自定义异常
在异常处理——上这篇我们提到了所有异常都派生自exception类,且说明了代码中使用了try-catch-throw关键字但未添加exception头文件的原因【添:未用到what()方法】。
这篇我们先探讨的是在添加exception头文件的情况下进行继承和重载exception类来定义新的异常(比如自己加的限定条件与超过限定条件的措施)。
what() 是一个由exception类提供的公共方法,用于返回异常原因。
具体步骤:
- .h文件中
添加exception头文件
自定义类并继承exception
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
#include<exception>
using namespace std;
class Exception :public exception {
public:
const char* what() const throw(){
//第一个const: 返回指向常量字符串的指针
//第二个const: 成员函数不会修改对象状态
// throw(): 小括号里面是空的,表示该函数不会抛出任何异常
return"my test exception";
}
};
int add(int v1, int v2);
void test02();
- .cpp中
调整add方法并明确异常点及对应反馈
补充异常捕捉细节
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
#include"myFunc.h"
using namespace std;
int add(int v1, int v2) {
if (v1 > 0) { //v1>0就抛出自定义异常
Exception myex;
throw myex;
}
return v1 + v2;
}
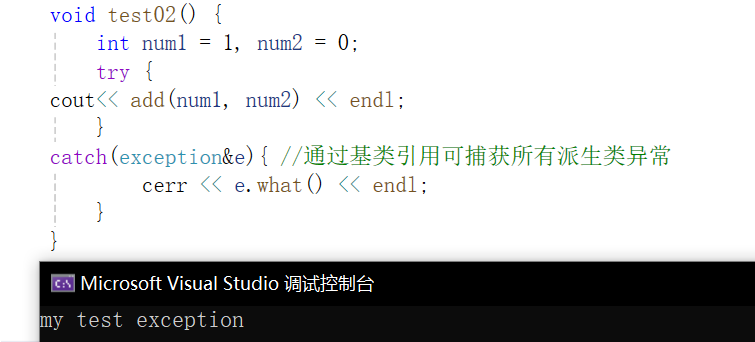
void test02() {
int num1 = 1, num2 = 0;
try {
cout<< add(num1, num2) << endl;
}
catch(exception&e){ //通过基类引用可捕获所有派生类异常
cerr << e.what() << endl;
}
}
int main() {
test02();
return 0;
}
练习

#pragma once
#include<iostream>
#include"myFunc.h"
using namespace std;
enum index{underflow,overflow};
int arr_index(int*arr,int n,int index) {
if (index < 0)throw underflow;
if (index > n - 1)throw overflow;
return arr[index];
}
int test03() {
int *arr= new int[10];
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
arr[i] = i;
}
try {
cout << arr_index(arr, 10,-2) << endl;
}
catch (index e) {
if (e == underflow) cout << "index underflow!" << endl;
if (e == overflow) cout << "index overflow!" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
int main() {
test03();
return 0;
}
嵌套类与局部类
嵌套类
嵌套类是定义在另一个类内部的类,根据是否使用static修饰符分为静态嵌套类和非静态嵌套类(即内部类)。
- 静态嵌套类:
使用static修饰,与外部类无直接关联,不能直接访问外部类的非静态成员。
实例化时无需依赖外部类对象。 - 非静态嵌套类(内部类):
可访问外部类的所有成员(包括私有成员),隐含持有外部类对象的引用。
实例化需通过外部类对象(以下实现为非静态嵌套类) - 特点:

class outClass {
public:
class innerClass {
public:
void func();
};
public:
outClass::innerClass obj;
void func() {
cout << "outClass func()" << endl; //外部
obj.func(); //内部
}
};
void outClass::innerClass::func() {
cout << "innerClass func()" << endl; //内部
}
局部类
局部类是在代码块(如方法、循环、条件语句)内部定义的类,作用域仅限于该代码块。
- 特点:
定义在方法或作用域内,仅在该块中可见。
可访问外部类的成员,但若定义在方法中,只能访问方法内的局部变量。
常用于实现特定接口或抽象类的临时实现。
void func() {
class localClass { //局部类
public:
int num=0;
void setNum(int n) {
num = n;
}
void showNum() {
cout << "num=" << num << endl;
}
};
localClass c;
c.setNum(1);
c.showNum();
}
调用
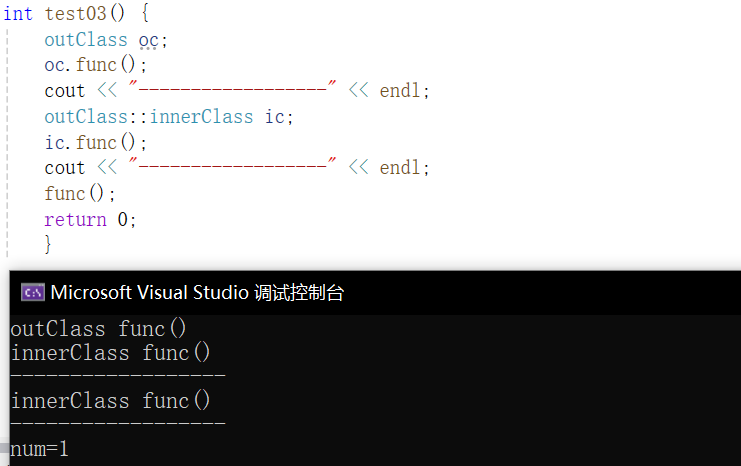
int test03() {
outClass oc;
oc.func();
cout << "------------------" << endl;
outClass::innerClass ic;
ic.func();
cout << "------------------" << endl;
func();
return 0;
}
int main() {
test03();
return 0;
}
梳理总结

























 1288
1288

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








