目录
前言:
栈的重要应用之一是表达式求值。本文以简单算术表达式为例展现这一应用。
提示:以下是本篇文章正文内容,代码注释较为详细,可供参考
一、计算思路及方法
1.表达式读取及存放
算术表达式可分为两部分:数字和运算符。例如有下列表达式:
a-b/c+d*e;
为了计算上述表达式的值,可以使用两个栈:一个数据栈和一个运算符栈。其中数据栈用于存放操作数(数字),运算符栈存放运算符。
2.存放顺序和运算规则
首先从左到右扫描表达式,遇到操作数时,将其压入操作数栈;遇到运算符时。与当前运算符栈的栈顶运算符比较优先级,若高于栈顶运算符的优先级或运算符栈为空,则将其压入运算符栈;否则将栈顶运算符弹出,并根据所弹出运算符的目数,弹出运算数栈中相应数目的操作数(例如“+”是耳目运算符,弹出两个运算数,而“sin”是一目,弹出一个)。然后做运算并将运算结果压入操作数栈,重复这一过程,直到当前运算符入栈(运算符栈内没有比当前运算符优先级高的其他运算符)。
继续扫描表达式,并执行相应操作,直到表达式结束。最后,如果两个栈非空,则逐个弹出运算符栈顶元素和操作符栈中相应数目的运算数,并执行相应运算,将结果压入操作数栈,重复此过程直到运算符栈为空,最后一次运算的结果便是表达式的值。
上述表达式 a-b/c+d*e的计算过程如下图所示:

从左到右扫描上述表达式。为了方便,运算符栈初始化一个优先级很低的符号 # 。根据上述操作规则: a 入操作数栈,运算符 - 入运算符栈, b 入操作数栈,运算符 / 的优先级高于栈顶运算符 - 的优先级,将其入栈。继续扫描, c 入操作数栈,运算符 + 的优先级低于运算符 / 的优先级,因此将运算符 / 弹出,并将两个操作数 c 和 b 依次弹出,做除法运算:b / c,将结果 t1 压入操作数栈。继续比较运算符 + 与栈顶运算符 - 的优先级,运算符 + 的优先级不高于运算符 - ,因此继续将操作数栈中的两个操作数 t1 和 a 弹出,做减法运算:a - t1,将结果 t2 压栈。
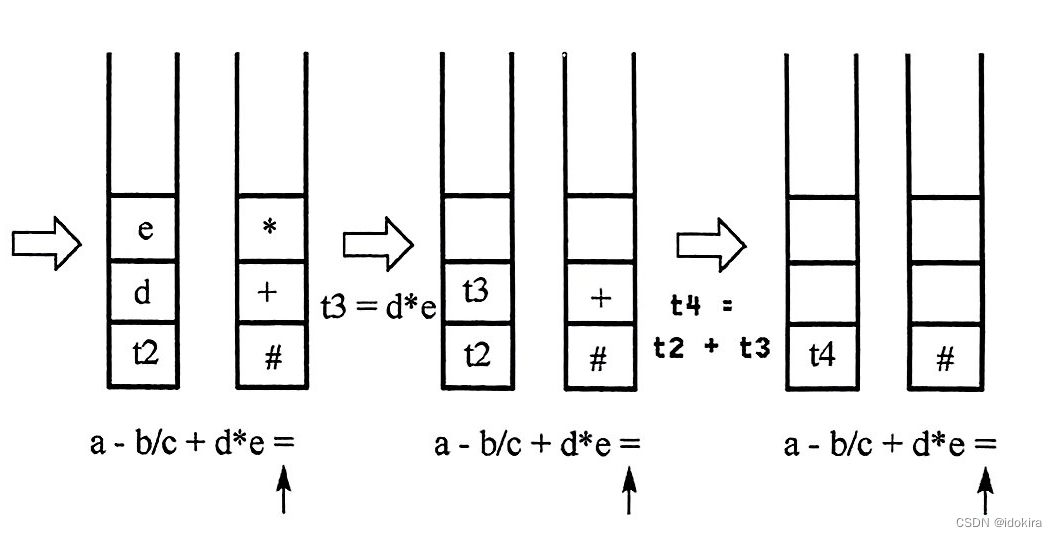
此时运算符已为初始状态,将运算符 + 压入运算符栈。继续扫描, d 入操作数栈,运算符 * 的优先级高于栈顶运算符 + 的优先级,将其压入运算符栈。继续扫描, e 入操作数栈,此时表达式扫描完毕(指针指向运算符 = )。逐个弹出运算符栈中的元素并执行相应操作:将 * 弹出, e 和 d 出栈,做乘法运算: d * e ,将结果 t3 压栈,最后将运算符 + 弹出, t3 和 t2 出栈,做加法运算: t2 + t3,所得结果 t4 便是上述表达式的值。
()括号优先级最高且比较特殊,这里这样实现:遇到“( ”时将其压入运算符栈,当遇到“ )”时,依次弹出运算符栈顶元素并进行相应目数计算,将计算结果压栈,重复上述操作,直到栈顶元素为“( ”停止并将“( ”出栈,至此完成“( ) ”内的运算。
对于sin,cos这样函数的运算符,我们将其识别后可以规定一个字母代替其(比如“ s ”代表“ sin ”,“ c ”代表“ cos ”,将其压入运算符栈然后将扫描指针跳过其剩余长度的扫描。
注意,为了保证算术运算符的左结合性,若当前运算符与栈顶运算符优先级相同,则将栈顶运算符弹出,执行相应运算。另外,对于双目运算符,在执行运算时首先弹出的操作数为运算符的右操作数,其后弹出的数为左操作数,如 b / c的运算过程。
二、代码实现
1.创建结点
关于结点的建立就不赘述了,这里要注意的是后面要用到的类模板Stack要先提前声明,否则在Node类里声明友元时会报错。
#include <cmath>
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template<class T> class Stack;
template<class T>
class Node {
private:
T m_data;//数据域
Node* m_next = nullptr;//指针域
public:
Node(const T& val) {
this->m_data = val;
} //有参构造
Node& operator=(const Node& rhs) = delete; //禁止赋值
friend class Stack<T>; //声明友元
};//创建结点2.创建栈
入栈出栈清空都是基本的写法,之前写的是类外实现,这里为了方便直接类内实现。
template<class T>
class Stack {
private:
Node<T>* m_top = nullptr;//创建头结点
public:
Stack() = default;//默认构造函数
Stack(const Stack&) = delete;//抑制复制
Stack& operator=(const Stack&) = delete;//抑制复制
~Stack() {
clear();
this->m_top = nullptr;
}//析构函数
void clear() {
Node<T>* p = nullptr;
while (this->m_top != nullptr) {
p = this->m_top;
this->m_top = this->m_top->m_next;
delete p;
}
}//清栈函数
void push(const T& val) {
Node<T>* node = new Node<T>(val);
node->m_next=this->m_top;
this->m_top = node;
}//入栈函数
void pop() {
if (empty()) { return; }
Node<T>* p = this->m_top;
this->m_top = this->m_top->m_next;
delete p;
}//出栈函数
bool empty()const { return this->m_top == nullptr; }//判断是否为空
const T& top() {
return this->m_top->m_data; }//访问头指针数据
};//创建栈3.创建计算器
其中m_num为操作数栈,m_opr为运算符栈 。
class Calculator {
private:
Stack<double> m_num;//用于存放数字
Stack<char> m_opr;//用于存放运算符
int precedence(const char& input)const;//判断优先级
double readNum(string::const_iterator& it);//读出数字
char readOpr(string::const_iterator& it);//读出运算符
void calculate();//弹出数字和运算符计算
bool isNum(string::const_iterator& c)const {
return *c >= '0' && *c <= '9' || *c == '.';
}//判断是否为数字
public:
~Calculator() {
this->m_num.clear();
this->m_opr.clear();
}//析构函数
Calculator() { this->m_opr.push('#'); }//初始化
double doIt(const string& exp);//计算算式函数
};(1)判断优先级
其中' s ', ' c ',' t ',' r ',分别代表sin、cos、tan、sqrt。
int Calculator::precedence(const char& input)const {
switch (input) {
case'=':return 0;
case'#':return 1;
case'+':case'-':return 2;
case'*':case'/':case'%':return 3;
case's':case'c':case't':case'r':return 4;
case'^':return 5;
default: return 1;
}
}//判断优先级(2)判断数字并读取
注意“ pi ”作为一种特殊的数字,判断方法为第一个字母为“ p ”且第二字母为“ i ”,atan(1.0)*4是计算pi的算式。
double Calculator::readNum(string::const_iterator& it) {
string t;
if (*it == 'p' && *(it + 1) == 'i') {
return atan(1.0) * 4;
}//判断是否为pi
while (isNum(it) || *it == '.') {
t += *it++;
}
while (isspace(*it)) {
++it; // 跳过空格
}
return stod(t);//讲字符串转换为double存入
}//读出数字(3)读取运算符
可以加入其他非基础运算符,只需要继续加入else if结构。
char Calculator::readOpr(string::const_iterator& it) {
string t1;
string t2;
t1 = *it;//第一个字母
t2 = *(it + 1);//第二个字母
while (isspace(*it)) {
++it; // 跳过空格
}
//cout << "读取运算符" << endl;
if (t1 == "s"&&t2=="i") {
//cout << "获取sin";
return 's';
}//sin
else if (t1 == "c") {
return 'c';
}//cos
else if (t1 == "t") {
return 't';
}//tan
else if (t1 == "s"&&t2=="q") {
return 'r';
}//sqrt
}//读出运算符(4)运算函数
先取出一个操作数作为右操作数,若为双目运算符则再弹出一个操作数作为左操作数。
void Calculator::calculate() {
if (this->m_num.empty()) {
return;
}
double rightnum = this->m_num.top(); //取出右边的运算数
this->m_num.pop();//从栈中弹出取出的运算数
switch (this->m_opr.top())
{
case's':
this->m_num.push(sin(rightnum)); //sin
break;
case'c':
this->m_num.push(cos(rightnum)); //cos
break;
case't':
this->m_num.push(tan(rightnum)); //tan
break;
case'r':
this->m_num.push(sqrt(rightnum)); //sqrt
break;
default: //判断是否为一目运算不为则往下进行
double leftnum = this->m_num.top(); //取出左边的运算数
this->m_num.pop();//从栈中弹出取出的运算数
if (this->m_opr.top() == '+') {
this->m_num.push(leftnum + rightnum);
} //+运算
else if (this->m_opr.top() == '-') {
this->m_num.push(leftnum - rightnum);
} //-运算
else if (this->m_opr.top() == '*') {
this->m_num.push(leftnum * rightnum);
} //*运算
else if (this->m_opr.top() == '/') {
this->m_num.push(leftnum / rightnum);
} // /运算
else if (this->m_opr.top() == '%') {
this->m_num.push(static_cast<int>(leftnum) % static_cast<int>(rightnum));
} //%运算
else if (this->m_opr.top() == '^') {
this->m_num.push(pow(leftnum, rightnum));
} //幂运算
break;
}
//cout << "清除运算符" << this->m_opr.top();
this->m_opr.pop();//从栈中弹出取出的运算符
}//运算函数(5)执行运算
- 运算前先清空计算器栈,扫描时跳过空格。
double Calculator::doIt(const string& exp) {
this->m_num.clear();//清除栈
for (auto it = exp.begin(); it != exp.end();) {
while (isspace(*it)) {
++it; // 跳过空格
}- 判断是否为数字
if (isNum(it)||*it=='p') {
this->m_num.push(readNum(it));
if (*it == 'p') {
++it;
++it;
}//若为pi则跳过i的循环
//cout << "获取数字" << this->m_num.top();
}//先判断是否为数字- 判断是否为括号()运算符
else if(*it=='(') {
this->m_opr.push(*it);
//cout << "获取运算符1" << this->m_opr.top();
++it;
}//判断是否在括号里
else if (*it == ')') {
while (this->m_opr.top() != '(') {
calculate();
}
//cout << "清除运算符" << this->m_opr.top() << endl;
this->m_opr.pop();//弹出"("结束括号内的运算
++it;
}//若遇到")"则持续进行运算直到运算符栈顶为"("- 若前面都不是则判断运算符优先级
else {
while (precedence(*it) <= precedence(this->m_opr.top())) {
if (this->m_opr.top() == '#') {
//cout << "终止";
break;
}
calculate();
}//- 判断是否为普通运算符
if (*it != '='&&*it!='s' && *it != 'c' && *it != 't' ) {
this->m_opr.push(*it);//将普通运算符入栈
}- 都不是则为特殊运算符,识别后记得逃出特殊运算符识别,例如:sin识别后要跳2位,sqrt识别后要跳3位
else {
if (*it =='s' || *it == 'c' || *it == 't') {
this->m_opr.push(this->readOpr(it));
if (this->readOpr(it) == 'r') {
++it;
} //若为sqrt则需要多跳一位
++it;
++it;
} //入栈后跳出该字符的判断
} //将特殊运算符入栈
++it;
}
} //这是第一个for遍历的括号- 完成遍历(计算),弹出结果
return this->m_num.top();//遍历后返回数据栈数据,得到结果
}以上便完成了整个计算步骤,最后得出结果。
4.main函数
下面仅测试案例,也可以选择cin输入,记得表达式结尾带“ = ”。
int main()
{
string a = "3-2*4+(6-1)/2+5=";
string b = "sin(pi/6)=";
Calculator cal;
double c = cal.doIt(a);
double d = cal.doIt(b);
cout << "第一个结果是:" << c << endl << "第二个结果是:" << d << endl;
}三、完整代码
以下是完整代码展示,由于个人水平有限,如有错误/不严谨的地方敬请指正。
#include <cmath>
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template<class T> class Stack;
template<class T>
class Node {
private:
T m_data;//数据域
Node* m_next = nullptr;//指针域
public:
Node(const T& val) {
this->m_data = val;
} //有参构造
Node& operator=(const Node& rhs) = delete; //禁止赋值
friend class Stack<T>; //声明友元
};//创建结点
template<class T>
class Stack {
private:
Node<T>* m_top = nullptr;//创建头结点
public:
Stack() = default;//默认构造函数
Stack(const Stack&) = delete;//抑制复制
Stack& operator=(const Stack&) = delete;//抑制复制
~Stack() {
clear();
this->m_top = nullptr;
}//析构函数
void clear() {
Node<T>* p = nullptr;
while (this->m_top != nullptr) {
p = this->m_top;
this->m_top = this->m_top->m_next;
delete p;
}
}//清栈函数
void push(const T& val) {
Node<T>* node = new Node<T>(val);
node->m_next=this->m_top;
this->m_top = node;
}//入栈函数
void pop() {
if (empty()) { return; }
Node<T>* p = this->m_top;
this->m_top = this->m_top->m_next;
delete p;
}//出栈函数
bool empty()const { return this->m_top == nullptr; }//判断是否为空
const T& top() {
return this->m_top->m_data; }//访问头指针数据
};//创建栈
class Calculator {
private:
Stack<double> m_num;//用于存放数字
Stack<char> m_opr;//用于存放运算符
int precedence(const char& input)const;//判断优先级
double readNum(string::const_iterator& it);//读出数字
char readOpr(string::const_iterator& it);//读出运算符
void calculate();//弹出数字和运算符计算
bool isNum(string::const_iterator& c)const {
return *c >= '0' && *c <= '9' || *c == '.';
} //判断是否为数字
public:
~Calculator() {
this->m_num.clear();
this->m_opr.clear();
} //析构函数
Calculator() { this->m_opr.push('#'); } //初始化
double doIt(const string& exp); //计算算式函数
};
int Calculator::precedence(const char& input)const {
switch (input) {
case'=':return 0;
case'#':return 1;
case'+':case'-':return 2;
case'*':case'/':case'%':return 3;
case's':case'c':case't':case'r':return 4;
case'^':return 5;
default: return 1;
}
} //判断优先级
double Calculator::readNum(string::const_iterator& it) {
string t;
if (*it == 'p' && *(it + 1) == 'i') {
return atan(1.0) * 4;
} //判断是否为pi
while (isNum(it) || *it == '.') {
t += *it++;
}
while (isspace(*it)) {
++it; // 跳过空格
}
return stod(t); //将字符串转换为double存入
}/ /读出数字
char Calculator::readOpr(string::const_iterator& it) {
string t1;
string t2;
t1 = *it; //第一个字母
t2 = *(it + 1);//第二个字母
while (isspace(*it)) {
++it; // 跳过空格
}
if (t1 == "s"&&t2=="i") {
//cout << "获取sin";
return 's';
} //sin
else if (t1 == "c") {
return 'c';
} //cos
else if (t1 == "t") {
return 't';
} //tan
else if (t1 == "s"&&t2=="q") {
return 'r';
}//sqrt
} //读出运算符
void Calculator::calculate() {
if (this->m_num.empty()) {
return;
}
double rightnum = this->m_num.top(); //取出右边的运算数
this->m_num.pop(); //从栈中弹出取出的运算数
switch (this->m_opr.top())
{
case's':
this->m_num.push(sin(rightnum));
break;
case'c':
this->m_num.push(cos(rightnum));
break;
case't':
this->m_num.push(tan(rightnum));
break;
case'r':
this->m_num.push(sqrt(rightnum));
break;
default://判断是否为一目运算不为则往下进行
double leftnum = this->m_num.top();//取出左边的运算数
//cout << "弹出二次数:" << this->m_num.top();
this->m_num.pop();//从栈中弹出取出的运算数
if (this->m_opr.top() == '+') {
this->m_num.push(leftnum + rightnum);
}
else if (this->m_opr.top() == '-') {
this->m_num.push(leftnum - rightnum);
}
else if (this->m_opr.top() == '*') {
this->m_num.push(leftnum * rightnum);
}
else if (this->m_opr.top() == '/') {
this->m_num.push(leftnum / rightnum);
}
else if (this->m_opr.top() == '%') {
this->m_num.push(static_cast<int>(leftnum) % static_cast<int>(rightnum));
}
else if (this->m_opr.top() == '^') {
this->m_num.push(pow(leftnum, rightnum));
}
break;
}
this->m_opr.pop(); //从栈中弹出取出的运算符
} //运算函数
double Calculator::doIt(const string& exp) {
this->m_num.clear(); //清除栈
for (auto it = exp.begin(); it != exp.end();) {
while (isspace(*it)) {
++it; // 跳过空格
}
if (isNum(it)||*it=='p') {
this->m_num.push(readNum(it));
if (*it == 'p') {
++it;
++it;
} //若为pi则跳过i的循环
}//先判断是否为数字
else if(*it=='(') {
this->m_opr.push(*it);
++it;
}//判断是否在括号里
else if (*it == ')') {
while (this->m_opr.top() != '(') {
calculate();
}
this->m_opr.pop();//弹出"("结束括号内的运算
++it;
}//若遇到")"则持续进行运算直到运算符栈顶为"("
else {
while (precedence(*it) <= precedence(this->m_opr.top())) {
if (this->m_opr.top() == '#') {
break;
}
calculate();
}//
if (*it != '='&&*it!='s' && *it != 'c' && *it != 't' ) {
this->m_opr.push(*it);//将普通运算符入栈
}
else {
if (*it =='s' || *it == 'c' || *it == 't') {
this->m_opr.push(this->readOpr(it));
if (this->readOpr(it) == 'r') {
++it;
}//若为sqrt则需要多跳一位
++it;
++it;
}//入栈后跳出该字符的判断
}//将特殊运算符入栈
++it;
}
}
return this->m_num.top();//遍历后返回数据栈数据,得到结果
}
int main()
{
string a = "3-2*4+(6-1)/2+5=";
string b = "sin(pi/6)=";
Calculator cal;
double c = cal.doIt(a);
double d = cal.doIt(b);
cout << "第一个结果是:" << c << endl << "第二个结果是:" << d << endl;
}
之后也会每周更新C++数据结构和算法的相关内容,将逐渐由浅入深,感兴趣的朋友可以点个赞和关注。





















 1261
1261











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








