#include<iostream.h>
class animal
{
public:
animal()
{
cout<<"animal construst"<<endl;
}
~animal()
{
cout<<"animal destrust"<<endl;
}
void eat()
{
cout<<"animal eat"<<endl;
}
void sleep()
{
cout<<"animal sleep"<<endl;
}
void breathe()
{
cout<<"animal breathe"<<endl;
}
};
class fish:public animal
{
public:
fish()
{
cout<<"fish construct"<<endl;
}
~fish()
{
cout<<"fish destruct"<<endl;
}
};
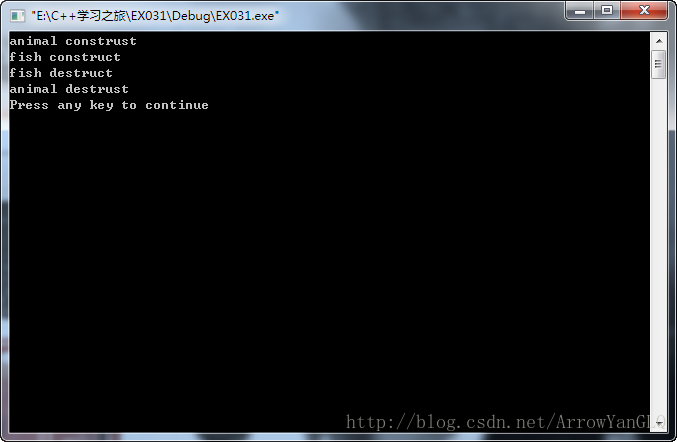
void main()
{
fish fh;
}注意animal和fish的构造函数和析构函数的调用顺序;
2、在子类中调用父类的带参数的构造函数
下面修改一下animal类的构造函数,增加参数height和weight,表示动物的高度和重量。
#include<iostream.h>
class animal
{
public:
<span style="color:#ff0000;">animal(int height,int weight)</span>
{
cout<<"animal construst"<<endl;
}
~animal()
{
cout<<"animal destrust"<<endl;
}
void eat()
{
cout<<"animal eat"<<endl;
}
void sleep()
{
cout<<"animal sleep"<<endl;
}
void breathe()
{
cout<<"animal breathe"<<endl;
}
};
class fish:public animal
{
public:
fish()
{
cout<<"fish construct"<<endl;
}
~fish()
{
cout<<"fish destruct"<<endl;
}
};
void main()
{
fish fh;
}
原因是当我们构造fish类的对象fh时,它需要先构造animal类的对象,调用animal类的构造函数(不带参数的构造函数),而在程序中,animal类只有一个带参数的构造函数,编译时,因找不到animal类中的默认构造函数出错。因此,在构造fish类的对象时(调用fish类的构造函数时)要想办法去调用animal类的带参数的构造函数。方式如下,在构造子类时,显式的去调用父类的带参数的构造函数。
#include<iostream.h>
class animal
{
public:
animal(int height,int weight)
{
cout<<"animal construst"<<endl;
}
~animal()
{
cout<<"animal destrust"<<endl;
}
void eat()
{
cout<<"animal eat"<<endl;
}
void sleep()
{
cout<<"animal sleep"<<endl;
}
void breathe()
{
cout<<"animal breathe"<<endl;
}
};
class fish:public animal
{
public:
<span style="color:#ff0000;">fish():animal(400,300)</span>
{
cout<<"fish construct"<<endl;
}
~fish()
{
cout<<"fish destruct"<<endl;
}
};
void main()
{
fish fh;
}3、类的继承及类中成员的访问特性
public定义的成员可以在任何地方被访问。
protected定义的成员只能在该类及其子类中被访问。
private定义的成员只能在该类自身中访问。
如果在定义派生类时没有指定如何继承访问权限,则默认为private。
如果派生类以private访问权限继承基类,则基类中的成员在派生类中都变成了private类型的访问权限。
如果派生类以public访问权限继承基类,则基类中的成员在派生类中仍以原来的访问权限在派生类中出现。
如果派生类以protected访问权限继承基类,则基类中的public和protected成员在派生类中都变成了protected类型的访问权限。
注意:基类中的private成员不能被派生类访问,因此,private成员不能被派生类所继承。
4、多重继承
定义形式:
class派生类名:访问权限 基类名称,访问权限 基类名称,访问权限 基类名称
{
。。。。。。
};
例如B类是由类C和类D派生的:
classB:publicC,publicD
{
。。。。。
};
多重函数使程序编写更具有灵活性,但是需要注意的地方也不少:
#include<iostream.h>
class B1
{
public:
void output();
};
class B2
{
public:
void output();
};
void B1::output()
{
cout<<"call the class B1"<<endl;
}
void B2::output()
{
cout<<"call the class B2"<<endl;
}
<span style="color:#ff0000;">class A:public B1,public B2</span>
{
public:
void show();
};
void A::show()
{
cout<<"call the class A"<<endl;
}
void main()
{
A a;
<span style="color:#ff0000;">a.output();</span>
a.show();
}
在前面加上virtual关键字就可以实现虚拟继承,使用虚拟继承后, 当系统碰到多重继承的时候就会自动先加入一个output()的拷贝,当再次请求一个output()的拷贝的时候就会被忽略,保证继承类成员函数的唯一性 。





















 8490
8490











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








