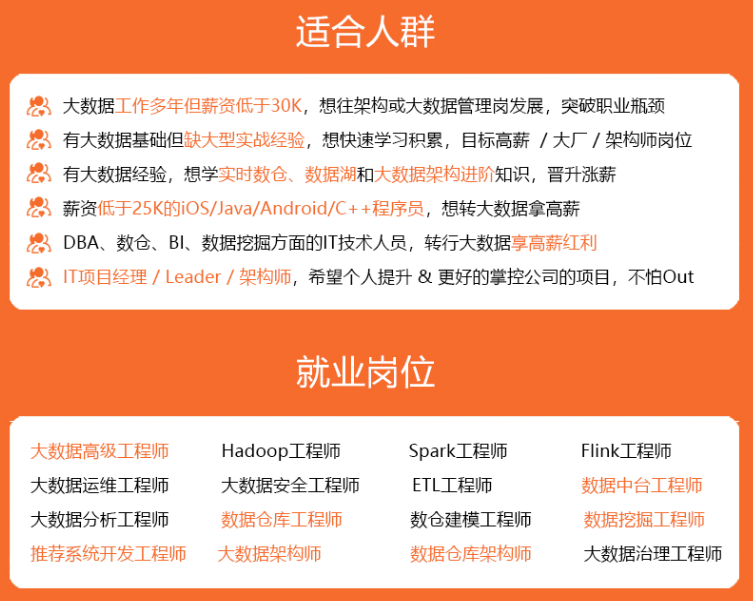
既有适合小白学习的零基础资料,也有适合3年以上经验的小伙伴深入学习提升的进阶课程,涵盖了95%以上大数据知识点,真正体系化!
由于文件比较多,这里只是将部分目录截图出来,全套包含大厂面经、学习笔记、源码讲义、实战项目、大纲路线、讲解视频,并且后续会持续更新
import org.apache.shiro.authz.SimpleAuthorizationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.realm.AuthorizingRealm;
import org.apache.shiro.subject.PrincipalCollection;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
public class CustomRealm extends AuthorizingRealm {
//此处用Map集合模拟用户-角色-权限之间的关联关系,实际开发中会从数据库进行查询
private final Map<String,String> userInfoMap = new HashMap<>();
{
userInfoMap.put(“jack”,“123”);
userInfoMap.put(“atguigu”,“123456”);
}
//role -> permission
private final Map<String, Set> permissionMap = new HashMap<>();
{
Set set1 = new HashSet<>();
Set set2 = new HashSet<>();
set1.add(“video:find”);
set1.add(“video:buy”);
set2.add(“video:add”);
set2.add(“video:delete”);
permissionMap.put(“jack”,set1);
permissionMap.put(“atguigu”,set2);
}
//user -> role
private final Map<String,Set> roleMap = new HashMap<>();
{
Set set1 = new HashSet<>();
Set set2 = new HashSet<>();
set1.add(“role1”);
set1.add(“role2”);
set2.add(“root”);
roleMap.put(“jack”,set1);
roleMap.put(“atguigu”,set2);
}
//进行权限校验的时候会调用
@Override
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principals) {
System.out.println(“权限 doGetAuthorizationInfo”);
String name = (String)principals.getPrimaryPrincipal();
Set permissions = getPermissionsByNameFromDB(name);
Set roles = getRolesByNameFromDB(name);
SimpleAuthorizationInfo simpleAuthorizationInfo = new SimpleAuthorizationInfo();
simpleAuthorizationInfo.setRoles(roles);
simpleAuthorizationInfo.setStringPermissions(permissions);
return simpleAuthorizationInfo;
}
//当用户登陆的时候会调用
@Override
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException {
System.out.println(“认证 doGetAuthenticationInfo”);
//从token获取身份信息,token代表用户输入的信息
String name = (String)token.getPrincipal();
//模拟从数据库中取密码
String pwd = getPwdByUserNameFromDB(name);
if( pwd == null || “”.equals(pwd)){
return null;
}
SimpleAuthenticationInfo simpleAuthenticationInfo = new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(name, pwd, this.getName());
return simpleAuthenticationInfo;
}
/**
* 模拟从数据库获取用户角色集合
* @param name
* @return
*/
private Set getRolesByNameFromDB(String name) {
return roleMap.get(name);
}
/**
* 模拟从数据库获取权限集合
* @param name
* @return
*/
private Set getPermissionsByNameFromDB(String name) {
return permissionMap.get(name);
}
private String getPwdByUserNameFromDB(String name) {
return userInfoMap.get(name);
}
}
然后我们编写测试类,来验证是否正确:
package com.atguigu.shiro.demo;
import org.apache.shiro.SecurityUtils;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.UsernamePasswordToken;
import org.apache.shiro.mgt.DefaultSecurityManager;
import org.apache.shiro.subject.Subject;
import org.junit.Test;
public class AuthenticationTest {
private CustomRealm customRealm = new CustomRealm();
private DefaultSecurityManager defaultSecurityManager = new DefaultSecurityManager();
@Before
public void init(){
//构建环境
defaultSecurityManager.setRealm(customRealm);
SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(defaultSecurityManager);
}
@Test
public void testAuthentication() {
//获取当前操作的主体
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
//用户输入的账号密码
UsernamePasswordToken usernamePasswordToken = new UsernamePasswordToken(“jack”, “123”);
subject.login(usernamePasswordToken);
//登录
System.out.println(" 认证结果:"+subject.isAuthenticated());
//拿到主体标示属性
System.out.println(" getPrincipal=" + subject.getPrincipal());
subject.checkRole(“role1”);
System.out.println(“是否有对应的角色:”+subject.hasRole(“role1”));
System.out.println(“是否有对应的权限:”+subject.isPermitted(“video:add”));
}
}
运行测试用例,结果如下:

2. 深入Shiro源码解读认证授权流程
2.1 认证流程源码解读
1)我们以subject.login(token)为起点进行断点调试
2)DelegatingSubject.login(token)会将身份认证请求委托给DefaultSecurityManager的login()方法进行处理,接着继续进入DefaultSecurityManager的login()方法
public class DelegatingSubject implements Subject {
…
public void login(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException {
this.clearRunAsIdentitiesInternal();
//调用DefaultSecurityManager的login方法进行身份信息认证
Subject subject = this.securityManager.login(this, token);
…
}
…
}
3)DefaultSecurityManager的login()方法会调用AuthenticatingSecurityManager的authenticate()方法进行验证,接着继续进入AuthenticatingSecurityManager的authenticate()方法
public class DefaultSecurityManager extends SessionsSecurityManager {
…
public Subject login(Subject subject, AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException {
AuthenticationInfo info;
try {
//调用AuthenticatingSecurityManager的authenticate()方法进行验证
info = this.authenticate(token);
} catch (AuthenticationException var7) {
…
}
Subject loggedIn = this.createSubject(token, info, subject);
this.onSuccessfulLogin(token, info, loggedIn);
return loggedIn;
}
…
}
4)AuthenticatingSecurityManager的authenticate()方法会调用AbstractAuthenticator的authenticate()方法进行验证,接着继续进入AbstractAuthenticator的authenticate()方法
public abstract class AuthenticatingSecurityManager extends RealmSecurityManager {
…
public AuthenticationInfo authenticate(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException {
//调用AbstractAuthenticator的authenticate()方法进行验证
return this.authenticator.authenticate(token);
}
…
}
5)AbstractAuthenticator的authenticate()方法会调用ModularRealmAuthenticator的doAuthenticate()方法进行验证,接着继续进入ModularRealmAuthenticator的doAuthenticate()方法
public abstract class AbstractAuthenticator implements Authenticator, LogoutAware {
…
public final AuthenticationInfo authenticate(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException {
if (token == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(“Method argument (authentication token) cannot be null.”);
} else {
log.trace(“Authentication attempt received for token [{}]”, token);
AuthenticationInfo info;
try {
//调用ModularRealmAuthenticator的doAuthenticate()进行验证
info = this.doAuthenticate(token);
if (info == null) {
String msg = “No account information found for authentication token [” + token + "] by this " + “Authenticator instance. Please check that it is configured correctly.”;
throw new AuthenticationException(msg);
}
} catch (Throwable var8) {
…
}
log.debug(“Authentication successful for token [{}]. Returned account [{}]”, token, info);
this.notifySuccess(token, info);
return info;
}
}
…
}
6)ModularRealmAuthenticator的doAuthenticate()方法会获取相应的realm,由于我们目前只配置了一个realm,所以会执行doSingleRealmAuthentication()方法,接着会AuthenticatingRealm的getAuthenticationInfo()方法,接着继续进入AuthenticatingRealm的getAuthenticationInfo()方法
public class ModularRealmAuthenticator extends AbstractAuthenticator{
…
protected AuthenticationInfo doAuthenticate(AuthenticationToken authenticationToken) throws AuthenticationException {
this.assertRealmsConfigured();
//获取当前配置的realm
Collection realms = this.getRealms();
//如果当前配置realm个数为1,则执行doSingleRealmAuthentication()方法,否则执行doMultiRealmAuthentication()
return realms.size() == 1 ? this.doSingleRealmAuthentication((Realm)realms.iterator().next(), authenticationToken) : this.doMultiRealmAuthentication(realms, authenticationToken);
}
protected AuthenticationInfo doSingleRealmAuthentication(Realm realm, AuthenticationToken token) {
if (!realm.supports(token)) {
String msg = “Realm [” + realm + “] does not support authentication token [” + token + "]. Please ensure that the appropriate Realm implementation is " + “configured correctly or that the realm accepts AuthenticationTokens of this type.”;
throw new UnsupportedTokenException(msg);
} else {
AuthenticationInfo info = realm.getAuthenticationInfo(token);
if (info == null) {
String msg = “Realm [” + realm + "] was unable to find account data for the " + “submitted AuthenticationToken [” + token + “].”;
throw new UnknownAccountException(msg);
} else {
return info;
}
}
}
…
}
7)在此可以看到,AuthenticatingRealm的getAuthenticationInfo()方法会调用我们自定义配置realm的doGetAuthenticationInfo(token)获取认证信息,并且调用AuthenticatingRealm的assertCredentialsMatch方法进行密码匹配认证
public abstract class AuthenticatingRealm extends CachingRealm implements Initializable{
…
public final AuthenticationInfo getAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException {
AuthenticationInfo info = this.getCachedAuthenticationInfo(token);
if (info == null) {
// 调用自定义配置realm的doGetAuthenticationInfo(token)方法
info = this.doGetAuthenticationInfo(token);
log.debug(“Looked up AuthenticationInfo [{}] from doGetAuthenticationInfo”, info);
if (token != null && info != null) {
this.cacheAuthenticationInfoIfPossible(token, info);
}
} else {
log.debug(“Using cached authentication info [{}] to perform credentials matching.”, info);
}
if (info != null) {
// 对获取的认证信息进行密码验证
this.assertCredentialsMatch(token, info);
} else {
log.debug(“No AuthenticationInfo found for submitted AuthenticationToken [{}]. Returning null.”, token);
}
return info;
}
…
}
到此,我们的认证流程就结束了,通过源码可以看到认证流程到最后就是调用的我们自定义realm并重写的doGetAuthenticationInfo(token)方法,从以上的源码分析,可以得到以下方法调用的时序图:

2.2 授权流程源码解读
1)授权流程我们以subject.checkRole()方法为起点进行断点调试
2)DelegatingSubject的checkRole()方法会将授权请求委托给AuthorizingSecurityManager的checkRole()方法进行处理,接着继续进入AuthorizingSecurityManager的checkRole()方法
public class DelegatingSubject implements Subject {
…
public void checkRole(String role) throws AuthorizationException {
this.assertAuthzCheckPossible();
//将请求委托给AuthorizingSecurityManager的checkRole()方法
this.securityManager.checkRole(this.getPrincipals(), role);
}
…
}
3)AuthorizingSecurityManager的checkRole()方法会将请求委托给ModularRealmAuthorizer的checkRole()方法进行处理,接着继续进入ModularRealmAuthorizer的checkRole()方法
public abstract class AuthorizingSecurityManager extends AuthenticatingSecurityManager {
…
public void checkRole(PrincipalCollection principals, String role) throws AuthorizationException {
//将请求委托给ModularRealmAuthorizer的checkRole()方法
this.authorizer.checkRole(principals, role);
}
…
}
4)ModularRealmAuthorizer的checkRole()方法会调用AuthorizingRealm的hasRole()方法验证当前用户是否有相应的权限,若没有相应的权限,则会抛出异常,接着继续进入AuthorizingRealm的hasRole()方法
public class ModularRealmAuthorizer implements Authorizer, PermissionResolverAware, RolePermissionResolverAware {
…
public void checkRole(PrincipalCollection principals, String role) throws AuthorizationException {
this.assertRealmsConfigured();
//验证当前用户是否有相应的权限,如果没有,则会抛出异常
if (!this.hasRole(principals, role)) {
throw new UnauthorizedException(“Subject does not have role [” + role + “]”);
}
}
public boolean hasRole(PrincipalCollection principals, String roleIdentifier) {
this.assertRealmsConfigured();
Iterator var3 = this.getRealms().iterator();
Realm realm;
do {
if (!var3.hasNext()) {
return false;
}
realm = (Realm)var3.next();
//调用AuthorizingRealm的hasRole()方法进行验证,如果有相应权限则返回true,否则返回false
} while(!(realm instanceof Authorizer) || !((Authorizer)realm).hasRole(principals, roleIdentifier));
return true;
}
…
}
5)AuthorizingRealm的hasRole()方法会通过getAuthorizationInfo()方法进行调用自定义realm并重写的doGetAuthorizationInfo()方法获取当前用户拥有的授权信息
public abstract class AuthorizingRealm extends AuthenticatingRealm implements Authorizer, Initializable, PermissionResolverAware, RolePermissionResolverAware {
…
public boolean hasRole(PrincipalCollection principal, String roleIdentifier) {
AuthorizationInfo info = this.getAuthorizationInfo(principal);
return this.hasRole(roleIdentifier, info);
}
protected AuthorizationInfo getAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principals) {
if (principals == null) {
return null;
} else {
AuthorizationInfo info = null;
…
if (info == null) {
//调用自定义realm并重写的doGetAuthorizationInfo()方法获取当前用户的授权信息
info = this.doGetAuthorizationInfo(principals);
//如果授权信息存在并且存在缓存,则将当前授权信息进行缓存
if (info != null && cache != null) {
if (log.isTraceEnabled()) {
log.trace(“Caching authorization info for principals: [” + principals + “].”);
}
key = this.getAuthorizationCacheKey(principals);
cache.put(key, info);
}
}
return info;
}
}
…
}
到此,我们的授权流程就结束了,通过源码可以看到授权流程到最后就是调用的我们自定义realm并重写的doGetAuthorizationInfo()方法,从以上的源码分析,可以得到以下方法调用的时序图:

至此,我们就通过源码把Shiro的认证以及授权流程解读完了,java培训由上边分析我们可以知道Shiro认证授权的时候,会调用我们自定义Realm时重写的doGetAuthenticationInfo()方法以及doGetAuthorizationInfo()方法进行获取当前主体的认证以及授权信息,所以我们需要根据项目的具体情况在自定义Realm中定义获取认证以及授权信息的逻辑。
3. Shiro数据安全之数据加解密
- 为什么需要加解密?
- 在之前的学习中,我们在数据库中保存的密码都是明文的,一旦数据库数据泄露,那就会造成不可估算的损失。
- 什么是散列算法?
- 一般叫hash,简单的说就是一种将任意长度的消息压缩到某一固定长度的消息摘要的函数,适合存储密码,比如MD5
- 什么是salt(盐) ?
- 如果直接通过散列函数得到加密数据,容易被对应解密网站暴力破解,一般会在应用程序里面加特殊的字段进行处理,比如用户id,例子:加密数据 = MD5(明文密码+用户id), 破解难度会更大,也可以使用多重散列,比如多次md5
- Shiro如何根据用户传过来的密码进行加密与数据库密码进行匹配?
- Shiro会使用AuthenticatingRealm的assertCredentialsMatch()方法进行验证密码是否正确
- 因此,在Shiro中我们一般会自定义密码验证规则,示例如下:
@Bean
public HashedCredentialsMatcher hashedCredentialsMatcher(){
HashedCredentialsMatcher hashedCredentialsMatcher = new HashedCredentialsMatcher();
//散列算法,使用MD5算法;
hashedCredentialsMatcher.setHashAlgorithmName(“md5”);
//散列的次数,比如散列两次,相当于 md5(md5(“xxx”));
hashedCredentialsMatcher.setHashIterations(2);
return hashedCredentialsMatcher;
}
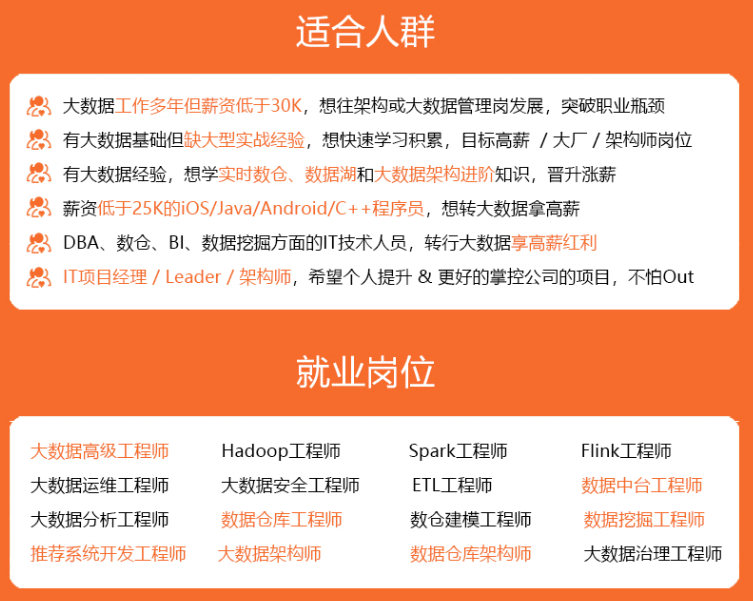
既有适合小白学习的零基础资料,也有适合3年以上经验的小伙伴深入学习提升的进阶课程,涵盖了95%以上大数据知识点,真正体系化!
由于文件比较多,这里只是将部分目录截图出来,全套包含大厂面经、学习笔记、源码讲义、实战项目、大纲路线、讲解视频,并且后续会持续更新
- 一般叫hash,简单的说就是一种将任意长度的消息压缩到某一固定长度的消息摘要的函数,适合存储密码,比如MD5
- 什么是salt(盐) ?
- 如果直接通过散列函数得到加密数据,容易被对应解密网站暴力破解,一般会在应用程序里面加特殊的字段进行处理,比如用户id,例子:加密数据 = MD5(明文密码+用户id), 破解难度会更大,也可以使用多重散列,比如多次md5
- Shiro如何根据用户传过来的密码进行加密与数据库密码进行匹配?
- Shiro会使用AuthenticatingRealm的assertCredentialsMatch()方法进行验证密码是否正确
- 因此,在Shiro中我们一般会自定义密码验证规则,示例如下:
@Bean
public HashedCredentialsMatcher hashedCredentialsMatcher(){
HashedCredentialsMatcher hashedCredentialsMatcher = new HashedCredentialsMatcher();
//散列算法,使用MD5算法;
hashedCredentialsMatcher.setHashAlgorithmName(“md5”);
//散列的次数,比如散列两次,相当于 md5(md5(“xxx”));
hashedCredentialsMatcher.setHashIterations(2);
return hashedCredentialsMatcher;
}
[外链图片转存中…(img-jl5HDfEM-1715668292886)]
[外链图片转存中…(img-o2krxpDG-1715668292886)]
[外链图片转存中…(img-YMekfym0-1715668292886)]
既有适合小白学习的零基础资料,也有适合3年以上经验的小伙伴深入学习提升的进阶课程,涵盖了95%以上大数据知识点,真正体系化!
由于文件比较多,这里只是将部分目录截图出来,全套包含大厂面经、学习笔记、源码讲义、实战项目、大纲路线、讲解视频,并且后续会持续更新






















 360
360

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








