(1)thymeleaf模板引擎既能用于web环境下,也能用于非web环境下,在非web环境下,它能直接显示模板上的静态数据,在web环境下,它能像jsp一样从后台接收数据并替换掉模板上的静态数据。
(2)thymeleaf是基于html的,以html标签为载体,thymeleaf要寄托在html的标签下实现对数据的展示。
2.2使用
Thymeleaf的使用非常简单,只需要把我们的html页面放在类路径下的templates下,thymeleaf就可以帮我们自动渲染了。
(1)导入依赖
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf
(2)在resources下建立一个目录templates
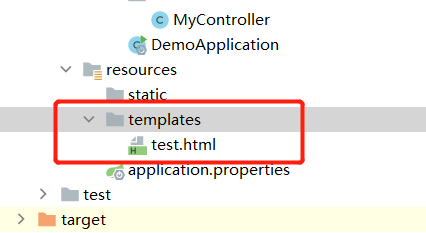
(3)编写test.html
一心同学
(4)编写 Controller类
@Controller
public class MyController {
@RequestMapping(“/test”)
public String test1(){
return “test”;
}
}
(5)运行
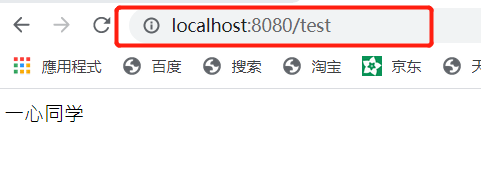
测试成功!说明成功访问到了templates目录。
3.Thymeleaf语法
=============
由于Thymeleaf的语法太多了,一心同学只在这里讲几个常见的语法,对于其它的语法可以前往官网进行查阅
官网:Thymeleaf
常见的语法
- ${}: 标准变量表达式
- 选择变量表达式 *{} 和 th:object
- 链接(URL)表达式 和 th:href
- th标签之th:action
- th标签之th:each
- th标签之th:switch/th:case
前提:
导入thymeleaf的名称空间
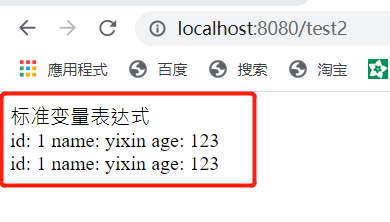
3.1 ${}: 标准变量表达式
Controller:
@RequestMapping(“/test2”)
public String test2(Model model) {
model.addAttribute(“msg”, “标准变量表达式”);
Blog blog=new Blog();
blog.setId(1);
blog.setName(“yixin”);
blog.setPwd(“123”);
model.addAttribute(“blog”,blog);
return “test”;
}
test.html:
一心同学
span默认文本内容
id: xx
name: xxx
pwd: xxx
运行:

3.2 选择变量表达式 *{} 和 th:object
*{}: 选择变量表达式
标准变量表达式和选择变量表达式可以混合使用 ;
先用 th:object来绑定 blog 对象, 然后用 * 来代表这个 blog对象
span默认文本内容
id: xxx
name: xxx
age: xxx
id: xxx
name: xxx
age: xxx
运行:
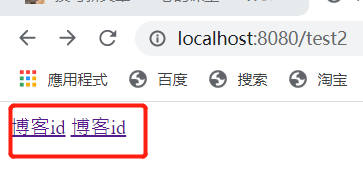
3.3 链接(URL)表达式 和 th:href
使用说明:
URL表达式
语法:@{…}
URL表达式可用于
(1)绝对URL,比如:
(2)相对URL,相对于页面,比如:
(3)相对于URL,相对于项目上下文,比如:
查看(项目的上下文名会被自动添加)
Controller类:
@RequestMapping(“/test2”)
public String test2(Model model) {
model.addAttribute(“msg”, “标准变量表达式”);
Blog blog=new Blog();
blog.setId(1);
blog.setName(“yixin”);
blog.setPwd(“123”);
model.addAttribute(“blog”,blog);
return “test3”;
}
@RequestMapping(“/blog”)
@ResponseBody
public String getUserById(Integer id) {
System.out.println(“id=” + id);
return “id=” + id;
}
test3.html:
运行:
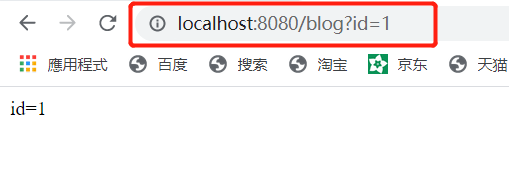
3.4 th标签之th:action
Controller类:
@RequestMapping(“/test2”)
public String test2(Model model) {
model.addAttribute(“msg”, “标准变量表达式”);
Blog blog=new Blog();
blog.setId(1);
blog.setName(“yixin”);
blog.setPwd(“123”);
model.addAttribute(“blog”,blog);
return “test4”;
}
@RequestMapping(“/blog”)
@ResponseBody
public String getUserById(Integer id) {
System.out.println(“id=” + id);
return “id=” + id;
}
test4.html:
id:
运行:
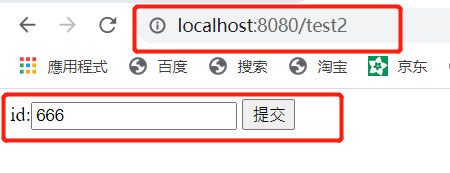
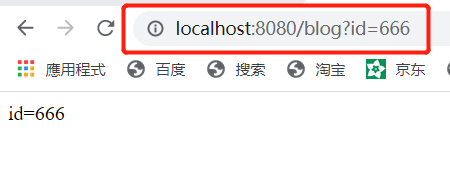
3.5 th标签之th:each
Controller类:
@RequestMapping(“/test2”)
public String test2(Model model) {
model.addAttribute(“msg”, “标准变量表达式”);
Blog blog=new Blog();
blog.setId(1);
blog.setName(“yixin”);
blog.setPwd(“123”);
model.addAttribute(“blog”,blog);
return “test4”;
}
@RequestMapping(“/blogList”)
public String hello(Model model) {
List blogList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++) {
Blog blog=new Blog();
blog.setId(i);
blog.setPwd(“abcd”+i);
blog.setName(“一心”+i);
blogList.add(blog);
}
model.addAttribute(“blogList”, blogList);
return “test5”;
}
test5.html:
xxx
xxx
xxx
运行:
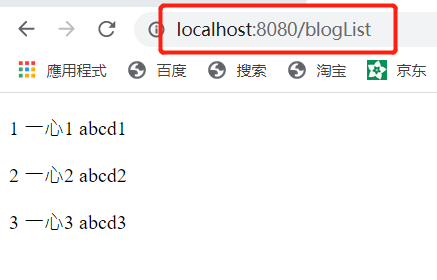
3.6 th标签之th:switch/th:case
Controller类:
@RequestMapping(“/test2”)
public String test2(Model model) {
model.addAttribute(“msg”, “标准变量表达式”);
Blog blog=new Blog();
blog.setId(1);
blog.setName(“yixin”);
blog.setPwd(“123”);
model.addAttribute(“blog”,blog);
return “test6”;
}
test6.html:
























 664
664

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








