T1:Going Home
题目
On a grid map there are n little men and n houses. In each unit time, every little man can move one unit step, either horizontally, or vertically, to an adjacent point. For each little man, you need to pay a $1 travel fee for every step he moves, until he enters a house. The task is complicated with the restriction that each house can accommodate only one little man.
Your task is to compute the minimum amount of money you need to pay in order to send these n little men into those n different houses. The input is a map of the scenario, a ‘.’ means an empty space, an ‘H’ represents a house on that point, and am ‘m’ indicates there is a little man on that point.
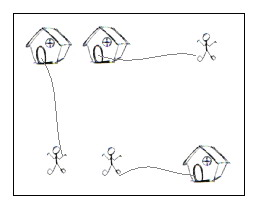
You can think of each point on the grid map as a quite large square, so it can hold n little men at the same time; also, it is okay if a little man steps on a grid with a house without entering that house.
Input
There are one or more test cases in the input. Each case starts with a line giving two integers N and M, where N is the number of rows of the map, and M is the number of columns. The rest of the input will be N lines describing the map. You may assume both N and M are between 2 and 100, inclusive. There will be the same number of 'H’s and 'm’s on the map; and there will be at most 100 houses. Input will terminate with 0 0 for N and M.
Output
For each test case, output one line with the single integer, which is the minimum amount, in dollars, you need to pay.
Sample Input
2 2
.m
H.
5 5
HH…m
…
…
…
mm…H
7 8
…H…
…H…
…H…
mmmHmmmm
…H…
…H…
…H…
0 0
Sample Output
2
10
28
题解
简单题意就是一张图, H H H表示一间屋子, m m m表示一个人,现在每个人要走到一间屋子里,消耗的费用为两点之间的距离,求每个都有一个房子的最小耗费
是一道很裸的费用流问题,这里本蒟蒻选择了
E
K
+
S
P
F
A
EK+SPFA
EK+SPFA
我们考虑建图问题,先建一个超级源点s和一个超级汇点t,然后将所有房子
H
H
H和s建边,容量定义为1,边权免费,同理把所有人在的
m
m
m和t建边,容量为1,边权免费
最后的边权决定于房子和人的搭配,这个边权就是矩阵里面两个点之间的距离,容量仍然是1,因为一人一间房

CODE
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
#define INF 1e9
#define MAXM 1000005
#define MAXN 100005
struct node {
int v, w, next, c, flow;
}edge[MAXM];
queue < int > q;
vector < pair < int, int > > h, m;
//处理出每一个房子和人所在的位置,第一关键字是行,第二关键字是列
int cnt, N, M, s, t;
int head[MAXN], dis[MAXN], pre[MAXN];
bool vis[MAXN];
void add ( int x, int y, int flow, int fi ) {
edge[cnt].next = head[x];
edge[cnt].v = y;
edge[cnt].w = fi;
edge[cnt].c = flow;
edge[cnt].flow = 0;
head[x] = cnt ++;
}
bool spfa () {
memset ( vis, 0, sizeof ( vis ) );
memset ( dis, 0x7f, sizeof ( dis ) );
memset ( pre, -1, sizeof ( pre ) );
while ( ! q.empty() )
q.pop();
q.push( s );
dis[s] = 0;
vis[s] = 1;
while ( ! q.empty() ) {
int u = q.front();
q.pop();
vis[u] = 0;
for ( int i = head[u];i != -1;i = edge[i].next ) {
int v = edge[i].v;
if ( dis[v] > dis[u] + edge[i].w && edge[i].c > edge[i].flow ) {
dis[v] = dis[u] + edge[i].w;
pre[v] = i;
if ( ! vis[v] ) {
q.push( v );
vis[v] = 1;
}
}
}
}
return pre[t] != -1;
}
void MCMF ( int &maxflow, int &mincost ) {
maxflow = mincost = 0;
while ( spfa() ) {
int MIN = INF;
for ( int i = pre[t];i != -1;i = pre[edge[i ^ 1].v] )
MIN = min ( MIN, edge[i].c - edge[i].flow );
for ( int i = pre[t];i != -1;i = pre[edge[i ^ 1].v] ) {
edge[i].flow += MIN;
edge[i ^ 1].flow -= MIN;
mincost += MIN * edge[i].w;
}
maxflow += MIN;
}
}
int Fabs ( int x ) {
if ( x < 0 )
return -x;
return x;
}
int main() {
while ( scanf ( "%d %d", &N, &M ) ) {
if ( N == 0 && M == 0 )
return 0;
memset ( head, -1, sizeof ( head ) );
cnt = 0;
h.clear();
m.clear();
for ( int i = 1;i <= N;i ++ ) {
getchar();
for ( int j = 1;j <= M;j ++ ) {
char ch;
scanf ( "%c", &ch );
if ( ch == 'H' )
h.push_back( make_pair ( i, j ) );
if ( ch == 'm' )
m.push_back ( make_pair ( i, j ) );
}
}
s = 0;t = N * M + 1;
for ( int i = 0;i < h.size();i ++ ) {
//与超级源点建边
add ( s, ( h[i].first - 1 ) * M + h[i].second, 1, 0 );
add ( ( h[i].first - 1 ) * M + h[i].second, s, 0, 0 );
for ( int j = 0;j < m.size();j ++ ) {
//屋子与人建边,算是一种hash吧,毕竟每一个人和每一件房子都是独一无二的
add ( ( h[i].first - 1 ) * M + h[i].second, ( m[j].first - 1 ) * M + m[j].second, 1, Fabs ( h[i].first - m[j].first ) + Fabs ( h[i].second - m[j].second ) );
add ( ( m[j].first - 1 ) * M + m[j].second, ( h[i].first - 1 ) * M + h[i].second, 0, - Fabs ( h[i].first - m[j].first ) - Fabs ( h[i].second - m[j].second ) );
}
}
//与超级汇点建边
for ( int i = 0;i < m.size();i ++ ) {
add ( ( m[i].first - 1 ) * M + m[i].second, t, 1, 0 );
add ( t, ( m[i].first - 1 ) * M + m[i].second, 0, 0 );
}
int maxflow, mincost;
MCMF ( maxflow, mincost );
printf ( "%d\n", mincost );
}
return 0;
}
T2:Minimum Cost
题目
Dearboy, a goods victualer, now comes to a big problem, and he needs your help. In his sale area there are N shopkeepers (marked from 1 to N) which stocks goods from him.Dearboy has M supply places (marked from 1 to M), each provides K different kinds of goods (marked from 1 to K). Once shopkeepers order goods, Dearboy should arrange which supply place provide how much amount of goods to shopkeepers to cut down the total cost of transport.
It’s known that the cost to transport one unit goods for different kinds from different supply places to different shopkeepers may be different. Given each supply places’ storage of K kinds of goods, N shopkeepers’ order of K kinds of goods and the cost to transport goods for different kinds from different supply places to different shopkeepers, you should tell how to arrange the goods supply to minimize the total cost of transport.
Input
The input consists of multiple test cases. The first line of each test case contains three integers N, M, K (0 < N, M, K < 50), which are described above. The next N lines give the shopkeepers’ orders, with each line containing K integers (there integers are belong to [0, 3]), which represents the amount of goods each shopkeeper needs. The next M lines give the supply places’ storage, with each line containing K integers (there integers are also belong to [0, 3]), which represents the amount of goods stored in that supply place.
Then come K integer matrices (each with the size N * M), the integer (this integer is belong to (0, 100)) at the i-th row, j-th column in the k-th matrix represents the cost to transport one unit of k-th goods from the j-th supply place to the i-th shopkeeper.
The input is terminated with three "0"s. This test case should not be processed.
Output
For each test case, if Dearboy can satisfy all the needs of all the shopkeepers, print in one line an integer, which is the minimum cost; otherwise just output “-1”.
Sample Input
1 3 3
1 1 1
0 1 1
1 2 2
1 0 1
1 2 3
1 1 1
2 1 1
1 1 1
3
2
20
0 0 0
Sample Output
4
-1
题解
其实这道题有点考语文,输入太**

我们考虑建一个超级源点和超级汇点,
在源点和店主的需求之间建一条边,没有中间商赚差价,容量自然就是店主的订单量,
同理在供应地点和超级汇点之间建一条边,也没有中间商赚差价,容量为供应地点生产的产品数;
最后就是店主与供应地点之间的建边,因为有
k
k
k种不同的商品,所以一个供应地点跟一个店主之间的成本也会随着
k
k
k的不一样而改变,两个解决办法

1.把一个供应地点拆成
k
k
k个彼此独立的供应柜台,专门只销售一种类型的
由上面我们就可以发现,柜台之间是彼此独立的,互不影响,所以我们就有了第二种解决方案
2.把费用流拆成
k
k
k次一种商品的费用流,每次费用流都只处理一种商品,这样建边就不那么冗长
CODE
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
#define INF 1e9
#define MAXN 100
struct node {
int v, w, next, c, flow;
}edge[MAXN * MAXN];
queue < int > q;
int cnt, n, m, k, s, t;
int head[MAXN], dis[MAXN], pre[MAXN], need[MAXN][MAXN], num[MAXN][MAXN], matrix[MAXN][MAXN][MAXN];
bool vis[MAXN];
void add ( int x, int y, int flow, int cost ) {
edge[cnt].next = head[x];
edge[cnt].v = y;
edge[cnt].w = cost;
edge[cnt].c = flow;
edge[cnt].flow = 0;
head[x] = cnt ++;
}
bool spfa () {
memset ( vis, 0, sizeof ( vis ) );
memset ( dis, 0x7f, sizeof ( dis ) );
memset ( pre, -1, sizeof ( pre ) );
while ( ! q.empty() )
q.pop();
q.push( s );
dis[s] = 0;
vis[s] = 1;
while ( ! q.empty() ) {
int u = q.front();
q.pop();
vis[u] = 0;
for ( int i = head[u];~ i;i = edge[i].next ) {
int v = edge[i].v;
if ( dis[v] > dis[u] + edge[i].w && edge[i].c > edge[i].flow ) {
dis[v] = dis[u] + edge[i].w;
pre[v] = i;
if ( ! vis[v] ) {
q.push( v );
vis[v] = 1;
}
}
}
}
return pre[t] != -1;
}
void MCMF ( int &maxflow, int &mincost ) {
maxflow = mincost = 0;
while ( spfa() ) {
int MIN = INF;
for ( int i = pre[t];~ i;i = pre[edge[i ^ 1].v] )
MIN = min ( MIN, edge[i].c - edge[i].flow );
for ( int i = pre[t];~ i;i = pre[edge[i ^ 1].v] ) {
edge[i].flow += MIN;
edge[i ^ 1].flow -= MIN;
mincost += MIN * edge[i].w;
}
maxflow += MIN;
}
}
int main() {
while ( scanf ( "%d %d %d", &n, &m, &k ) != EOF ) {
if ( n == 0 && m == 0 && k == 0 )
return 0;
int sum = 0;
for ( int i = 1;i <= n;i ++ )
for ( int j = 1;j <= k;j ++ ) {
scanf ( "%d", &need[i][j] );
sum += need[i][j];
}
for ( int i = 1;i <= m;i ++ )
for ( int j = 1;j <= k;j ++ )
scanf ( "%d", &num[i][j] );
for ( int i = 1;i <= k;i ++ )
for ( int j = 1;j <= n;j ++ )
for ( int p = 1;p <= m;p ++ )
scanf ( "%d", &matrix[i][j][p] );
s = 0;t = n + m + 1;
int result = 0, Flow = 0;
for ( int i = 1;i <= k;i ++ ) {
memset ( head, -1, sizeof ( head ) );
cnt = 0;
for ( int j = 1;j <= n;j ++ ) {
add ( s, j, need[j][i], 0 );
add ( j, s, 0, 0 );
}
for ( int j = 1;j <= n;j ++ )
for ( int p = 1;p <= m;p ++ ) {
add ( j, n + p, num[p][i], matrix[i][j][p] );
add ( n + p, j, 0, -matrix[i][j][p] );
}
for ( int j = 1;j <= m;j ++ ) {
add ( j + n, t, num[j][i], 0 );
add ( t, j + n, 0, 0 );
}
int mincost, maxflow;
MCMF ( maxflow, mincost );
result += mincost;
Flow += maxflow;
}
if ( Flow == sum )
printf ( "%d\n", result );
else
printf ( "-1\n" );
}
return 0;
}
T3:工作安排
你的公司接到了一批订单。订单要求你的公司提供n类产品,产品被编号为 1 n 1~n 1 n,其中第i类产品共需要Ci件。公司共有m名员工,员工被编号为 1 m 1~m 1 m员工能够制造的产品种类有所区别。一件产品必须完整地由一名员工制造,不可以由某名员工制造一部分配件后,再转交给另外一名员工继续进行制造。
我们用一个由0和1组成的m*n的矩阵A来描述每名员工能够制造哪些产品。矩阵的行和列分别被编号为 1 m 1~m 1 m和 1 n 1~n 1 n,Ai,j为1表示员工i能够制造产品j,为0表示员工i不能制造产品j。
如果公司分配了过多工作给一名员工,这名员工会变得不高兴。我们用愤怒值来描述某名员工的心情状态。愤怒值越高,表示这名员工心情越不爽,愤怒值越低,表示这名员工心情越愉快。员工的愤怒值与他被安排制造的产品数量存在某函数关系,鉴于员工们的承受能力不同,不同员工之间的函数关系也是有所区别的。
对于员工i,他的愤怒值与产品数量之间的函数是一个Si+1段的分段函数。当他制造第 1 T i 1~Ti 1 Ti,1件产品时,每件产品会使他的愤怒值增加Wi,1,当他制造第 T i , 1 + 1 T i , 2 Ti,1+1~Ti,2 Ti,1+1 Ti,2件产品时,每件产品会使他的愤怒值增加 W i , 2 … … Wi,2…… Wi,2……为描述方便,设 T i , 0 = 0 , T i , s i + 1 = + ∞ , Ti,0=0,Ti,si+1=+∞, Ti,0=0,Ti,si+1=+∞,那么当他制造第 T i , j − 1 + 1 T i , j Ti,j-1+1~Ti,j Ti,j−1+1 Ti,j件产品时,每件产品会使他的愤怒值增加 W i , j , 1 ≤ j ≤ S i + 1 Wi,j, 1≤j≤Si+1 Wi,j,1≤j≤Si+1。
你的任务是制定出一个产品的分配方案,使得订单条件被满足,并且所有员工的愤怒值之和最小。由于我们并不想使用Special Judge,也为了使选手有更多的时间研究其他两道题目,你只需要输出最小的愤怒值之和就可以了。
Input
第一行包含两个正整数m和n,分别表示员工数量和产品的种类数;
第二行包含n 个正整数,第i个正整数为Ci;
以下m行每行n 个整数描述矩阵A;
下面m个部分,第i部分描述员工i的愤怒值与产品数量的函数关系。每一部分由三行组成:第一行为一个非负整数Si,第二行包含Si个正整数,其中第j个正整数为Ti,j,如果Si=0那么输入将不会留空行(即这一部分只由两行组成)。第三行包含Si+1个正整数,其中第j个正整数为Wi,j。
Output
仅输出一个整数,表示最小的愤怒值之和。
Sample Input
2 3
2 2 2
1 1 0
0 0 1
1
2
1 10
1
2
1 6
Sample Output
24
Hint
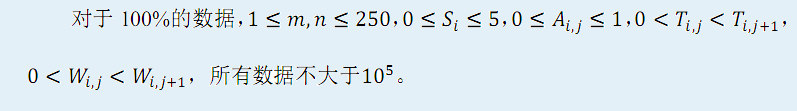
题解
考语文啊~~

这道题的提示,保证了愤怒值是单调递增的,就是费用流的关键,给我们的解题提供了保障
我们考虑对于一堆产品,第一阶段的产品生产的愤怒值一定小于后面阶段的产品生产的愤怒值,那么我们把愤怒值当成费用,我们一定会先选择第一阶段的流量边再选择第二阶段的流量边,这样就不会出现直接生产第二阶段导致我们的出错
那么我们就建一个超级源点和超级汇点,源点和员工之间连边,员工和产品之间连边,边数就是员工的愤怒阶段 + 1 +1 +1,最后一段是 i n f inf inf,每个阶段对应的容量就是该阶段的产品数,费用就是愤怒值;最后是产品和汇点之间连边
CODE
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
#define INF 1e9
#define LL long long
#define MAXN 1005
struct node {
int v, next;
LL w, c, flow;
}edge[MAXN * MAXN];
queue < int > q;
int cnt, n, m, s, t;
int head[MAXN], pre[MAXN], C[MAXN], a[MAXN][MAXN], b[MAXN];
bool vis[MAXN];
LL dis[MAXN];
void add ( int x, int y, LL flow, LL cost ) {
edge[cnt].next = head[x];
edge[cnt].v = y;
edge[cnt].w = cost;
edge[cnt].c = flow;
edge[cnt].flow = 0;
head[x] = cnt ++;
}
bool spfa () {
memset ( vis, 0, sizeof ( vis ) );
memset ( dis, 0x7f, sizeof ( dis ) );
memset ( pre, -1, sizeof ( pre ) );
while ( ! q.empty() )
q.pop();
q.push( s );
dis[s] = 0;
vis[s] = 1;
while ( ! q.empty() ) {
int u = q.front();
q.pop();
vis[u] = 0;
for ( int i = head[u];~ i;i = edge[i].next ) {
int v = edge[i].v;
if ( dis[v] > dis[u] + edge[i].w && edge[i].c > edge[i].flow ) {
dis[v] = dis[u] + edge[i].w;
pre[v] = i;
if ( ! vis[v] ) {
q.push( v );
vis[v] = 1;
}
}
}
}
return pre[t] != -1;
}
void MCMF ( LL &maxflow, LL &mincost ) {
maxflow = mincost = 0;
while ( spfa() ) {
LL MIN = INF;
for ( int i = pre[t];~ i;i = pre[edge[i ^ 1].v] )
MIN = min ( MIN, edge[i].c - edge[i].flow );
for ( int i = pre[t];~ i;i = pre[edge[i ^ 1].v] ) {
edge[i].flow += MIN;
edge[i ^ 1].flow -= MIN;
mincost += MIN * edge[i].w;
}
maxflow += MIN;
}
}
int main() {
memset ( head, -1, sizeof ( head ) );
scanf ( "%d %d", &m, &n );
s = 0;t = n + m + 1;
for ( int i = 1;i <= n;i ++ ) {
scanf ( "%d", &C[i] );
add ( s, i, C[i], 0 );
add ( i, s, 0, 0 );
}
for ( int i = 1;i <= m;i ++ )
for ( int j = 1;j <= n;j ++ ) {
scanf ( "%d", &a[i][j] );
if ( a[i][j] ) {
add ( j, i + n, INF, 0 );
add ( i + n, j, 0, 0 );
}
}
for ( int i = 1;i <= m;i ++ ) {
int S;
scanf ( "%d", &S );
for ( int j = 1;j <= S;j ++ )
scanf ( "%d", &b[j] );
b[S + 1] = INF;
for ( int j = 1;j <= S + 1;j ++ ) {
int w;
scanf ( "%d", &w );
add ( i + n, t, ( b[j] - b[j - 1] ), w );
add ( t, i + n, 0, -w );
}
}
LL maxflow, mincost;
MCMF ( maxflow, mincost );
printf ( "%lld", mincost );
return 0;
}






















 2705
2705











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








