一.什么是栈
1.栈的定义
栈是一种特殊类型的线性表,它的特点是仅允许在其一端进行插入(入栈)和删除(弹出)操作。这一端称为栈顶,而相对的另一端称为栈底。
2.栈的特点
栈遵循“后进先出”(LIFO)的原则,也就是说新加入的元素总是位于栈顶,先入栈的元素总是最后出栈。
3.基本操作
- 入栈(Push):将元素推送到栈顶
- 出栈(Pop):删除栈顶元素
① 入栈
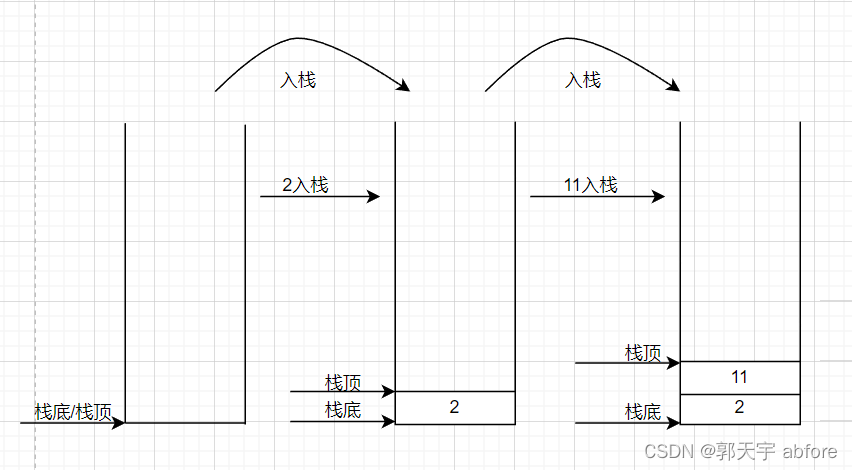
② 出栈

二. 栈的基本操作
1.顺序栈
顺序栈是一种使用数组实现的栈,也称为数组栈。其基本思路是通过数组来存储栈中的元素,并通过栈顶指针指示栈顶元素在数组中的位置。
- 代码实现
public interface myStack<T>{
// 入栈
void push(T ele);
// 出栈
T pop();
// 查看当前栈顶元素
T peek();
// 判断栈是否为空
boolean isEmpty();
// 获取栈内的元素个数
int getSize();
}
public class MyArray<T> {
private T[] arr;
private int size;
private int capacity; //容积
// 构造方法
public MyArray(int capacity) {
// 入参判断
if (capacity <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("输入容积异常!");
}
this.capacity = capacity;
this.size = 0;
this.arr = (T[]) new Object[this.capacity];
}
// 获取元素个数
public int getSize() {
return this.size;
}
// 获取容积
public int getCapacity() {
return this.capacity;
}
// 添加元素
public void add(T item) {
this.arr[this.size] = item;
this.size++;
}
// 向指定位置添加元素
public void addValueByIndex(int index, T value) {
if (index < 0 || index > this.size) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("索引异常!");
}
if (this.size == this.capacity) {
resize(this.capacity * 2);
}
for (int i = this.size - 1; i >= index; i--) {
this.arr[i + 1] = this.arr[i];
}
this.arr[index] = value;
this.size++;
}
// 扩容
private void resize(int newCapacity) {
T[] newArr = (T[]) new Object[newCapacity];
for (int i = 0; i < this.size; i++) {
newArr[i] = this.arr[i];
}
// 改变容器与容积
this.arr = newArr;
this.capacity = newCapacity;
}
// 判空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return this.size == 0;
}
// 修改元素
public void modifyValueByIndex(int index, T value) {
// 入参判断
if (index < 0 || index > capacity) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("索引异常!");
}
this.arr[index] = value;
}
// 获取指定位置的值
public T getValueByIndex(int index) {
// 入参判断
if (index < 0 || index > capacity) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("索引异常!");
}
return this.arr[index];
}
// 查询指定的值在数组中是否存在,存在返回索引,不存在返回-1
public int containsValue(T value) {
for (int i = 0; i < this.size; i++) {
if (value.equals(this.arr[i])) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
// 删除指定位置的元素
public T deleteValueByIndex(int index) {
// 入参判断
if (index < 0 || index > capacity) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("索引异常");
}
// 1.找到删除的位置的元素
T deValue = this.arr[index];
// 2.将删除元素之后的元素前移
for (int j = index + 1; j < this.size; j++) {
this.arr[j - 1] = this.arr[j];
}
this.size--;
// 判断是否缩容
if (this.size <= this.capacity / 4 && this.capacity / 2 > 0) {
resize(this.capacity / 2);
}
return deValue;
}
public T removeFromLast() {
T delVal = this.arr[this.size - 1];
this.size--;
return delVal;
}
public T getValue() {
return getValueByIndex(this.size - 1);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append("{");
for (int i = 0; i < this.size; i++) {
sb.append(this.arr[i]);
if (i < this.size - 1) {
sb.append(",");
}
}
sb.append("}");
return sb.toString();
}
}
// 以数组为栈的数据存储结构
public class ArrStack<T> implements myStack<T> {
private MyArray<T> data;
int size;
public ArrStack() {
this.data = new MyArray<>(100);
this.size = 0;
}
@Override
public void push(T ele) {
this.data.add(ele);
this.size++;
}
@Override
public T pop() {
if(this.data.isEmpty()){
return null;
}
return this.data.removeFromLast();
}
@Override
public T peek() {
return this.data.getValue();
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return this.size == 0;
}
@Override
public int getSize() {
return this.size;
}
}
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Random;
public class StackTest<T> {
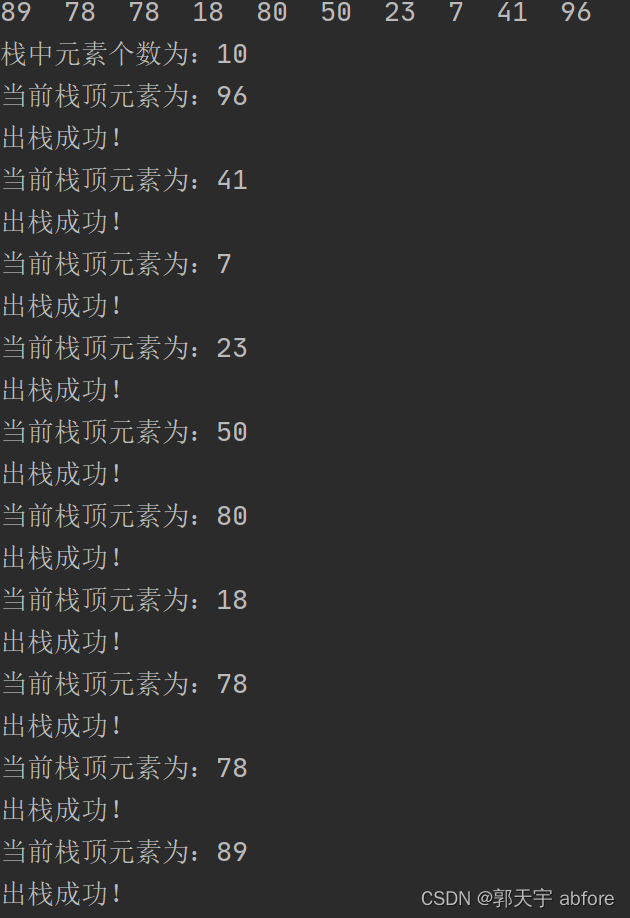
public void test(myStack<T> stack, ArrayList<T> list){
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
// 入栈
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
stack.push(list.get(i));
System.out.print(list.get(i) + " ");
}
System.out.println();
// 获取栈中元素个数
System.out.println("栈中元素个数为:" + stack.getSize());
// 出栈
for (int i = 0; i < stack.getSize(); i++) {
// 查看栈顶元素
System.out.println("当前栈顶元素为:" + stack.peek());
stack.pop();
if(!stack.isEmpty()){
System.out.println("出栈成功!");
}
}
long endTime = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println("总耗时:" + (endTime - startTime) / 1000000000.0 + "s");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
StackTest<Integer> t = new StackTest<>();
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
ArrStack<Integer> arrStack = new ArrStack<>();
LinkedStack<Integer> stack = new LinkedStack<>();
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
list.add(random.nextInt(100));
}
t.test(arrStack,list);
}
}
2.链表栈
链栈是一种基于链表实现的栈,其特点是无需事先分配固定长度的存储空间,栈的长度可以动态增长或缩小,避免了顺序栈可能存在的空间浪费和存储溢出问题。
- 代码实现(与上述顺序栈相比,只是数据存储的存储采用了链表的方式)
import java.util.Optional;
public class LinkedStack<T> implements myStack<T>{
private LinkedList<T> data;
public LinkedStack() {
this.data = new LinkedList<>();
}
@Override
public void push(T ele) {
this.data.addInHead(ele);
}
@Override
public T pop() {
return (T) this.data.deleteHead();
}
@Override
public T peek() {
Optional<T> optional = this.data.getHead();
if(optional.isPresent()){
return (T) optional;
}else{
throw new RuntimeException();
}
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return this.data.isEmpty();
}
@Override
public int getSize() {
return this.data.getSize();
}
}
import java.util.Optional;
public class LinkedList<T> {
class Node<T> {
T data;
Node next;
public Node(T data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
public Node(T data, Node next) {
this.data = data;
this.next = next;
}
}
private Node head;
private int size;
public LinkedList() {
this.head = new Node(null);
this.size = 0;
}
// 判空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return this.size == 0;
}
// 向头部添加元素
public void addInHead(T data) {
addInAny(0, data);
}
// 向尾部添加元素
public void addInTail(T data) {
addInAny(this.size, data);
}
// 向任意位置添加元素
public void addInAny(int index, T data) {
if (index < 0 || index > this.size) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("非法索引!");
}
Node node = new Node(data);
// 寻找插入位置的前驱结点
Node pre = this.head;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
pre = pre.next;
}
node.next = pre.next;
pre.next = node;
this.size++;
}
// 从链表中查找指定元素
public boolean contains(T data) {
Node curNode = this.head.next;
while (curNode != null) {
if (curNode.data.equals(data)) {
return true;
}
curNode = curNode.next;
}
return false;
}
// 删除头结点
public Optional deleteHead() {
if (this.head.next == null) {
return Optional.empty();
}
Node delNode = this.head.next;
this.head.next = delNode.next;
delNode.next = null;
return Optional.ofNullable(delNode.data);
}
// 删除尾节点
public Optional deleteTail() {
if (this.head.next == null) {
return Optional.empty();
}
Node curNode = this.head.next;
while (curNode.next.next != null) {
curNode = curNode.next;
}
Node delNode = curNode.next;
curNode.next = delNode.next;
delNode.next = null;
this.size--;
return Optional.ofNullable(delNode.data);
}
// 删除指定位置的元素
public Optional deleteInIndex(int index) {
if (this.head == null) {
return Optional.empty();
}
if (index < 0 || index >= this.size) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("索引异常!");
}
Node pre = this.head;
// 找删除结点的前驱结点
int i = 0;
while (i < index) {
pre = pre.next;
i++;
}
Node delNode = pre.next;
pre.next = delNode.next;
delNode.next = null;
this.size--;
return Optional.ofNullable(delNode.data);
}
// 根据值删除元素
public int deleteByData(T val) {
int count = 0;
Node pre = this.head;
while (pre.next != null) {
Node curNode = pre.next;
if (curNode.data.equals(val)) {
pre.next = pre.next.next;
curNode.next = null;
this.size--;
count++;
} else {
pre = pre.next;
}
}
return count;
}
// 获取元素个数
public int getSize() {
return this.size;
}
// 获取链表头结点
public Optional getHead() {
if (this.head.next == null) {
return Optional.empty();
}
return Optional.ofNullable(this.head.next.data);
}
//获取链表尾结点
public Optional getTail() {
if (this.head.next == null) {
return Optional.empty();
}
Node curNode = this.head.next;
while (curNode != null) {
curNode = curNode.next;
if (curNode.next == null)
break;
}
return Optional.ofNullable(curNode.data);
}
// 获取任意位置的元素
public Optional getIndex(int index) {
if (this.head.next == null) {
return Optional.empty();
}
if (index < 0 || index >= this.size) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("索引异常!");
}
Node curNode = this.head.next;
int i = 0;
while (i < index) {
curNode = curNode.next;
i++;
}
return Optional.ofNullable(curNode.data);
}
// 重写toString方法
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
Node curNode = this.head.next;
while (curNode != null) {
sb.append(curNode.data + "--->");
curNode = curNode.next;
}
sb.append("null");
return sb.toString();
}
}
三.栈的应用
栈常用来解决递归、括号匹配、表达式求值等问题。
1.例题一:有效的括号(20. 有效的括号 - 力扣(LeetCode))
① 题目分析:
我们遍历给定的字符串 s。当遇到一个左括号时,我们会期望在后续的遍历中,有一个相同类型的右括号将其闭合。由于后遇到的左括号要先闭合,因此我们可以将这个左括号放入栈中。
当我们遇到一个右括号时,我们需要将一个相同类型的左括号闭合。此时,我们可以取出栈顶的左括号并判断它们是否是相同类型的括号。如果不是相同的类型,或者栈中并没有左括号,那么字符串 s 无效。
② 代码实现
import java.util.Stack;
public class LeetCode_20 {
public boolean isValid(String s) {
Stack<Character> c = new Stack<>();
// 入参判断
if (s == null || s.length() == 0) {
return true;
}
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
// 碰到左括号就入栈
if (s.charAt(i) == '(' || s.charAt(i) == '[' || s.charAt(i) == '{') {
c.push(s.charAt(i));
}
if (c.empty()) {
return false;
}
// 没有相匹配的括号就return false
if (((s.charAt(i) == ')' && c.pop() != '(') || (s.charAt(i) == ']' && c.pop() != '[') || (s.charAt(i) == '}' && c.pop() != '{'))) {
return false;
}
}
return c.empty();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "(()[]{}";
LeetCode_20 leetCode_20 = new LeetCode_20();
System.out.println(leetCode_20.isValid(s));
}
}

2.例题二:基本计算器II(227. 基本计算器 II - 力扣(LeetCode))
① 题目分析
由于乘除优先于加减计算,因此不妨考虑先进行所有乘除运算,并将这些乘除运算后的整数值放回原表达式的相应位置,则随后整个表达式的值,就等于所有整数加减后的值。
基于上述想法,我们可以用一个栈,保存这些进行乘除运算后的整数的值。对于加减号后的数字,将其直接入栈;对于乘除号后的数字,可以直接与栈顶元素计算,并替换栈顶元素为计算后的结果。
② 代码实现
import java.util.Stack;
public class LeetCode_227 {
public int calculate(String s) {
s = s.trim(); //去掉字符串两端的空格
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
char c = '+';
int num = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); ++i) {
if (Character.isDigit(s.charAt(i))) { //判断当前字符是否是数字
num = num * 10 + s.charAt(i) - '0'; //处理两位及两位以上的数字
}
// 判断当前字符是不是运算符号,对最后一个数字做特殊处理
if ((!Character.isDigit(s.charAt(i)) && s.charAt(i) != ' ') || i == s.length() - 1) {
switch (c) {
case '+':
stack.push(num);
break;
case '-':
stack.push(-num);
break;
case '*':
stack.push(stack.pop() * num);
break;
default:
stack.push(stack.pop() / num);
}
c = s.charAt(i); //记录下当前的运算符号
num = 0; //重置
}
}
int res = 0;
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
res += stack.pop();
}
return res;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = " 13+5 / 2 -3 ";
LeetCode_227 leetCode_227 = new LeetCode_227();
System.out.println("计算结果为:" + leetCode_227.calculate(s));
}
}






















 6950
6950











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










