ReentrantLock
ReentrantLock作为java.util.concurrent.locks中重要的一个锁,是很值得初学者研究的,现在就以一位初学者的视角来看ReentrantLock的主要原理
底层数据结构
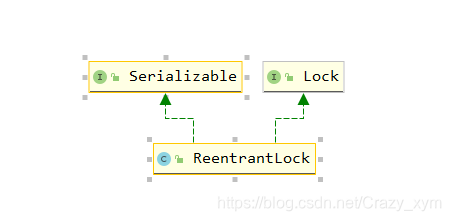
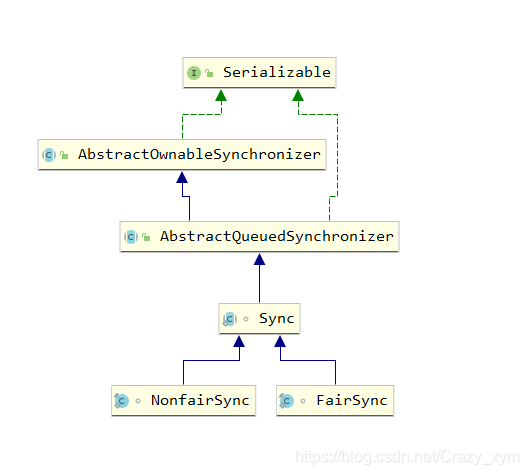
根据类图(IDEA中ALT+SHIFT+CTRL+U)可以看出重入锁是分为FairSync(公平)和NonfairSync(非公平)的。
/** Synchronizer providing all implementation mechanics */
// 真正的锁机制是基于AQS实现的
private final Sync sync;
public ReentrantLock() {
sync = new NonfairSync();
}
public ReentrantLock(boolean fair) {
sync = fair ? new FairSync() : new NonfairSync();
}
在初始化时,如果不传参数,则默认初始化非公平锁。
/**
* The synchronization state.
*/
private volatile int state;
这个state在AbstractQueuedSynchronizer中定义。意思是重入了几次。
公平?非公平
公平的意思是指当线程获取锁时需要进行排队,排到你的时候你才能获取锁。
非公平的意思是指线程在获取锁的时候可以进行插队,如果插队失败再排队。
lock()
重入锁的lock()行为是由sync决定。
FairSync 时
final void lock() {
acquire(1);
}
public final void acquire(int arg) {
if (!tryAcquire(arg) &&
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))
selfInterrupt();
}
可以看见尝试设置state为1
首先来分析tryAcquire
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread(); // 获取当前调用的线程
int c = getState(); // 获取当前重入的次数
if (c == 0) { // 如果为0 说明没有人使用这把锁
if (!hasQueuedPredecessors() && // 如果自己前面没有人排队了,尝试CAS设置重入次数为1
compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current); // 设置当前线程持有锁
return true;
}
}
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) { // 如果当前线程和持有锁的线程一致
int nextc = c + acquires; // 增加重入次数
if (nextc < 0)
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc); // 更新重入次数
return true;
}
return false;
}
/**
* 判断是否队列中存在排队线程
*/
public final boolean hasQueuedPredecessors() {
// The correctness of this depends on head being initialized
// before tail and on head.next being accurate if the current
// thread is first in queue.
Node t = tail; // Read fields in reverse initialization order
Node h = head;
Node s;
return h != t && // head 和 tail 不同 并且 head的后一个为空 或者 后一个和调用线程不是同一个就返回true
((s = h.next) == null || s.thread != Thread.currentThread());
}
经过上面一通操作,如果失败则需要调用acquireQueued()
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {
boolean failed = true;
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor(); // 获取前驱节点
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) { // 如果前驱节点为头并且设置成功了,则将当前的线程节点置为head
setHead(node);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return interrupted;
}
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) && // 接入队列成功,然后阻塞自己,等待其他人来唤醒
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
interrupted = true;
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
private static boolean shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(Node pred, Node node) {
int ws = pred.waitStatus; // 当前线程节点的前驱等待状态
if (ws == Node.SIGNAL) // 如果是SIGNAL,说明可以在当前锁持有者release时通知它。
return true;
if (ws > 0) { // 说明状态为CANCELLED = 1,需要进行跳过,找到新的等待中的前驱节点
do {
node.prev = pred = pred.prev;
} while (pred.waitStatus > 0);
pred.next = node; // 接到前驱节点后面
} else { // 状态一定为0 或者 PROPAGATE,我们需要在阻塞前尝试一次状态变更
compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL);
}
return false;
}
NonfairSync 时
final void lock() {
if (compareAndSetState(0, 1))
setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread());
else
acquire(1);
}
可以看出,在FairSync的acquire之前进行了一次CAS,如果成功也就意味着抢到了锁,体现了非公平的性质。那么NonfairSync的acquire和FairSync的一样吗?
首先还是同样的代码
public final void acquire(int arg) {
if (!tryAcquire(arg) &&
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))
selfInterrupt();
}
发现有一点点不同了
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
return nonfairTryAcquire(acquires);
}
final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
if (c == 0) {
if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) { // FairSync时是需要判断是否当前节点就是Head的,而NonFairSync就没有判断
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0) // overflow
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}
acquireQueued() 的代码和FairSync的一致就不贴了,主要还是这个tryAcquire的不同。正是这个不同导致公平锁模式需要老实排队,而非公平锁则有机会插队。
unlock()
public void unlock() {
sync.release(1);
}
这个解锁就和公平不公平没有关系了
public final boolean release(int arg) {
if (tryRelease(arg)) {
Node h = head;
if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0)
unparkSuccessor(h);
return true;
}
return false;
}
发现调用tryRelease
protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases) {
int c = getState() - releases; // 计算新的重入次数
if (Thread.currentThread() != getExclusiveOwnerThread()) // 如果当前线程和持有者不一致,抛出异常
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
boolean free = false;
if (c == 0) { // 如果重入次数为0了,说明已经没人使用了,需要将持有者设置为null
free = true;
setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);
}
setState(c);
return free;
}
在释放锁后需要唤醒队列中的线程节点
private void unparkSuccessor(Node node) {
/*
* If status is negative (i.e., possibly needing signal) try
* to clear in anticipation of signalling. It is OK if this
* fails or if status is changed by waiting thread.
*/
int ws = node.waitStatus;
if (ws < 0)
compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, ws, 0);
/*
* 当后继为Null或者Cancalled状态时,需要从尾部开始向前遍历找到当前线程的下一个节点
*/
Node s = node.next;
if (s == null || s.waitStatus > 0) {
s = null;
for (Node t = tail; t != null && t != node; t = t.prev)
if (t.waitStatus <= 0)
s = t;
}
if (s != null) // 如果存在下一个阻塞的节点就唤醒它
LockSupport.unpark(s.thread);
}
CAS
cas是指Compare-And-Swap,底层调用UnSafe类的public final native boolean compareAndSwapInt(Object var1, long var2, int var4, int var5);其中var1是对象在JVM中地址(猜的),var2是对象相对于内存的偏移量,var4是期待值,var5是新值,当期待值和和对象真实值一致的时候,将对象值设置成新值。
在C的实现中可以看到Atomic::cmpxchg(x,addr,e)这是一条原子指令,因此保证CAS的原子性。























 2399
2399











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








