reverse_complement() - 对序列取反补
seq = 'ATCG'
rc_seq = reverse_complement(seq)
translate() - 将DNA序列翻译成氨基酸序列
dna_seq = 'ATGCTGAACTG'
aa_seq = translate(dna_seq)
gc_content() - 计算序列的GC含量
seq = 'ATCGATCG'
gc = gc_content(seq)
subsample() - 对序列进行子抽样
input = fastq('input.fastq.gz')
subsampled = subsample(input, fraction=0.1)
merge() - 合并两个或多个序列文件
input1 = fastq('input1.fastq.gz')
input2 = fastq('input2.fastq.gz')
merged = merge(input1, input2)
average_quality() - 计算序列的平均质量
input = fastq('input.fastq.gz')
avg_qual = average_quality(input)
trim_polya() - 对序列进行poly(A)尾修剪
input = fastq('input.fastq.gz')
trimmed = trim_polya(input)
annotate() - 对序列进行注释
input = ... # 一些序列
annotation = ... # 一些注释信息
annotated = annotate(input, with=annotation)
to_fasta() - 将序列文件转换为FASTA格式
input = fastq('input.fastq.gz')
fasta = to_fasta(input)
to_fastq() - 将序列文件转换为FASTQ格式
input = fasta('input.fasta')
fastq = to_fastq(input)
reverse() - 对序列进行反转
seq = 'ATCG'
reversed_seq = reverse(seq)
complement() - 对序列进行互补
seq = 'ATCG'
comp_seq = complement(seq)
is_paired() - 判断序列是否成对出现
input = fastq('input.fastq.gz')
paired = is_paired(input)
pair() - 对成对的序列进行配对
input = fastq('input.fastq.gz')
paired = pair(input)
is_unique() - 判断序列是否唯一
input = fastq('input.fastq.gz')
unique = is_unique(input)
unique_only() - 选择唯一的序列
input = fastq('input.fastq.gz')
unique = unique_only(input)
random() - 生成一个随机数
rand_num = random()
shuffle() - 对序列进行随机重排
input = fastq('input.fastq.gz')
shuffled = shuffle(input)
annotate_gff() - 对序列进行基因组注释
input = fasta('input.fasta')
gff_file = 'annotation.gff'
annotated = annotate_gff(input, gff_file)
align() - 对序列进行局部或全局比对
input = fasta('input.fasta')
ref_seq = fasta('reference.fasta')
alignment = align(input, ref_seq)
align_sam() - 对序列进行SAM格式比对
input = fasta('input.fasta')
sam_file = 'alignment.sam'
aligned = align_sam(input, sam_file)
align_bam() - 对序列进行BAM格式比对
input = fasta('input.fasta')
bam_file = 'alignment.bam'
aligned = align_bam(input, bam_file)
compress() - 对文件进行压缩
input_file = 'input.txt'
compressed_file = compress(input_file, format='gzip')
decompress() - 对文件进行解压缩
compressed_file = 'input.gz'
decompressed_file = decompress(compressed_file)
distance() - 计算两个序列之间的距离
seq1 = 'ATCG'
seq2 = 'AGCG'
dist = distance(seq1, seq2)
intersect() - 计算两个序列集合的交集
input1 = fasta('input1.fasta')
input2 = fasta('input2.fasta')
intersected = intersect(input1, input2)
union() - 计算两个序列集合的并集
input1 = fasta('input1.fasta')
input2 = fasta('input2.fasta')
unioned = union(input1, input2)
subtract() - 计算两个序列集合的差集
input1 = fasta('input1.fasta')
input2 = fasta('input2.fasta')
subtracted = subtract(input1, input2)
average() - 计算一组数字的平均值
data = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
avg = average(data)
maximum() - 计算一组数字的最大值
data = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
max_val = maximum(data)
minimum() - 计算一组数字的最小值
data = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
min_val = minimum(data)
standard_deviation() - 计算一组数字的标准差
data
常见生信分析代码片段
下面是常用的NGless功能函数处理宏基因组数据的代码片段:
从FASTQ文件中过滤低质量的reads,并将结果输出到新文件中:
ngless "1.0"
input = fastq('input.fq')
preprocess(input, phred=33) using |read|:
if read.avg_qual < 20:
discard
input | keep | add_sequence_length | sum | write(`filtered.fq`, compression=Fastq)
根据OTU表将reads映射到参考数据库,并生成OTU表:
ngless "1.0"
input = fastq('input.fq')
reference = fasta('ref.fasta')
mapped = map(input, reference, exact=False, sensitive=True)
otu_table(mapped, reference) | write(`otu_table.txt`, format="csv")
对OTU表进行物种注释,并生成注释表:
ngless "1.0"
otu_table = csv('otu_table.csv')
annotation_db = csv('annotation_db.csv')
annotated = annotate_species(otu_table, annotation_db)
annotated | write(`annotated_otu_table.csv`, format="csv")
根据OTU丰度信息生成热图:
ngless "1.0"
otu_table = csv('otu_table.csv')
heatmap(otu_table) | write(`heatmap.png`, format="png")
对样品进行稀释,并生成稀释后的OTU表:
ngless "1.0"
otu_table = csv('otu_table.csv')
diluted = dilute(otu_table, factor=10)
diluted | write(`diluted_otu_table.csv`, format="csv")
对OTU表进行组间差异分析,使用差异显著性检验方法:
ngless "1.0"
otu_table = csv('otu_table.csv')
groups = csv('groups.csv')
differential(abundance(otu_table), groups) | write(`differential_analysis.csv`, format="csv")
对样品进行Beta多样性分析,并生成PCoA图:
ngless "1.0"
otu_table = csv('otu_table.csv')
pcoa_table = pcoa(otu_table)
pcoa_table | plot(`pcoa.png`, format="png")
对OTU表进行功能注释,并生成功能注释表:
ngless "1.0"
otu_table = csv('otu_table.csv')
gene_db = csv('gene_db.csv')
annotated = annotate_functions(otu_table, gene_db)
annotated | write(`annotated_otu_table.csv`, format="csv")
根据OTU表进行物种多样性分析,并生成物种多样性指数表:
ngless "1.0"
otu_table = csv('otu_table.csv')
diversity_indices(otu_table) | write(`diversity_indices.csv`, format="csv")
对样品进行Alpha多样性分析,并生成稀释曲线图:
ngless "1.0"
otu_table = csv('otu_table.csv')
alpha_table = alpha_diversity(otu_table)
alpha_table | plot(`alpha_diversity.png`, format="png")
对OTU表进行物种丰度分析,并生成物种丰度柱状图:
ngless "1.0"
otu_table = csv('otu_table.csv')
species_abundance(otu_table) | plot(`species_abundance.png`, format="png")
根据OTU表进行共生网络分析,并生成共生网络图:
ngless "1.0"
otu_table = csv('otu_table.csv')
cooccurrence_network(otu_table) | plot(`cooccurrence_network.png`, format="png")
对样品进行微生物组成分析,并生成样品组成饼图:
ngless "1.0"
otu_table = csv('otu_table.csv')
sample_composition(otu_table) | plot(`sample_composition.png`, format="png")
对OTU表进行代谢通路分析,并生成代谢通路富集柱状图:
ngless "1.0"
otu_table = csv('otu_table.csv')
pathway_db = csv('pathway_db.csv')
enriched_pathways(otu_table, pathway_db) | plot(`enriched_pathways.png`, format="png")
对OTU表进行进化分析,并生成进化树:
ngless "1.0"
otu_table = csv('otu_table.csv')
evolutionary_analysis(otu_table) | plot(`evolutionary_tree.png`, format="png")
将多个OTU表进行合并:
ngless "1.0"
otu_table1 = csv('otu_table1.csv')
otu_table2 = csv('otu_table2.csv')
combined = merge(otu_table1, otu_table2)
combined | write(`merged_otu_table.csv`, format="csv")
对OTU表进行样品分类,并生成分类树:
ngless "1.0"
otu_table = csv('otu_table.csv')
taxonomy_tree(otu_table) | plot(`taxonomy_tree.png`, format="png")
根据OTU表进行功能富集分析,并生成功能富集柱状图:
ngless "1.0"
otu_table = csv('otu_table.csv')
gene_set_db = csv('gene_set_db.csv')
enriched_functions(otu_table, gene_set_db) | plot(`enriched_functions.png`, format="png")
对样品进行Gamma多样性分析,并生成Gamma多样性曲线:
ngless "1.0"
otu_table = csv('otu_table.csv')
gamma_table = gamma_diversity(otu_table)
gamma_table | plot(`gamma_diversity.png`, format="png")
对OTU表进行进化树构建,并生成进化树:
ngless "1.0"
otu_table = csv('otu_table.csv')
phylogenetic_tree(otu_table) | plot(`phylogenetic_tree.png`, format="png")
请注意,这些代码片段仅为示例,并不一定适用于所有NGless版本和数据集。在实际使用时,请根据具体情况进行修改和调整。
NGLess的使用示例
人类肠道宏基因组学的功能和分类分析
步骤概述:
- 准备数据:获取并准备用于分析的原始测序数据。
- 质量控制和过滤:对原始数据进行质量控制、去除低质量序列和去除宿主DNA等。
- 人类肠道宏基因组分类:对数据进行分类,识别宿主肠道微生物。
- 功能注释:对宏基因组数据进行功能注释,识别和分析肠道微生物的功能特征。
详细步骤:
步骤 1: 准备数据
- 下载并准备用于肠道宏基因组学的原始测序数据,例如来自人类肠道样本的元组装数据(metagenomic sequencing data)。
步骤 2: 质量控制和过滤
- 使用 NGLess 进行质量控制和过滤,例如使用 FastQC 进行质量评估,然后使用 NGLess 进行质量过滤:
-
ngless 'input = fastq(‘data.fastq.gz’)
preprocess(input, keep_singles=False) using |read|:
if len(read) < 45:
discard;
elif count(N) > 0.1:
discard;
else:
keep;
##### 步骤 3: 人类肠道宏基因组分类
* 使用 NGLess 和相应的数据库进行宏基因组分类。示例中使用 Silva 数据库进行分类:
ngless ‘input = fastq(‘filtered_data.fastq.gz’)
preprocessed = preprocess(input)
m1 = map(preprocessed, reference=‘silva’)’
##### 步骤 4: 功能注释
* 对宏基因组数据进行功能注释,例如使用 Diamond 或者 BLAST 进行序列比对,并使用相应的数据库(例如KEGG、COG、GO等)进行功能注释:
ngless ‘input = fastq(‘filtered_data.fastq.gz’)
preprocessed = preprocess(input)
m1 = map(preprocessed, reference=‘silva’)
annotated = annotate(m1, data=‘kegg’)’
#### 注意事项:
* 这些是一些基本步骤,具体的分析流程和参数设置可能会因实验设计和所使用的数据库而有所不同。
* 示例代码中使用了 NGLess 的 DSL 语法,实际使用时可能需要根据具体的数据和数据库进行调整和优化。
* 在执行代码之前,请确保您已了解数据处理和分析的需求,并正确设置参数以获得最佳结果。
#### 全流程脚本
ngless “1.0”
import “parallel” version “0.6”
import “mocat” version “0.0”
import “motus” version “0.1”
import “igc” version “0.0”
samples = readlines(‘igc.demo.short’)
sample = lock1(samples)
input = load_fastq_directory(sample)
input = preprocess(input, keep_singles=False) using |read|:
read = substrim(read, min_quality=25)
if len(read) < 45:
discard
mapped = map(input, reference=‘hg19’)
mapped = select(mapped) using |mr|:
mr = mr.filter(min_match_size=45, min_identity_pc=90, action={unmatch})
if mr.flag({mapped}):
discard
input = as_reads(mapped)
mapped = map(input, reference=‘igc’, mode_all=True)
counts = count(mapped,
features=[‘KEGG_ko’, ‘eggNOG_OG’],
normalization={scaled})
collect(counts,
current=sample,
allneeded=samples,
ofile=‘igc.profiles.txt’)
mapped = map(input, reference=‘motus’, mode_all=True)
counted = count(mapped, features=[‘gene’], multiple={dist1})
motus_table = motus(counted)
collect(motus_table,
current=sample,
allneeded=samples,
ofile=‘motus-counts.txt’)
## 案例分析脚本demo
[https://ngless.embl.de/\_static/gut-metagenomics-tutorial-presentation/scripts/1\_preproc.ngl]( )
ngless “0.0”
import “mocat” version “0.0”
input = load_mocat_sample(‘SAMN05615097.short’)
preprocess(input, keep_singles=False) using |read|:
read = substrim(read, min_quality=25)
if len(read) < 45:
discard
write(input, ofile=‘preproc.fq.gz’)
[https://ngless.embl.de/\_static/gut-metagenomics-tutorial-presentation/scripts/2\_map\_hg19.ngl]( )
ngless “0.0”
import “mocat” version “0.0”
input = load_mocat_sample(‘SAMN05615097.short’)
preprocess(input, keep_singles=False) using |read|:
read = substrim(read, min_quality=25)
if len(read) < 45:
discard
mapped = map(input, reference=‘hg19’)
mapped = select(mapped) using |mr|:
mr = mr.filter(min_match_size=45, min_identity_pc=90, action={unmatch})
if mr.flag({mapped}):
discard
write(mapped, ofile=‘mapped.bam’)
[https://ngless.embl.de/\_static/gut-metagenomics-tutorial-presentation/scripts/3\_taxprofile.ngl]( )
ngless “0.0”
import “mocat” version “0.0”
import “motus” version “0.1”
import “specI” version “0.1”
input = load_mocat_sample(‘SAMN05615097.short’)
preprocess(input, keep_singles=False) using |read|:
read = substrim(read, min_quality=25)
if len(read) < 45:
discard
mapped = map(input, reference=‘hg19’)
mapped = select(mapped) using |mr|:
mr = mr.filter(min_match_size=45, min_identity_pc=90, action={unmatch})
if mr.flag({mapped}):
discard
input = as_reads(mapped)
mapped = map(input, reference=‘motus’, mode_all=True)
mapped = select(mapped) using |mr|:
mr = mr.filter(min_match_size=45, min_identity_pc=97, action={drop})
if not mr.flag({mapped}):
discard
counted = count(mapped, features=[‘gene’], multiple={dist1})
write(motus(counted),
ofile=‘motus.counts.txt’)
input = as_reads(mapped)
mapped = map(input, reference=‘refmg’)
mapped = select(mapped) using |mr|:
mr = mr.filter(min_match_size=45, min_identity_pc=97, action={drop})
if not mr.flag({mapped}):
discard
write(count(mapped,
features=[‘species’],
include_minus1=True),
ofile=‘species.raw.counts.txt’)
[https://ngless.embl.de/\_static/gut-metagenomics-tutorial-presentation/scripts/4\_parallel.ngl]( )
ngless “0.0”
import “parallel” version “0.0”
import “mocat” version “0.0”
import “motus” version “0.1”
import “specI” version “0.1”
samples = readlines(‘igc.demo.short’)
sample = lock1(samples)
input = load_mocat_sample(sample)
preprocess(input, keep_singles=False) using |read|:
read = substrim(read, min_quality=25)
if len(read) < 45:
discard
mapped = map(input, reference=‘hg19’)
mapped = select(mapped) using |mr|:
mr = mr.filter(min_match_size=45, min_identity_pc=90, action={unmatch})
if mr.flag({mapped}):
discard
input = as_reads(mapped)
mapped = map(input, reference=‘motus’, mode_all=True)
counted = count(mapped, features=[‘gene’], multiple={dist1})
motus_table = motus(counted)
collect(motus_table,
current=sample,
allneeded=samples,
ofile=‘motus-counts.txt’)
input = as_reads(mapped)
mapped = map(input, reference=‘refmg’)
mapped = select(mapped) using |mr|:
mr = mr.filter(min_match_size=45, min_identity_pc=97, action={drop})
if not mr.flag({mapped}):
discard
collect(count(mapped,
features=[‘species’],
include_minus1=True),
current=sample,
allneeded=samples,
ofile=‘species.raw.counts.txt’)
[https://ngless.embl.de/\_static/gut-metagenomics-tutorial-presentation/scripts/5\_w\_igc.ngl]( )
ngless “0.0”
import “parallel” version “0.0”
import “mocat” version “0.0”
import “motus” version “0.1”
import “igc” version “0.0”
import “specI” version “0.1”
samples = readlines(‘igc.demo.short’)
sample = lock1(samples)
input = load_mocat_sample(sample)
preprocess(input, keep_singles=False) using |read|:
read = substrim(read, min_quality=25)
if len(read) < 45:
discard
mapped = map(input, reference=‘hg19’)
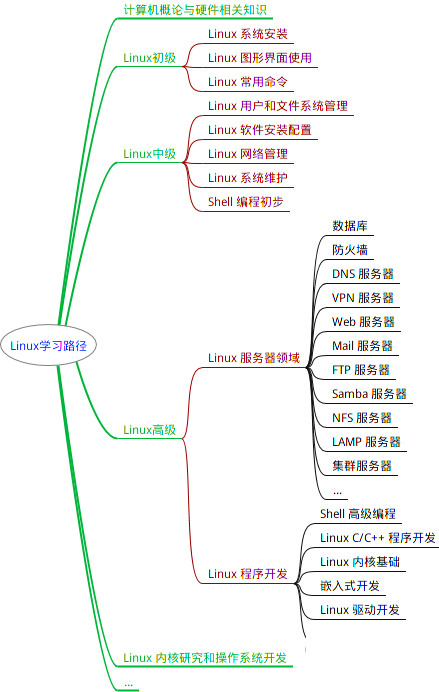
最全的Linux教程,Linux从入门到精通
======================
-
linux从入门到精通(第2版)
-
Linux系统移植
-
Linux驱动开发入门与实战
-
LINUX 系统移植 第2版
-
Linux开源网络全栈详解 从DPDK到OpenFlow

第一份《Linux从入门到精通》466页
====================
内容简介
====
本书是获得了很多读者好评的Linux经典畅销书**《Linux从入门到精通》的第2版**。本书第1版出版后曾经多次印刷,并被51CTO读书频道评为“最受读者喜爱的原创IT技术图书奖”。本书第﹖版以最新的Ubuntu 12.04为版本,循序渐进地向读者介绍了Linux 的基础应用、系统管理、网络应用、娱乐和办公、程序开发、服务器配置、系统安全等。本书附带1张光盘,内容为本书配套多媒体教学视频。另外,本书还为读者提供了大量的Linux学习资料和Ubuntu安装镜像文件,供读者免费下载。

本书适合广大Linux初中级用户、开源软件爱好者和大专院校的学生阅读,同时也非常适合准备从事Linux平台开发的各类人员。
需要《Linux入门到精通》、《linux系统移植》、《Linux驱动开发入门实战》、《Linux开源网络全栈》电子书籍及教程的工程师朋友们劳烦您转发+评论
























 5万+
5万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








