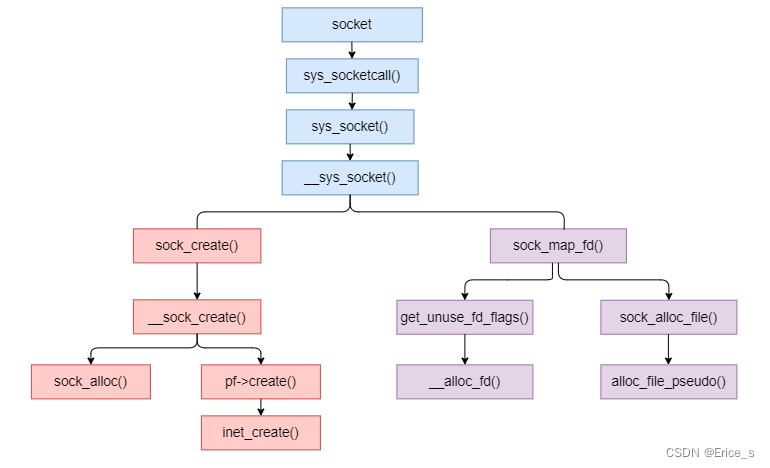
本文将以socket函数为例,分析它在Linux5.12.10内核中的实现,先观此图,宏观上把握它在内核中的函数调用关系:
socket函数API
socket 函数原型:
#include <sys/socket.h>
int socket(int domain, int type, int protocol)
该函数用于创建一个新的socket。
第一个参数:
domain:协议簇,常用的协议簇有:AF_INET, AF_INET6, AF_LOCAL。这个参数决定了socket的地址类型,这个应该很好理解AF_INET用于ipv4地址,AF_INET6用于ipv6地址,AF_LOCAL用于本地进程间通信。
第二个参数:
type:socket类型有好几种,主要是两种:SOCK_STREAM、SOCK_DGRAM(数据报),通俗说就是字节流socket和数据报socket,当你在创建的使用使用哪一种由第二个参数指定。stream socket基于TCP协议,是一个有序、可靠、全双工的字节流通道。datagram socket基于UDP协议,不需要建立和维持连接,可能会丢失或错乱。
第三个参数:
protocol:指定协议,常用协议有IPPROTO_TCP、IPPROTO_UDP、IPPROTO_STCP、IPPROTO_TICP等,分别对应TCP协议,UDP协议,STCP协议,TICP协议。通常这个参数设置为0,表示自适应协议
所以这个函数通常这样用:
int socket_fd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
在Linux下一个进程默认打开的文件描述符是1024个,也就是说一个进程最多能创建1024个socket,超过就会报Too many open files(这个问题在工作中也会遇到)。通过ulimit命令可以查看到
# ulimit -a
core file size (blocks, -c) unlimited
data seg size (kbytes, -d) unlimited
scheduling priority (-e) 0
file size (blocks, -f) unlimited
pending signals (-i) 29414
max locked memory (kbytes, -l) 16384
max memory size (kbytes, -m) unlimited
open files (-n) 1024
pipe size (512 bytes, -p) 8
POSIX message queues (bytes, -q) 819200
real-time priority (-r) 0
stack size (kbytes, -s) 8192
cpu time (seconds, -t) unlimited
max user processes (-u) 29414
virtual memory (kbytes, -v) unlimited
file locks (-x) unlimited
如果你要修改这个上限到2021个:
# ulimit -HSn 2021
内核源码
//~/linux-5.12.10/include/linux/socket.h 头文件
extern int __sys_socket(int family, int type, int protocol);
socket函数调用结束后,用户层看到返回一个整型的句柄,但是内核在内部会创建一系列的socket相关的内核对象(不是只有一个对象)
// ~/linux-5.12.10/net/socket.c line:1481
/* Mask which covers at least up to SOCK_MASK-1. The
* remaining bits are used as flags. */
#define SOCK_TYPE_MASK 0xf
int __sys_socket(int family, int type, int protocol)
{
int retval;
struct socket *sock;
int flags;
//... 略去参数合法性校验代码
retval = sock_create(family, type, protocol, &sock);
if (retval < 0)
return retval;
return sock_map_fd(sock, flags & (O_CLOEXEC | O_NONBLOCK));
}
SYSCALL_DEFINE3(socket, int, family, int, type, int, protocol)
{
return __sys_socket(family, type, protocol);
}
sock_create
sock_create是创建socket的主要位置,其中sock_create又调用__sock_create
// ~/linux-5.12.10/net/socket.c line:1337
/*
//net_proto_family结构体定义了每一个协议族的新建socket句柄
struct net_proto_family {
int family;
int (*create)(struct net *net, struct socket *sock,
int protocol, int kern);
struct module *owner;
};
static const struct net_proto_family __rcu *net_families[NPROTO] __read_mostly;
*/
int __sock_create(struct net *net, int family, int type, int protocol,
struct socket **res, int kern)
{
int err;
struct socket *sock;
const struct net_proto_family *pf;
/*
* Check protocol is in range
*/
if (family < 0 || family >= NPROTO)
return -EAFNOSUPPORT;
if (type < 0 || type >= SOCK_MAX)
return -EINVAL;
/* Compatibility.
This uglymoron is moved from INET layer to here to avoid
deadlock in module load.
*/
if (family == PF_INET && type == SOCK_PACKET) {
pr_info_once("%s uses obsolete (PF_INET,SOCK_PACKET)\n",
current->comm);
family = PF_PACKET;
}
err = security_socket_create(family, type, protocol, kern);
if (err)
return err;
/*
* Allocate the socket and allow the family to set things up. if
* the protocol is 0, the family is instructed to select an appropriate
* default.
*/
// 分配socket对象,如果protocol为0 将会被设置合适的协议
sock = sock_alloc();
if (!sock) {
net_warn_ratelimited("socket: no more sockets\n");
return -ENFILE; /* Not exactly a match, but its the
closest posix thing */
}
sock->type = type;
#ifdef CONFIG_MODULES
/* Attempt to load a protocol module if the find failed.
*
* 12/09/1996 Marcin: But! this makes REALLY only sense, if the user
* requested real, full-featured networking support upon configuration.
* Otherwise module support will break!
*/
if (rcu_access_pointer(net_families[family]) == NULL)
request_module("net-pf-%d", family);
#endif
// 获取每个协议族的操作表
rcu_read_lock();
pf = rcu_dereference(net_families[family]);
err = -EAFNOSUPPORT;
if (!pf)
goto out_release;
/*
* We will call the ->create function, that possibly is in a loadable
* module, so we have to bump that loadable module refcnt first.
*/
if (!try_module_get(pf->owner))
goto out_release;
/* Now protected by module ref count */
rcu_read_unlock();
/// 调用指定协议族的创建函数,对于AF_INET对应的是inet_create
err = pf->create(net, sock, protocol, kern);
if (err < 0)
goto out_module_put;
/*
* Now to bump the refcnt of the [loadable] module that owns this
* socket at sock_release time we decrement its refcnt.
*/
if (!try_module_get(sock->ops->owner))
goto out_module_busy;
/*
* Now that we're done with the ->create function, the [loadable]
* module can have its refcnt decremented
*/
module_put(pf->owner);
err = security_socket_post_create(sock, family, type, protocol, kern);
if (err)
goto out_sock_release;
*res = sock;
return 0;
out_module_busy:
err = -EAFNOSUPPORT;
out_module_put:
sock->ops = NULL;
module_put(pf->owner);
out_sock_release:
sock_release(sock);
return err;
out_release:
rcu_read_unlock();
goto out_sock_release;
}
inet_create
在 __sock_create 里,首先调用sock_alloc来分配一个struct socket内核对象,接着获取协议族的操作函数表,并调用其create方法。对于AF_INET协议族来说,执行到的是inet_create方法
//~/linux-5.12.10/net/ipv4/af_inet.c
/*
/* This is used to register socket interfaces for IP protocols. */
struct inet_protosw {
struct list_head list;
/* These two fields form the lookup key. */
unsigned short type; /* This is the 2nd argument to socket(2). */
unsigned short protocol; /* This is the L4 protocol number. */
struct proto *prot;
const struct proto_ops *ops;
unsigned char flags; /* See INET_PROTOSW_* below. */
};
#define list_for_each_entry_rcu list_for_each_entry
#define list_for_each_entry(pos, head, member) \
for (pos = list_first_entry(head, typeof(*pos), member); \
&pos->member != (head); \
pos = list_next_entry(pos, member))
*/
static int inet_create(struct net *net, struct socket *sock, int protocol,
int kern)
{
struct sock *sk;
struct inet_protosw *answer;
struct inet_sock *inet;
struct proto *answer_prot;
unsigned char answer_flags;
int try_loading_module = 0;
int err;
if (protocol < 0 || protocol >= IPPROTO_MAX)
return -EINVAL;
sock->state = SS_UNCONNECTED;
/* Look for the requested type/protocol pair. */
lookup_protocol:
err = -ESOCKTNOSUPPORT;
rcu_read_lock();
list_for_each_entry_rcu(answer, &inetsw[sock->type], list) {
err = 0;
/* Check the non-wild match. */
if (protocol == answer->protocol) {
if (protocol != IPPROTO_IP)
break;
} else {
/* Check for the two wild cases. */
if (IPPROTO_IP == protocol) {
protocol = answer->protocol;
break;
}
if (IPPROTO_IP == answer->protocol)
break;
}
err = -EPROTONOSUPPORT;
}
//...
err = -EPERM;
if (sock->type == SOCK_RAW && !kern &&
!ns_capable(net->user_ns, CAP_NET_RAW))
goto out_rcu_unlock;
//将 inet_stream_ops 赋值到sock->ops
sock->ops = answer->ops;
answer_prot = answer->prot;
answer_flags = answer->flags;
rcu_read_unlock();
WARN_ON(!answer_prot->slab);
err = -ENOBUFS;
// 分配sock对象,并把answer_prot赋值到sock->sk_prot
sk = sk_alloc(net, PF_INET, GFP_KERNEL, answer_prot, kern);
if (!sk)
goto out;
err = 0;
if (INET_PROTOSW_REUSE & answer_flags)
sk->sk_reuse = SK_CAN_REUSE;
inet = inet_sk(sk);
inet->is_icsk = (INET_PROTOSW_ICSK & answer_flags) != 0;
inet->nodefrag = 0;
if (SOCK_RAW == sock->type) {
inet->inet_num = protocol;
if (IPPROTO_RAW == protocol)
inet->hdrincl = 1;
}
if (net->ipv4.sysctl_ip_no_pmtu_disc)
inet->pmtudisc = IP_PMTUDISC_DONT;
else
inet->pmtudisc = IP_PMTUDISC_WANT;
inet->inet_id = 0;
// 对sock对象进行初始化
sock_init_data(sock, sk);
sk->sk_destruct = inet_sock_destruct;
sk->sk_protocol = protocol;
sk->sk_backlog_rcv = sk->sk_prot->backlog_rcv;
inet->uc_ttl = -1;
inet->mc_loop = 1;
inet->mc_ttl = 1;
inet->mc_all = 1;
inet->mc_index = 0;
inet->mc_list = NULL;
inet->rcv_tos = 0;
sk_refcnt_debug_inc(sk);
if (inet->inet_num) {
/* It assumes that any protocol which allows
* the user to assign a number at socket
* creation time automatically
* shares.
*/
inet->inet_sport = htons(inet->inet_num);
/* Add to protocol hash chains. */
err = sk->sk_prot->hash(sk);
if (err) {
sk_common_release(sk);
goto out;
}
}
if (sk->sk_prot->init) {
err = sk->sk_prot->init(sk);
if (err) {
sk_common_release(sk);
goto out;
}
}
if (!kern) {
err = BPF_CGROUP_RUN_PROG_INET_SOCK(sk);
if (err) {
sk_common_release(sk);
goto out;
}
}
out:
return err;
out_rcu_unlock:
rcu_read_unlock();
goto out;
}
当流程走到inet_create函数的时候根据type去inetsw数组中找到对应类型套接字的inet_protosw结构体,我们前面提到协议栈中已经定义了PF_INET协议族支持的inet_protosw结构体,总共有4个。
找到inet_protosw结构体以后还需要进一步判断protocol和inet_protosw中定义的protocol是否是一致的。内核中定义支持的protocol有一个特殊的值IPPROTO_IP(IPPROTO_IP为0),可以理解为一个通配符也可以理解为一个默认值,就是说我不指定protocol,由内核自己决定使用哪一个protocol。
那么内核根据什么来选择protocol呢?就是根据内核定义的全局inetsw中对应类型的inet_protosw中的protocol。
/* Upon startup we insert all the elements in inetsw_array[] into
* the linked list inetsw.
*/
// static struct list_head inetsw[SOCK_MAX];
// inetsw_array挂在链表上
static struct inet_protosw inetsw_array[] =
{
{
.type = SOCK_STREAM,
.protocol = IPPROTO_TCP,
.prot = &tcp_prot,
.ops = &inet_stream_ops,
.flags = INET_PROTOSW_PERMANENT |
INET_PROTOSW_ICSK,
},
{
.type = SOCK_DGRAM,
.protocol = IPPROTO_UDP,
.prot = &udp_prot,
.ops = &inet_dgram_ops,
.flags = INET_PROTOSW_PERMANENT,
},
{
.type = SOCK_DGRAM,
.protocol = IPPROTO_ICMP,
.prot = &ping_prot,
.ops = &inet_sockraw_ops,
.flags = INET_PROTOSW_REUSE,
},
{
.type = SOCK_RAW,
.protocol = IPPROTO_IP, /* wild card */ //0
.prot = &raw_prot,
.ops = &inet_sockraw_ops,
.flags = INET_PROTOSW_REUSE,
}
};
// ~/linux-5.12.10/net/ipv4/af_inet.c inet_create函数
// int socket_fd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
// 初始化protocol为0, type为SOCK_STREAM
// 经过list_for_each_entry_rcu遍历,protocol修正为IPPROTO_TCP
// protocol = answer->protocol --> protocol = IPPROTO_TCP
// 如果type为SOCK_DGRAM, 则protocol被修正为IPPROTO_UDP
list_for_each_entry_rcu(answer, &inetsw[sock->type], list) {
err = 0;
/* Check the non-wild match. */
if (protocol == answer->protocol) {
if (protocol != IPPROTO_IP)
break;
} else {
/* Check for the two wild cases. */
if (IPPROTO_IP == protocol) {
protocol = answer->protocol;
break;
}
if (IPPROTO_IP == answer->protocol)
break;
}
err = -EPROTONOSUPPORT;
}
继续看sock_init_data实现
// ~/linux-5.12.10/net/core/sock.c
void sock_init_data(struct socket *sock, struct sock *sk)
{
sk_init_common(sk);
sk->sk_send_head = NULL;
timer_setup(&sk->sk_timer, NULL, 0);
sk->sk_allocation = GFP_KERNEL;
sk->sk_rcvbuf = sysctl_rmem_default;
sk->sk_sndbuf = sysctl_wmem_default;
sk->sk_state = TCP_CLOSE;
sk_set_socket(sk, sock);
sock_set_flag(sk, SOCK_ZAPPED);
if (sock) {
sk->sk_type = sock->type;
RCU_INIT_POINTER(sk->sk_wq, &sock->wq);
sock->sk = sk;
sk->sk_uid = SOCK_INODE(sock)->i_uid;
} else {
RCU_INIT_POINTER(sk->sk_wq, NULL);
sk->sk_uid = make_kuid(sock_net(sk)->user_ns, 0);
}
rwlock_init(&sk->sk_callback_lock);
if (sk->sk_kern_sock)
lockdep_set_class_and_name(
&sk->sk_callback_lock,
af_kern_callback_keys + sk->sk_family,
af_family_kern_clock_key_strings[sk->sk_family]);
else
lockdep_set_class_and_name(
&sk->sk_callback_lock,
af_callback_keys + sk->sk_family,
af_family_clock_key_strings[sk->sk_family]);
sk->sk_state_change = sock_def_wakeup;
sk->sk_data_ready = sock_def_readable;
sk->sk_write_space = sock_def_write_space;
sk->sk_error_report = sock_def_error_report;
sk->sk_destruct = sock_def_destruct;
sk->sk_frag.page = NULL;
sk->sk_frag.offset = 0;
sk->sk_peek_off = -1;
sk->sk_peer_pid = NULL;
sk->sk_peer_cred = NULL;
sk->sk_write_pending = 0;
sk->sk_rcvlowat = 1;
sk->sk_rcvtimeo = MAX_SCHEDULE_TIMEOUT;
sk->sk_sndtimeo = MAX_SCHEDULE_TIMEOUT;
sk->sk_stamp = SK_DEFAULT_STAMP;
#if BITS_PER_LONG==32
seqlock_init(&sk->sk_stamp_seq);
#endif
atomic_set(&sk->sk_zckey, 0);
#ifdef CONFIG_NET_RX_BUSY_POLL
sk->sk_napi_id = 0;
sk->sk_ll_usec = sysctl_net_busy_read;
#endif
sk->sk_max_pacing_rate = ~0UL;
sk->sk_pacing_rate = ~0UL;
WRITE_ONCE(sk->sk_pacing_shift, 10);
sk->sk_incoming_cpu = -1;
sk_rx_queue_clear(sk);
/*
* Before updating sk_refcnt, we must commit prior changes to memory
* (Documentation/RCU/rculist_nulls.rst for details)
*/
smp_wmb();
refcount_set(&sk->sk_refcnt, 1);
atomic_set(&sk->sk_drops, 0);
}
当软中断上收到数据包时会调用sk_data_ready函数指针(实际被设置成了sock_def_readable())来唤醒在sock上等待的进程。
sock_alloc
sock_alloc函数分配一个struct socket结构体,将sockfs相关属性填充在socket_alloc结构体的vfs_inode变量中,以限定后续对这个sock文件允许的操作。sock_alloc()里体现了linux一切皆文件(Everything is a file)理念,即使用文件系统来管理socket,这也是VFS所要达到的效果
struct socket *sock_alloc(void)
{
struct inode *inode;
struct socket *sock;
inode = new_inode_pseudo(sock_mnt->mnt_sb);
if (!inode)
return NULL;
sock = SOCKET_I(inode);
inode->i_ino = get_next_ino();
inode->i_mode = S_IFSOCK | S_IRWXUGO;
inode->i_uid = current_fsuid();
inode->i_gid = current_fsgid();
inode->i_op = &sockfs_inode_ops;
return sock;
}
sock_map_fd
static int sock_map_fd(struct socket *sock, int flags)
{
struct file *newfile;
int fd = get_unused_fd_flags(flags);
if (unlikely(fd < 0)) {
sock_release(sock);
return fd;
}
newfile = sock_alloc_file(sock, flags, NULL);
if (!IS_ERR(newfile)) {
fd_install(fd, newfile);
return fd;
}
put_unused_fd(fd);
return PTR_ERR(newfile);
}
// linux-5.12.10/fs/file.c
int __get_unused_fd_flags(unsigned flags, unsigned long nofile)
{
return alloc_fd(0, nofile, flags);
}
int get_unused_fd_flags(unsigned flags)
{
return __get_unused_fd_flags(flags, rlimit(RLIMIT_NOFILE));
}
sock_map_fd–>get_unused_fd_flags–>__get_unused_fd_flags–>alloc_fd获取一个可用的fd
/*
* allocate a file descriptor, mark it busy.
*/
static int alloc_fd(unsigned start, unsigned end, unsigned flags)
{
struct files_struct *files = current->files;
unsigned int fd;
int error;
struct fdtable *fdt;
spin_lock(&files->file_lock);
repeat:
fdt = files_fdtable(files);
fd = start;
if (fd < files->next_fd)
fd = files->next_fd;
if (fd < fdt->max_fds)
fd = find_next_fd(fdt, fd);
/*
* N.B. For clone tasks sharing a files structure, this test
* will limit the total number of files that can be opened.
*/
error = -EMFILE;
if (fd >= end)
goto out;
error = expand_files(files, fd);
if (error < 0)
goto out;
/*
* If we needed to expand the fs array we
* might have blocked - try again.
*/
if (error)
goto repeat;
if (start <= files->next_fd)
files->next_fd = fd + 1;
__set_open_fd(fd, fdt);
if (flags & O_CLOEXEC)
__set_close_on_exec(fd, fdt);
else
__clear_close_on_exec(fd, fdt);
error = fd;
#if 1
/* Sanity check */
if (rcu_access_pointer(fdt->fd[fd]) != NULL) {
printk(KERN_WARNING "alloc_fd: slot %d not NULL!\n", fd);
rcu_assign_pointer(fdt->fd[fd], NULL);
}
#endif
out:
spin_unlock(&files->file_lock);
return error;
}
sock_map_fd–>get_unused_fd_flags–>__get_unused_fd_flags–>sock_alloc_file分配struct file结构
// net/socket.c
/*
* Obtains the first available file descriptor and sets it up for use.
*
* These functions create file structures and maps them to fd space
* of the current process. On success it returns file descriptor
* and file struct implicitly stored in sock->file.
* Note that another thread may close file descriptor before we return
* from this function. We use the fact that now we do not refer
* to socket after mapping. If one day we will need it, this
* function will increment ref. count on file by 1.
*
* In any case returned fd MAY BE not valid!
* This race condition is unavoidable
* with shared fd spaces, we cannot solve it inside kernel,
* but we take care of internal coherence yet.
*/
/**
* sock_alloc_file - Bind a &socket to a &file
* @sock: socket
* @flags: file status flags
* @dname: protocol name
*
* Returns the &file bound with @sock, implicitly storing it
* in sock->file. If dname is %NULL, sets to "".
* On failure the return is a ERR pointer (see linux/err.h).
* This function uses GFP_KERNEL internally.
*/
struct file *sock_alloc_file(struct socket *sock, int flags, const char *dname)
{
struct file *file;
if (!dname)
dname = sock->sk ? sock->sk->sk_prot_creator->name : "";
file = alloc_file_pseudo(SOCK_INODE(sock), sock_mnt, dname,
O_RDWR | (flags & O_NONBLOCK),
&socket_file_ops);
if (IS_ERR(file)) {
sock_release(sock);
return file;
}
sock->file = file;
file->private_data = sock;
stream_open(SOCK_INODE(sock), file);
return file;
}
相关数据结构
// file: include/linux/net.h
struct socket_wq {
/* Note: wait MUST be first field of socket_wq */
wait_queue_head_t wait;
struct fasync_struct *fasync_list;
unsigned long flags; /* %SOCKWQ_ASYNC_NOSPACE, etc */
struct rcu_head rcu;
} ____cacheline_aligned_in_smp;
/**
* struct socket - general BSD socket
* @state: socket state (%SS_CONNECTED, etc)
* @type: socket type (%SOCK_STREAM, etc)
* @flags: socket flags (%SOCK_NOSPACE, etc)
* @ops: protocol specific socket operations
* @file: File back pointer for gc
* @sk: internal networking protocol agnostic socket representation
* @wq: wait queue for several uses
*/
struct socket {
socket_state state;
short type;
unsigned long flags;
struct file *file;
struct sock *sk;
const struct proto_ops *ops;
struct socket_wq wq;
};
至此,一个tcp对象,确切地说是AF_INET协议族下的SOCK_STREAM对象就算创建完成了。这里花费了一个socket系统调用的开销。
ref: https://www.cnblogs.com/liyuanhong/articles/10591069.html























 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










