-
1
-
2
创建 3 个元素的向量:
# 创建 3 个元素的向量 a = tf.constant([1,2, 3.]) a, a.shape
-
1
-
2
-
3
(<tf.Tensor: id=3, shape=(3,), dtype=float32, numpy=array([1., 2., 3.], dtype=float32)>, TensorShape([3]))
-
1
-
2
定义矩阵
# 创建 2 行 2 列的矩阵 a = tf.constant([[1,2],[3,4]]) a, a.shape
-
1
-
2
-
3
(<tf.Tensor: id=4, shape=(2, 2), dtype=int32, numpy= array([[1, 2], [3, 4]])>, TensorShape([2, 2]))
-
1
-
2
-
3
三维张量可以定义为:
# 创建 3 维张量 tf.constant([[[1,2],[3,4]],[[5,6],[7,8]]])
-
1
-
2
<tf.Tensor: id=5, shape=(2, 2, 2), dtype=int32, numpy= array([[[1, 2], [3, 4]],
[[5, 6],
[7, 8]]])>
-
1
-
2
-
3
-
4
-
5
-
6
通过传入字符串对象即可创建字符串类型的张量
# 创建字符串 a = tf.constant('Hello, Deep Learning.') a
-
1
-
2
-
3
<tf.Tensor: id=6, shape=(), dtype=string, numpy=b'Hello, Deep Learning.'>
- 1
1.2 字符串类型
通过传入字符串对象即可创建字符串类型的张量
# 创建字符串 a = tf.constant('Hello, Deep Learning.') a
-
1
-
2
-
3
<tf.Tensor: id=7, shape=(), dtype=string, numpy=b'Hello, Deep Learning.'>
- 1
在 tf.strings 模块中,提供了常见的字符串类型的工具函数,如小写化 lower()、 拼接
join()、 长度 length()、 切分 split()等。
# 小写化字符串 tf.strings.lower(a)
-
1
-
2
<tf.Tensor: id=8, shape=(), dtype=string, numpy=b'hello, deep learning.'>
- 1
1.3 布尔类型
布尔类型的张量只需要传入 Python 语言的布尔类型数据,转换成 TensorFlow 内部布尔型即可。
# 创建布尔类型标量 tf.constant(True)
-
1
-
2
<tf.Tensor: id=9, shape=(), dtype=bool, numpy=True>
- 1
创建布尔类型的向量
# 创建布尔类型向量 tf.constant([True, False])
-
1
-
2
<tf.Tensor: id=10, shape=(2,), dtype=bool, numpy=array([ True, False])>
- 1
需要注意的是, TensorFlow 的布尔类型和 Python 语言的布尔类型并不等价,不能通用
# 创建 TF 布尔张量 a = tf.constant(True) # TF 布尔类型张量与 python 布尔类型比较 print(a is True) # 仅数值比较 print(a == True)
-
1
-
2
-
3
-
4
-
5
-
6
False tf.Tensor(True, shape=(), dtype=bool)
-
1
-
2
对于数值类型的张量,可以保持为不同字节长度的精度,如浮点数 3.14 既可以保存为
16-bit 长度,也可以保存为 32-bit 甚至 64-bit 的精度。Bit 位越长,精度越高,同时占用的内存空间也就越大。常用的精度类型有 tf.int16, tf.int32, tf.int64, tf.float16, tf.float32, tf.float64,其中 tf.float64 即为 tf.double。
在创建张量时,可以指定张量的保存精度
# 创建指定精度的张量 tf.constant(123456789, dtype=tf.int16)
-
1
-
2
<tf.Tensor: id=14, shape=(), dtype=int16, numpy=-13035>
- 1
对于浮点数, 高精度的张量可以表示更精准的数据,例如采用 tf.float32 精度保存π时,实际保存的数据为 3.1415927
import numpy as np # 从 numpy 中导入 pi 常量 np.pi # 32 位 tf.constant(np.pi, dtype=tf.float32)
-
1
-
2
-
3
-
4
-
5
<tf.Tensor: id=16, shape=(), dtype=float32, numpy=3.1415927>
- 1
如果采用 tf.float64 精度保存π,则能获得更高的精度
tf.constant(np.pi, dtype=tf.float64) # 64 位
- 1
<tf.Tensor: id=17, shape=(), dtype=float64, numpy=3.141592653589793>
- 1
2.1 读取精度
通过访问张量的 dtype 成员属性可以判断张量的保存精度
a = tf.constant(np.pi, dtype=tf.float16)
# 读取原有张量的数值精度
print(‘before:’,a.dtype)
# 如果精度不符合要求,则进行转换
if a.dtype != tf.float32:
# tf.cast 函数可以完成精度转换
a = tf.cast(a,tf.float32)
# 打印转换后的精度
print(‘after :’,a.dtype)
-
1
-
2
-
3
-
4
-
5
-
6
-
7
-
8
-
9
-
10
before: <dtype: 'float16'> after : <dtype: 'float32'>
-
1
-
2
2.2 类型转换
系统的每个模块使用的数据类型、 数值精度可能各不相同, 对于不符合要求的张量的类型及精度, 需要通过 tf.cast 函数进行转换
# 创建 tf.float16 低精度张量 a = tf.constant(np.pi, dtype=tf.float16) # 转换为高精度张量 tf.cast(a, tf.double)
-
1
-
2
-
3
-
4
<tf.Tensor: id=21, shape=(), dtype=float64, numpy=3.140625>
- 1
进行类型转换时,需要保证转换操作的合法性, 例如将高精度的张量转换为低精度的张量时,可能发生数据溢出隐患:
a = tf.constant(123456789, dtype=tf.int32) # 转换为低精度整型 tf.cast(a, tf.int16)
-
1
-
2
-
3
<tf.Tensor: id=23, shape=(), dtype=int16, numpy=-13035>
- 1
布尔类型与整型之间相互转换也是合法的, 是比较常见的操作
a = tf.constant([True, False]) # 布尔类型转整型 tf.cast(a, tf.int32)
-
1
-
2
-
3
<tf.Tensor: id=25, shape=(2,), dtype=int32, numpy=array([1, 0])>
- 1
一般默认 0 表示 False, 1 表示 True,在 TensorFlow 中,将非 0 数字都视为 True,
a = tf.constant([-1, 0, 1, 2]) # 整型转布尔类型 tf.cast(a, tf.bool)
-
1
-
2
-
3
<tf.Tensor: id=27, shape=(4,), dtype=bool, numpy=array([ True, False, True, True])>
- 1
为了区分需要计算梯度信息的张量与不需要计算梯度信息的张量,TensorFlow 增加了一种专门的数据类型来支持梯度信息的记录:tf.Variable。tf.Variable 类型在普通的张量类型基础上添加了 name,trainable 等属性来支持计算图的构建。由于梯度运算会消耗大量的计算资源,而且会自动更新相关参数,对于不需要的优化的张量,如神经网络的输入 X,不需要通过 tf.Variable 封装;相反,对于需要计算梯度并优化的张量,如神经网络层的W 和𝒃,需要通过 tf.Variable 包裹以便 TensorFlow 跟踪相关梯度信息。
通过 tf.Variable()函数可以将普通张量转换为待优化张量:
# 创建 TF 张量 a = tf.constant([-1, 0, 1, 2]) # 转换为 Variable 类型 aa = tf.Variable(a) # Variable 类型张量的属性, 名字, 是否求导数 aa.name, aa.trainable
-
1
-
2
-
3
-
4
-
5
-
6
('Variable:0', True)
- 1
name 属性用于命名计算图中的变量,这套命名体系是 TensorFlow 内部维护的, 一般不需要用户关注 name 属性;
trainable属性表征当前张量是否需要被优化,创建 Variable 对象时是默认启用优化标志,可以设置trainable=False 来设置张量不需要优化。
# 直接创建 Variable 张量 tf.Variable([[1,2],[3,4]])
-
1
-
2
<tf.Variable 'Variable:0' shape=(2, 2) dtype=int32, numpy= array([[1, 2], [3, 4]])>
-
1
-
2
-
3
4.1 从数组、列表对象创建
通过 tf.convert_to_tensor 函数可以创建新 Tensor,并将保存在 Python List 对象或者Numpy Array 对象中的数据导入到新 Tensor 中。
# 从列表创建张量 tf.convert_to_tensor([1,2.])
-
1
-
2
<tf.Tensor: id=44, shape=(2,), dtype=float32, numpy=array([1., 2.], dtype=float32)>
- 1
# 从数组中创建张量 tf.convert_to_tensor(np.array([[1,2.],[3,4]]))
-
1
-
2
<tf.Tensor: id=45, shape=(2, 2), dtype=float64, numpy= array([[1., 2.], [3., 4.]])>
-
1
-
2
-
3
4.2 创建全0或全1张量
创建全 0 的矩阵
# 创建全 0 矩阵,指定 shape 为 2 行 2 列 tf.zeros([2,2])
-
1
-
2
<tf.Tensor: id=56, shape=(2, 2), dtype=float32, numpy= array([[0., 0.], [0., 0.]], dtype=float32)>
-
1
-
2
-
3
创建全 1 的矩阵
# 创建全 1 矩阵,指定 shape 为 3 行 2 列 tf.ones([3,2])
-
1
-
2
<tf.Tensor: id=59, shape=(3, 2), dtype=float32, numpy= array([[1., 1.], [1., 1.], [1., 1.]], dtype=float32)>
-
1
-
2
-
3
-
4
通过 tf.zeros_like, tf.ones_like 可以方便地新建与某个张量 shape 一致, 且内容为全 0 或全 1 的张量。
# 创建一个矩阵 a = tf.ones([2,3]) # 创建一个与 a 形状相同,但是全 0 的新矩阵 tf.zeros_like(a)
-
1
-
2
-
3
-
4
总结一下
面试前要精心做好准备,简历上写的知识点和原理都需要准备好,项目上多想想难点和亮点,这是面试时能和别人不一样的地方。
还有就是表现出自己的谦虚好学,以及对于未来持续进阶的规划,企业招人更偏爱稳定的人。
开源分享:【大厂前端面试题解析+核心总结学习笔记+真实项目实战+最新讲解视频】
万事开头难,但是程序员这一条路坚持几年后发展空间还是非常大的,一切重在坚持。
为了帮助大家更好更高效的准备面试,特别整理了《前端工程师面试手册》电子稿文件。
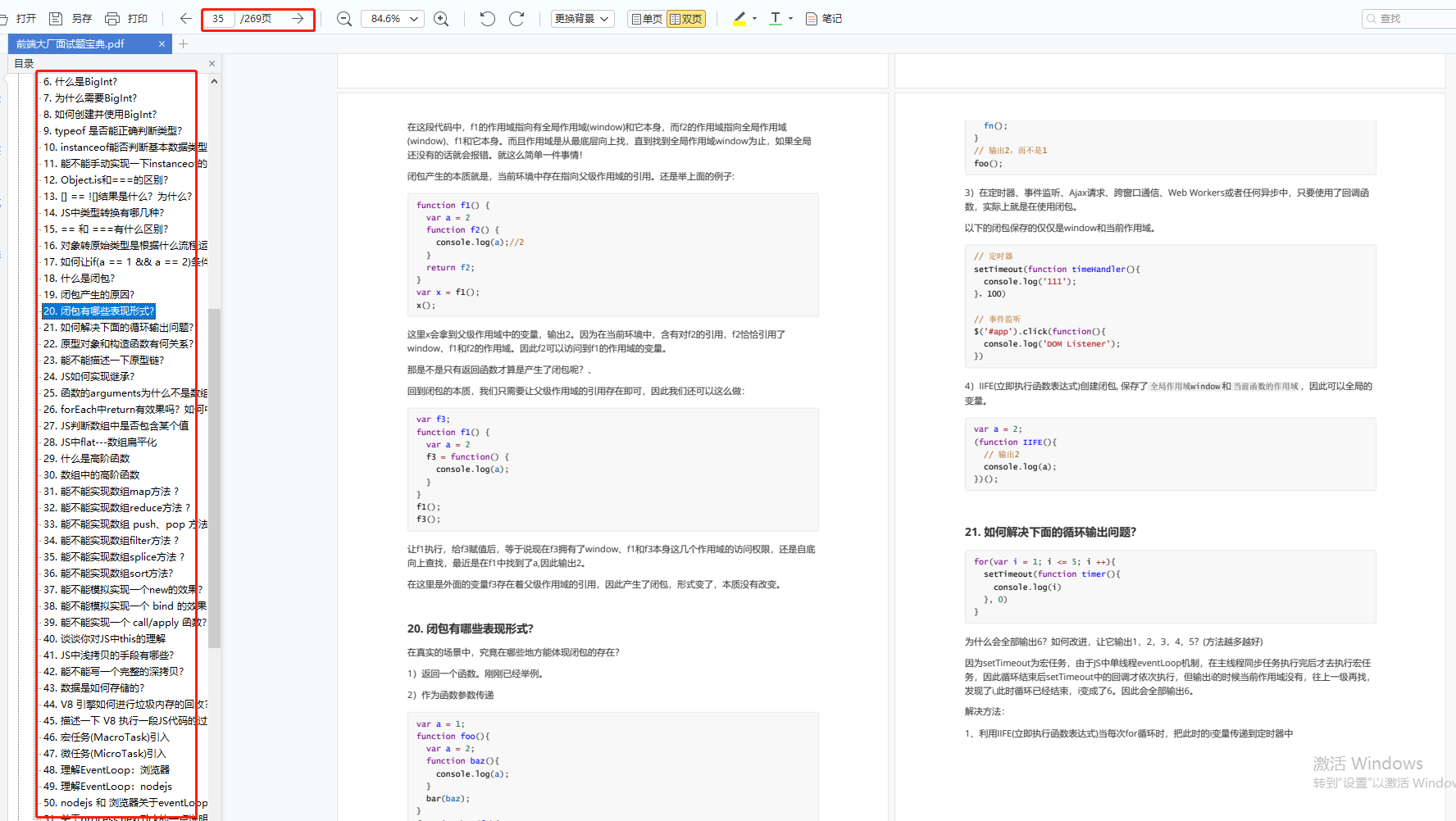
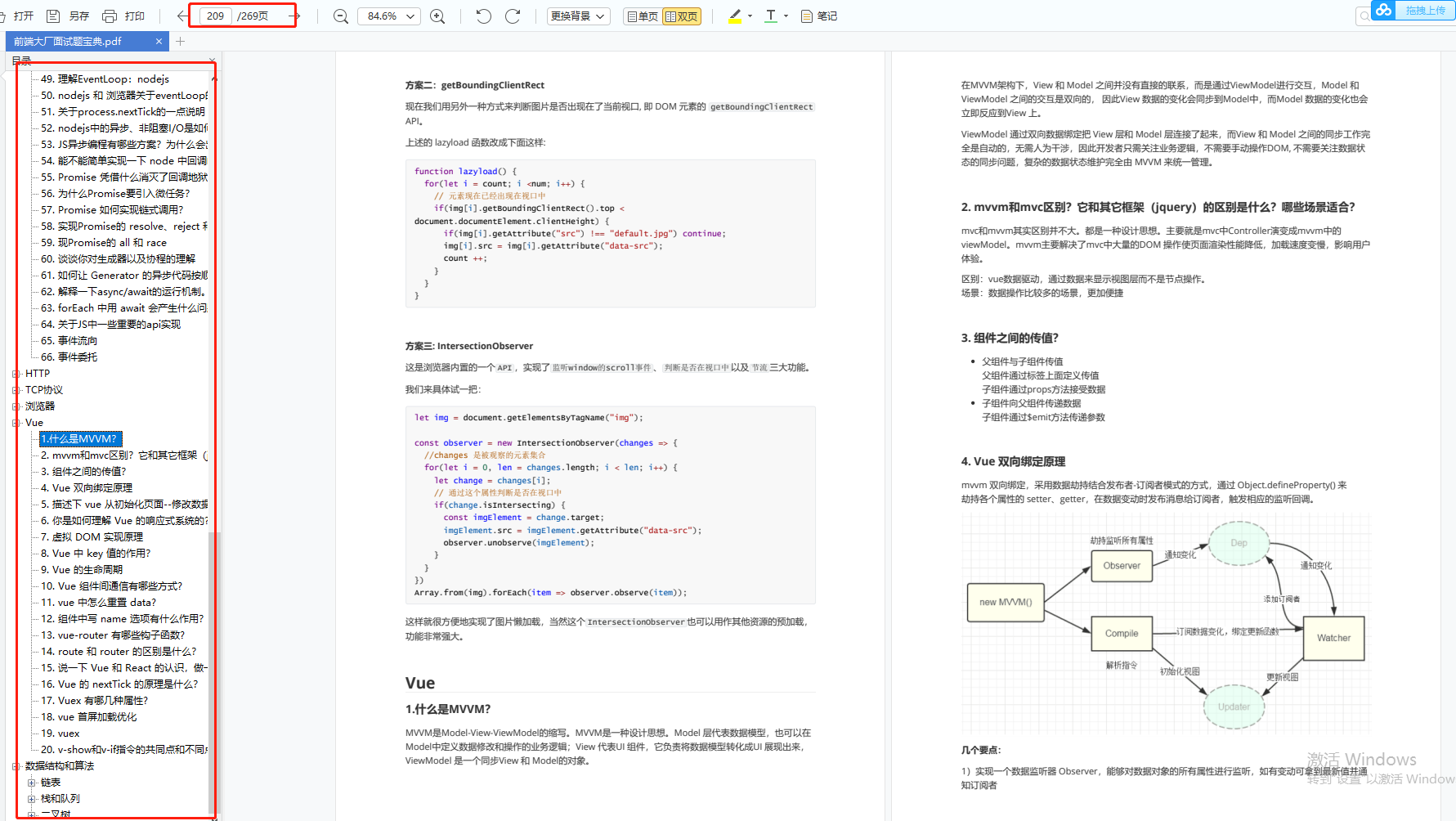
前端面试题汇总
JavaScript
性能
linux
前端资料汇总
前端工程师岗位缺口一直很大,符合岗位要求的人越来越少,所以学习前端的小伙伴要注意了,一定要把技能学到扎实,做有含金量的项目,这样在找工作的时候无论遇到什么情况,问题都不会大。






















 205
205

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








