目录
1.指针
1.1指针三要素:
- 运算符&:可以取对象或基本类型变量的地址。
- 运算符*:可以获取指针指向的内容
int main(){
//指针三要素
int num = 10;
int *p1 = NULL , *p2 = NULL; //1.声明指针变量,必须初始化(NULL=整数0)
p1 = # //2.取num地址,赋值给指针
p2 = #
cout << "p1的值:"<<p1 <<endl;
cout<<"num = "<<num<<endl;
*p1 = 20; //3.利用指针修改num的值
cout<<"num = "<<num<<endl;
*p2 = 50; //利用指针修改num的值
cout<<"num = "<<num<<endl;
cout << "p1的值:"<<p1 <<endl;
cout << "p2的值:"<<*p2 <<endl;
return 0;
}
1.2修饰结构体struct
指针指向结构体:
- p->member
- (*p).member

Student zhaoyan = { "yan",2000,true}; //实例化结构体
Student *pStu = &zhaoyan; //取这个结构体的地址
strncpy(pStu->name,"Li",4); //将pStu->name修改为Li
pStu->born = 2021;
(*pStu).born = 2002;
pStu->male = false;
cout << zhaoyan.name << " was born in " << zhaoyan.born
<< ". Gender: " << (zhaoyan.male ? "male" : "female") << endl;
//打印指针地址
printf("address of zhaoyan: %p\n",pStu); //C style p:输出指针地址
cout<< "addres of zhaoyan: "<< pStu <<endl; //C++ style
cout<< "addres of zhaoyan: "<< &zhaoyan <<endl; //C++ style
cout<< "addres of zhaoyan.born: "<< &(zhaoyan.born) <<endl; //C++ style
cout<<"sizeof(pStu):" << sizeof(pStu) <<endl;
return 0;1.3 Pointers of Pointers
指针也是变量,也有地址:任何指针变量都占4个字节
int num = 10;
int *p = #
int **pp = &p; //指针的指针
*(*pp) =20;
cout<< "num=:"<<num<<endl;
return 0;1.4constant修饰 pointer
int main() { int num = 1; int another = 2; //You cannot change the value that p1 points to through p1 const int * p1 = # 指向的地址不变,即num不变 *p1 = 3; //error 不能利用指针修改指针指向的值 num = 3; //okay //You cannot change value of p2 (address) int * const p2 = # 内存里地址的值不变 ,即(*a)不变 *p2 = 3; //okay 只能通过指针修改指针指向的值 p2 = &another; //error //You can change neither const int* const p3 = # *p3 = 3; //error p3 = &another; // error return 0; }
例子:
为了函数求和等,传入只读的数
int foo(const char * p)
{
// the value that p points to cannot be changed
// play a trick?
char * p2 = p; //syntax error
//...
return 0;
}2指针和数组
2.1.数组的地址是连续的
Student stu[128];
Student *p0 = &stu[0]; //主要中括号的优先级比&高
Student *p1 = &stu[1];
Student *p2 = &stu[2];
Student *p3 = &stu[3];
printf("p0=%p\n",p0);
printf("p1=%p\n",p1);
printf("p2=%p\n",p2);
printf("p3=%p\n",p3);
//相同的操作
stu[1].born = 2000;
p1->born =2000;将数组名可以看作一个指针:
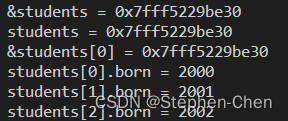
Student students[128]; printf("&students = %p\n", &students); printf("students = %p\n", students); printf("&students[0] = %p\n", &students[0]); Student * p = students; p[0].born = 2000; p[1].born = 2001; p[2].born = 2002; printf("students[0].born = %d\n", students[0].born); printf("students[1].born = %d\n", students[1].born); printf("students[2].born = %d\n", students[2].born);
2.2pointer arithmetic:指针的代数运算
- p+num or num+p points :指向数组p的第num个元素
- p - num :指向第-num个数组
给参数加()是为了优先级:更安全
//用宏来打印数组:宏是不能换行的
#define PRINT_ARRAY(array,n)\
for(int i=0;i<(n);i++)\ //最好加一个()防止优先级
cout<<"array["<<i<<"] = " <<(array)[idx] <<endl; 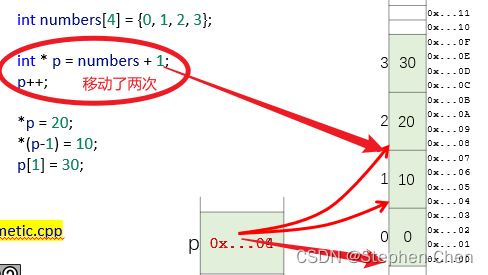
int main(){
int numbers[4] = {0,1,2,3};
PRINT_ARRAY(numbers,4);
int *p = numbers+1; //指向值为1的元素
p++; //指向值为2的元素
cout << "numbers = " << numbers << endl;
cout << "p = " << p << endl;
*p =20; //change 2 to 20
*(p-1) = 20; //change 1to 10
p[1] = 30; //change 3 to 30
PRINT_ARRAY(numbers,4);
return 0;
}注意:指针不能去了不该去的地方!这种错误最难找
小心越界:有时候会报错,有时不报错
int num = 0; int * p = # p[-1] = 2; //out of bound p[0] = 3; //okay *(p+1) = 4; //out of bound
2.3指针和数组的不同
- 数组是const指针
- sizeof运算符指向指针将返回地址的大小(4或8)
- 数组中所有元素的总大小可以通过sizeof运算符获得
int numbers[4] = {0, 1, 2, 3}; int * p = numbers; cout << sizeof(numbers) << endl; //4*sizeof(int) cout << sizeof(p) << endl; // 4 or 8 cout << sizeof(double *) << endl; // 4 or 8
3.内存分配:
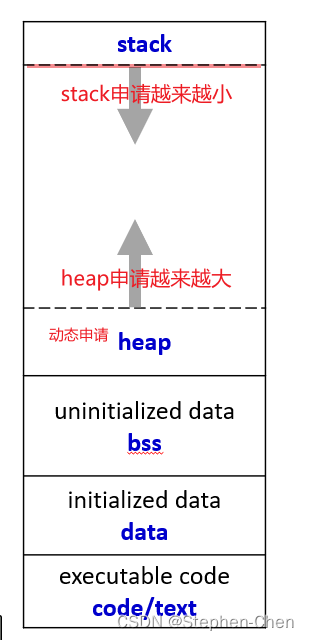
在head上可以申请很大的内存使用,
- 分配未初始化存储的大小字节 malloc函数:。
void* malloc(size_t size)
- 分配4个字节并将指针显式转换为(int*)
int *p1 = (int*)malloc(4)
- Question:
int *p1 = (int*)malloc(3) //申请3个字节,但是int*需要4个字节 //但是不会报错,因为内存至少分配16个字节
内存的释放:
- 必须显式释放动态分配的内存!:free函数
void free(void* ptr);
- Question:
p = (int *) malloc(4 * sizeof(int)); // ... p = (int *) malloc(8 * sizeof(int)); // ... free (p);
内存泄漏:
案例:
void foo() { int* p = (int*) malloc(sizeof(int)); return; }上述的函数没有释放就return,在内存就找不到申请指针p的地址;必须在函数内释放
内存泄漏: 没有变量保留第一个地址。内存管理系统不会自动解除分配。浪费内存!
int main()
{
int * p = NULL;
p = (int *) malloc(4 * sizeof(int));
// some statements
p = (int *) malloc(8 * sizeof(int));
// some statements
free (p);
// the first memory will not be freed
for(int i = 0; i < 1024; i++)
{
p = (int *) malloc(1024 * 1024 * 1024);
}
printf("End\n");
return 0;
}C++中申请释放内存:
new:
//allocate an int, default initializer (do nothing) int * p1 = new int; //allocate an int, initialized to 0 int * p2 = new int(); //allocate an int, initialized to 5 int * p3 = new int(5); //allocate an int, initialized to 0 int * p4 = new int{};//C++11 //allocate an int, initialized to 5 int * p5 = new int {5};//C++11 //allocate a Student object, default initializer Student * ps1 = new Student; //allocate a Student object, initialize the members Student * ps2 = new Student {"Yu", 2020, 1}; //C++11 //allocate 16 int, default initializer (do nothing) int * pa1 = new int[16]; //allocate 16 int, zero initialized int * pa2 = new int[16](); //allocate 16 int, zero initialized int * pa3 = new int[16]{}; //C++11 //allocate 16 int, the first 3 element are initialized to 1,2,3, the rest 0 int * pa4 = new int[16]{1,2,3}; //C++11 //allocate memory for 16 Student objects, default initializer Student * psa1 = new Student[16]; //allocate memory for 16 Student objects, the first two are explicitly initialized Student * psa2 = new Student[16]{{"Li", 2000,1}, {"Yu", 2001,1}}; //C++11 cout << psa2[1].name << endl; cout << psa2[1].born << endl;delete:
//deallocate memory delete p1; //deallocate memory delete ps1; //deallocate the memory of the array delete pa1; //deallocate the memory of the array delete []pa2; //deallocate the memory of the array, and call the destructor of the first element delete psa1; //deallocate the memory of the array, and call the destructors of all the elements //调所有的析构函数 delete []psa2; //最好用这种方法,删除数组结构体里所有内容






















 1948
1948











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








