LeetCode 513.找树左下角的值
1、题目
题目链接:513. 找树左下角的值
给定一个二叉树的 根节点 root,请找出该二叉树的 最底层 最左边 节点的值。
假设二叉树中至少有一个节点。
示例 1:
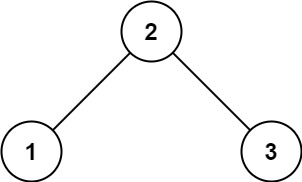
输入: root = [2,1,3]
输出: 1
示例 2:
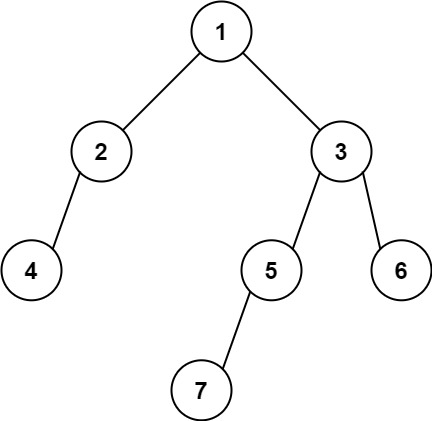
输入: [1,2,3,4,null,5,6,null,null,7]
输出: 7
提示:
- 二叉树的节点个数的范围是 [1,104]
- -231 <= Node.val <= 231 - 1
2、深度优先搜索(递归)
思路
这道题要在二叉树的 最后一行 找到 最左边的值。
如果使用递归法,如何判断是最后一行呢,其实就是深度最大的叶子节点一定是最后一行。所以要找深度最大的叶子节点。
那么如何找最左边的呢?可以使用前序遍历(当然中序,后序都可以,因为本题没有中间节点的处理逻辑,只要左优先就行),保证优先左边搜索,然后记录深度最大的叶子节点,此时就是树的最后一行最左边的值。
我们使用 maxDepth 用来记录最大深度,result 记录最大深度最左节点的数值。
在写递归时,我们要先明确递归三部曲:
- 确定递归函数的参数和返回值
参数必须有要遍历的树的根节点,depth 用来记录当前深度,maxDepth 用来记录最大深度,result 记录最大深度最左节点的数值。 这里就不需要返回值了,所以递归函数的返回类型为 void。
代码如下:
void traversal(TreeNode* root, int depth, int& maxDepth, int& result)
- 确定终止条件
当遇到叶子节点的时候,就需要统计一下最大的深度了,所以需要遇到叶子节点来更新最大深度。
代码如下:
// 如果当前节点是叶子节点
if (root->left == nullptr && root->right == nullptr) {
// 如果当前深度大于最大深度
if (depth > maxDepth) {
// 更新最大深度
maxDepth = depth;
// 更新结果值为当前节点的值
result = root->val;
}
return;
}
- 确定单层递归的逻辑
在找最大深度的时候,递归的过程中依然要使用回溯。
代码如下:
// 如果左子节点存在
if (root->left) {
// 深度加1
depth++;
// 递归遍历左子树
traversal(root->left, depth, maxDepth, result);
// 回溯,深度减1
depth--;
}
// 如果右子节点存在
if (root->right) {
// 深度加1
depth++;
// 递归遍历右子树
traversal(root->right, depth, maxDepth, result);
// 回溯,深度减1
depth--;
}
代码
#include <iostream>
#include <climits>
using namespace std;
//Definition for a binary tree node.
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
void traversal(TreeNode* root, int depth, int& maxDepth, int& result) {
// 如果当前节点是叶子节点
if (root->left == nullptr && root->right == nullptr) {
// 如果当前深度大于最大深度
if (depth > maxDepth) {
// 更新最大深度
maxDepth = depth;
// 更新结果值为当前节点的值
result = root->val;
}
return;
}
// 如果左子节点存在
if (root->left) {
// 深度加1
depth++;
// 递归遍历左子树
traversal(root->left, depth, maxDepth, result);
// 回溯,深度减1
depth--;
}
// 如果右子节点存在
if (root->right) {
// 深度加1
depth++;
// 递归遍历右子树
traversal(root->right, depth, maxDepth, result);
// 回溯,深度减1
depth--;
}
return;
}
int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == nullptr) {
return 0;
}
// 记录最大深度
int maxDepth = INT_MIN;
// 记录最大深度最左节点的数值
int result = 0;
traversal(root, 0, maxDepth, result);
return result;
}
};
int main() {
Solution s;
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(3);
root->left = new TreeNode(9);
root->right = new TreeNode(20);
root->right->left = new TreeNode(15);
root->right->right = new TreeNode(7);
cout << s.findBottomLeftValue(root) << endl;
return 0;
}
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度: O(n),其中 n 是二叉树的节点数目。需要遍历 n 个节点。
- 空间复杂度: O(n)。递归栈需要占用 O(n) 的空间。
3、深度优先搜索(递归精简版)
思路
在回溯的地方可以进行精简,在调用traversal函数时,depth加1,在递归结束时再减1,以确保在递归的不同层次上深度值是正确的。
代码如下:
traversal(root->right, depth + 1, maxDepth, result);
代码
class Solution {
public:
void traversal(TreeNode* root, int depth, int& maxDepth, int& result) {
// 如果当前节点是叶子节点
if (root->left == nullptr && root->right == nullptr) {
// 如果当前深度大于最大深度
if (depth > maxDepth) {
// 更新最大深度
maxDepth = depth;
// 更新结果值为当前节点的值
result = root->val;
}
return;
}
// 如果左子节点存在
if (root->left) {
// 递归遍历左子树,这里隐藏了回溯操作,在调用traversal函数时,depth加1,在递归结束时再减1
traversal(root->left, depth + 1, maxDepth, result);
}
// 如果右子节点存在
if (root->right) {
// 递归遍历右子树,这里隐藏了回溯操作,在调用traversal函数时,depth加1,在递归结束时再减1
traversal(root->right, depth + 1, maxDepth, result);
}
return;
}
int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == nullptr) {
return 0;
}
// 记录最大深度
int maxDepth = INT_MIN;
// 记录最大深度最左节点的数值
int result = 0;
traversal(root, 0, maxDepth, result);
return result;
}
};
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度: O(n),其中 n 是二叉树的节点数目。需要遍历 n 个节点。
- 空间复杂度: O(n)。递归栈需要占用 O(n) 的空间。
4、广度优先搜索(正向层序遍历)
思路
使用广度优先搜索遍历每一层的节点。遍历到最后一行的第一个结点就是要找的结点。
代码
class Solution {
public:
int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode* root) {
// 如果根节点为空,返回0
if (root == nullptr) {
return 0;
}
// 创建一个队列用于层序遍历
queue<TreeNode*> que;
// 记录结果
int result = 0;
// 将根节点入队
que.push(root);
// 当队列不为空时,进行循环
while (!que.empty()) {
// 获取当前层的节点个数
int size = que.size();
// 遍历当前层的节点
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
// 取出队首节点
TreeNode* node = que.front();
// 弹出队首节点
que.pop();
// 如果是当前层的第一个节点,更新结果
if (i == 0) {
result = node->val;
}
// 如果该节点有左子节点,将左子节点入队
if (node->left) {
que.push(node->left);
}
// 如果该节点有右子节点,将右子节点入队
if (node->right) {
que.push(node->right);
}
}
}
return result;
}
};
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度: O(n)
- 空间复杂度: O(n)
5、广度优先搜索(逆向层序遍历)
思路
使用广度优先搜索遍历每一层的节点。在遍历一个节点时,需要先把它的非空右子节点放入队列,然后再把它的非空左子节点放入队列,这样才能保证从右到左遍历每一层的节点。广度优先搜索所遍历的最后一个节点的值就是最底层最左边节点的值。
代码
class Solution {
public:
int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode* root) {
// 如果根节点为空,返回0
if (root == nullptr) {
return 0;
}
// 创建一个队列用于层序遍历
queue<TreeNode*> que;
// 记录结果
int result = 0;
// 将根节点入队
que.push(root);
// 当队列不为空时,进行循环
while (!que.empty()) {
// 获取队首节点
TreeNode* node = que.front();
que.pop();
// 如果该节点有右子节点,将右子节点入队
if (node->right) {
que.push(node->right);
}
// 如果该节点有右子节点,将右子节点入队
if (node->left) {
que.push(node->left);
}
// 更新结果为当前节点的值
result = node->val;
}
return result;
}
};
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度: O(n)
- 空间复杂度: O(n)






















 246
246











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








