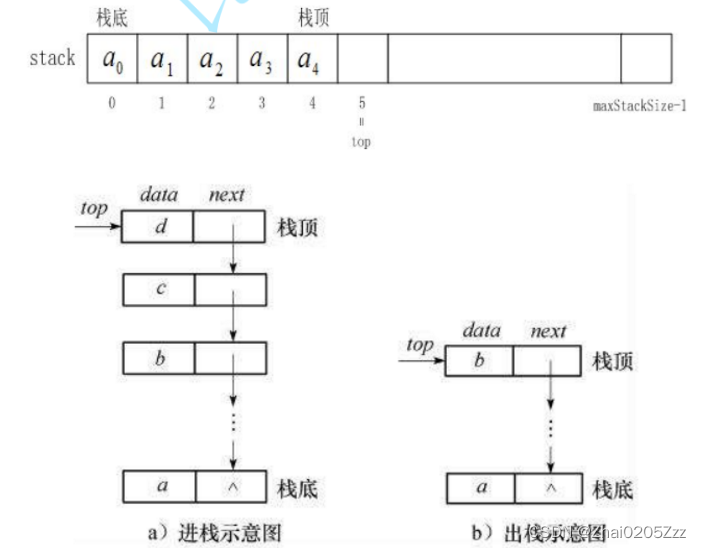
单链表右边当栈顶不好找上一个结点因此单链表可以让左边当栈顶,而双向链表可以。
数组的缺点是扩容(扩容也有问题:消耗和异地扩容),但数组的CPU高速缓存更好,因此选数组更好一点。
1.2栈的实现
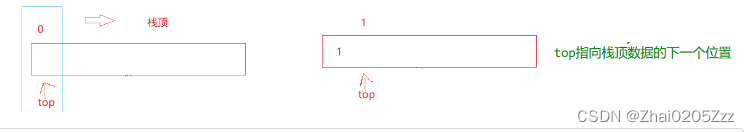
如果top要想指向栈顶元素那么初始化就不能为0;如果top是指向最后一个栈顶数据且没有数据时此时指向的是-1,指向-1就是指向栈顶元素。
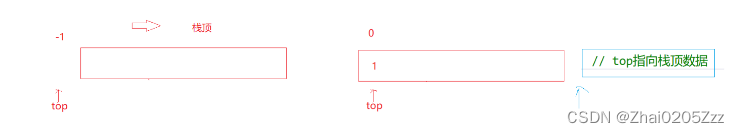
top指向栈顶元素的下一个位置:此时没有数据top指向0,有一个数据top指向1。(我们一般默认使用这种思路)
以下是使用顺序表实现栈:
//Stack.h #pragma once #include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include<stdbool.h> #include<assert.h> typedef int STDataType; typedef struct ST { STDataType* a; int top;//栈顶元素 int capacity;//容量 }ST; //初始化 void STInit(ST* pst); //销毁 void STDestroy(ST* pst); //进栈 void STPush(ST* pst, STDataType x); //删除 void STPop(ST* pst); //获取栈顶的数据 STDataType STTop(ST* pst); // 获取栈中有效元素个数 int StackSize(ST* pst); // 检测栈是否为空,如果为空返回非零结果,如果不为空返回0 int StackEmpty(ST* pst);
//Stack.c #include"Stack.h" //初始化 void STInit(ST* pst) { assert(pst); pst->a = NULL; pst->capacity = 0; //top指向栈顶元素的下一个位置 pst->top = 0; //top指向栈顶数据 /*pst->top = -1;*/ } //销毁 void STDestroy(ST* pst) { assert(pst); free(pst->a); pst->a = NULL; pst->capacity = pst->top = 0; } //进栈 void STPush(ST* pst, STDataType x) { assert(pst); //扩容 if (pst->top == pst->capacity) { int newCapacity = pst->capacity == 0 ? 4 :pst->capacity * 2;//初始化和capacity为0 STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(pst->a, newCapacity * sizeof(STDataType)); if (tmp == NULL) { perror("realloc fail!"); return; } pst->a = tmp; pst->capacity = newCapacity; } pst->a[pst->top++] = x; //pst->top++; } //出栈 void STPop(ST* pst) { assert(pst); assert(pst->top > 0);//检查栈不为空 pst->top--; } //获取栈顶的数据 STDataType STTop(ST* pst) { assert(pst); assert(pst->top > 0); return pst->a[pst->top - 1]; } // 获取栈中有效元素个数 int StackSize(ST* pst) { assert(pst); return pst->top; } // 检测栈是否为空,如果为空返回非零结果,如果不为空返回0 bool STEmpty(ST* pst) { assert(pst); return pst->top == 0; }
//test.c #include"Stack.h" void test() { ST s; STInit(&s); STPush(&s,1); printf("%d ", STTop(&s)); STPop(&s); STPush(&s,2); STPush(&s,3); STPush(&s,4); while (!StackEmpty(&s)) { printf("%d ", STTop(&s)); STPop(&s); } STDestroy(&s); } int main() { test(); return 0; }
1.3 顺序表和列表的区别

顺序栈:是静态分配的,最大空间容量受到限制。
链栈:是静态分配的,不需要考虑空间不够。






















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








