总结
机会是留给有准备的人,大家在求职之前应该要明确自己的态度,熟悉求职流程,做好充分的准备,把一些可预见的事情做好。
对于应届毕业生来说,校招更适合你们,因为绝大部分都不会有工作经验,企业也不会有工作经验的需求。同时,你也不需要伪造高大上的实战经验,以此让自己的简历能够脱颖而出,反倒会让面试官有所怀疑。
你在大学时期应该明确自己的发展方向,如果你在大一就确定你以后想成为Java工程师,那就不要花太多的时间去学习其他的技术语言,高数之类的,不如好好想着如何夯实Java基础。下图涵盖了应届生乃至转行过来的小白要学习的Java内容:
请转发本文支持一下


android:layout_height=“wrap_content”
android:layout_marginLeft=“10dp”
android:layout_weight=“1”
android:layout_gravity=“right”
android:orientation=“horizontal”>
<Button
android:id=“@+id/button”
android:layout_width=“70dp”
android:layout_height=“wrap_content”
android:layout_marginLeft=“10dp”
android:layout_gravity=“right”
android:layout_weight=“1”
android:textSize=“15sp”
android:text=“修改” />
<Button
android:id=“@+id/button4”
android:layout_width=“70dp”
android:layout_height=“wrap_content”
android:layout_gravity=“right”
android:layout_weight=“1”
android:textSize=“15sp”
android:text=“删除” />
2、添加表头的xml,创建list_header.xml
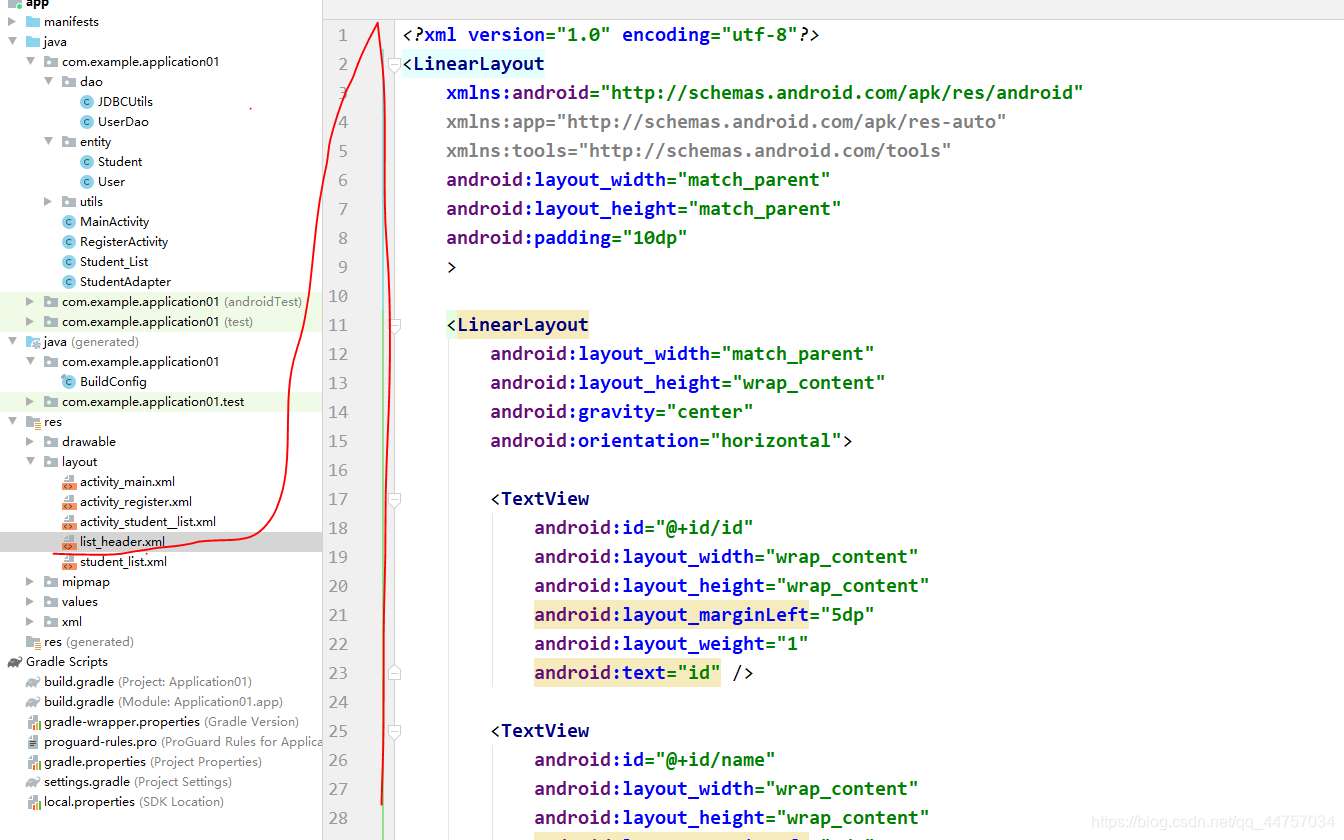
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android=“http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android”
xmlns:app=“http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto”
xmlns:tools=“http://schemas.android.com/tools”
android:layout_width=“match_parent”
android:layout_height=“match_parent”
android:padding=“10dp”
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width=“match_parent”
android:layout_height=“wrap_content”
android:gravity=“center”
android:orientation=“horizontal”>
<TextView
android:id=“@+id/id”
android:layout_width=“wrap_content”
android:layout_height=“wrap_content”
android:layout_marginLeft=“5dp”
android:layout_weight=“1”
android:text=“id” />
<TextView
android:id=“@+id/name”
android:layout_width=“wrap_content”
android:layout_height=“wrap_content”
android:layout_marginLeft=“5dp”
android:layout_weight=“1”
android:text=“姓名” />
<TextView
android:id=“@+id/age”
android:layout_width=“wrap_content”
android:layout_height=“wrap_content”
android:layout_marginLeft=“5dp”
android:layout_weight=“1”
android:text=“年龄” />
<TextView
android:id=“@+id/address”
android:layout_width=“wrap_content”
android:layout_height=“wrap_content”
android:layout_marginLeft=“5dp”
android:layout_weight=“1”
android:text=“地址” />
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width=“wrap_content”
android:layout_height=“wrap_content”
android:layout_marginLeft=“10dp”
android:layout_weight=“1”
android:layout_gravity=“right”
android:orientation=“horizontal”>
<TextView
android:id=“@+id/button”
android:layout_width=“70dp”
android:layout_height=“wrap_content”
android:layout_marginLeft=“10dp”
android:layout_gravity=“right”
android:layout_weight=“1”
android:textSize=“15sp”
android:text=“修改” />
<TextView
android:id=“@+id/button4”
android:layout_width=“70dp”
android:layout_height=“wrap_content”
android:layout_gravity=“right”
android:layout_weight=“1”
android:textSize=“15sp”
android:text=“删除” />
3、在adapter当中动态加载表头
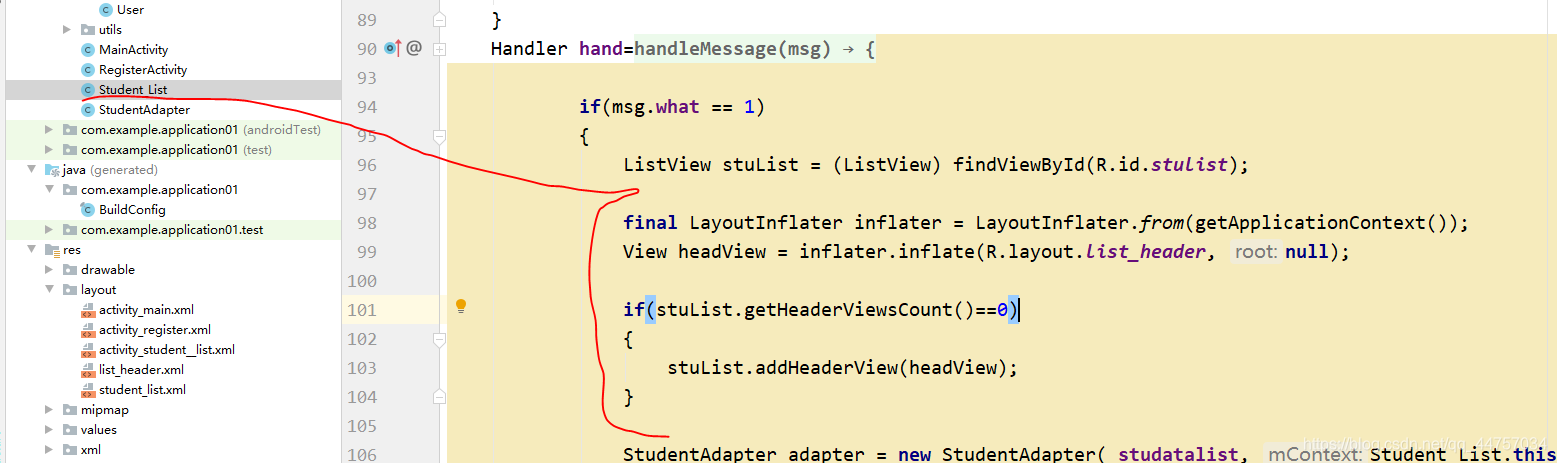
final LayoutInflater inflater = LayoutInflater.from(getApplicationContext());
View headView = inflater.inflate(R.layout.list_header, null);
if(stuList.getHeaderViewsCount()==0)
{
stuList.addHeaderView(headView);
}
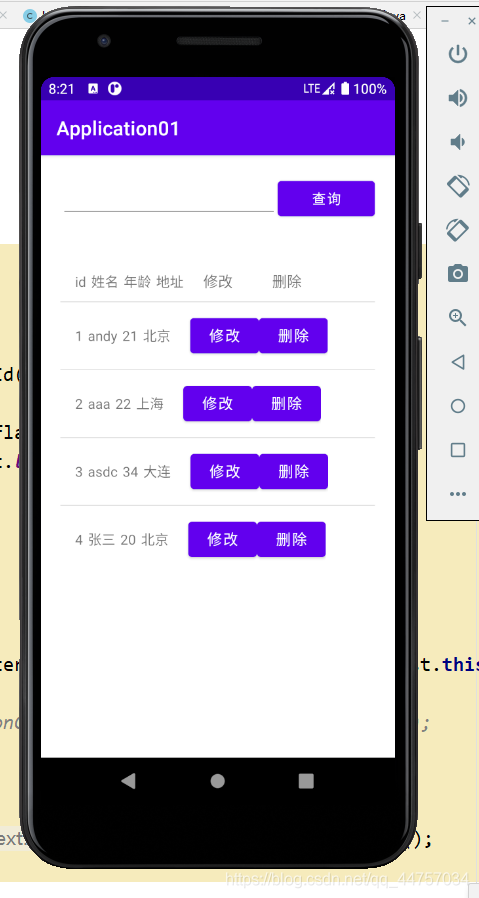
(一)安卓端
1、创建显示学生信息的页面
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android=“http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android”
xmlns:app=“http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto”
xmlns:tools=“http://schemas.android.com/tools”
android:layout_width=“match_parent”
android:layout_height=“match_parent”
tools:context=“.StudentUpdate”>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width=“match_parent”
android:layout_height=“match_parent”
android:orientation=“vertical”
tools:layout_editor_absoluteX=“219dp”
tools:layout_editor_absoluteY=“207dp”
android:padding=“50dp”
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width=“match_parent”
android:layout_height=“wrap_content”
android:orientation=“horizontal”>
<TextView
android:id=“@+id/textView”
android:layout_width=“wrap_content”
android:layout_height=“wrap_content”
android:layout_weight=“1”
android:textSize=“15sp”
android:text=“ID:” />
<TextView
android:id=“@+id/id”
android:layout_width=“wrap_content”
android:layout_height=“wrap_content”
android:layout_weight=“1”
android:ems=“10”
/>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width=“match_parent”
android:layout_height=“wrap_content”
android:orientation=“horizontal”>
<TextView
android:layout_width=“wrap_content”
android:layout_height=“wrap_content”
android:layout_weight=“1”
android:textSize=“15sp”
android:text=“昵称:” />
<EditText
android:id=“@+id/name”
android:layout_width=“wrap_content”
android:layout_height=“wrap_content”
android:layout_weight=“1”
android:ems=“10”
android:inputType=“textPersonName”
/>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width=“match_parent”
android:layout_height=“wrap_content”
android:orientation=“horizontal”>
<TextView
android:id=“@+id/textView2”
android:layout_width=“wrap_content”
android:layout_height=“wrap_content”
android:layout_weight=“1”
android:textSize=“15sp”
android:text=“年龄:”
/>
<EditText
android:id=“@+id/age”
android:layout_width=“wrap_content”
android:layout_height=“wrap_content”
android:layout_weight=“1”
android:ems=“10”
/>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width=“match_parent”
android:layout_height=“wrap_content”
android:orientation=“horizontal”>
<TextView
android:layout_width=“wrap_content”
android:layout_height=“wrap_content”
android:layout_weight=“1”
android:textSize=“15sp”
android:text=“地址:”
/>
<EditText
android:id=“@+id/address”
android:layout_width=“wrap_content”
android:layout_height=“wrap_content”
android:layout_weight=“1”
android:ems=“10”
android:inputType=“phone”
/>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width=“match_parent”
android:layout_height=“wrap_content”
android:orientation=“horizontal”>
<Button
android:layout_marginTop=“50dp”
android:id=“@+id/button2”
android:layout_width=“match_parent”
android:layout_height=“wrap_content”
android:text=“提交”
android:onClick=“updatestudent”
/>
<Button
android:id=“@+id/button3”
android:layout_width=“match_parent”
android:layout_height=“wrap_content”
android:text=“重置” />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
2、在student_list.xml页面上的按钮上添加onClick
3、完善Student_List当中的update方法
public void update(View view){
LinearLayout linearLayout = (LinearLayout)(view.getParent().getParent());
TextView idEd = linearLayout.findViewById(R.id.id);
TextView nameEd = linearLayout.findViewById(R.id.name);
TextView ageEd = linearLayout.findViewById(R.id.age);
TextView addressEd = linearLayout.findViewById(R.id.address);
Intent intent=new Intent();
intent.putExtra(“id”, idEd.getText().toString());
intent.putExtra(“name”, nameEd.getText().toString());
intent.putExtra(“age”, ageEd.getText().toString());
intent.putExtra(“address”, addressEd.getText().toString());
intent.setClass(this, StudentUpdate.class);
startActivity(intent );
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(),“修改”,Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
4、StudentUpdate当中获取对应Intent 对象当中的值并放入到页面当中的修改框当中
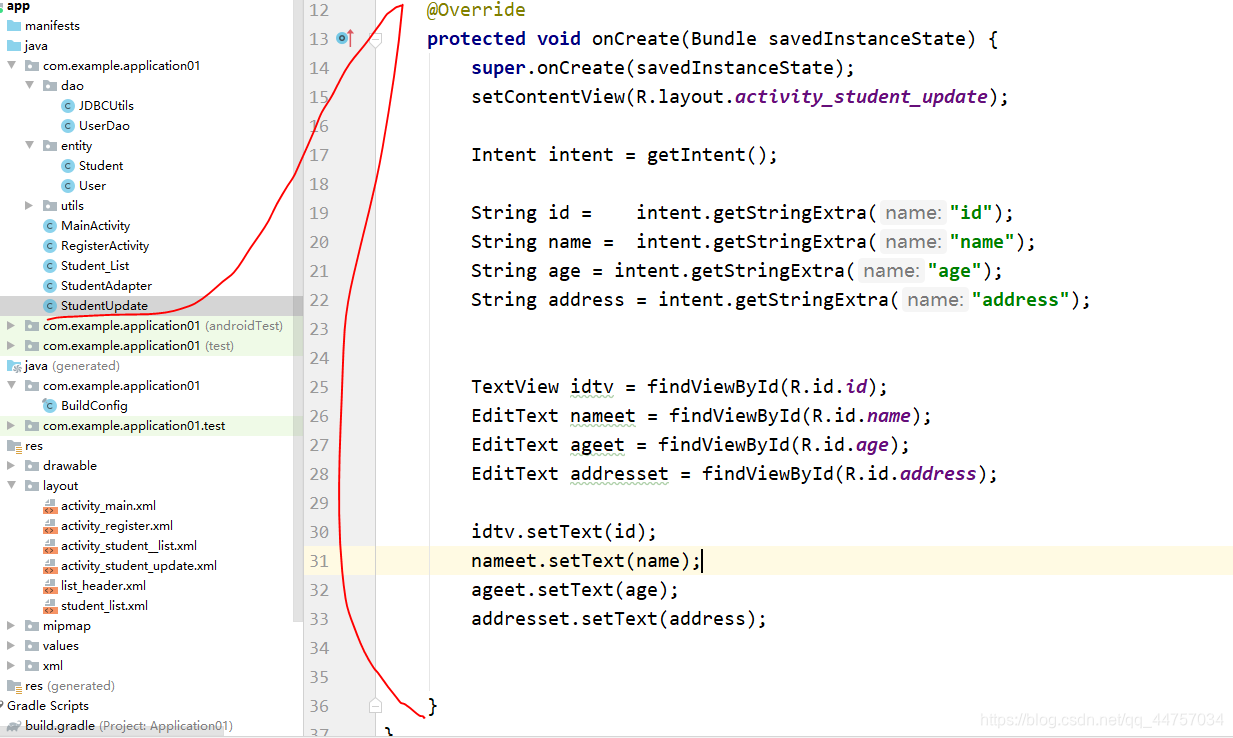
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_student_update);
Intent intent = getIntent();
String id = intent.getStringExtra(“id”);
String name = intent.getStringExtra(“name”);
String age = intent.getStringExtra(“age”);
String address = intent.getStringExtra(“address”);
TextView idtv = findViewById(R.id.id);
EditText nameet = findViewById(R.id.name);
EditText ageet = findViewById(R.id.age);
EditText addresset = findViewById(R.id.address);
idtv.setText(id);
nameet.setText(name);
ageet.setText(age);
addresset.setText(address);
}
运行测试
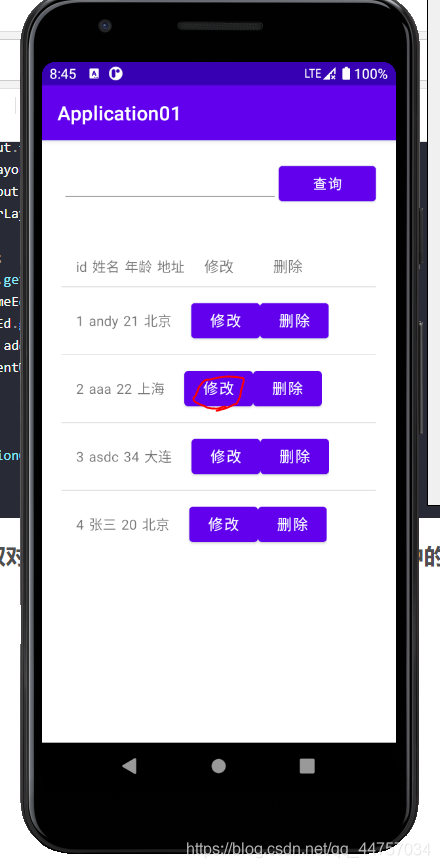
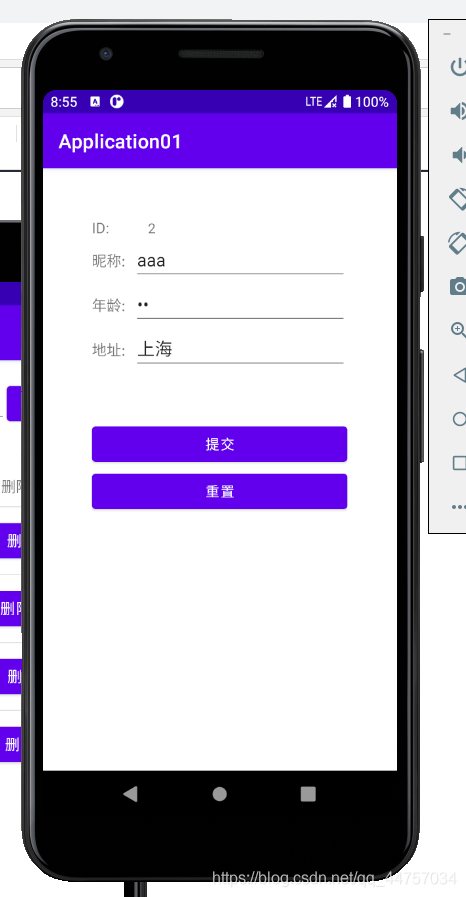
(二)web端
1、创建更新学生信息的dao

public boolean update(Student stu){
String sql=“update student set name=?,age=?,address=? where id=?”;
Connection con = JDBCUtils.getConn();
try {
PreparedStatement pst=con.prepareStatement(sql);
pst.setString(1,stu.getName());
pst.setInt(2,stu.getAge());
pst.setString(3,stu.getAddress() );
pst.setInt(4,stu.getId() );
int value = pst.executeUpdate();
if(value>0){
return true;
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}finally {
JDBCUtils.close(con);
}
return false;
}
2、创建对应更新学生信息的Servlet

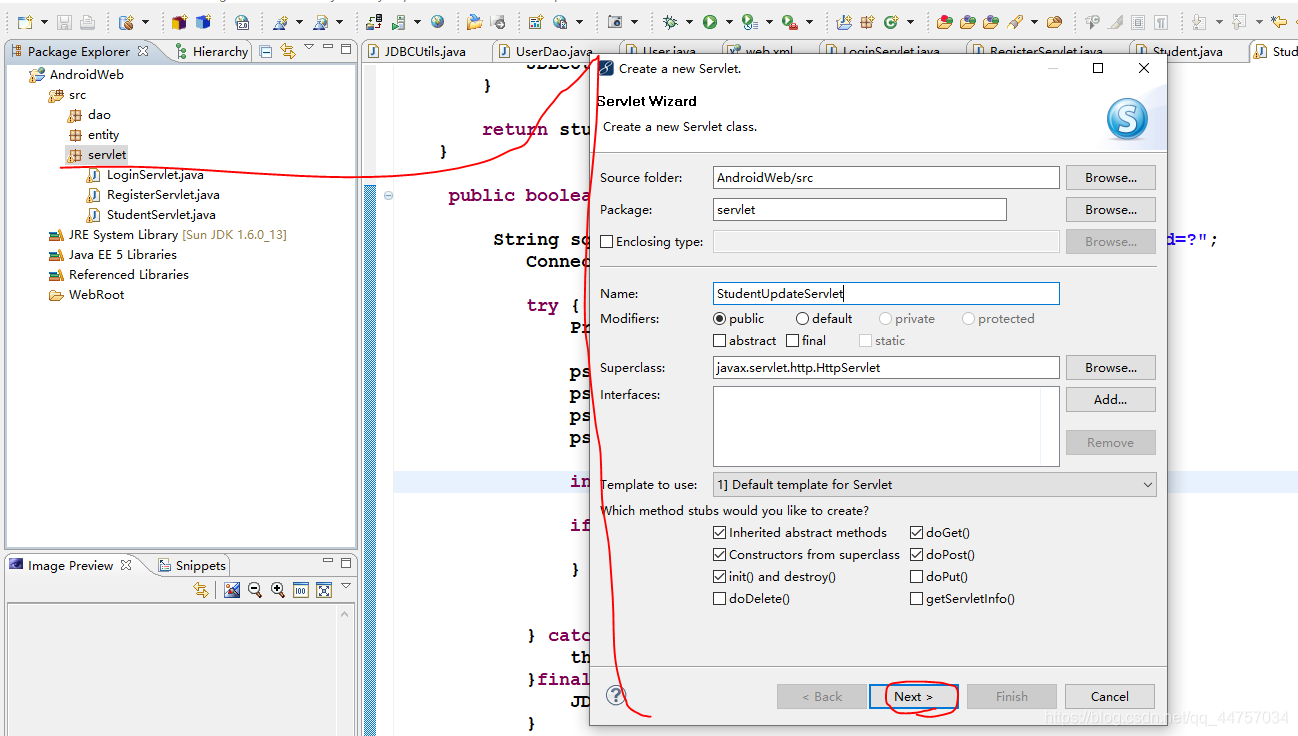
完善StudentUpdateServlet
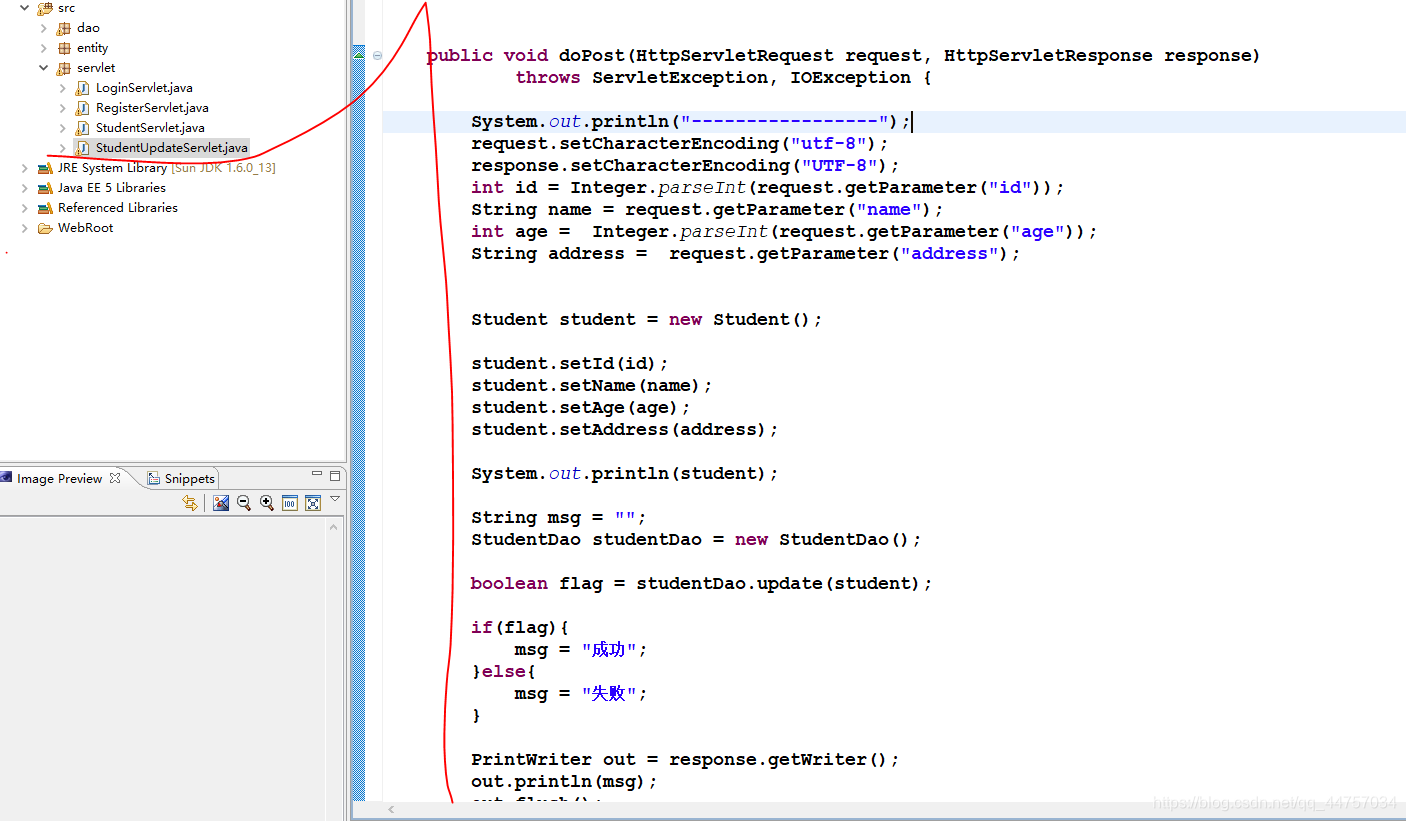
public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println(“-----------------”);
request.setCharacterEncoding(“utf-8”);
response.setCharacterEncoding(“UTF-8”);
int id = Integer.parseInt(request.getParameter(“id”));
String name = request.getParameter(“name”);
int age = Integer.parseInt(request.getParameter(“age”));
String address = request.getParameter(“address”);
Student student = new Student();
student.setId(id);
student.setName(name);
student.setAge(age);
student.setAddress(address);
String msg = “”;
StudentDao studentDao = new StudentDao();
boolean flag = studentDao.update(student);
if(flag){
msg = “成功”;
}else{
msg = “失败”;
}
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
out.println(msg);
out.flush();
out.close();
}
(三)安卓端
最后
2020年在匆匆忙忙慌慌乱乱中就这么度过了,我们迎来了新一年,互联网的发展如此之快,技术日新月异,更新迭代成为了这个时代的代名词,坚持下来的技术体系会越来越健壮,JVM作为如今是跳槽大厂必备的技能,如果你还没掌握,更别提之后更新的新技术了。

更多JVM面试整理:

meter(“address”);
Student student = new Student();
student.setId(id);
student.setName(name);
student.setAge(age);
student.setAddress(address);
String msg = “”;
StudentDao studentDao = new StudentDao();
boolean flag = studentDao.update(student);
if(flag){
msg = “成功”;
}else{
msg = “失败”;
}
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
out.println(msg);
out.flush();
out.close();
}
(三)安卓端
最后
2020年在匆匆忙忙慌慌乱乱中就这么度过了,我们迎来了新一年,互联网的发展如此之快,技术日新月异,更新迭代成为了这个时代的代名词,坚持下来的技术体系会越来越健壮,JVM作为如今是跳槽大厂必备的技能,如果你还没掌握,更别提之后更新的新技术了。
[外链图片转存中…(img-zlvW9iEh-1715807317045)]
更多JVM面试整理:
[外链图片转存中…(img-ae6aT4DT-1715807317045)]





















 459
459

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








