2 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
-
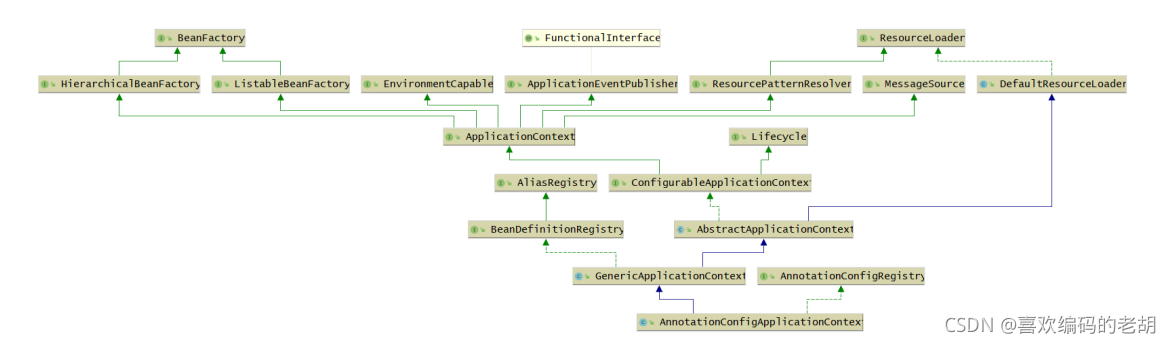
ConfigurableApplicationContext:继承了ApplicationContext接口,增加了,添加事件监听 器、添加BeanFactoryPostProcessor、设置Environment,获取 ConfigurableListableBeanFactory等功能
-
AbstractApplicationContext:实现了ConfigurableApplicationContext接口
-
GenericApplicationContext:继承了AbstractApplicationContext,实现了 BeanDefinitionRegistry接口,拥有了所有ApplicationContext的功能,并且可以注册 BeanDefinition,注意这个类中有一个属性(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory)
-
AnnotationConfigRegistry:可以单独注册某个为类为BeanDefinition(可以处理该类上的 @Configuration注解,已经可以处理**@Bean注解**),同时可以扫描
-
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext:继承了GenericApplicationContext,实现了 AnnotationConfigRegistry接口,拥有了以上所有的功能
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
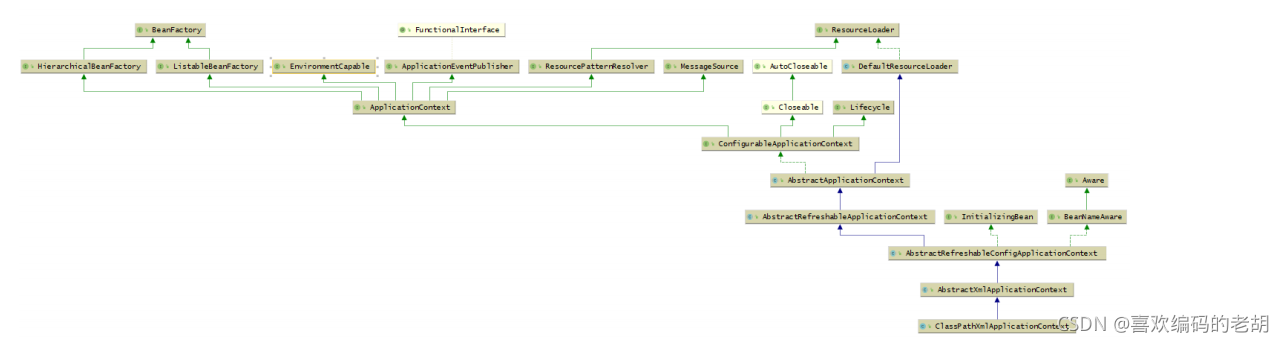
它也是继承了AbstractApplicationContext,但是相对于AnnotationConfigApplicationContext而 言,功能没有AnnotationConfigApplicationContext强大,比如不能注册BeanDefinition
上面的图 可以不用完全理解; 再后面源码 陈述完之后 再回头看. 就会清晰很多;
以下对ApplicationContext 接口实现 进行一个功能实现;
MessageSource 国际化;
@Bean
public MessageSource messageSource() {
ResourceBundleMessageSource messageSource = new ResourceBundleMessageSource();
messageSource.setBasename(“messages”);
return messageSource;
}
//使用的时候 直接拿到 Context context.getMessage(“test”, null, new Locale(“en_CN”));
Resource 资源;
//这地方与File 类似; 是直接使用容器Context 进行读取资源; 源码中有很多 这样读取资源的方式;
Resource resource = context.getResource(“资源路径 可以为网络资源;”);
try {
System.out.println(resource.contentLength());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
Resource[] resources = new Resource[0];
try {
resources = context.getResources(“classpath:com/huf/*.class”);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
for (Resource resource2 : resources) {
System.out.println(resource.contentLength());
System.out.println(resource.getFilename());
}
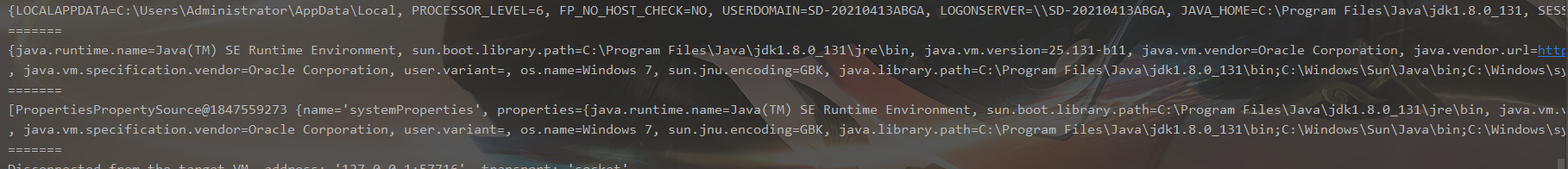
Environment: 获取运行时环境
Map<String, Object> systemEnvironment = context.getEnvironment().getSystemEnvironment();
System.out.println(systemEnvironment);
System.out.println(“=======”);
Map<String, Object> systemProperties = context.getEnvironment().getSystemProperties();
System.out.println(systemProperties);
System.out.println(“=======”);
MutablePropertySources propertySources = context.getEnvironment().getPropertySources();
System.out.println(propertySources);
System.out.println(“=======”);
结果为:
ApplicationListener: 监听机制
@Bean
public ApplicationListener applicationListener() {
return new ApplicationListener() {
@Override public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
System.out.println(“接收到了一个事件”);
}
};
}
//再Context调用 context.publishEvent(“kkk”); 即可;
======================================================================
在Spring源码中,有可能需要把String转成其他类型,所以在Spring源码中提供了一些技术来更方便 的做对象的类型转化,关于类型转化的应用场景, 后续看源码的过程中会遇到很多。
PropertyEditor 实际上是JDK提供的类型转换;
package com.huf.editor;
import com.huf.entity.Student;
import java.beans.PropertyEditor;
import java.beans.PropertyEditorSupport;
/**
-
实际上是JDK自带的转换器;
-
auth:huf
*/
public class StringToStudentPropertyEditor extends PropertyEditorSupport implements PropertyEditor {
@Override
public void setAsText(String text) throws IllegalArgumentException {
Student student = new Student();
student.setStudentName(text);
this.setValue(student);
}
}
//使用方式:
StringToStudentPropertyEditor propertyEditor = new StringToStudentPropertyEditor();
propertyEditor.setAsText(“1”);
Student student = (Student) propertyEditor.getValue();
System.out.println(value);
@Bean
public CustomEditorConfigurer customEditorConfigurer() {
CustomEditorConfigurer customEditorConfigurer = new CustomEditorConfigurer();
Map<Class<?>, Class<? extends PropertyEditor>> propertyEditorMap = new HashMap<>();
propertyEditorMap.put(Student.class, StringToStudentPropertyEditor.class);
customEditorConfigurer.setCustomEditors(propertyEditorMap);
return customEditorConfigurer;
}
Spring提供的 强大类型转换
package com.huf.conversion;
import com.huf.entity.Student;
import org.springframework.core.convert.TypeDescriptor;
import org.springframework.core.convert.converter.ConditionalGenericConverter;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Set;
/**
- auth:huf
*/
public class StudentConversion implements ConditionalGenericConverter {
@Override
public boolean matches(TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType) {
return sourceType.getType().equals(String.class) && targetType.getType().equals(Student.class)
}
@Override
public Set getConvertibleTypes() {
return Collections.singleton(new ConvertiblePair(String.class, Student.class));
}
@Override
public Object convert(Object source, TypeDescriptor typeDescriptor, TypeDescriptor typeDescriptor1) {
Student student = new Student();
student.setStudentName((String)source);
return student;
}
}
//转换方式为:
DefaultConversionService conversionService = new DefaultConversionService();
conversionService.addConverter(new StudentConversion());
Student value = conversionService.convert(“1”, Student.class);
System.out.println(value);
//再ConFig 注册方式为:
@Bean
public ConversionServiceFactoryBean conversionService() {
ConversionServiceFactoryBean conversionServiceFactoryBean = new ConversionServiceFactoryBean();
conversionServiceFactoryBean.setConverters(Collections.singleton(new StudentConversion()));
return conversionServiceFactoryBean;
}
//以下是Spring的方式:
SimpleTypeConverter typeConverter = new SimpleTypeConverter();
typeConverter.registerCustomEditor(Student.class, new StringToStudentPropertyEditor());
typeConverter.setConversionService(conversionService);
Student value = typeConverter.convertIfNecessary(“1”, Student.class);
System.out.println(value);
=======================================================================
factoryBean 是创建Bean的一种方式 与 @Bean是有区别的; 他们之间的生命周期 是不同的;
这里注意了
package com.huf.factorybean;
import com.huf.service.impl.StudentServiceImpl;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.FactoryBean;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
- auth: huf
*/
@Component
public class HufFactoryBean implements FactoryBean {
@Override
public Object getObject() throws Exception {
return new StudentServiceImpl();
}
@Override
public Class<?> getObjectType() {
return StudentServiceImpl.class;
}
}
当我们用context.getBean() 来获取对象的时候; 该对象是StudentServiceImpl对象 以下是截图:
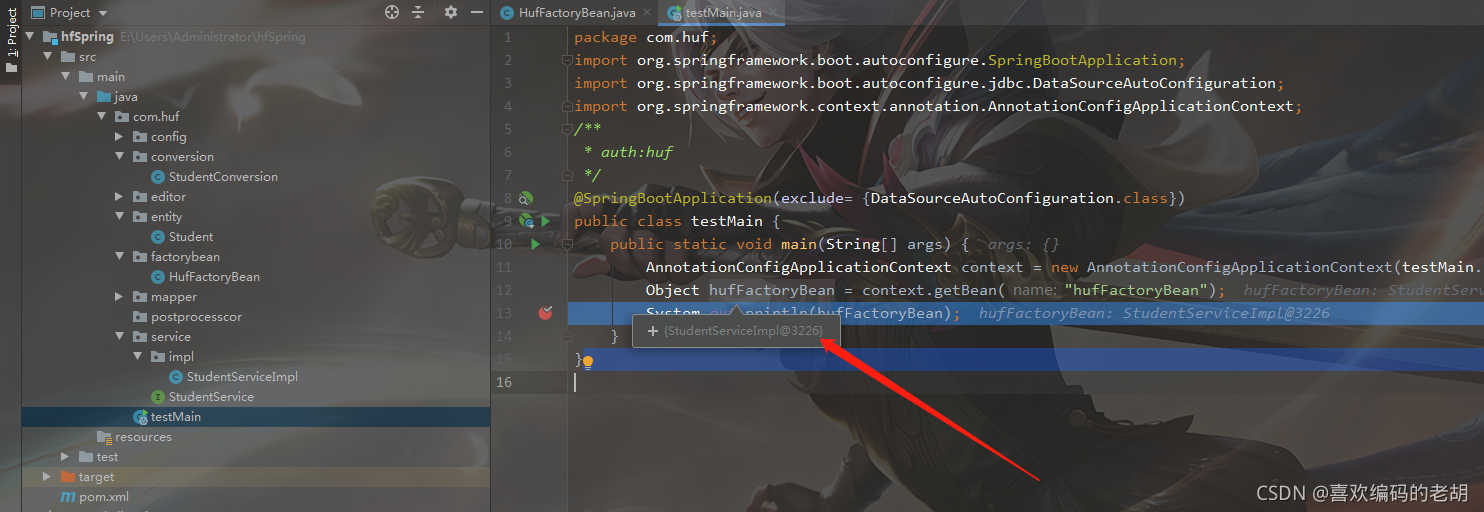
他们两个方式注册成为Bean 但是它们两个的生命周期有什么不一样 以下我来证明:
用@Bean的生命周期是完整的; 也就是走初始化前 初始化后;
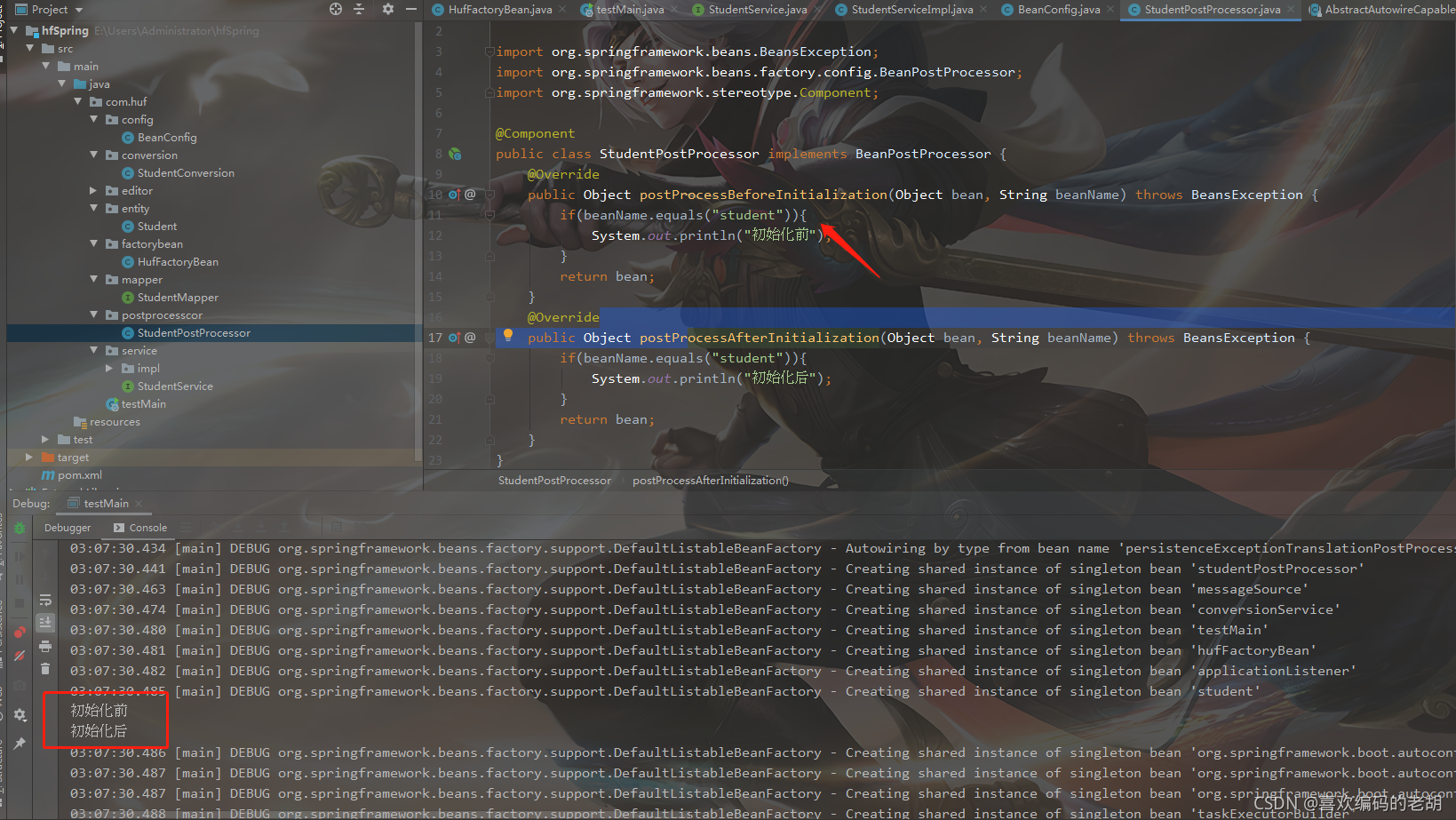
在使用FactoryBean的时候 生命周期是不完整的 只执行初始化后:
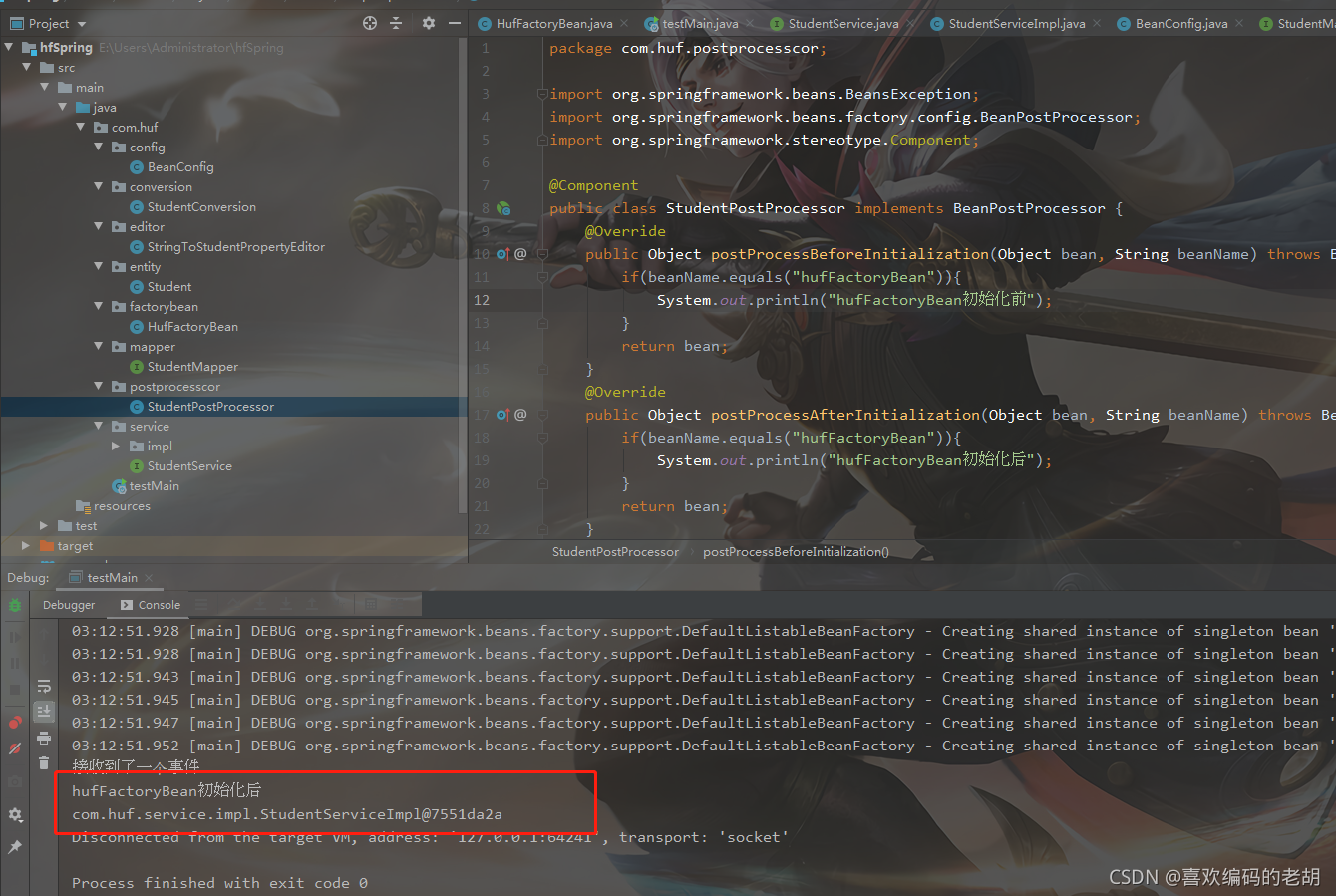
=======================================================================================
这两个Filter是Spring扫描过程中用来过滤的。ExcludeFilter表示排除过滤器,IncludeFilter表示包 含过滤器。 比如以下配置,表示扫描com.huf这个包下面的所有类,但是排除Student类,也就是就算 它上面有@Component注解也不会成为Bean。
@ComponentScan(value = “com.huf”,
excludeFilters =
{@ComponentScan.Filter( type = FilterType.ASSIGNABLE_TYPE,
classes = Student.class)}.)
@ComponentScan(value = “com.huf”,
自我介绍一下,小编13年上海交大毕业,曾经在小公司待过,也去过华为、OPPO等大厂,18年进入阿里一直到现在。
深知大多数Java工程师,想要提升技能,往往是自己摸索成长或者是报班学习,但对于培训机构动则几千的学费,着实压力不小。自己不成体系的自学效果低效又漫长,而且极易碰到天花板技术停滞不前!
因此收集整理了一份《2024年Java开发全套学习资料》,初衷也很简单,就是希望能够帮助到想自学提升又不知道该从何学起的朋友,同时减轻大家的负担。


既有适合小白学习的零基础资料,也有适合3年以上经验的小伙伴深入学习提升的进阶课程,基本涵盖了95%以上Java开发知识点,真正体系化!
由于文件比较大,这里只是将部分目录截图出来,每个节点里面都包含大厂面经、学习笔记、源码讲义、实战项目、讲解视频,并且会持续更新!
如果你觉得这些内容对你有帮助,可以扫码获取!!(备注Java获取)

最后,附一张自己面试前准备的脑图:

面试前一定少不了刷题,为了方便大家复习,我分享一波个人整理的面试大全宝典
- Java核心知识整理

- Spring全家桶(实战系列)

Step3:刷题
既然是要面试,那么就少不了刷题,实际上春节回家后,哪儿也去不了,我自己是刷了不少面试题的,所以在面试过程中才能够做到心中有数,基本上会清楚面试过程中会问到哪些知识点,高频题又有哪些,所以刷题是面试前期准备过程中非常重要的一点。
以下是我私藏的面试题库:

很多人感叹“学习无用”,实际上之所以产生无用论,是因为自己想要的与自己所学的匹配不上,这也就意味着自己学得远远不够。无论是学习还是工作,都应该有主动性,所以如果拥有大厂梦,那么就要自己努力去实现它。
最后祝愿各位身体健康,顺利拿到心仪的offer!
《一线大厂Java面试题解析+核心总结学习笔记+最新讲解视频+实战项目源码》,点击传送门即可获取!
…(img-y7yF5jsu-1712112712377)]
- Spring全家桶(实战系列)
[外链图片转存中…(img-JjTERomP-1712112712378)]
Step3:刷题
既然是要面试,那么就少不了刷题,实际上春节回家后,哪儿也去不了,我自己是刷了不少面试题的,所以在面试过程中才能够做到心中有数,基本上会清楚面试过程中会问到哪些知识点,高频题又有哪些,所以刷题是面试前期准备过程中非常重要的一点。
以下是我私藏的面试题库:
[外链图片转存中…(img-VquuEMob-1712112712378)]
很多人感叹“学习无用”,实际上之所以产生无用论,是因为自己想要的与自己所学的匹配不上,这也就意味着自己学得远远不够。无论是学习还是工作,都应该有主动性,所以如果拥有大厂梦,那么就要自己努力去实现它。
最后祝愿各位身体健康,顺利拿到心仪的offer!
《一线大厂Java面试题解析+核心总结学习笔记+最新讲解视频+实战项目源码》,点击传送门即可获取!






















 5万+
5万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








