Link1:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1575
Tr A
Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 3628 Accepted Submission(s): 2705
每组数据的第一行有n(2 <= n <= 10)和k(2 <= k < 10^9)两个数据。接下来有n行,每行有n个数据,每个数据的范围是[0,9],表示方阵A的内容。
2 2 2 1 0 0 1 3 99999999 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
2 2686
AC code:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<map>
#define LL long long
#define MAXN 1000010
using namespace std;
const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
//----以下为矩阵快速幂模板-----//
const int mod=9973;
const int NUM=11;//定义矩阵能表示的最大维数
int N;//N表示矩阵的维数,以下的矩阵加法、乘法、快速幂都是按N维矩阵运算的
struct Mat{//矩阵的类
int a[NUM][NUM];
void init()//将其初始化为单位矩阵
{
memset(a,0,sizeof(a));
for(int i=0;i<NUM;i++)
{
a[i][i]=1;
}
}
};
Mat add(Mat a,Mat b)//(a+b)%mod 矩阵加法
{
Mat ans;
for(int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<N;j++)
{
ans.a[i][j]=a.a[i][j]+b.a[i][j];
ans.a[i][j]%=mod;
}
}
return ans;
}
Mat mul(Mat a,Mat b) //(a*b)%mod 矩阵乘法
{
Mat ans;
for(int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<N;j++)
{
ans.a[i][j]=0;
for(int k=0;k<N;k++)
{
ans.a[i][j]+=a.a[i][k]*b.a[k][j];
}
ans.a[i][j]%=mod;
}
}
return ans;
}
Mat power(Mat a,int num)//(a^n)%mod 矩阵快速幂
{
Mat ans;
ans.init();
while(num)
{
if(num&1)
{
ans=mul(ans,a);
}
num>>=1;
a=mul(a,a);
}
return ans;
}
Mat pow_sum(Mat a,int num)//(a+a^2+a^3....+a^n)%mod 矩阵的幂和
{
int m;
Mat ans,pre;
if(num==1)
return a;
m=num/2;
pre=pow_sum(a,m);
ans=add(pre,mul(pre,power(a,m)));
if(num&1)
ans=add(ans,power(a,num));
return ans;
}
void output(Mat a)//输出矩阵
{
for(int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<N;j++)
{
printf("%d%c",a.a[i][j],j==N-1?'\n':' ');
}
}
}
//----以上为矩阵快速幂模板-----//
int main()
{
int t,n,k,ans,i,j;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--)
{
scanf("%d%d",&n,&k);
N=n;
ans=0;
Mat a,temp;
for(i=0;i<N;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<N;j++)
{
scanf("%d",&a.a[i][j]);
}
}
temp=power(a,k);
for(i=0;i<N;i++)
{
ans=(ans+temp.a[i][i])%mod;
}
printf("%d\n",ans);
}
return 0;
}
Link2:http://poj.org/problem?id=3070
|
Fibonacci
Description In the Fibonacci integer sequence, F0 = 0, F1 = 1, and Fn = Fn − 1 + Fn − 2 for n ≥ 2. For example, the first ten terms of the Fibonacci sequence are: 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, … An alternative formula for the Fibonacci sequence is
Given an integer n, your goal is to compute the last 4 digits of Fn. Input The input test file will contain multiple test cases. Each test case consists of a single line containing n (where 0 ≤ n ≤ 1,000,000,000). The end-of-file is denoted by a single line containing the number −1. Output For each test case, print the last four digits of Fn. If the last four digits of Fn are all zeros, print ‘0’; otherwise, omit any leading zeros (i.e., print Fn mod 10000). Sample Input 0 9 999999999 1000000000 -1 Sample Output 0 34 626 6875 Hint As a reminder, matrix multiplication is associative, and the product of two 2 × 2 matrices is given by
Also, note that raising any 2 × 2 matrix to the 0th power gives the identity matrix:
Source |
注意:题目中给出的那个斐波那契数列的矩阵表示规律:

这个要记住!!!有时做一些规律题时涉及求F(n)时会用到!!!可利用矩阵快速幂求矩阵{1,1,1,0}的n次幂,在求得的矩阵中,第一行第二列的元素就是F(n)!!!下面有一些题就是利用这个{1,1,1,0}矩阵做的。
AC code:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<map>
#define LL long long
#define MAXN 1000010
using namespace std;
const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
//----以下为矩阵快速幂模板-----//
const int mod=10000;
const int NUM=11;//定义矩阵能表示的最大维数
int N;//N表示矩阵的维数,以下的矩阵加法、乘法、快速幂都是按N维矩阵运算的
struct Mat{//矩阵的类
int a[NUM][NUM];
void init()//将其初始化为单位矩阵
{
memset(a,0,sizeof(a));
for(int i=0;i<NUM;i++)
{
a[i][i]=1;
}
}
};
Mat add(Mat a,Mat b)//(a+b)%mod 矩阵加法
{
Mat ans;
for(int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<N;j++)
{
ans.a[i][j]=a.a[i][j]+b.a[i][j];
ans.a[i][j]%=mod;
}
}
return ans;
}
Mat mul(Mat a,Mat b) //(a*b)%mod 矩阵乘法
{
Mat ans;
for(int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<N;j++)
{
ans.a[i][j]=0;
for(int k=0;k<N;k++)
{
ans.a[i][j]+=a.a[i][k]*b.a[k][j];
}
ans.a[i][j]%=mod;
}
}
return ans;
}
Mat power(Mat a,int num)//(a^n)%mod 矩阵快速幂
{
Mat ans;
ans.init();
while(num)
{
if(num&1)
{
ans=mul(ans,a);
}
num>>=1;
a=mul(a,a);
}
return ans;
}
Mat pow_sum(Mat a,int num)//(a+a^2+a^3....+a^n)%mod 矩阵的幂和
{
int m;
Mat ans,pre;
if(num==1)
return a;
m=num/2;
pre=pow_sum(a,m);
ans=add(pre,mul(pre,power(a,m)));
if(num&1)
ans=add(ans,power(a,num));
return ans;
}
void output(Mat a)//输出矩阵
{
for(int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<N;j++)
{
printf("%d%c",a.a[i][j],j==N-1?'\n':' ');
}
}
}
//----以上为矩阵快速幂模板-----//
int main()
{
int t,n,k,ans,i,j;
while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF)
{
if(n==-1)
break;
Mat a,f;
N=2;
a.a[0][0]=a.a[0][1]=a.a[1][0]=1;
a.a[1][1]=0;
f=power(a,n);
printf("%d\n",f.a[0][1]);
}
return 0;
}
Link3:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1568
Fibonacci
Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 3970 Accepted Submission(s): 1830
(f[0]=0,f[1]=1;f[i] = f[i-1]+f[i-2](i>=2))的值全部给背了下来。
接下来,CodeStar决定要考考他,于是每问他一个数字,他就要把答案说出来,不过有的数字太长了。所以规定超过4位的只要说出前4位就可以了,可是CodeStar自己又记不住。于是他决定编写一个程序来测验zouyu说的是否正确。
0 1 2 3 4 5 35 36 37 38 39 40
0 1 1 2 3 5 9227 1493 2415 3908 6324 1023
因为(1-sqrt(5))/2的绝对值小于1
所以当i较大的时候,往往可以忽略掉这一项
f(i)≈((1+Sqrt(5))/2)^n/sqrt(5);
所以,刚才列举出的HDOJ的1568,可以很简单的20以内直接求解,20以上采用这个公式,或者用log(N)求幂的算法求解 。
fibonacci公式:
对公式取对数:
最后一项小于0并且很小可以不用计算。
假设给出一个数10234432,
那么log10(10234432)=log10(1.0234432*10^7)=log10(1.0234432)+7;
log10(1.0234432)就是log10(10234432)的小数部分.
10^0.010063744=1.023443198
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<queue>
#include<vector>
#include<map>
#include<cmath>
#define LL long long
#define MAXN 1000010
using namespace std;
double f[33];
int main()
{
//freopen("D:\in.txt","r",stdin);
int n,i;
f[0]=0;
f[1]=1;
for(i=2;i<=20;i++)
{
f[i]=f[i-1]+f[i-2];
}
//printf("%.0f\n",f[20]);
while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF)
{
if(n<=20)
printf("%.0f\n",f[n]);
else
{
int answer;
double t=-0.5*log10(5.0)+n*log10(0.5*(1.0+sqrt(5.0)));
double ans=t-floor(t);
ans=pow(10,ans);
answer=(int)(ans*1000);
printf("%d\n",answer);
}
}
return 0;
} Fibonacci Again
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 44266 Accepted Submission(s): 21120
Print the word "no" if not.
0 1 2 3 4 5
no no yes no no no
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<map>
#define LL long long
#define MAXN 1000010
using namespace std;
const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
//----以下为矩阵快速幂模板-----//
const int mod=3;//模3,故这里改为3即可
const int NUM=11;//定义矩阵能表示的最大维数
int N;//N表示矩阵的维数,以下的矩阵加法、乘法、快速幂都是按N维矩阵运算的
struct Mat{//矩阵的类
int a[NUM][NUM];
void init()//将其初始化为单位矩阵
{
memset(a,0,sizeof(a));
for(int i=0;i<NUM;i++)
{
a[i][i]=1;
}
}
};
Mat add(Mat a,Mat b)//(a+b)%mod 矩阵加法
{
Mat ans;
for(int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<N;j++)
{
ans.a[i][j]=a.a[i][j]+b.a[i][j];
ans.a[i][j]%=mod;
}
}
return ans;
}
Mat mul(Mat a,Mat b) //(a*b)%mod 矩阵乘法
{
Mat ans;
for(int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<N;j++)
{
ans.a[i][j]=0;
for(int k=0;k<N;k++)
{
ans.a[i][j]+=a.a[i][k]*b.a[k][j];
}
ans.a[i][j]%=mod;
}
}
return ans;
}
Mat power(Mat a,int num)//(a^n)%mod 矩阵快速幂
{
Mat ans;
ans.init();
while(num)
{
if(num&1)
{
ans=mul(ans,a);
}
num>>=1;
a=mul(a,a);
}
return ans;
}
Mat pow_sum(Mat a,int num)//(a+a^2+a^3....+a^n)%mod 矩阵的幂和
{
int m;
Mat ans,pre;
if(num==1)
return a;
m=num/2;
pre=pow_sum(a,m);
ans=add(pre,mul(pre,power(a,m)));
if(num&1)
ans=add(ans,power(a,num));
return ans;
}
void output(Mat a)//输出矩阵
{
for(int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<N;j++)
{
printf("%d%c",a.a[i][j],j==N-1?'\n':' ');
}
}
}
//----以上为矩阵快速幂模板-----//
int main()
{
int t,n,k,i,j;
while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF)
{
if(n==-1)
break;
if(n==0||n==1)
{
printf("no\n");
}
else
{
Mat a,f,fa,ans;
N=2;
fa.a[0][0]=11;
fa.a[0][1]=7;
a.a[0][0]=a.a[0][1]=a.a[1][0]=1;
a.a[1][1]=0;
f=power(a,n-1);
for(int i=0;i<1;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<N;j++)
{
ans.a[i][j]=0;
for(int k=0;k<N;k++)
{
ans.a[i][j]=(ans.a[i][j]+fa.a[i][k]*f.a[k][j])%3;
}
}
}
//printf("%d\n",ans.a[0][0]);
if(ans.a[0][0]%3==0)
printf("yes\n");
else
{
printf("no\n");
}
}
}
return 0;
}
Gauss Fibonacci
Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 2796 Accepted Submission(s): 1158
How good an opportunity that Gardon can not give up! The "Problem GF" told by Angel is actually "Gauss Fibonacci".
As we know ,Gauss is the famous mathematician who worked out the sum from 1 to 100 very quickly, and Fibonacci is the crazy man who invented some numbers.
Arithmetic progression:
g(i)=k*i+b;
We assume k and b are both non-nagetive integers.
Fibonacci Numbers:
f(0)=0
f(1)=1
f(n)=f(n-1)+f(n-2) (n>=2)
The Gauss Fibonacci problem is described as follows:
Given k,b,n ,calculate the sum of every f(g(i)) for 0<=i<n
The answer may be very large, so you should divide this answer by M and just output the remainder instead.
Each of them will not exceed 1,000,000,000.
2 1 4 100 2 0 4 100
21 12
分析:看到数据的范围,我们就应该想到普通的暴力是不可取的,所以这道题需要解决两个问题,一个是如何快速的计算Fibonacci数列的第g(i)项,二是如何快速的将它们相加求和。
首先来解决第一个问题,本文的主题不就是快速的计算递推式的任意一项吗?所以,先让我们来找找前面的提到过的构造矩阵,从数列的递推式出发:f(n)= f(n-1)+ f(n-2),我们换一个简洁一些的等式:c = a + b(c是本项,a是后第一项,b是后第二项)。很明显,我们最后所得到的矩阵中必须要包含a+b一项,因为这正是我们想要计算的,同时我们的初始矩阵也不难想到,必须要有a和b,这样才能得到下一项c,那么关键就是构造矩阵了,其实反推一下就可以了,具体看的图: 。如此一来只需要将上面第一个矩阵开i次幂,然后乘上第二个矩阵,就可以得到包含Fibonacci数列第i项的第i个矩阵了,其中a=0,b=1。(即利用矩阵快速幂求矩阵{1,1,1,0}的n次幂,在求得的矩阵中,第一行第二列的元素就是Fibonacci数列第n项F(n))
。如此一来只需要将上面第一个矩阵开i次幂,然后乘上第二个矩阵,就可以得到包含Fibonacci数列第i项的第i个矩阵了,其中a=0,b=1。(即利用矩阵快速幂求矩阵{1,1,1,0}的n次幂,在求得的矩阵中,第一行第二列的元素就是Fibonacci数列第n项F(n))
接下来需要解决第二个问题,由于g(i)= k*i + b的,所以题目要求计算的就是f(b)+ f(k+b)+ f(k*2+b)+ ... + f(k*(n-1)+b),依据上面的构造矩阵,我们用矩阵A重写前面的等式,即:A^b+ A^(k+b)+ A^(k*2+b)+ ... + A^(k*(n-1)+b),继续变形:A^b*(1+ A^k+ A^(k*2)+ ... + A^(k*(n-1)),令矩阵B=A^k,那么A^b*(1+ B ^1+ B^2)+ ... + B^(n-1)),结果已经很明显了,还记得二分吗?括号里面的和不正是上一次我们写过的二分求和么。到此,结果就可以快速的计算出来了。
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<map>
#define LL long long
#define MAXN 1000010
using namespace std;
const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
//----以下为矩阵快速幂模板-----//
//const int mod=3;//模3,故这里改为3即可
int mod;
const int NUM=11;//定义矩阵能表示的最大维数
int N;//N表示矩阵的维数,以下的矩阵加法、乘法、快速幂都是按N维矩阵运算的
struct Mat{//矩阵的类
LL a[NUM][NUM];
void init()//将其初始化为单位矩阵
{
memset(a,0,sizeof(a));
for(int i=0;i<NUM;i++)
{
a[i][i]=1;
}
}
};
Mat add(Mat a,Mat b)//(a+b)%mod 矩阵加法
{
Mat ans;
for(int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<N;j++)
{
ans.a[i][j]=(a.a[i][j]%mod)+(b.a[i][j]%mod);
ans.a[i][j]%=mod;
}
}
return ans;
}
Mat mul(Mat a,Mat b) //(a*b)%mod 矩阵乘法
{
Mat ans;
for(int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<N;j++)
{
ans.a[i][j]=0;
for(int k=0;k<N;k++)
{
ans.a[i][j]=(ans.a[i][j]%mod)+(a.a[i][k]%mod)*(b.a[k][j]%mod);
}
ans.a[i][j]%=mod;
}
}
return ans;
}
Mat power(Mat a,int num)//(a^n)%mod 矩阵快速幂
{
Mat ans;
ans.init();
while(num)
{
if(num&1)
{
ans=mul(ans,a);
}
num>>=1;
a=mul(a,a);
}
return ans;
}
Mat pow_sum(Mat a,int num)//(a+a^2+a^3....+a^n)%mod 矩阵的幂和
{
int m;
Mat ans,pre;
if(num==1)
return a;
m=num/2;
pre=pow_sum(a,m);
ans=add(pre,mul(pre,power(a,m)));
if(num&1)
ans=add(ans,power(a,num));
return ans;
}
void output(Mat a)//输出矩阵
{
for(int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<N;j++)
{
printf("%lld%c",a.a[i][j],j==N-1?'\n':' ');
}
}
}
//----以上为矩阵快速幂模板-----//
int main()
{
int k,b,n,m;
while(scanf("%d%d%d%d",&k,&b,&n,&m)!=EOF)
{
Mat A,B,E,ans;
N=2;
mod=m;
A.a[0][0]=A.a[0][1]=A.a[1][0]=1;
A.a[1][1]=0;
E.init();
B=power(A,k);
ans=mul(power(A,b),(add(E,pow_sum(B,n-1))));
printf("%lld\n",ans.a[0][1]);
}
return 0;
}
Link6:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1757
A Simple Math Problem
Time Limit: 3000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 3485 Accepted Submission(s): 2101
If x < 10 f(x) = x.
If x >= 10 f(x) = a0 * f(x-1) + a1 * f(x-2) + a2 * f(x-3) + …… + a9 * f(x-10);
And ai(0<=i<=9) can only be 0 or 1 .
Now, I will give a0 ~ a9 and two positive integers k and m ,and could you help Lele to caculate f(k)%m.
In each case, there will be two lines.
In the first line , there are two positive integers k and m. ( k<2*10^9 , m < 10^5 )
In the second line , there are ten integers represent a0 ~ a9.
10 9999 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 20 500 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0
45 104
 ^(n-9);
^(n-9);
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<map>
#define LL long long
#define MAXN 1000010
using namespace std;
const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
//----以下为矩阵快速幂模板-----//
//const int mod=3;//模3,故这里改为3即可
int mod;
const int NUM=12;//定义矩阵能表示的最大维数
int N;//N表示矩阵的维数,以下的矩阵加法、乘法、快速幂都是按N维矩阵运算的
struct Mat{//矩阵的类
LL a[NUM][NUM];
void init()//将其初始化为单位矩阵
{
memset(a,0,sizeof(a));
for(int i=0;i<NUM;i++)
{
a[i][i]=1;
}
}
};
Mat add(Mat a,Mat b)//(a+b)%mod 矩阵加法
{
Mat ans;
for(int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<N;j++)
{
ans.a[i][j]=(a.a[i][j]%mod)+(b.a[i][j]%mod);
ans.a[i][j]%=mod;
}
}
return ans;
}
Mat mul(Mat a,Mat b) //(a*b)%mod 矩阵乘法
{
Mat ans;
for(int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<N;j++)
{
ans.a[i][j]=0;
for(int k=0;k<N;k++)
{
ans.a[i][j]=(ans.a[i][j]%mod)+(a.a[i][k]%mod)*(b.a[k][j]%mod);
}
ans.a[i][j]%=mod;
}
}
return ans;
}
Mat power(Mat a,int num)//(a^n)%mod 矩阵快速幂
{
Mat ans;
ans.init();
while(num)
{
if(num&1)
{
ans=mul(ans,a);
}
num>>=1;
a=mul(a,a);
}
return ans;
}
Mat pow_sum(Mat a,int num)//(a+a^2+a^3....+a^n)%mod 矩阵的幂和
{
int m;
Mat ans,pre;
if(num==1)
return a;
m=num/2;
pre=pow_sum(a,m);
ans=add(pre,mul(pre,power(a,m)));
if(num&1)
ans=add(ans,power(a,num));
return ans;
}
void output(Mat a)//输出矩阵
{
for(int i=0;i<N;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<N;j++)
{
printf("%lld%c",a.a[i][j],j==N-1?'\n':' ');
}
}
}
//----以上为矩阵快速幂模板-----//
int main()
{
int k,m,i,j,kk;
LL a[11];
while(scanf("%d%d",&kk,&m)!=EOF)
{
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
{
scanf("%lld",&a[i]);
}
if(kk<10)
printf("%d\n",k%m);
else
{
Mat A,B,mi,ans;
N=10;
mod=m;
memset(A.a,0,sizeof(A.a));
memset(B.a,0,sizeof(B.a));
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
{
A.a[0][i]=9-i;
B.a[i][0]=a[i];
B.a[i][i+1]=1;
}
//output(A);
//output(B);
B=power(B,kk-9);
for(int i=0;i<1;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<N;j++)
{
ans.a[i][j]=0;
for(int k=0;k<N;k++)
{
ans.a[i][j]=(ans.a[i][j]%mod)+(A.a[i][k]%mod)*(B.a[k][j]%mod);
}
ans.a[i][j]%=mod;
}
}
printf("%lld\n",ans.a[0][0]%mod);
}
}
return 0;
}











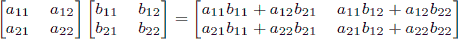 .
. .
.


















 269
269

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










