自我介绍一下,小编13年上海交大毕业,曾经在小公司待过,也去过华为、OPPO等大厂,18年进入阿里一直到现在。
深知大多数HarmonyOS鸿蒙开发工程师,想要提升技能,往往是自己摸索成长或者是报班学习,但对于培训机构动则几千的学费,着实压力不小。自己不成体系的自学效果低效又漫长,而且极易碰到天花板技术停滞不前!
因此收集整理了一份《2024年HarmonyOS鸿蒙开发全套学习资料》,初衷也很简单,就是希望能够帮助到想自学提升又不知道该从何学起的朋友,同时减轻大家的负担。

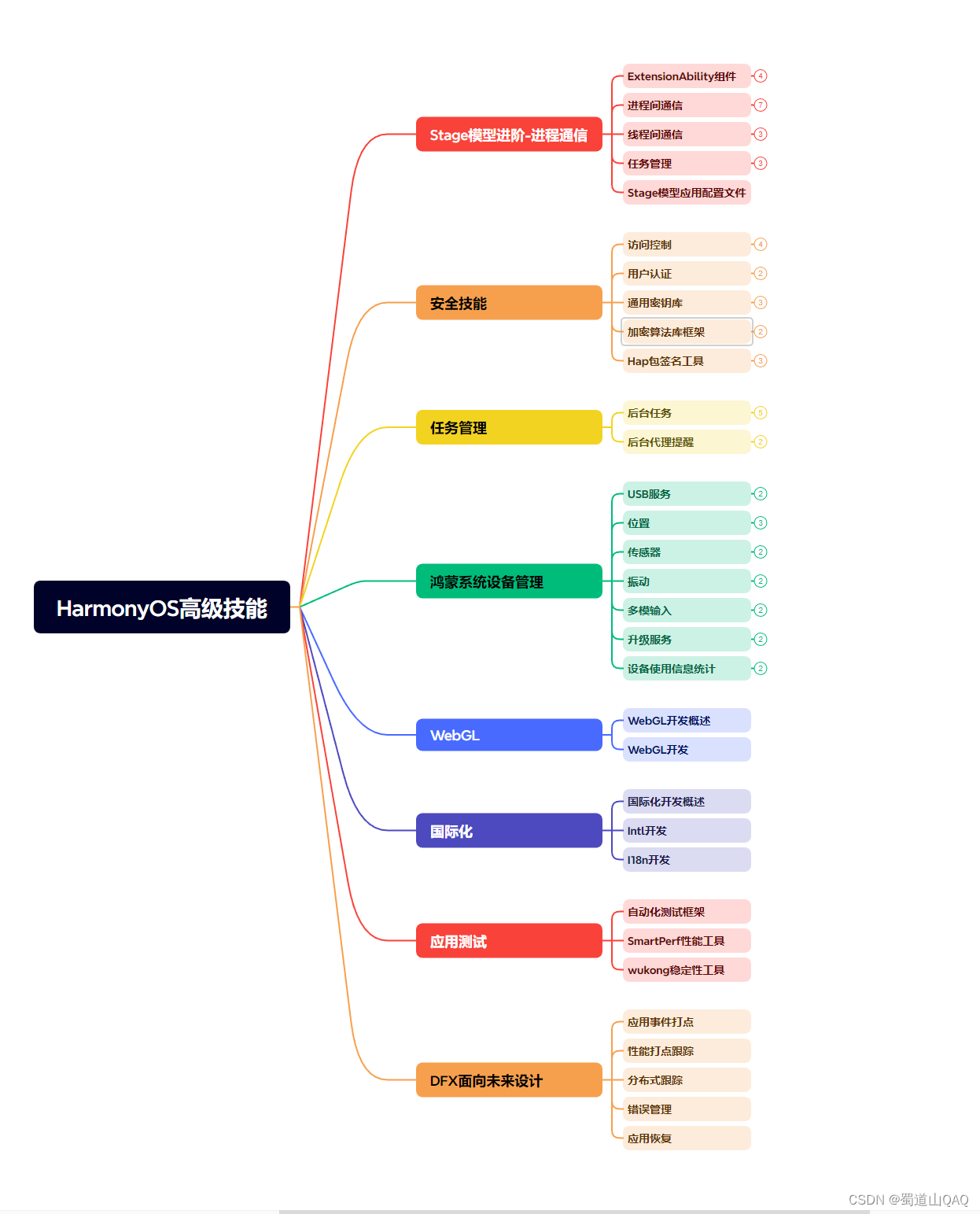



既有适合小白学习的零基础资料,也有适合3年以上经验的小伙伴深入学习提升的进阶课程,基本涵盖了95%以上HarmonyOS鸿蒙开发知识点,真正体系化!
由于文件比较大,这里只是将部分目录大纲截图出来,每个节点里面都包含大厂面经、学习笔记、源码讲义、实战项目、讲解视频,并且会持续更新
如果你觉得这些内容对你有帮助,可以添加VX:vip204888 (备注鸿蒙获取)

一个人可以走的很快,但一群人才能走的更远。不论你是正从事IT行业的老鸟或是对IT行业感兴趣的新人,都欢迎扫码加入我们的的圈子(技术交流、学习资源、职场吐槽、大厂内推、面试辅导),让我们一起学习成长!
这是一个简单的登录 UI,其背后包含任何类型的登录业务逻辑。我不会使用任何一种状态管理,只会使用旧的好setState()。这只是一个简单的代码示例来展示包的使用。
好的,让我们编码。
首先,我们需要将包添加到pubspec.yaml文件中。

是的,但是…如何flutter_secure_storage工作?
正如报告中的那样README.md,我们所要做的就是:
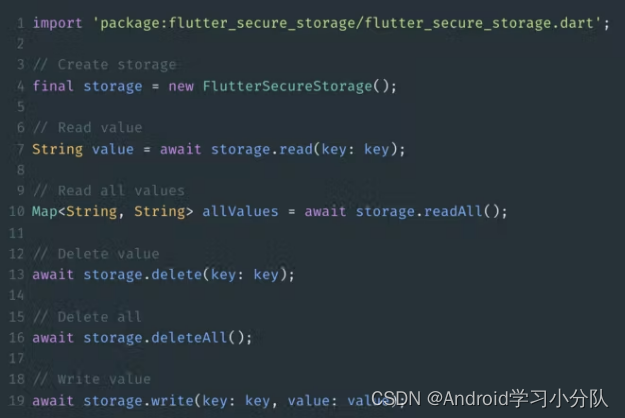
这是一个非常简单的包,是的。
如您所见,在第 4 行,我们创建了一个存储,使我们能够读取和存储数据。
在第 7 行,我们读取并解密由标签标识的 String 值,如果不在存储中,则为keynull 。key请记住:key不应为空。
在第 19 行,我们存储并加密value由标签标识的对象key。如果key已经在存储中,则其关联value将被更改。如果value为空,则删除与value给定的关联key。
对于我们的用例,我们需要:
- FlutterSecureStorage存储实例;
- 两个TextEditingController与两个TextInputField小部件关联以收集用户凭据;
- 一种将write数据存储起来的方法;
- 一种read从存储中获取数据的方法;
所以让我们定义前两点:)

然后,我们定义_onFormSubmit()存储用户凭据的方法。Sing In此方法是与按钮关联的操作。仅当验证表单时,该方法才会负责将数据保存在存储中。

然后,我们定义方法_readFromStorage()。我们从 中调用这个方法initState(),这样在构建我们的 UI 之前就会检索到存储中的信息。
在创建 State 时,从框架中调用 initState() 方法。(所以它只被调用一次,在 UI 被绘制之前)。

通过这种方式,我们得到了以下屏幕截图中显示的行为。
在第一次登录时,用户输入他们的凭据并按下登录按钮。
稍后,当他再次打开应用程序时,他会发现他的凭据已经输入到表单中。


做得好!这些简单的说明将允许您向应用程序添加自动登录功能,但最重要的是,存储的信息将在安全存储中加密。
通过这些简单的步骤,您的应用程序将升级。
结论
flutter_secure_storage 是一个非常简单的包,只需几个简单的步骤,我们就可以将用户数据加密保存在安全存储中。
【Android 详细知识点思维脑图(技能树)】
其实Android开发的知识点就那么多,面试问来问去还是那么点东西。所以面试没有其他的诀窍,只看你对这些知识点准备的充分程度。so,出去面试时先看看自己复习到了哪个阶段就好。
虽然 Android 没有前几年火热了,已经过去了会四大组件就能找到高薪职位的时代了。这只能说明 Android 中级以下的岗位饱和了,现在高级工程师还是比较缺少的,很多高级职位给的薪资真的特别高(钱多也不一定能找到合适的),所以努力让自己成为高级工程师才是最重要的。
过去了会四大组件就能找到高薪职位的时代了。这只能说明 Android 中级以下的岗位饱和了,现在高级工程师还是比较缺少的,很多高级职位给的薪资真的特别高(钱多也不一定能找到合适的),所以努力让自己成为高级工程师才是最重要的。























 384
384

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








