Surf算法是一把牛刀,我们可以很轻易的从网上或各种OpenCV教程里找到Surf的用例,把例程中的代码或贴或敲过来,满心期待的按下F5,当屏幕终于被满屏花花绿绿的小圆点或者N多道连接线条霸占时,内心的民族自豪感油然而生,仿佛屠龙宝刀在手,屁颠屁颠的很开心。
如果对Surf的探究或者使用到此为止,我觉得只是用Surf这把牛刀吓唬了一个小鸡仔,万里长征才刚刚开始第一步,最少有三个问题需要得到解答:
- 1. 保存特征点信息的keyPoints向量内每个元素包含有哪些内容?
- 2. 通过comput方法生成的特征描述子是一个Mat矩阵,该Mat矩阵的结构是怎样的?
- 3. 特征点匹配后生成一个DMatch型的向量matches,这个matches里边的内容又是什么,以及如何有效操作众多匹配信息,为之后在实际中的应用做好基础?
这三个基本的问题得不到一个很好的答案,所谓的利用Sruf进行图像的拼接、融合,物体识别,3D建模等应用应该连纸上谈兵都算不上吧~
通过一个小例子,尝试对这三个问题进行解读。
1. 保存特征点信息的keyPoints向量内每个元素包含有哪些内容?
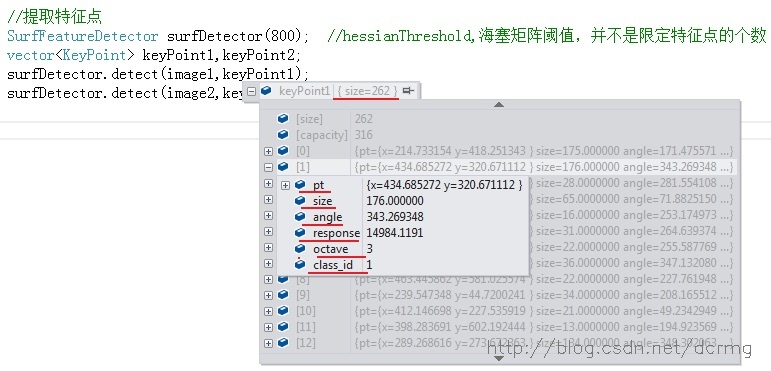
keyPoints数据结构包含的内容有:
- response:特征点的响应强度,代表该点的稳健程度,可以在Surf特征探测器的含参构造函数中设置响应强度的最低阈值,如: SurfFeatureDetector surfDetector(800);
2. 通过comput方法生成的特征描述子是一个Mat矩阵,该Mat矩阵的结构是怎样的?
经过归一化后的描述子Mat矩阵显示:


这两个长的很大条的图像就是描述子的图像显示,图像的行数是特征点的个数,上例中图像1的特征点数比图像二的少,表现出来就是图像的高度小一些。
图像的列数是描述特征点的描述子的维度数,在Surf中,维度是64,在SIft中,维度是128,所以如果使用Sift特征的话,图像应该宽两倍。
3. 特征点匹配后生成一个DMatch型的向量matches,这个matches里边的内容又是什么,以及如何有效操作众多匹配信息,为之后在实际中的应用做好基础?
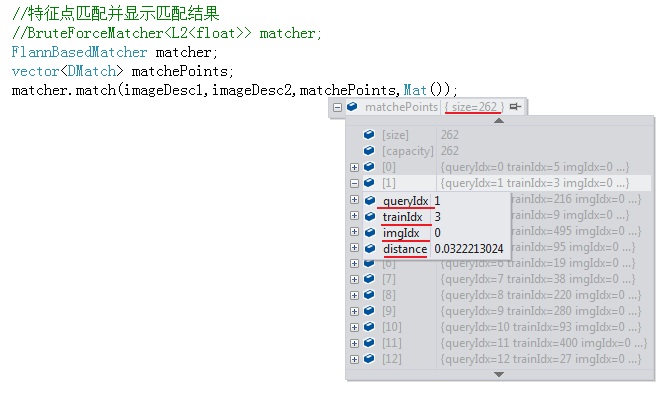
matches数据结构包含的内容有:
- queryIdx:当前“匹配点”在查询图像的特征在KeyPoints1向量中的索引号,可以据此找到匹配点在查询图像中的位置
- trainIdx:当前“匹配点”在训练(模板)图像的特征在KeyPoints2向量中的索引号,可以据此找到匹配点在训练图像中的位置
- imgIdx:当前匹配点对应训练图像(如果有若干个)的索引,如果只有一个训练图像跟查询图像配对,即两两配对,则imgIdx=0
- distance:连个特征点之间的欧氏距离,越小表明匹配度越高
4. 匹配特征点sort排序
sort方法可以对匹配点进行从小到大的排序:
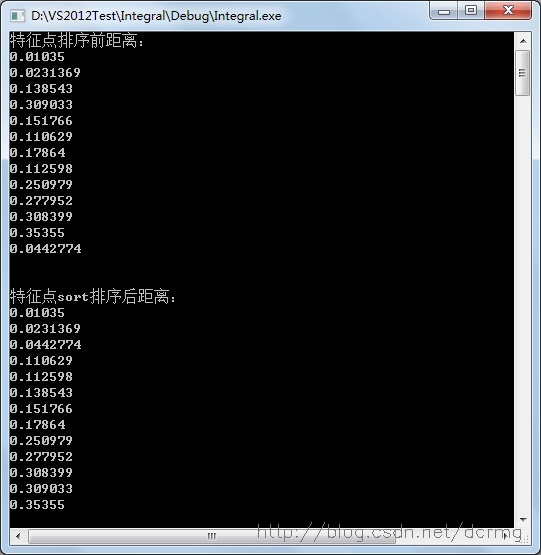
使用sort排序之前,每个匹配点对间的距离(即匹配稳健性程度)是随机分布的,排序之后,距离按由小到大的顺序排列,越靠前的,匹配度越高,可以通过排序后把靠前的匹配提取出来。
本例中提取前10个最优匹配(匹配很完美吧,因为这是同一幅图像~):
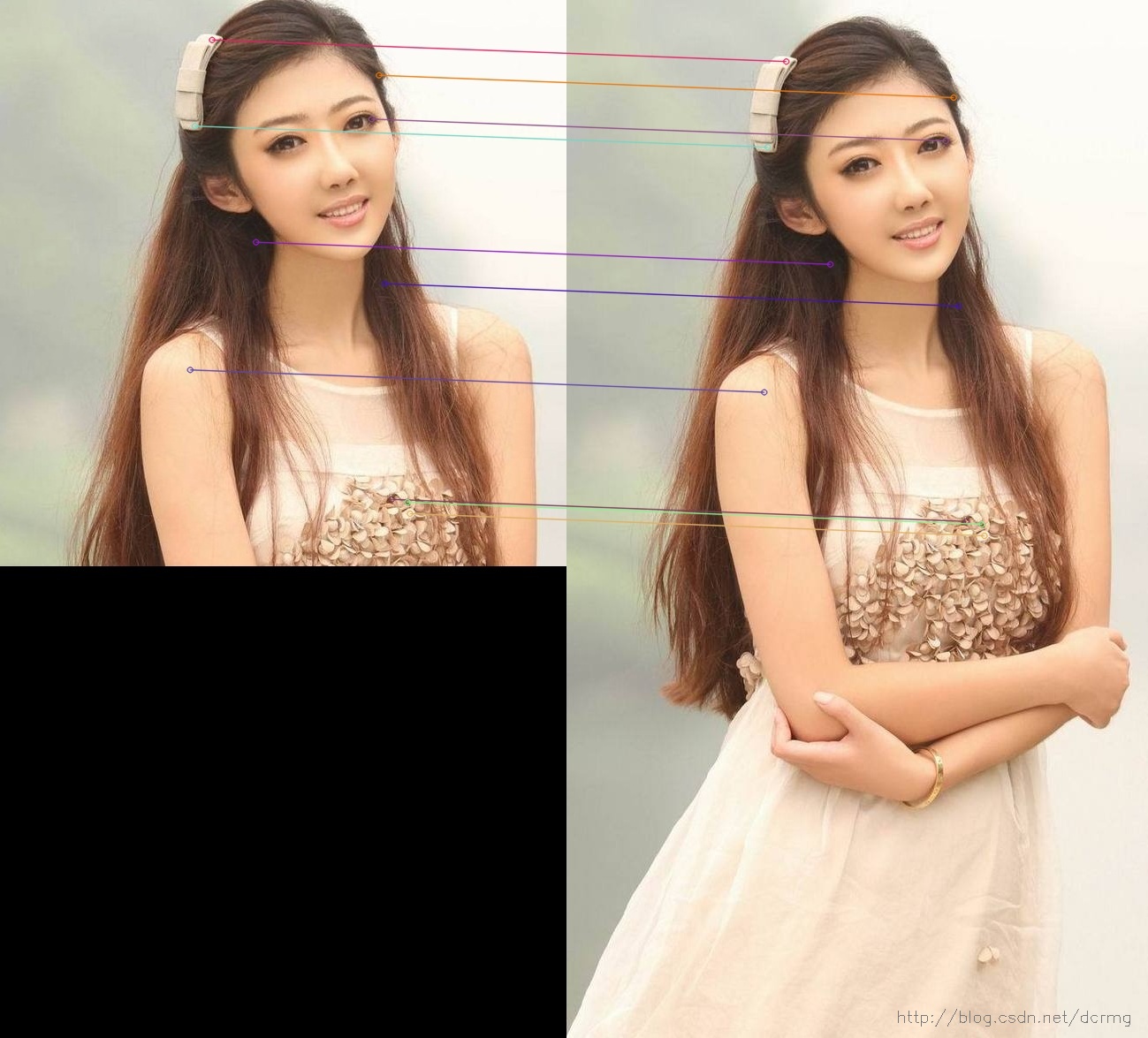

以下是完整的程序,有兴趣可参考:
- #include "highgui/highgui.hpp"
- #include "opencv2/nonfree/nonfree.hpp"
- #include "opencv2/legacy/legacy.hpp"
- #include <iostream>
-
- using namespace cv;
- using namespace std;
-
- int main(int argc,char *argv[])
- {
- Mat image01=imread(argv[1]);
- Mat image02=imread(argv[2]);
- Mat image1,image2;
- image1=image01.clone();
- image2=image02.clone();
-
-
- SurfFeatureDetector surfDetector(800);
- vector<KeyPoint> keyPoint1,keyPoint2;
- surfDetector.detect(image1,keyPoint1);
- surfDetector.detect(image2,keyPoint2);
-
-
- drawKeypoints(image1,keyPoint1,image1,Scalar::all(-1));
- drawKeypoints(image2,keyPoint2,image2,Scalar::all(-1),DrawMatchesFlags::DRAW_RICH_KEYPOINTS);
- imshow("KeyPoints of image1",image1);
- imshow("KeyPoints of image2",image2);
-
-
- SurfDescriptorExtractor SurfDescriptor;
- Mat imageDesc1,imageDesc2;
- SurfDescriptor.compute(image1,keyPoint1,imageDesc1);
- SurfDescriptor.compute(image2,keyPoint2,imageDesc2);
-
-
- Mat imageDescShow1;
- Mat imageDescShow2;
- normalize(imageDesc1,imageDescShow1,0,255,CV_MINMAX);
- normalize(imageDesc2,imageDescShow2,0,255,CV_MINMAX);
- convertScaleAbs(imageDescShow1,imageDescShow1);
- convertScaleAbs(imageDescShow2,imageDescShow2);
- imshow("描述子1",imageDescShow1);
- imshow("描述子2",imageDescShow2);
-
-
-
- FlannBasedMatcher matcher;
- vector<DMatch> matchePoints;
- matcher.match(imageDesc1,imageDesc2,matchePoints,Mat());
-
-
- cout<<"特征点排序前距离:"<<endl;
- for(int i=0;i<matchePoints.size();i++)
- {
- cout<<matchePoints[i].distance<<endl;
- }
- cout<<endl<<endl;
- cout<<"特征点sort排序后距离:"<<endl;
- sort(matchePoints.begin(),matchePoints.end());
- for(int i=0;i<matchePoints.size();i++)
- {
- cout<<matchePoints[i].distance<<endl;
- }
-
-
-
- vector<DMatch> goodMatchePoints;
- for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
- {
- goodMatchePoints.push_back(matchePoints[i]);
- }
-
-
- Mat imageOutput;
- drawMatches(image01,keyPoint1,image02,keyPoint2,goodMatchePoints,imageOutput,Scalar::all(-1),
- Scalar::all(-1),vector<char>(),DrawMatchesFlags::NOT_DRAW_SINGLE_POINTS);
- imwrite("E:\\ss.jpg",imageOutput);
- imshow("Mathch Points",imageOutput);
- waitKey();
- return 0;
- }






























 2万+
2万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








