db.close()

创建数据库命令执行一次就可以,后面我们在创建的数据库中进行其他的操作,如果创建的数据已经存在程序会报错`"Can't create database 'spiders'; database exists"`
拓展:
>
> 如果在创建数据库的不能确认数据库是否存在,但是也不想在创建数据库的时候发生报错可以使用下列语句:`create database if not exists dbname`
>
>
>
### 创建数据表、
表必须创建在数据库内,所以我们需要在连接数据库以后,需要指定操作那个数据库
import pymysql
连接数据库
db = pymysql.connect(host=‘localhost’,user=‘root’,password=‘123456’,port=3306,db=‘spiders’)
创建数据库的游标
cursor = db.cursor()
sql = “create table if not exists students(id varchar(255) not null,name varchar(255) not null,age int not null,primary key (id))”
cursor.execute(sql)
db.close()

这次的在连接mysql的时候`connect`函数新增了一个参数,`db='spiders'`指定我们要连接的数据库,后面创建的表也会创建到当前数据库。
创建数据库的`sql`语句是 `"create table if not exists students(id varchar(255) not null,name varchar(255) not null,age int not null,primary key (id))"`
创建的数据库名为`students`,三列 `id`、`name`、`age`,都是非空,主键为`id`
### 插入数据
import pymysql
db = pymysql.connect(user=‘root’,password=‘123456’,host=‘localhost’,port=3306,db=‘spiders’)
cursor = db.cursor()
id = ‘10005’
name = ‘zhangsan’
age = ‘20’
#方式1
sql = “insert into students(id,name,age) values('”+id+“‘,’”+name+“‘,’”+age+“')”
cursor.execute(sql)
方式2
sql = “insert into students(id,name,age) values(‘{}’,‘{}’,‘{}’)”.format(id,name,age)
cursor.execute(sql)
方式3(推荐)
sql = “insert into students(id,name,age) values(%s,%s,%s)”
cursor.execute(sql,(id,name,age))
db.commit()
db.close()
通过三种sql语句的编写形式我们能够发现。方式3的最为简洁,通过使用`%s`来进行占位,然后再通过`execute()`函数将数据传入sql语句中组成完整的sql语句。
>
> 在执行execute()方法之后必须要commit()方法才能将数据插入到表中,这个设计到了事务的原子性问题,事务机制可以确保数据一致性,事务有4个属性:原子性、一致性、隔离性、持久性。
>
>
>
| 属性 | 描述 |
| --- | --- |
| 原子性 | 事务是一个不可分割的工作单位,事务中包括的操作要么都执行,要么都不执行 |
| 一致性 | 事务必须是数据库中一个一致性状态转变到另一个一致性状态,一致性与原子性是密切相关的 |
| 隔离性 | 一个事务不能被其他事务干扰,即一个事务内部的操作及使用的数据对并发的其他事务时隔离的,并发的各个事务之间不能相互干扰 |
| 持久性 | 持久性也称永久性,指一个事务一旦提交,它对数据库中数据的改变就应该是永久性的,接下来的其他操作或故障不应该对其有任何影响 |
### 查询数据
在数据库操作的过程中使用最多的就是查询操作
import pymysql
db = pymysql.connect(user=‘root’,password=‘123456’,host=‘localhost’,port=3306,db=‘spiders’)
try:
sql = ‘select * from students’
cursor = db.cursor()
cursor.execute(sql)
d1 = cursor.fetchone()
print(“获取一条数据”,d1)
all_d = cursor.fetchall()
print(“获取所有数据”,all_d)
# sql = “insert into students(id,name,age) values('”+id+“‘,’”+name+“‘,’”+age+“')”
except:
print(“Error”)
db.close()
数据库中的数据
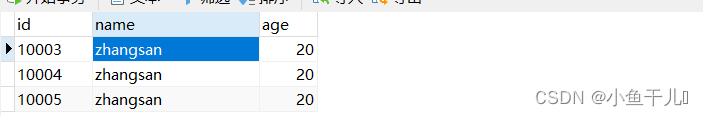
输出:

通过结果我们能够看到`etchone()`执行正常,拿出了一条数据,但是`fetchall()`明明是查询所有,但是结果只有除了第一条之外的数据,关于这个现象我们可以从游标的角度来解释,一开始游标在第一行执行`etchone()`之后游标就跑到第二行,再执行`fetchall()`的时候就从第二行开始查询直至末尾。
可以简单的理解etchone()查询游标所在的一行数据,fetchall()查询当前游标至结束的所有行数据。
使用where进行条件查询
查询id大于10003的数据
import pymysql
db = pymysql.connect(user=‘root’,password=‘123456’,host=‘localhost’,port=3306,db=‘spiders’)
try:
sql = ‘select * from students where id>10003’
cursor = db.cursor()
cursor.execute(sql)
all_d = cursor.fetchall()
print(“获取所有数据”,all_d)
# sql = “insert into students(id,name,age) values('”+id+“‘,’”+name+“‘,’”+age+“')”
except:
print(“Error”)
db.close()
输出:
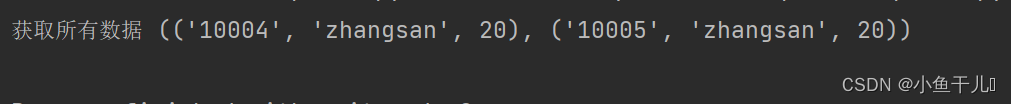
### 更新数据
跟新数据,有时候我们再会对数据库中原来的数据进行修改
import pymysql
db = pymysql.connect(user=‘root’,password=‘123456’,host=‘localhost’,port=3306,db=‘spiders’)
try:
sql = ‘update students set name=%s where id=%s’
cursor = db.cursor()
cursor.execute(sql,(‘李四’,‘10004’))
db.commit()
except:
db.rollback()
db.close()
### 删除数据
根据条件删除数据,删除id小于10004的数据
import pymysql
db = pymysql.connect(user=‘root’,password=‘123456’,host=‘localhost’,port=3306,db=‘spiders’)
try:
sql = ‘delete from students where id<%s’
cursor = db.cursor()
cursor.execute(sql,(‘10004’))
db.commit()
except:
db.rollback()
db.close()
### 实战应用
在实际应用时,一般数据都是字典或者对象这种数据,所以需要我们在拼接SQL语句的时候更加的灵活。
插入数据,若数据存在更新数据
import pymysql
data = {
‘id’:‘10006’,
‘name’:‘王五’,
‘age’:45
}
连接数据库
网上学习资料一大堆,但如果学到的知识不成体系,遇到问题时只是浅尝辄止,不再深入研究,那么很难做到真正的技术提升。
一个人可以走的很快,但一群人才能走的更远!不论你是正从事IT行业的老鸟或是对IT行业感兴趣的新人,都欢迎加入我们的的圈子(技术交流、学习资源、职场吐槽、大厂内推、面试辅导),让我们一起学习成长!
大堆,但如果学到的知识不成体系,遇到问题时只是浅尝辄止,不再深入研究,那么很难做到真正的技术提升。**
一个人可以走的很快,但一群人才能走的更远!不论你是正从事IT行业的老鸟或是对IT行业感兴趣的新人,都欢迎加入我们的的圈子(技术交流、学习资源、职场吐槽、大厂内推、面试辅导),让我们一起学习成长!





















 646
646

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








