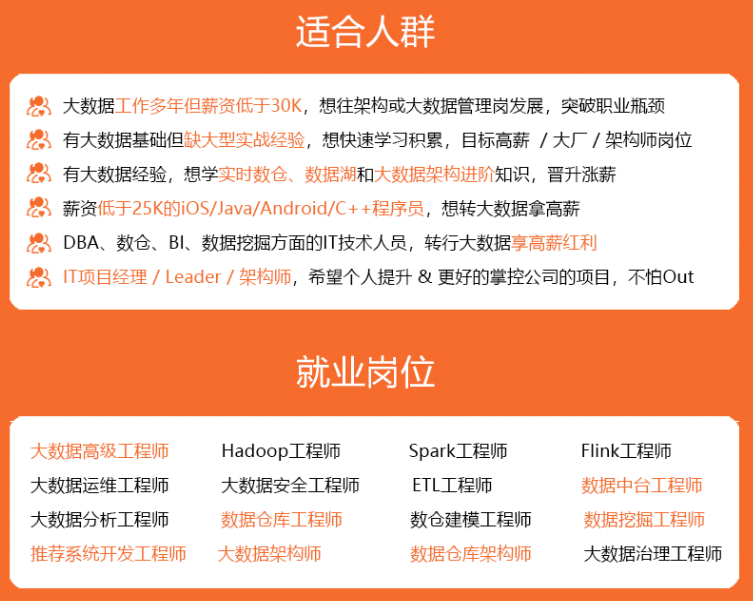
既有适合小白学习的零基础资料,也有适合3年以上经验的小伙伴深入学习提升的进阶课程,涵盖了95%以上大数据知识点,真正体系化!
由于文件比较多,这里只是将部分目录截图出来,全套包含大厂面经、学习笔记、源码讲义、实战项目、大纲路线、讲解视频,并且后续会持续更新
/**
* Constructs an empty <tt>LinkedHashMap</tt> instance with the
* specified initial capacity, load factor and ordering mode.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity
* @param loadFactor the load factor
* @param accessOrder the ordering mode - <tt>true</tt> for
* access-order, <tt>false</tt> for insertion-order
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is negative
* or the load factor is nonpositive
*/
public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity,
float loadFactor,
boolean accessOrder) {
super(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
this.accessOrder = accessOrder;
}
put
- 同HashMap,但重写了afterNodeInsertion。
- void afterNodeInsertion(boolean evict) { // possibly remove eldest
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> first;
if (evict && (first = head) != null && removeEldestEntry(first)) {
K key = first.key;
removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, true);
}
}
//可以自行重写该方法
protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry<K,V> eldest) {
return false;
}
public class LRUHashMap<K, V> extends LinkedHashMap<K, V>{
private final int MAX_CACHE_SIZE;
public BaseLRUCache(int cacheSize) {
super(cacheSize, 0.75f, true);
MAX_CACHE_SIZE = cacheSize;
}
@Override
protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry eldest) {
return size() > MAX_CACHE_SIZE;
}
}
get
public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V> e;
if ((e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null)
return null;
if (accessOrder)
afterNodeAccess(e);
return e.value;
}
void afterNodeAccess(Node<K,V> e) { // move node to last
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> last;
if (accessOrder && (last = tail) != e) {
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p =
(LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>)e, b = p.before, a = p.after;
p.after = null;
if (b == null)
head = a;
else
b.after = a;
if (a != null)
a.before = b;
else
last = b;
if (last == null)
head = p;
else {
p.before = last;
last.after = p;
}
tail = p;
++modCount;
}
}
remove
- 同HashMap,但重写了afterNodeRemoval。
void afterNodeRemoval(Node<K,V> e) { // unlink
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p =
(LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>)e, b = p.before, a = p.after;
p.before = p.after = null;
if (b == null)
head = a;
else
b.after = a;
if (a == null)
tail = b;
else
a.before = b;
}
遍历(迭代环形双向链表)
entrySet
public Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() {
Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> es;
return (es = entrySet) == null ? (entrySet = new LinkedEntrySet()) : es;
}
- 它使用的是该迭代器:
abstract class LinkedHashIterator {
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> next;
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> current;
int expectedModCount;
LinkedHashIterator() {
next = head;
expectedModCount = modCount;
current = null;
}
public final boolean hasNext() {
return next != null;
}
final LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> nextNode() {
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> e = next;
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
if (e == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
current = e;
next = e.after;
return e;
}
public final void remove() {
Node<K,V> p = current;
if (p == null)
throw new IllegalStateException();
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
current = null;
K key = p.key;
removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, false);
expectedModCount = modCount;
}
}
final class LinkedEntryIterator extends LinkedHashIterator
implements Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> {
public final Map.Entry<K,V> next() { return nextNode(); }
}
🚩TreeMap(底层是红黑树)
- 支持排序的Map实现。
- 基于红黑树实现,无容量限制。
- 是非线程安全的。
- TreeMap是根据key进行排序的,它的排序和定位需要依赖比较器或覆写Comparable接口,也因此不需要key覆写hashCode方法和equals方法,就可以排除掉重复的key,而HashMap的key则需要通过覆写hashCode方法和equals方法来确保没有重复的key
- TreeMap的查询、插入、删除效率均没有HashMap高,一般只有要对key排序时才使用TreeMap。
- TreeMap的key不能为null,而HashMap的key可以为null。
- TreeMap#Entry
static final class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
K key;
V value;
Entry<K,V> left;
Entry<K,V> right;
Entry<K,V> parent;
boolean color = BLACK;
/**
* Make a new cell with given key, value, and parent, and with
* {@code null} child links, and BLACK color.
*/
Entry(K key, V value, Entry<K,V> parent) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.parent = parent;
}
/**
* Returns the key.
*
* @return the key
*/
public K getKey() {
return key;
}
/**
* Returns the value associated with the key.
*
* @return the value associated with the key
*/
public V getValue() {
return value;
}
/**
* Replaces the value currently associated with the key with the given
* value.
*
* @return the value associated with the key before this method was
* called
*/
public V setValue(V value) {
V oldValue = this.value;
this.value = value;
return oldValue;
}
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))
return false;
Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o;
return valEquals(key,e.getKey()) && valEquals(value,e.getValue());
}
public int hashCode() {
int keyHash = (key==null ? 0 : key.hashCode());
int valueHash = (value==null ? 0 : value.hashCode());
return keyHash ^ valueHash;
}
public String toString() {
return key + "=" + value;
}
}
成员变量
private final Comparator<? super K> comparator;
private transient Entry<K,V> root;
/**
* The number of entries in the tree
*/
private transient int size = 0;
/**
* The number of structural modifications to the tree.
*/
private transient int modCount = 0;
构造方法
public TreeMap() {
comparator = null;
}
public TreeMap(Comparator<? super K> comparator) {
this.comparator = comparator;
}
put
public V put(K key, V value) {
Entry<K,V> t = root;
if (t == null) {
compare(key, key); // type (and possibly null) check
root = new Entry<>(key, value, null);
size = 1;
modCount++;
return null;
}
int cmp;
Entry<K,V> parent;
// split comparator and comparable paths
Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator;
if (cpr != null) {
do {
parent = t;
cmp = cpr.compare(key, t.key);
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}
else {
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key;
do {
parent = t;
cmp = k.compareTo(t.key);
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}
Entry<K,V> e = new Entry<>(key, value, parent);
if (cmp < 0)
parent.left = e;
else
parent.right = e;
fixAfterInsertion(e);
size++;
modCount++;
return null;
}
get
public V get(Object key) {
Entry<K,V> p = getEntry(key);
return (p==null ? null : p.value);
}
final Entry<K,V> getEntry(Object key) {
// Offload comparator-based version for sake of performance
if (comparator != null)
return getEntryUsingComparator(key);
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key;
Entry<K,V> p = root;
while (p != null) {
int cmp = k.compareTo(p.key);
if (cmp < 0)
p = p.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
p = p.right;
else
return p;
}
return null;
}
final Entry<K,V> getEntryUsingComparator(Object key) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
K k = (K) key;
Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator;
if (cpr != null) {
Entry<K,V> p = root;
while (p != null) {
int cmp = cpr.compare(k, p.key);
if (cmp < 0)
p = p.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
p = p.right;
else
return p;
}
}
return null;
}
remove
public V remove(Object key) {
Entry<K,V> p = getEntry(key);
if (p == null)
return null;
V oldValue = p.value;
deleteEntry(p);
return oldValue;
}
private void deleteEntry(Entry<K,V> p) {
modCount++;
size--;
// If strictly internal, copy successor's element to p and then make p
// point to successor.
if (p.left != null && p.right != null) {
Entry<K,V> s = successor(p);
p.key = s.key;
p.value = s.value;
p = s;
} // p has 2 children
// Start fixup at replacement node, if it exists.
Entry<K,V> replacement = (p.left != null ? p.left : p.right);
if (replacement != null) {
// Link replacement to parent
replacement.parent = p.parent;
if (p.parent == null)
root = replacement;
else if (p == p.parent.left)
p.parent.left = replacement;
else
p.parent.right = replacement;
// Null out links so they are OK to use by fixAfterDeletion.
p.left = p.right = p.parent = null;
// Fix replacement
if (p.color == BLACK)
fixAfterDeletion(replacement);
} else if (p.parent == null) { // return if we are the only node.
root = null;
} else { // No children. Use self as phantom replacement and unlink.
if (p.color == BLACK)
fixAfterDeletion(p);
if (p.parent != null) {
if (p == p.parent.left)
p.parent.left = null;
else if (p == p.parent.right)
p.parent.right = null;
p.parent = null;
}
}
}
containsKey
public boolean containsKey(Object key) {
return getEntry(key) != null;
}
containsValue
public boolean containsValue(Object value) {
for (Entry<K,V> e = getFirstEntry(); e != null; e = successor(e))
if (valEquals(value, e.value))
return true;
return false;
}
final Entry<K,V> getFirstEntry() {
Entry<K,V> p = root;
if (p != null)
while (p.left != null)
p = p.left;
return p;
}
static <K,V> TreeMap.Entry<K,V> successor(Entry<K,V> t) {
if (t == null)
return null;
else if (t.right != null) {
Entry<K,V> p = t.right;
while (p.left != null)
p = p.left;
return p;
} else {
Entry<K,V> p = t.parent;
Entry<K,V> ch = t;
while (p != null && ch == p.right) {
ch = p;
p = p.parent;
}
return p;
}
}
static final boolean valEquals(Object o1, Object o2) {
return (o1==null ? o2==null : o1.equals(o2));
}
遍历
public Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() {
EntrySet es = entrySet;
return (es != null) ? es : (entrySet = new EntrySet());
}
class EntrySet extends AbstractSet<Map.Entry<K,V>> {
public Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> iterator() {
return new EntryIterator(getFirstEntry());
}
}
abstract class PrivateEntryIterator<T> implements Iterator<T> {
Entry<K,V> next;
Entry<K,V> lastReturned;
int expectedModCount;
PrivateEntryIterator(Entry<K,V> first) {
expectedModCount = modCount;
lastReturned = null;
next = first;
}
public final boolean hasNext() {
return next != null;
}
final Entry<K,V> nextEntry() {
Entry<K,V> e = next;
if (e == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
next = successor(e);
lastReturned = e;
return e;
}
final Entry<K,V> prevEntry() {
Entry<K,V> e = next;
if (e == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
next = predecessor(e);
lastReturned = e;
return e;
}
public void remove() {
if (lastReturned == null)
throw new IllegalStateException();
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
// deleted entries are replaced by their successors
if (lastReturned.left != null && lastReturned.right != null)
next = lastReturned;
deleteEntry(lastReturned);
expectedModCount = modCount;
lastReturned = null;
}
}
final class EntryIterator extends PrivateEntryIterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> {
EntryIterator(Entry<K,V> first) {
super(first);
}
public Map.Entry<K,V> next() {
return nextEntry();
}
}
🚩ConcurrentHashMap(底层是数组+链表/红黑树,基于CAS+synchronized)
- JDK1.7前:分段锁
- 基于currentLevel划分出了多个Segment来对key-value进行存储,从而避免每次put操作都得锁住整个数组。在默认的情况下,最佳情况下可以允许16个线程并发无阻塞地操作集合对象,尽可能地减少并发时的阻塞现象。
- put、remove会加锁。get和containsKey不会加锁。
- 计算size:在不加锁的情况下遍历所有的段,读取其count以及modCount,这两个属性都是volatile类型的,并进行统计,再遍历一次所有的段,比较modCount是否有改变。如有改变,则再尝试两次机上动作。
- 如执行了三次上述动作,仍然有问题,则遍历所有段,分别进行加锁,然后进行计算,计算完毕后释放所有锁,从而完成计算动作。
- JDK1.8后:CAS+synchronized
- bin是桶 bucket的意思
- ConcurrentHashMap是延迟初始化的,只有在插入数据时,整个HashMap才被初始化为2的次方大小个桶(bin),每个bin包含哈希值相同的一系列Node(一般含有0或1个Node)。每个bin的第一个Node作为这个bin的锁,Hash值为零或者负的将被忽略;
- 每个bin的第一个Node插入用到CAS原理,这是在ConcurrentHashMap中最常发生的操作,其余的插入、删除、替换操作对bin中的第一个Node加锁,进行操作
- ConcurrentHashMap的size()函数一般比较少用,同时为了提高增删查改的效率,容器并未在内部保存一个size值,而且采用每次调用size()函数时累加各个bin中Node的个数计算得到,而且这一过程不加锁,即得到的size值不一定是最新的。
-
- ConcurrentHashMap#Node
- Node是最核心的内部类,它包装了key-value键值对,所有插入ConcurrentHashMap的数据都包装在这里面。它与HashMap中的定义很相似,但是但是有一些差别:它对value和next属性设置了volatile属性;’它不允许调用setValue方法直接改变Node的value域;它增加了find方法辅助map.get()方法。
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final int hash;
final K key;
volatile V val; // value和next是volatile的
volatile Node<K,V> next;
Node(int hash, K key, V val, Node<K,V> next) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
public final K getKey() { return key; }
public final V getValue() { return val; }
public final int hashCode() { return key.hashCode() ^ val.hashCode(); }
public final String toString(){ return key + "=" + val; }
public final V setValue(V value) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public final boolean equals(Object o) {
Object k, v, u; Map.Entry<?,?> e;
return ((o instanceof Map.Entry) &&
(k = (e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o).getKey()) != null &&
(v = e.getValue()) != null &&
(k == key || k.equals(key)) &&
(v == (u = val) || v.equals(u)));
}
/**
* Virtualized support for map.get(); overridden in subclasses.
*/
Node<K,V> find(int h, Object k) {
Node<K,V> e = this;
if (k != null) {
do {
K ek;
if (e.hash == h &&
((ek = e.key) == k || (ek != null && k.equals(ek))))
return e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
return null;
}
}
ConcurrentHashMap#TreeNode
- 当链表长度过长的时候,会转换为TreeNode。但是与HashMap不相同的是,它并不是直接转换为红黑树,而是把这些结点包装成TreeNode放在TreeBin对象中,由TreeBin完成对红黑树的包装。而且TreeNode在ConcurrentHashMap继承自Node类,而并非HashMap中的继承自LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>类,也就是说TreeNode带有next指针,这样做的目的是方便基于TreeBin的访问。
static final class TreeNode<K,V> extends Node<K,V> {
TreeNode<K,V> parent; // red-black tree links
TreeNode<K,V> left;
TreeNode<K,V> right;
TreeNode<K,V> prev; // needed to unlink next upon deletion
boolean red;
TreeNode(int hash, K key, V val, Node<K,V> next,
TreeNode<K,V> parent) {
super(hash, key, val, next);
this.parent = parent;
}
Node<K,V> find(int h, Object k) {
return findTreeNode(h, k, null);
}
/**
* Returns the TreeNode (or null if not found) for the given key
* starting at given root.
*/
final TreeNode<K,V> findTreeNode(int h, Object k, Class<?> kc) {
if (k != null) {
TreeNode<K,V> p = this;
do {
int ph, dir; K pk; TreeNode<K,V> q;
TreeNode<K,V> pl = p.left, pr = p.right;
if ((ph = p.hash) > h)
p = pl;
else if (ph < h)
p = pr;
else if ((pk = p.key) == k || (pk != null && k.equals(pk)))
return p;
else if (pl == null)
p = pr;
else if (pr == null)
p = pl;
else if ((kc != null ||
(kc = comparableClassFor(k)) != null) &&
(dir = compareComparables(kc, k, pk)) != 0)
p = (dir < 0) ? pl : pr;
else if ((q = pr.findTreeNode(h, k, kc)) != null)
return q;
else
p = pl;
} while (p != null);
}
return null;
}
}
ConcurrentHashMap#TreeBin
- 这个类并不负责包装用户的key、value信息,而是包装的很多TreeNode节点。它代替了TreeNode的根节点,也就是说在实际的ConcurrentHashMap“数组”中,存放的是TreeBin对象,而不是TreeNode对象,这是与HashMap的区别。另外这个类还带有了读写锁。
- 可以看到在构造TreeBin节点时,仅仅指定了它的hash值为TREEBIN常量,这也就是个标识位;同时也看到我们熟悉的红黑树构造方法。
/**
* TreeNodes used at the heads of bins. TreeBins do not hold user
* keys or values, but instead point to list of TreeNodes and
* their root. They also maintain a parasitic read-write lock
* forcing writers (who hold bin lock) to wait for readers (who do
* not) to complete before tree restructuring operations.
*/
static final class TreeBin<K,V> extends Node<K,V> {
TreeNode<K,V> root;
volatile TreeNode<K,V> first;
volatile Thread waiter;
volatile int lockState;
// values for lockState
static final int WRITER = 1; // set while holding write lock
static final int WAITER = 2; // set when waiting for write lock
static final int READER = 4; // increment value for setting read lock
/**
* Tie-breaking utility for ordering insertions when equal
* hashCodes and non-comparable. We don't require a total
* order, just a consistent insertion rule to maintain
* equivalence across rebalancings. Tie-breaking further than
* necessary simplifies testing a bit.
*/
static int tieBreakOrder(Object a, Object b) {
int d;
if (a == null || b == null ||
(d = a.getClass().getName().
compareTo(b.getClass().getName())) == 0)
d = (System.identityHashCode(a) <= System.identityHashCode(b) ?
-1 : 1);
return d;
}
/**
* Creates bin with initial set of nodes headed by b.
*/
TreeBin(TreeNode<K,V> b) {
super(TREEBIN, null, null, null);
this.first = b;
TreeNode<K,V> r = null;
for (TreeNode<K,V> x = b, next; x != null; x = next) {
next = (TreeNode<K,V>)x.next;
x.left = x.right = null;
if (r == null) {
x.parent = null;
x.red = false;
r = x;
}
else {
K k = x.key;
int h = x.hash;
Class<?> kc = null;
for (TreeNode<K,V> p = r;;) {
int dir, ph;
K pk = p.key;
if ((ph = p.hash) > h)
dir = -1;
else if (ph < h)
dir = 1;
else if ((kc == null &&
(kc = comparableClassFor(k)) == null) ||
(dir = compareComparables(kc, k, pk)) == 0)
dir = tieBreakOrder(k, pk);
TreeNode<K,V> xp = p;
if ((p = (dir <= 0) ? p.left : p.right) == null) {
x.parent = xp;
if (dir <= 0)
xp.left = x;
else
xp.right = x;
r = balanceInsertion(r, x);
break;
}
}
}
}
this.root = r;
assert checkInvariants(root);
}
}
ConcurrentHashMap#ForwardingNode
/**
* A node inserted at head of bins during transfer operations.
*/
static final class ForwardingNode<K,V> extends Node<K,V> {
final Node<K,V>[] nextTable;
ForwardingNode(Node<K,V>[] tab) {
super(MOVED, null, null, null);
this.nextTable = tab;
}
Node<K,V> find(int h, Object k) {
// loop to avoid arbitrarily deep recursion on forwarding nodes
outer: for (Node<K,V>[] tab = nextTable;;) {
Node<K,V> e; int n;
if (k == null || tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0 ||
(e = tabAt(tab, (n - 1) & h)) == null)
return null;
for (;;) {
int eh; K ek;
if ((eh = e.hash) == h &&
((ek = e.key) == k || (ek != null && k.equals(ek))))
return e;
if (eh < 0) {
if (e instanceof ForwardingNode) {
tab = ((ForwardingNode<K,V>)e).nextTable;
continue outer;
}
else
return e.find(h, k);
}
if ((e = e.next) == null)
return null;
}
}
}
}
ConcurrentHashMap#ReservationNode
/**
* A place-holder node used in computeIfAbsent and compute
*/
static final class ReservationNode<K,V> extends Node<K,V> {
ReservationNode() {
super(RESERVED, null, null, null);
}
Node<K,V> find(int h, Object k) {
return null;
}
}
节点类型
- hash值大于等于0,则是链表节点,Node
- hash值为-1 MOVED,则是forwarding nodes,存储nextTable的引用。只有table发生扩容的时候,ForwardingNode才会发挥作用,作为一个占位符放在table中表示当前节点为null或则已经被移动。
- hash值为-2 TREEBIN,则是红黑树根,TreeBin类型
- hash值为-3 RESERVED,则是reservation nodes,
- static final int MOVED = -1; // hash for forwarding nodes
static final int TREEBIN = -2; // hash for roots of trees
static final int RESERVED = -3; // hash for transient reservations
成员变量
/**
* The largest possible table capacity. This value must be
* exactly 1<<30 to stay within Java array allocation and indexing
* bounds for power of two table sizes, and is further required
* because the top two bits of 32bit hash fields are used for
* control purposes.
*/
private static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
/**
* The default initial table capacity. Must be a power of 2
* (i.e., at least 1) and at most MAXIMUM_CAPACITY.
*/
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 16;
/**
* The largest possible (non-power of two) array size.
* Needed by toArray and related methods.
*/
static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
/**
* The default concurrency level for this table. Unused but
* defined for compatibility with previous versions of this class.
*/
private static final int DEFAULT_CONCURRENCY_LEVEL = 16;
/**
* The load factor for this table. Overrides of this value in
* constructors affect only the initial table capacity. The
* actual floating point value isn't normally used -- it is
* simpler to use expressions such as {@code n - (n >>> 2)} for
* the associated resizing threshold.
*/
private static final float LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
/**
* The bin count threshold for using a tree rather than list for a
* bin. Bins are converted to trees when adding an element to a
* bin with at least this many nodes. The value must be greater
* than 2, and should be at least 8 to mesh with assumptions in
* tree removal about conversion back to plain bins upon
* shrinkage.
*/
static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8;
/**
* The bin count threshold for untreeifying a (split) bin during a
* resize operation. Should be less than TREEIFY_THRESHOLD, and at
* most 6 to mesh with shrinkage detection under removal.
*/
static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6;
/**
* The smallest table capacity for which bins may be treeified.
* (Otherwise the table is resized if too many nodes in a bin.)
* The value should be at least 4 * TREEIFY_THRESHOLD to avoid
* conflicts between resizing and treeification thresholds.
*/
static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64;
/**
* Minimum number of rebinnings per transfer step. Ranges are
* subdivided to allow multiple resizer threads. This value
* serves as a lower bound to avoid resizers encountering
* excessive memory contention. The value should be at least
* DEFAULT_CAPACITY.
*/
private static final int MIN_TRANSFER_STRIDE = 16;
/**
* The number of bits used for generation stamp in sizeCtl.
* Must be at least 6 for 32bit arrays.
*/
private static int RESIZE_STAMP_BITS = 16;
/**
* The maximum number of threads that can help resize.
* Must fit in 32 - RESIZE_STAMP_BITS bits.
*/
private static final int MAX_RESIZERS = (1 << (32 - RESIZE_STAMP_BITS)) - 1;
/**
* The bit shift for recording size stamp in sizeCtl.
*/
private static final int RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT = 32 - RESIZE_STAMP_BITS;
/*
* Encodings for Node hash fields. See above for explanation.
*/
static final int MOVED = -1; // hash for forwarding nodes
static final int TREEBIN = -2; // hash for roots of trees
static final int RESERVED = -3; // hash for transient reservations
static final int HASH_BITS = 0x7fffffff; // usable bits of normal node hash
/** Number of CPUS, to place bounds on some sizings */
static final int NCPU = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors();
/**
* The array of bins. Lazily initialized upon first insertion.
* Size is always a power of two. Accessed directly by iterators.
*/
transient volatile Node<K,V>[] table;
/**
* The next table to use; non-null only while resizing.
*/
private transient volatile Node<K,V>[] nextTable;
/**
* Base counter value, used mainly when there is no contention,
* but also as a fallback during table initialization
* races. Updated via CAS.
*/
private transient volatile long baseCount;
/**
* Table initialization and resizing control. When negative, the
* table is being initialized or resized: -1 for initialization,
* else -(1 + the number of active resizing threads). Otherwise,
* when table is null, holds the initial table size to use upon
* creation, or 0 for default. After initialization, holds the
* next element count value upon which to resize the table.
- 负数代表正在进行初始化或扩容操作
- -1代表正在初始化
- -N 表示有N-1个线程正在进行扩容操作
正数或0代表hash表还没有被初始化,这个数值表示初始化或下一次进行扩容的大小,这一点类似于扩容阈值的概念。还后面可以看到,它的值始终是当前ConcurrentHashMap容量的0.75倍,这与loadfactor是对应的。
*/
private transient volatile int sizeCtl;
/**
* The next table index (plus one) to split while resizing.
*/
private transient volatile int transferIndex;
/**
* Spinlock (locked via CAS) used when resizing and/or creating CounterCells.
*/
private transient volatile int cellsBusy;
/**
* Table of counter cells. When non-null, size is a power of 2.
*/
private transient volatile CounterCell[] counterCells;
// views
private transient KeySetView<K,V> keySet;
private transient ValuesView<K,V> values;
private transient EntrySetView<K,V> entrySet;
构造方法
public ConcurrentHashMap() {
}
/**
* Creates a new, empty map with an initial table size
* accommodating the specified number of elements without the need
* to dynamically resize.
*
* @param initialCapacity The implementation performs internal
* sizing to accommodate this many elements.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity of
* elements is negative
*/
public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
int cap = ((initialCapacity >= (MAXIMUM_CAPACITY >>> 1)) ?
MAXIMUM_CAPACITY :
tableSizeFor(initialCapacity + (initialCapacity >>> 1) + 1));
this.sizeCtl = cap;
}
/**
* Creates a new map with the same mappings as the given map.
*
* @param m the map
*/
public ConcurrentHashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
this.sizeCtl = DEFAULT_CAPACITY;
putAll(m);
}
/**
* Creates a new, empty map with an initial table size based on
* the given number of elements ({@code initialCapacity}) and
* initial table density ({@code loadFactor}).
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity. The implementation
* performs internal sizing to accommodate this many elements,
* given the specified load factor.
* @param loadFactor the load factor (table density) for
* establishing the initial table size
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity of
* elements is negative or the load factor is nonpositive
*
* @since 1.6
*/
public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
this(initialCapacity, loadFactor, 1);
}
/**
* Creates a new, empty map with an initial table size based on
* the given number of elements ({@code initialCapacity}), table
* density ({@code loadFactor}), and number of concurrently
* updating threads ({@code concurrencyLevel}).
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity. The implementation
* performs internal sizing to accommodate this many elements,
* given the specified load factor.
* @param loadFactor the load factor (table density) for
* establishing the initial table size
* @param concurrencyLevel the estimated number of concurrently
* updating threads. The implementation may use this value as
* a sizing hint.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is
* negative or the load factor or concurrencyLevel are
* nonpositive
*/
public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity,
float loadFactor, int concurrencyLevel) {
if (!(loadFactor > 0.0f) || initialCapacity < 0 || concurrencyLevel <= 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
if (initialCapacity < concurrencyLevel) // Use at least as many bins
initialCapacity = concurrencyLevel; // as estimated threads
long size = (long)(1.0 + (long)initialCapacity / loadFactor);
int cap = (size >= (long)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ?
MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : tableSizeFor((int)size);
this.sizeCtl = cap;
}
CAS
private static final sun.misc.Unsafe U;
- Unsafe类的几个CAS方法,可以原子性地修改对象的某个属性值
/**
* Atomically update Java variable to <tt>x</tt> if it is currently
* holding <tt>expected</tt>.
* @return <tt>true</tt> if successful
*/
public final native boolean compareAndSwapObject(Object o, long offset,
Object expected,
Object x);
/**
* Atomically update Java variable to <tt>x</tt> if it is currently
* holding <tt>expected</tt>.
* @return <tt>true</tt> if successful
*/
public final native boolean compareAndSwapInt(Object o, long offset,
int expected,
int x);
/**
* Atomically update Java variable to <tt>x</tt> if it is currently
* holding <tt>expected</tt>.
* @return <tt>true</tt> if successful
*/
public final native boolean compareAndSwapLong(Object o, long offset,
long expected,
long x);
/**
* Fetches a reference value from a given Java variable, with volatile
* load semantics. Otherwise identical to {@link #getObject(Object, long)}
*/
public native Object getObjectVolatile(Object o, long offset);
/**
* Stores a reference value into a given Java variable, with
* volatile store semantics. Otherwise identical to {@link #putObject(Object, long, Object)}
*/
public native void putObjectVolatile(Object o, long offset, Object x);
- Unsafe.getObjectVolatile可以直接获取指定内存的数据,保证了每次拿到数据都是最新的。
三个核心方法
- ConcurrentHashMap定义了三个原子操作,用于对指定位置的节点进行操作。正是这些原子操作保证了ConcurrentHashMap的线程安全。
static final <K,V> Node<K,V> tabAt(Node<K,V>[] tab, int i) {
return (Node<K,V>)U.getObjectVolatile(tab, ((long)i << ASHIFT) + ABASE);
}
static final <K,V> boolean casTabAt(Node<K,V>[] tab, int i,
Node<K,V> c, Node<K,V> v) {
return U.compareAndSwapObject(tab, ((long)i << ASHIFT) + ABASE, c, v);
}
static final <K,V> void setTabAt(Node<K,V>[] tab, int i, Node<K,V> v) {
U.putObjectVolatile(tab, ((long)i << ASHIFT) + ABASE, v);
}
初始化
- 对于ConcurrentHashMap来说,调用它的构造方法仅仅是设置了一些参数而已。而整个table的初始化是在向ConcurrentHashMap中插入元素的时候发生的。如调用put、computeIfAbsent、compute、merge等方法的时候,调用时机是检查table==null。
- 初始化方法主要应用了关键属性sizeCtl 如果这个值<0,表示其他线程正在进行初始化,就放弃这个操作。在这也可以看出ConcurrentHashMap的初始化只能由一个线程完成。如果获得了初始化权限,就用CAS方法将sizeCtl置为-1,防止其他线程进入。初始化数组后,将sizeCtl的值改为0.75*n。
private final Node<K,V>[] initTable() {
Node<K,V>[] tab; int sc;
while ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0) {
if ((sc = sizeCtl) < 0)
Thread.yield(); // lost initialization race; just spin
// 利用CAS方法把sizectl的值置为-1 表示本线程正在进行初始化
else if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, -1)) {
try {
if ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0) {
int n = (sc > 0) ? sc : DEFAULT_CAPACITY;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Node<K,V>[] nt = (Node<K,V>[])new Node<?,?>[n];
table = tab = nt;
// 相当于0.75*n 设置一个扩容的阈值
sc = n - (n >>> 2);
}
} finally {
sizeCtl = sc;
}
break;
}
}
return tab;
}
spread(hash)
- h是某个对象的hashCode返回值
static final int spread(int h) {
return (h ^ (h >>> 16)) & HASH_BITS;
}
- static final int HASH_BITS = 0x7fffffff; // usable bits of normal node hash
- 类似于Hashtable+HashMap的hash实现,Hashtable中也是和一个魔法值取与,保证结果一定为正数;HashMap中也是将hashCode与其移动低n位的结果再取异或,保证了对象的hashCode的高16位的变化能反应到低16位中,
size相关
成员变量
@sun.misc.Contended static final class CounterCell {
volatile long value;
CounterCell(long x) { value = x; }
}
/**
* Base counter value, used mainly when there is no contention,
* but also as a fallback during table initialization
* races. Updated via CAS.
*/
private transient volatile long baseCount;
/**
* Spinlock (locked via CAS) used when resizing and/or creating CounterCells.
*/
private transient volatile int cellsBusy;
/**
* Table of counter cells. When non-null, size is a power of 2.
*/
private transient volatile CounterCell[] counterCells;
- 每个CounterCell都对应一个bucket,CounterCell中的long值就是对应bucket的binCount。
- 计算总大小就是将所有bucket的binCount求和,而每个binCount都存储在CounterCell#value中,每当put或者remove时都会更新节点所在bucket对应的CounterCell#value。
size()
- 没有直接返回baseCount 而是统计一次这个值,而这个值其实也是一个大概的数值,因此可能在统计的时候有其他线程正在执行插入或删除操作。
public int size() {
long n = sumCount();
return ((n < 0L) ? 0 :
(n > (long)Integer.MAX_VALUE) ? Integer.MAX_VALUE :
(int)n);
}
- 在baseCount基础上再加上所有counterCell的值求和。
- 而在addCount时,会先尝试CAS更新baseCount,如果有冲突,则再尝试CAS更新随机的一个counterCell中的value,这样求和就是正确的size了。
final long sumCount() {
CounterCell[] as = counterCells;
CounterCell a;
long sum = baseCount;
if (as != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < as.length; ++i) {
if ((a = as[i]) != null)
// 所有counter的值求和
sum += a.value;
}
}
return sum;
}
put(若bucket第一个结点插入则使用CAS,否则加锁)
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(key, value, false);
}
整体流程就是首先定义不允许key或value为null的情况放入 。对于每一个放入的值,首先利用spread方法对key的hashcode进行一次hash计算,由此来确定这个值在table中的位置。
- 如果这个位置是空的,那么直接放入,而且不需要加锁操作。
- 如果这个位置存在结点,说明发生了hash碰撞,首先判断这个节点的类型。
- 如果是MOVED节点,则表示正在扩容,帮助进行扩容
- 如果是链表节点(hash >=0),则得到的结点就是hash值相同的节点组成的链表的头节点。需要依次向后遍历确定这个新加入的值所在位置。如果遇到hash值与key值都与新加入节点是一致的情况,则只需要更新value值即可。否则依次向后遍历,直到链表尾插入这个结点。 如果加入这个节点以后链表长度大于8,就把这个链表转换成红黑树。
- 如果这个节点的类型已经是树节点的话,直接调用树节点的插入方法进行插入新的值。
- addCount 增加计数值
/** Implementation for put and putIfAbsent */
final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException();
int hash = spread(key.hashCode());
int binCount = 0;
// 死循环,只有插入成功时才会跳出
for (Node<K,V>[] tab = table;;) {
Node<K,V> f; int n, i, fh;
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
// table为空则初始化(延迟初始化)
tab = initTable();
else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) {
// hash to index后正好为空,则CAS放入;如果失败那么进入下次循环继续尝试
if (casTabAt(tab, i, null,
new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value, null)))
break; // no lock when adding to empty bin
}
// 如果index处非空,且hash为MOVED(表示该节点是ForwardingNode),则表示有其它线程正在扩容,则一起进行扩容操作。
else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)
tab = helpTransfer(tab, f);
// 如果index处非空,且为链表节点或树节点
else {
V oldVal = null;
// 对某个bucket上执行添加操作仅需要锁住第一个Node即可(可以保证不会多线程同时对某个bucket进行写入)
synchronized (f) {
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {
// 1) 如果是链表节点,那么插入到链表中
if (fh >= 0) {
// binCount是该bucket中元素个数
binCount = 1;
for (Node<K,V> e = f;; ++binCount) {
K ek;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((ek = e.key) == key ||
(ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) {
oldVal = e.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
e.val = value;
break;
}
Node<K,V> pred = e;
if ((e = e.next) == null) {
pred.next = new Node<K,V>(hash, key,
value, null);
break;
}
}
}
// 2)如果是红黑树树根,那么插入到红黑树中
else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {
Node<K,V> p;
binCount = 2;
if ((p = ((TreeBin<K,V>)f).putTreeVal(hash, key,
value)) != null) {
oldVal = p.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
p.val = value;
}
}
}
}
// 插入节点/释放锁之后,如果大小合适调整为红黑树,那么将链表转为红黑树
if (binCount != 0) {
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD)
treeifyBin(tab, i);
if (oldVal != null)
return oldVal;
break;
}
}
}
// 将当前ConcurrentHashMap的元素数量+1 ,如果超过阈值,那么进行扩容
addCount(1L, binCount);
return null;
}
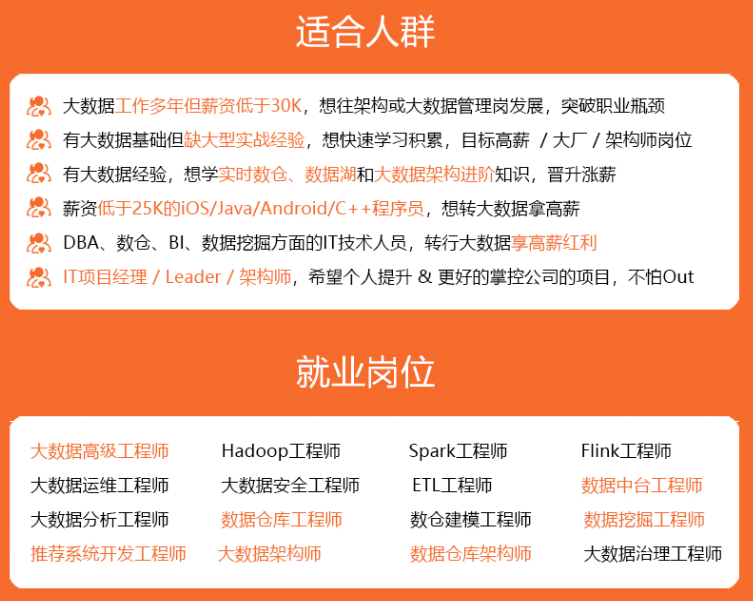
既有适合小白学习的零基础资料,也有适合3年以上经验的小伙伴深入学习提升的进阶课程,涵盖了95%以上大数据知识点,真正体系化!
由于文件比较多,这里只是将部分目录截图出来,全套包含大厂面经、学习笔记、源码讲义、实战项目、大纲路线、讲解视频,并且后续会持续更新
pred.next = new Node<K,V>(hash, key,
value, null);
break;
}
}
}
// 2)如果是红黑树树根,那么插入到红黑树中
else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {
Node<K,V> p;
binCount = 2;
if ((p = ((TreeBin<K,V>)f).putTreeVal(hash, key,
value)) != null) {
oldVal = p.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
p.val = value;
}
}
}
}
// 插入节点/释放锁之后,如果大小合适调整为红黑树,那么将链表转为红黑树
if (binCount != 0) {
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD)
treeifyBin(tab, i);
if (oldVal != null)
return oldVal;
break;
}
}
}
// 将当前ConcurrentHashMap的元素数量+1 ,如果超过阈值,那么进行扩容
addCount(1L, binCount);
return null;
}
[外链图片转存中...(img-iYsNBjwq-1715010085475)]
[外链图片转存中...(img-H1ixRA8p-1715010085475)]
[外链图片转存中...(img-DZSRhchY-1715010085475)]
**既有适合小白学习的零基础资料,也有适合3年以上经验的小伙伴深入学习提升的进阶课程,涵盖了95%以上大数据知识点,真正体系化!**
**由于文件比较多,这里只是将部分目录截图出来,全套包含大厂面经、学习笔记、源码讲义、实战项目、大纲路线、讲解视频,并且后续会持续更新**
**[需要这份系统化资料的朋友,可以戳这里获取](https://bbs.csdn.net/topics/618545628)**





















 1854
1854











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








