既有适合小白学习的零基础资料,也有适合3年以上经验的小伙伴深入学习提升的进阶课程,涵盖了95%以上大数据知识点,真正体系化!
由于文件比较多,这里只是将部分目录截图出来,全套包含大厂面经、学习笔记、源码讲义、实战项目、大纲路线、讲解视频,并且后续会持续更新
printf("NULL ");
return;
}
PostOrder(root->left);
PostOrder(root->right);
printf("%c ", root->data);
}
---
### 树结点的个数
🎤**分治思想,将大问题分成小问题解决,在二叉树里就是递归的思想**
int TreeSize(BTNode* root)
{
return root == NULL ? 0 : TreeSize(root->left) + TreeSize(root->right) + 1;
}
---
### 叶子结点的个数
🎤度为0的结点被称为叶子或终端结点
int TreeLeafSize(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL)
{
return 1;
}
return TreeLeafSize(root->left) + TreeLeafSize(root->right);
}
---
### 层序遍历
🎤这里需要用到队列,最后我会把所有代码放在下面
🎤层序遍历的核心思想就是上一层出队的时候带着下一层所有的结点进队
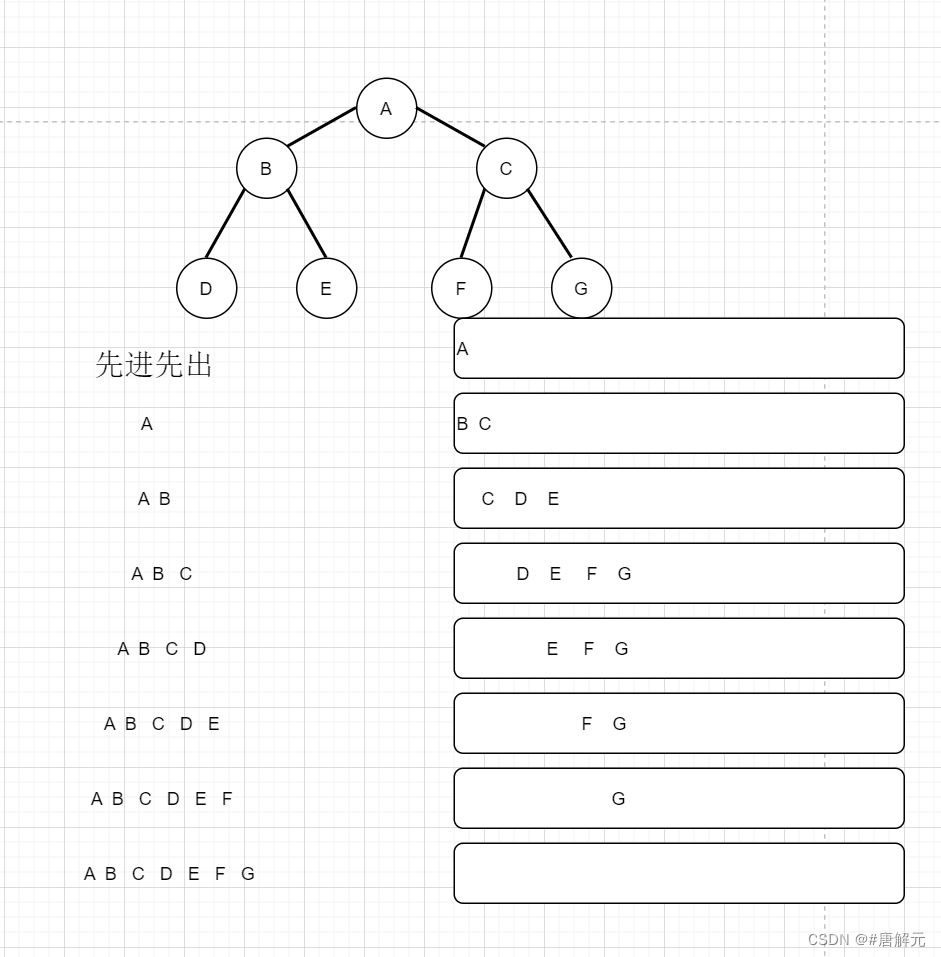
//层序遍历,核心思想:上一层出队的时候带下一层的结点进队
void LevelOrder(BTNode* root)
{
Queue q;
QueueInit(&q);
if (root)
{
QueuePush(&q, root);
}
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);
QueuePop(&q);
printf(“%c “, front->data);
if (root->left)
{
QueuePush(&q, front->left);
}
if (root->right)
{
QueuePush(&q, front->right);
}
}
printf(”\n”);
QueueDestory(&q);
}
---
### 二叉树的销毁
🎤**如果我们用前序或者中序来遍历销毁的话,会发现,有的结点找不到了,而后续遍历销毁却避开这个问题。**
void TreeDestory(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return;
}
TreeDestory(root->left);
TreeDestory(root->right);
free(root);
root = NULL;
}
---
## 代码
**因为我们层序遍历中,用到了队,我就直接把队列的定义和实现的代码放了进来。** **到这里,我相信大家对二叉树已经掌握了🎉🎉🎉,有错误大家可以指出哦,有疑问也可以问我,大家共同进步,后续会持续更新《数据结构》的相关内容,大家喜欢的话可以关注一下,😚😚😚**下面是项目代码,大家参考一下。****
### test.c
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include"Queue.h"
typedef char BTDataType;
typedef struct BinaryTreeNode
{
struct BinaryTreeNode* left;//左孩子
struct BinaryTreeNode* right;//右孩子
BTDataType data;
}BTNode;
void PrevOrder(BTNode* root)//前序
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("NULL “);
return;
}
printf(”%c ", root->data);
PrevOrder(root->left);
PrevOrder(root->right);
}
void InOrder(BTNode* root)//中序
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("NULL “);
return;
}
InOrder(root->left);
printf(”%c ", root->data);
InOrder(root->right);
}
void PostOrder(BTNode* root)//后序
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("NULL “);
return;
}
PostOrder(root->left);
PostOrder(root->right);
printf(”%c ", root->data);
}
//分治思想–大问题分成小问题来解决,也就是递归
int TreeSize(BTNode* root)
{
return root == NULL ? 0 : TreeSize(root->left) + TreeSize(root->right) + 1;
}
//求叶子结点的个数
int TreeLeafSize(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL)
{
return 1;
}
return TreeLeafSize(root->left) + TreeLeafSize(root->right);
}
//层序遍历,核心思想:上一层出队的时候带下一层的结点进队
void LevelOrder(BTNode* root)
{
Queue q;
QueueInit(&q);
if (root)
{
QueuePush(&q, root);
}
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);
QueuePop(&q);
printf(“%c “, front->data);
if (root->left)
{
QueuePush(&q, front->left);
}
if (root->right)
{
QueuePush(&q, front->right);
}
}
printf(”\n”);
QueueDestory(&q);
}
//树的销毁–用后序的思想,一步一步销毁就行了
void TreeDestory(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return;
}
TreeDestory(root->left);
TreeDestory(root->right);
free(root);
root = NULL;
}
int main()
{
BTNode* A = (BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));
A->data = ‘A’;
A->left = NULL;
A->right = NULL;
BTNode\* B = (BTNode\*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));
B->data = 'B';
B->left = NULL;
B->right = NULL;
BTNode\* C = (BTNode\*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));
C->data = 'C';
C->left = NULL;
C->right = NULL;
BTNode\* D = (BTNode\*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));
D->data = 'D';
D->left = NULL;
D->right = NULL;
BTNode\* E = (BTNode\*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));
E->data = 'E';
E->left = NULL;
E->right = NULL;
//链接
A->left = B;
A->right = C;
B->left = D;
B->right = E;
PrevOrder(A);
printf("\n");
InOrder(A);
printf("\n");
PostOrder(A);
printf("\n");
printf("TreeSizeA:%d\n", TreeSize(A));
printf("TreeSizeB:%d\n", TreeSize(B));
printf("TreeLeafSizeA:%d\n", TreeLeafSize(A));
printf("TreeLeafSizeB:%d\n", TreeLeafSize(B));
LevelOrder(A);
TreeDestory(A);
return 0;
}
---
### Queue.h
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
//前置声明
struct BinaryTreeNode;
typedef struct BinaryTreeNode* QDataType;
typedef struct QueueNode
{
struct QueueNode* next;
QDataType data;
}QNode;
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode* head;
QNode* tail;
}Queue;
//初始化
void QueueInit(Queue* pq);
//销毁
void QueueDestory(Queue* pq);
//入队—队尾入
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x);
//出队—队头出
void QueuePop(Queue* pq);
//取队头数据
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq);
//取队尾数据
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq);
//数据个数
int QueueSize(Queue* pq);
//判空
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq);
---
### Queue.c
#include"Queue.h"
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}
void QueueDestory(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QNode\* cur = pq->head;
while (cur)
{
QNode\* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}
//入队—队尾入
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)
{
assert(pq);
QNode\* newnode = (QNode\*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));//新结点的创建
if (newnode == NULL)
{
printf("malloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
//先把新申请的结点的数据域和指针域赋值
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
//如果队列中没有一个结点的时候
if (pq->tail == NULL)
{
pq->head = pq->tail = newnode;
}
//如果队列中有结点的时候
else
{
pq->tail->next = newnode;
pq->tail = newnode;//链接之后让tail成为新的尾
}
}
//出队—队头出
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->tail);//既然是出队列,那么就要判断队列是不为空的,空了还出个毛线
if (pq->head->next == NULL)//当队列中只剩下一个结点的时候,防止tail成为野指针
{
free(pq->head);
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}
else//多个结点
{
QNode\* next = pq->head->next;
free(pq->head);
pq->head = next;
}
}
//取队头数据
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->head);//先判断一下队头数据是不是空,如果为空就不能调用
return pq->head->data;//很简单,直接返回队头的数据即可
}
//取队尾数据
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->head);//同上
return pq->tail->data;//直接返回队尾的数据即可
}
//数据个数
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
//这次就需要遍历链表,也是非常简单的
assert(pq);
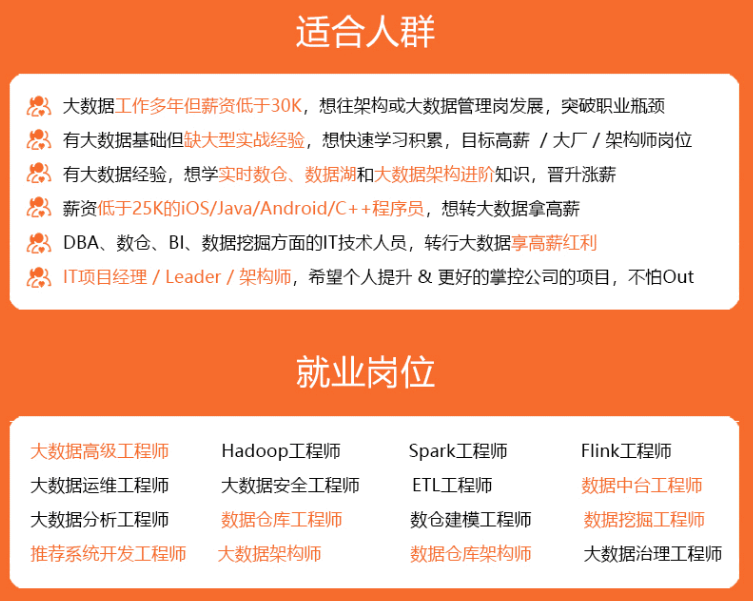
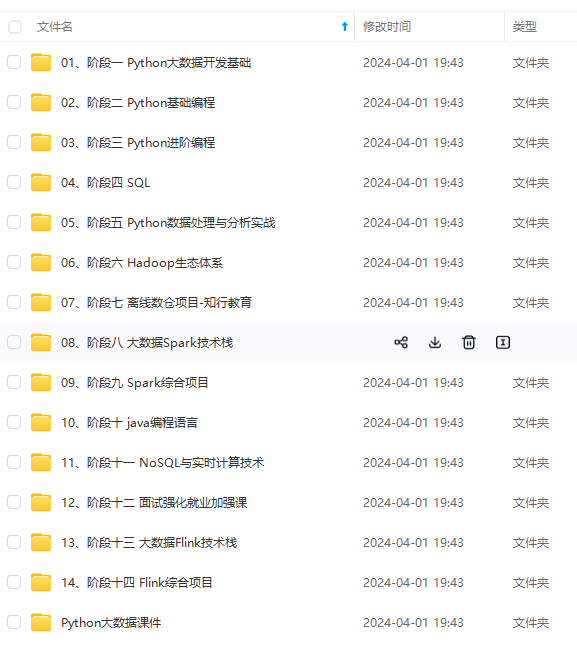
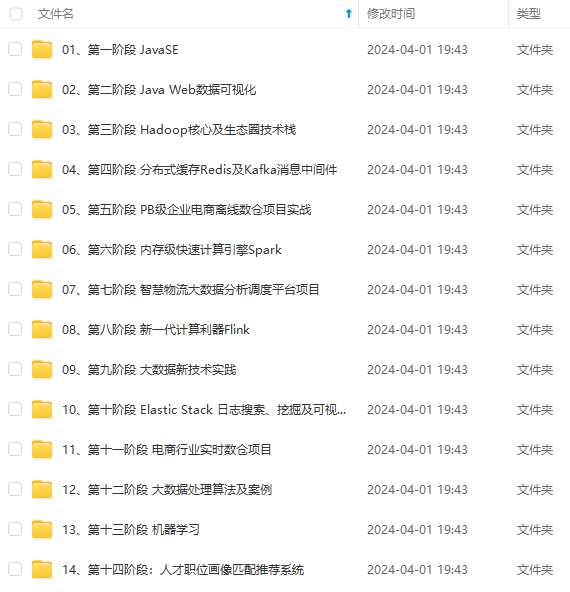
既有适合小白学习的零基础资料,也有适合3年以上经验的小伙伴深入学习提升的进阶课程,涵盖了95%以上大数据知识点,真正体系化!
由于文件比较多,这里只是将部分目录截图出来,全套包含大厂面经、学习笔记、源码讲义、实战项目、大纲路线、讲解视频,并且后续会持续更新
return pq->tail->data;//直接返回队尾的数据即可
}
//数据个数
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
//这次就需要遍历链表,也是非常简单的
assert(pq);
[外链图片转存中…(img-XKblFsSw-1715441582375)]
[外链图片转存中…(img-dnPRD6Iu-1715441582376)]
[外链图片转存中…(img-Ywdw5sVd-1715441582376)]
既有适合小白学习的零基础资料,也有适合3年以上经验的小伙伴深入学习提升的进阶课程,涵盖了95%以上大数据知识点,真正体系化!
由于文件比较多,这里只是将部分目录截图出来,全套包含大厂面经、学习笔记、源码讲义、实战项目、大纲路线、讲解视频,并且后续会持续更新






















 985
985











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








