本篇所用到的测试shapfile文件下载地址:
链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1S-TrFp_r8zyf_d0oBUeWqg
GeoTools英文帮助文档地址:
Geotools modules 18-SNAPSHOT API 【18英文帮助文档】
一、项目GeoTools模块的依赖添加
1.整个pom.xml
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.appleyk</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-web</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>Java-Web</name>
<!-- 继承官网最新父POM【假设当前项目不再继承其他POM】 -->
<!-- http://projects.spring.io/spring-boot/#quick-start -->
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>1.5.9.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<!-- 使用Java8,嘗試使用新特新【stream和lambda】 -->
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
<geotools.version>17.0</geotools.version>
<postgresql.version>42.1.4</postgresql.version>
</properties>
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>osgeo</id>
<name>Open Source Geospatial Foundation Repository</name>
<url>http://download.osgeo.org/webdav/geotools/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<!-- Starter POMs是可以包含到应用中的一个方便的依赖关系描述符集合 -->
<!-- 该Starters包含很多你搭建项目, 快速运行所需的依赖, 并提供一致的, 管理的传递依赖集。 -->
<!-- 大多数的web应用都使用spring-boot-starter-web模块进行快速搭建和运行。 -->
<!-- spring-boot-starter-web -->
<!-- 对全栈web开发的支持, 包括Tomcat和 spring-webmvc -->
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 添加Mybatis、Spring-Mybatis依赖 -->
<!-- mybatis-spring-boot-starter继承树那是相当全面 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.1.1</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 添加分页插件PageHelper的依赖 -->
<!-- pagehelper-spring-boot-starter的继承树那也是相当丰富啊 -->
<!-- 使用的是PageHelper5.0.1 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.pagehelper</groupId>
<artifactId>pagehelper-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.1.1</version>
</dependency>
<!-- jackson -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.2.41</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-core</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- MySql驱动依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Spring 单元测试 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- 添加热部署 devtools:监听文件变动 -->
<!-- 当Java文件改动时,Spring-boo会快速重新启动 -->
<!-- 最简单的测试,就是随便找一个文件Ctrl+S一下,就可以看到效果 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<!-- optional=true,依赖不会传递 -->
<!-- 本项目依赖devtools;若依赖本项目的其他项目想要使用devtools,需要重新引入 -->
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<!-- JUnit单元测试 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 添加GeoTools依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.geotools</groupId>
<artifactId>gt-shapefile</artifactId>
<version>${geotools.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.geotools</groupId>
<artifactId>gt-swing</artifactId>
<version>${geotools.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 添加geotools-jdbc -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.geotools.jdbc</groupId>
<artifactId>gt-jdbc-postgis</artifactId>
<version>${geotools.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- postgresql -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.postgresql</groupId>
<artifactId>postgresql</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/tk.mybatis/mapper-spring-boot-starter -->
<dependency>
<groupId>tk.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mapper-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.1.5</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<!-- Spring Boot包含一个Maven插件, 它可以将项目打包成一个可执行jar -->
<build>
<!-- 解决配置资源文件被漏掉问题 -->
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/resources</directory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.properties</include>
<include>**/*.xml</include>
</includes>
<filtering>false</filtering>
</resource>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/java</directory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.properties</include>
<include>**/*.xml</include>
</includes>
<filtering>false</filtering>
</resource>
</resources>
<plugins>
<!-- boot-maven插件 -->
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<includes>
<include>**/*Documentation.java</include>
</includes>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
<packaging>war</packaging>
</project>
2.其中比较重要的依赖如下:
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>osgeo</id>
<name>Open Source Geospatial Foundation Repository</name>
<url>http://download.osgeo.org/webdav/geotools/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<!-- JUnit单元测试 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 添加GeoTools依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.geotools</groupId>
<artifactId>gt-shapefile</artifactId>
<version>${geotools.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.geotools</groupId>
<artifactId>gt-swing</artifactId>
<version>${geotools.version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
现在最新的版本 好像是 18
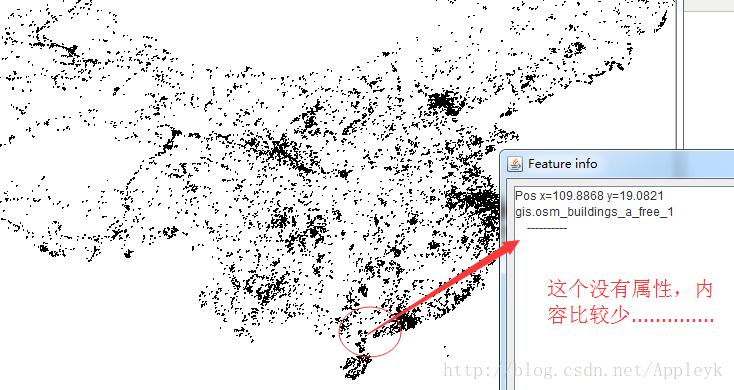
二、利用GeoTools工具包,打开一张shapfile文件,并显示和操作
(1)
(2)day01.java (这个放在单元测试里面,部分功能不能用)
package com.appleyk.geotools;
import java.io.File;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
import org.geotools.data.FileDataStore;
import org.geotools.data.FileDataStoreFinder;
import org.geotools.data.shapefile.ShapefileDataStore;
import org.geotools.data.simple.SimpleFeatureSource;
import org.geotools.map.FeatureLayer;
import org.geotools.map.Layer;
import org.geotools.map.MapContent;
import org.geotools.styling.SLD;
import org.geotools.styling.Style;
import org.geotools.swing.JMapFrame;
import org.geotools.swing.data.JFileDataStoreChooser;
/**
* 利用GeoTools工具包,打开一张shapfile文件,并显示
* @author yukun24@126.com
* @date 2017年12月6日-上午9:30:27
*/
public class day01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//1.数据源选择 shp扩展类型的
File file = JFileDataStoreChooser.showOpenFile("shp", null);
if(file==null){
return;
}
//2.得到打开的文件的数据源
FileDataStore store = FileDataStoreFinder.getDataStore(file);
//3.设置数据源的编码,防止中文乱码
((ShapefileDataStore)store).setCharset(Charset.forName("UTF-8"));
/**
* 使用FeatureSource管理要素数据
* 使用Style(SLD)管理样式
* 使用Layer管理显示
* 使用MapContent管理所有地图相关信息
*/
//4.以java对象的方式访问地理信息
SimpleFeatureSource featureSource = store.getFeatureSource();
//5.创建映射内容,并将我们的shapfile添加进去
MapContent mapContent = new MapContent();
//6.设置容器的标题
mapContent.setTitle("Appleyk's GeoTools");
//7.创建简单样式
Style style = SLD.createSimpleStyle(featureSource.getSchema());
//8.显示【shapfile地理信息+样式】
Layer layer = new FeatureLayer(featureSource, style);
//9.将显示添加进map容器
mapContent.addLayer(layer);
//10.窗体打开,高大尚的操作开始
JMapFrame.showMap(mapContent);
}
}
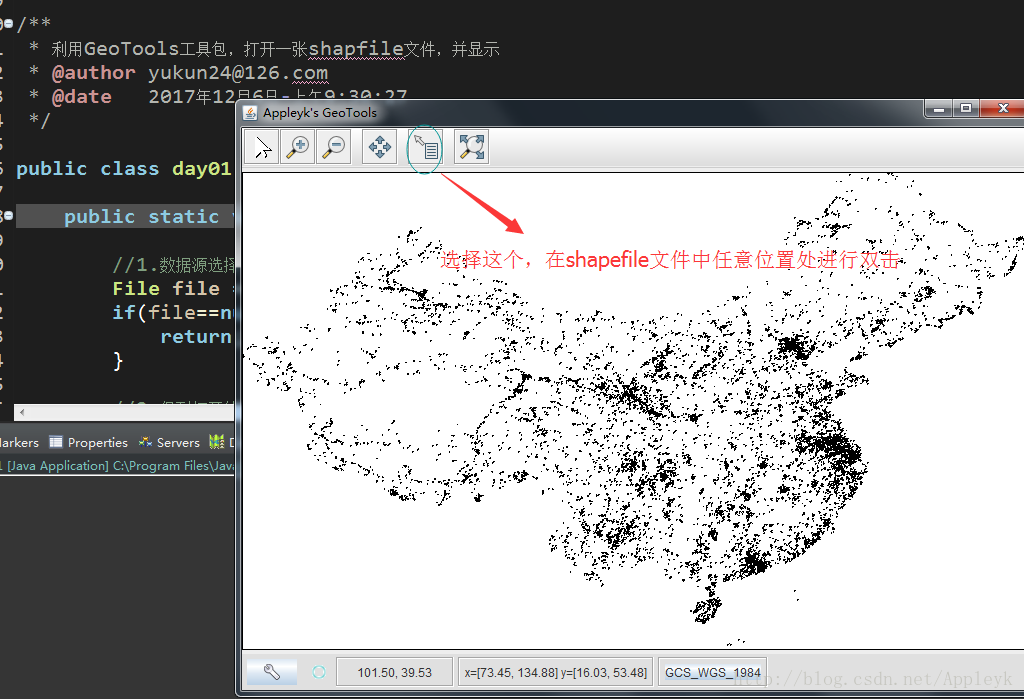
(3)运行main方法,效果如下
A.
B.
C.
三、利用GeoTools工具包,读写shapfile文件
开始放大招了,代码都是在测试单元里面写的,直接全部贴出
(1)
(3)GeoToolsTest01.java
package com.appleyk.geotools.learn;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import org.geotools.data.FeatureSource;
import org.geotools.data.FeatureWriter;
import org.geotools.data.Transaction;
import org.geotools.data.shapefile.ShapefileDataStore;
import org.geotools.data.shapefile.ShapefileDataStoreFactory;
import org.geotools.data.shapefile.dbf.DbaseFileHeader;
import org.geotools.data.shapefile.dbf.DbaseFileReader;
import org.geotools.data.shapefile.files.ShpFiles;
import org.geotools.data.shapefile.shp.ShapefileReader;
import org.geotools.data.simple.SimpleFeatureIterator;
import org.geotools.data.simple.SimpleFeatureSource;
import org.geotools.feature.FeatureCollection;
import org.geotools.feature.FeatureIterator;
import org.geotools.feature.simple.SimpleFeatureTypeBuilder;
import org.geotools.referencing.crs.DefaultGeographicCRS;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.opengis.feature.Property;
import org.opengis.feature.simple.SimpleFeature;
import org.opengis.feature.simple.SimpleFeatureType;
import com.vividsolutions.jts.geom.Coordinate;
import com.vividsolutions.jts.geom.GeometryFactory;
import com.vividsolutions.jts.geom.Point;
public class GeoToolsTest01 {
/**
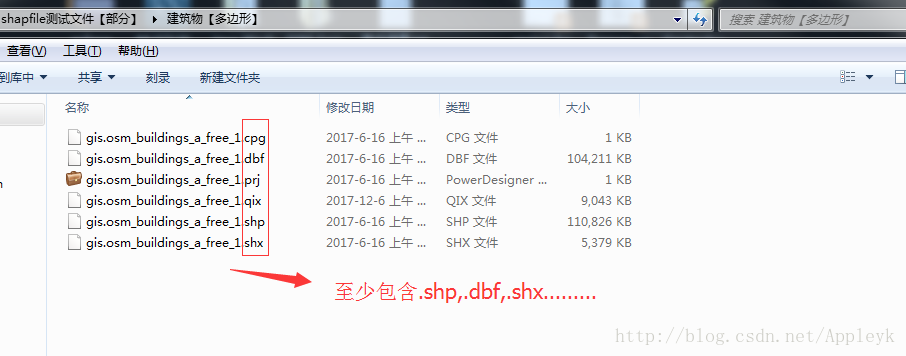
* shape格式文件最少包含3个文件,他们的后缀是:.shp, .dbf, .shx
.shp存储地理形状和位置信息
.dbf存储属性信息
.shx是索引文件
*/
//1.读DBF文件
@Test
public void ReadDBF() throws Exception{
String path = "E:\\china-latest-free\\gis.osm_pois_free_1.dbf";
//1.DbaseFileReader 用来读dbf文件
DbaseFileReader reader = null;
reader = new DbaseFileReader(new ShpFiles(path), true, Charset.forName("UTF-8"));
//2.从文件中获取标题
DbaseFileHeader header = reader.getHeader();
//3.得到标题的字段【域】有多少个
int numFileds = header.getNumFields();
System.out.println("字段【列】的个数:"+numFileds);
//先输出列名
for(int i=0;i<numFileds;i++){
System.out.print(header.getFieldName(i)+"\t");
}
System.out.println();
int stop = 0;
//4.迭代读取记录 只读取前30条
while(reader.hasNext()){
if(stop>30){
break;
}
//获取下一个记录【条目】
Object[] entry = reader.readEntry();
for(int i =0;i<numFileds;i++){
Object value = entry[i];
System.out.print(value+"\t");
}//end for
System.out.println();
stop++;
}//end while
if(reader!=null){
reader.close();
}
}
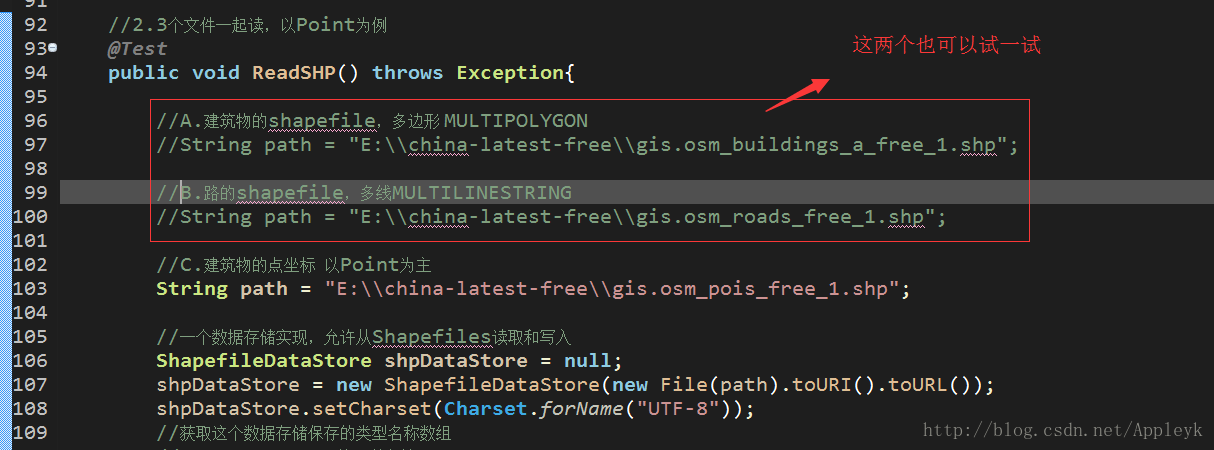
//2.3个文件一起读,以Point为例
@Test
public void ReadSHP() throws Exception{
//A.建筑物的shapefile,多边形 MULTIPOLYGON
//String path = "E:\\china-latest-free\\gis.osm_buildings_a_free_1.shp";
//B.路的shapefile,多线MULTILINESTRING
//String path = "E:\\china-latest-free\\gis.osm_roads_free_1.shp";
//C.建筑物的点坐标 以Point为主
String path = "E:\\china-latest-free\\gis.osm_pois_free_1.shp";
//一个数据存储实现,允许从Shapefiles读取和写入
ShapefileDataStore shpDataStore = null;
shpDataStore = new ShapefileDataStore(new File(path).toURI().toURL());
shpDataStore.setCharset(Charset.forName("UTF-8"));
//获取这个数据存储保存的类型名称数组
//getTypeNames:获取所有地理图层
String typeName = shpDataStore.getTypeNames()[0];
//通过此接口可以引用单个shapefile、数据库表等。与数据存储进行比较和约束
FeatureSource<SimpleFeatureType, SimpleFeature> featureSource = null;
featureSource = (FeatureSource<SimpleFeatureType, SimpleFeature>)shpDataStore.getFeatureSource(typeName);
//一个用于处理FeatureCollection的实用工具类。提供一个获取FeatureCollection实例的机制
FeatureCollection<SimpleFeatureType, SimpleFeature> result=featureSource.getFeatures();
//System.out.println(result.size());
FeatureIterator<SimpleFeature> iterator = result.features();
//迭代 特征 只迭代30个 太大了,一下子迭代完,非常耗时
int stop = 0;
while(iterator.hasNext()){
if(stop >30){
break;
}
SimpleFeature feature = iterator.next();
Collection<Property> p = feature.getProperties();
Iterator<Property> it = p.iterator();
//特征里面的属性再迭代,属性里面有字段
System.out.println("================================");
while(it.hasNext()){
Property pro = it.next();
//如果是点的话,基本上第一个属性字段表示的就是类型
if(pro.getValue() instanceof Point){
Point point = (Point)pro.getValue();
System.out.println("【位置】PointX = "+point.getX()+",PoinxY = "+point.getY());
}
//其余的,正常输出
else{
System.out.println(pro.getName()+"\t = "+pro.getValue());
}
}//end 里层while
stop++;
}//end 最外层 while
iterator.close();
}
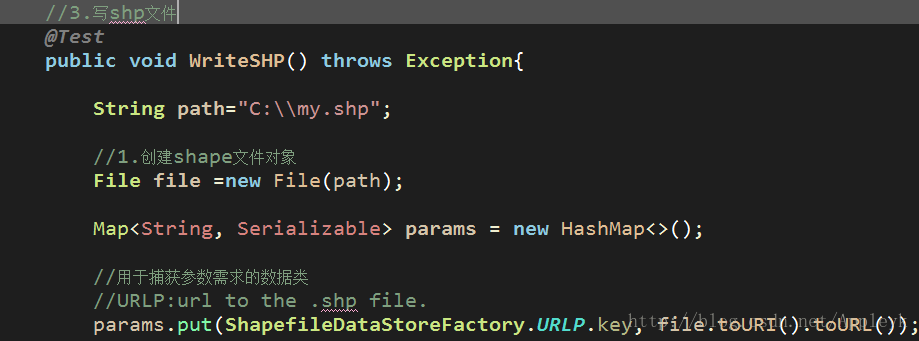
//3.写shp文件,:
@Test
public void WriteSHP() throws Exception{
String path="C:\\my.shp";
//1.创建shape文件对象
File file =new File(path);
Map<String, Serializable> params = new HashMap<>();
//用于捕获参数需求的数据类
//URLP:url to the .shp file.
params.put(ShapefileDataStoreFactory.URLP.key, file.toURI().toURL());
//2.创建一个新的数据存储——对于一个还不存在的文件。
ShapefileDataStore ds = (ShapefileDataStore) new ShapefileDataStoreFactory().createNewDataStore(params);
//3.定义图形信息和属性信息
//SimpleFeatureTypeBuilder 构造简单特性类型的构造器
SimpleFeatureTypeBuilder tBuilder = new SimpleFeatureTypeBuilder();
//设置
//WGS84:一个二维地理坐标参考系统,使用WGS84数据
tBuilder.setCRS(DefaultGeographicCRS.WGS84);
tBuilder.setName("shapefile");
//添加 一个点
tBuilder.add("the_geom", Point.class);
//添加一个id
tBuilder.add("osm_id", Long.class);
//添加名称
tBuilder.add("name", String.class);
//添加描述
tBuilder.add("des", String.class);
//设置此数据存储的特征类型
ds.createSchema(tBuilder.buildFeatureType());
//设置编码
ds.setCharset(Charset.forName("UTF-8"));
//设置writer
//为给定的类型名称创建一个特性写入器
//1.typeName:特征类型
//2.transaction :事物,写入失败,回滚
//3.ShapefileDataStore::getTypeNames:
/*public String[] getTypeNames()
获取这个数据存储保存的类型名称数组。
ShapefileDataStore总是返回一个名称
*/
FeatureWriter<SimpleFeatureType, SimpleFeature> writer = ds.getFeatureWriter(
ds.getTypeNames()[0], Transaction.AUTO_COMMIT);
//Interface SimpleFeature:一个由固定列表值以已知顺序组成的SimpleFeatureType实例。
//写一个点
SimpleFeature feature = writer.next();
//SimpleFeature ::setAttribute(String attrName, Object val)
//给指定的属性名称添加一个对象 POINT
double x = 116.123; //X轴坐标
double y = 39.345 ; //Y轴坐标
/*
* Coordinate : GeoAPI几何接口的实现
一个轻量级的类,用于存储二维笛卡尔平面上的坐标。
它不同于点,它是几何的一个子类。
不同于类型点的对象(包含额外的信息,如信封、精确模型和空间引用系统信息),
坐标只包含有序值和访问方法。
*/
Coordinate coordinate = new Coordinate(x, y);
//GeometryFactory:提供一套实用的方法,用于从坐标列表中构建几何对象。
//构造一个几何图形工厂,生成具有浮动精度模型的几何图形和一个0的空间引用ID。
Point point = new GeometryFactory().createPoint(coordinate);
feature.setAttribute("the_geom",point);
feature.setAttribute("osm_id", 1234567890l);
feature.setAttribute("name", "帅鱼");
feature.setAttribute("des", "爱宝宝");
//再来一个点
feature = writer.next();
x = 116.456;
y = 39.678 ;
coordinate = new Coordinate(x, y);
point = new GeometryFactory().createPoint(coordinate);
feature.setAttribute("the_geom",point);
feature.setAttribute("osm_id", 1234567891l);
feature.setAttribute("name", "宝宝");
feature.setAttribute("des", "爱帅鱼");
//写入
writer.write();
//关闭
writer.close();
//释放资源
ds.dispose();
//读取shapefile文件的图形信息
ShpFiles shpFiles = new ShpFiles(path);
/*ShapefileReader(
ShpFiles shapefileFiles,
boolean strict, --是否是严格的、精确的
boolean useMemoryMapped,--是否使用内存映射
GeometryFactory gf, --几何图形工厂
boolean onlyRandomAccess--是否只随机存取
)
*/
ShapefileReader reader = new ShapefileReader(shpFiles,
false, true, new GeometryFactory(), false);
while(reader.hasNext()){
System.out.println(reader.nextRecord().shape());
}
reader.close();
}
//4.读shp文件【几何信息+属性信息】
@Test
public void SHPRead() throws Exception{
//基于上面新建的shapfile文件,进行读取
String path = "C:\\my.shp";
//构建shapefile数据存储的实例
ShapefileDataStoreFactory dataStoreFactory = new ShapefileDataStoreFactory();
//基于路径构建文件对象
File file = new File(path);
//构建一个已存在的shapfile数据源
//ShapefileDataStore:数据存储实现,允许从Shapefiles读取和写入
ShapefileDataStore ds = (ShapefileDataStore) dataStoreFactory.createDataStore(file.toURI().toURL());
//设置编码,防止中文读取乱码
ds.setCharset(Charset.forName("UTF-8"));
//getFeatureSource():ContentFeatureSource
//这个特性是由 FeatureCollection提供的操作完成的。单独的特征记忆实现由子类提供:
//SimpleFeatureSource特征资源明确地使用FeatureCollection【集合】,可迭代
SimpleFeatureSource featureSource = ds.getFeatureSource();
//getFeatures():以FeatureCollection的形式检索所有特性。
//一个用于处理FeatureCollection的实用工具类。提供一个获取FeatureCollection实例的机制
FeatureCollection<SimpleFeatureType, SimpleFeature> result=featureSource.getFeatures();
System.out.println("几何对象总过有:"+result.size());
//features():返回一个FeatureIterator迭代器
SimpleFeatureIterator it =(SimpleFeatureIterator) result.features();
while(it.hasNext()){
SimpleFeature feature = it.next();
//迭代属性【属性我们可以理解为一个几何对象的属性节点,也就是对一个几何图形的描述字段】
Iterator<Property> ip = feature.getProperties().iterator();
System.out.println("========================");
//再来个while
while(ip.hasNext()){
Property pro = ip.next();
System.out.println(pro.getName()+" = "+pro.getValue());
}//end 属性迭代
}
it.close();
}
}
四、读DBF文件【不包含矢量数据】
(1)
(2)

五、读SHP文件【包含矢量坐标,以几何图形Point为例】
(1)
(2)

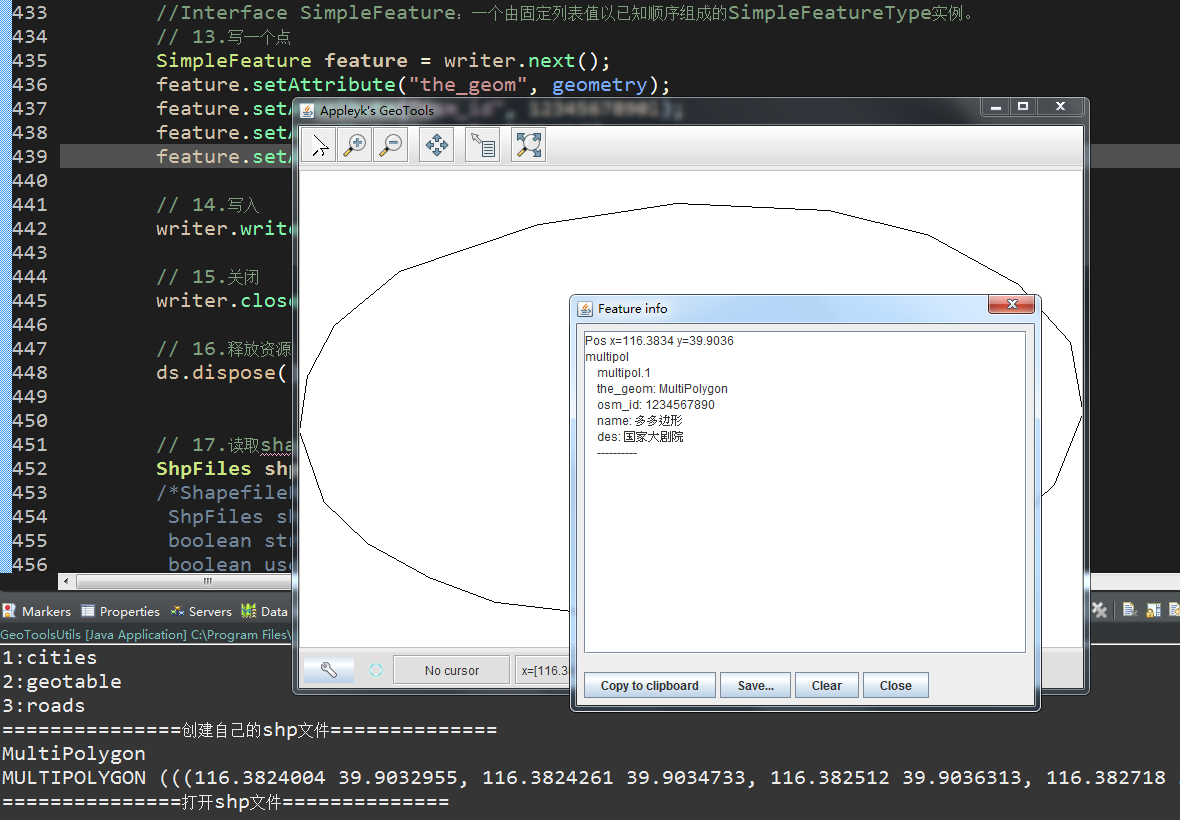
六、写SHP文件
写了两个点,一个点代表我,一个点代表我的宝宝,
(1)
(2)没写之前,C盘没shp

(3)写入后,控制台输出写入的俩个点的几何图形信息

(4)读一下,C盘下面创建的shp文件
A.

1. 两个点【Point】已经显示出来了

2. 点开其中一个点,查看详细信息
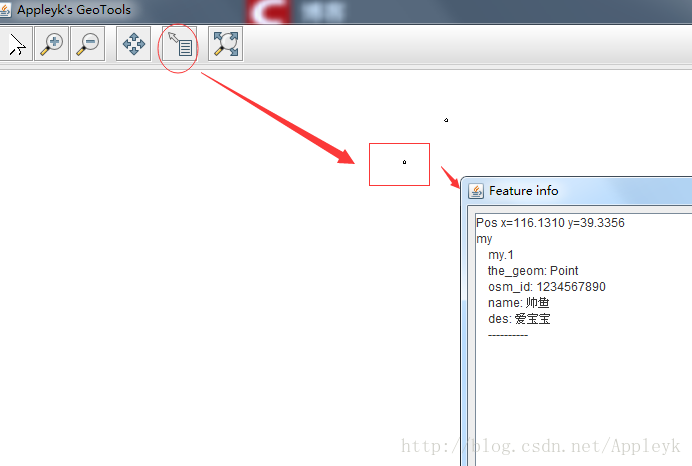
C.这样有什么用呢? shapefile文件读取后,信息可存进数据库

七、读SHP文件【几何信息+属性内容】
(1)
(2)
补充:
整个项目目录树如下:
数据库查询如下:
----获取多边形内边界个数st_numinteriorring
select st_numinteriorring(geom) from geotable where name = '国家大剧院';
--获取几何对象的维数 st_dimension(geometry)
select st_dimension(geom) from geotable where name = '国家大剧院';
--获取几何对象中的点个数 st_numpoints(geometry)
select st_numpoints(geom) from geotable where name = '国家大剧院';
--判断几何对象的类型 st_geometrytype
select st_geometrytype(geom) from geotable where name = '国家大剧院';
--获取几何对象的WKT描述 ST_AsText(geometry)
select st_astext(geom) from geotable where name = '国家大剧院';
--获取几何对象信息
select geom from geotable where name = '国家大剧院';
整个项目的GitHub下载地址如下:
https://github.com/kobeyk/Spring-Boot-ShpReader.git
本篇的shp测试文件在我一开始提供的百度云盘的链接里
链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1S-TrFp_r8zyf_d0oBUeWqg
下一篇:






























 2184
2184











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








