算法复杂度学习
时间复杂度
选择排序的时间复杂度:
- 最坏的:an^2 + bn + c => O(n^2)
- 最优的:n => O(n),使用符号Ω
- 平均的:O(n^2),使用符号θ
评价一个算法的好坏:先看时间复杂度,再分析不同数据样本下的实际运行时间(也就是“常数项时间”)
时间复杂度是按照最差的情况来写的
空间复杂度
- O(1)
- 定义若干个变量
- O(n)
- 定义一个[n]一维数组
- O(n^2)
- 定义一个[N][N]的二维数组
排序
选择排序
public static void selectorSort(int[] arr) {
if(arr==null||arr.length<2) return;
for(int i=0;i<arr.length-1;i++) {
int minIdx = i;
for(int j=i+1;j<arr.length;j++) {
if(arr[minIdx]>arr[j]) minIdx = j;
}
swap(arr,i,minIdx);
}
}
冒泡排序
public static void bubbleSort(int[] arr) {
if(arr==null||arr.length<2) return;
//冒泡,就是不断往最后一个地方冒泡
for(int i=arr.length-1;i>0;i--) {
for(int j=0;j<i;j++) {
if(arr[j]>arr[j+1]) swap(arr,j,j+1);
}
}
}
插入排序
public static void insertionSort(int[] arr) {
if(arr==null||arr.length<2) return;
//我要保证0-i有序
for(int i=1;i<arr.length;i++) {
for(int j=i;j>0&&arr[j]<arr[j-1];j--) {
swap(arr,j-1,j);
}
}
}
归并排序
代码
public static void mergeSort(int[] arr) {
if(arr == null||arr.length < 2) return;
process(arr,0,arr.length-1);
}
private static void process(int[] arr,int l,int r) {
if(l == r) return;
int mid = l + ( (r-l) >> 1 );
process(arr,l,mid);
process(arr,mid+1,r);
merge(arr,l,mid,r);
}
private static void merge(int[] arr,int l,int mid,int r) {
int[] helper = new int[r-l+1];
int p1 = l;
int p2 = mid+1;
int i = 0;
while(p1<=mid && p2<=r) helper[i++] = arr[p1]<arr[p2]?arr[p1++]:arr[p2++];
while(p1<=mid) helper[i++] = arr[p1++];
while(p2<=r) helper[i++] = arr[p2++];
for(i=0;i<helper.length;i++) arr[l+i] = helper[i];
}
master应用
T(N) = 2T(N/2) + O(N)
a = 2,b = 2,d = 1
log(2,2) = 1 = d
可知时间复杂度为O(N^d * logN) = O(NlogN)
实质
为什么它的时间复杂度比上面三个优秀
因为这个算法没有浪费比较,就是说之前的比较结果被保存起来了,后面再比较的时候可以利用之前比较的结果,而上面的O(N^2)的算法,没有做到这一点,它们每次比较只是获益了一个元素,没有把比较传递下去。
相关题目
小和问题
public class T1_小和问题 {
//问题描述,给你一个数组,对应每个元素,其前面比它小的加起来记作a,把每个元素的a加起来就是答案
//我们的处理:后面比当前元素a大的有n个,变量ans为答案,则 ans += a*n
public static int minSum(int[] arr) {
if(arr == null || arr.length < 1) return 0;
return process(arr, 0, arr.length-1);
}
private static int process(int[] arr,int l,int r) {
if(l == r) return 0;
int mid = l + ((r-l)>>1);
return process(arr, l, mid)+process(arr, mid+1, r)+merge(arr, l, mid, r);
}
private static int merge(int[] arr,int l,int mid,int r) {
int[] helper = new int[r-l+1];
int res = 0;
int i=0;
int p1 = l;
int p2 = mid + 1;
while(p1<=mid&&p2<=r) {
if(arr[p1]<arr[p2]) {
res += (r-p2+1)*arr[p1];
helper[i++] = arr[p1++];
}else if(arr[p1]>arr[p2]) {
helper[i++] = arr[p2++];
}else {
//这个是唯一和普通归并有一点不一样的地方
helper[i++] = arr[p2++];
}
}
while(p1<=mid) helper[i++] = arr[p1++];
while(p2<=r) helper[i++] = arr[p2++];
for(i=0;i<helper.length;i++) arr[l+i] = helper[i];
return res;
}
}
逆序对
public class T2_逆序对 {
//如果前面一个数字大于后面的数字,则这两个数字组成一个逆序对
public static int reverseSum(int[] arr) {
if(arr==null || arr.length < 2) return 0;
return process(arr,0,arr.length-1);
}
private static int process(int[] arr,int l,int r) {
if(l == r) return 0;
int m = l + ((r-l)>>1);
return process(arr, l, m)+process(arr, m+1, r)+merge(arr,l,m,r);
}
private static int merge(int[] arr,int l,int m,int r) {
int res = 0;
int[] helper = new int[r-l+1];
int p1 = l;
int p2 = m+1;
int i = 0;
//这个过程,逻辑上我们将p1看成右边的,p2看成左边的,就好像上面最小和了
while(p1<=m&&p2<=r) {
if(arr[p1]>arr[p2]) {
res += m - p1 + 1;
helper[i++] = arr[p2++];
}else if(arr[p1]<arr[p2]) {
helper[i++] = arr[p1++];
}else {
helper[i++] = arr[p1++];
}
}
while(p1<=m) {
helper[i++] = arr[p1++];
}
while(p2<=r) {
helper[i++] = arr[p2++];
}
for(i=0;i<helper.length;i++) arr[i+l] = helper[i];
return res;
}
}
快速排序
荷兰国旗问题1
- 给你一个数组arr,和一个数num。[i]>num放数组右边,[i]<=num放左边
import java.util.Arrays;
public class T1_荷兰旗问题1 {
//给你一个数组arr,和一个数num。[i]>num放数组右边,[i]<=num放左边
public static void process(int[] arr,int num) {
int l = -1;
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++) {
if(arr[i]>num) continue;
else {
swap(arr,l+1,i);
l++;
}
}
}
public static void swap(int[] arr,int i,int j) {
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
//数据生成器
public static int[] generator(int minValue,int maxValue,int length) {
int[] res = new int[length];
for(int i=0;i<length;i++) {
res[i] = (int)(Math.random() * (maxValue - minValue)) + minValue;
}
return res;
}
//判断器
public static boolean judge(int[] arr,int num) {
int i= 0;
for(;i<arr.length;i++) {
if(arr[i]>num) break;
}
for(;i<arr.length;i++) {
if(arr[i]<=num) return false;
}
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(int i=1;i<=1000;i++) {
//数据生成
int minValue = (int)(Integer.MIN_VALUE * Math.random());
int maxValue = (int)(Integer.MAX_VALUE * Math.random());
int length = i*10;
int num = minValue + ((maxValue-minValue)>>1);
int[] arr = generator(minValue, maxValue, length);
process(arr,num);
if(judge(arr,num)) {
System.out.println("测试通过第"+i+"组数据");
}else {
System.out.println("测试失败");
System.out.println("处理后的数组:"+Arrays.toString(arr));
System.out.println("num: "+num);
break;
}
}
//特殊例子
int[] arr = {1,1,2,3,2};
process(arr, 2);
System.out.println(judge(arr, 2));
}
}
荷兰国旗问题2
- 给你一个数组arr,和一个数num。[i]>num放数组右边,[i]<num放左边,等于放中间
import java.util.Arrays;
public class T2_荷兰旗问题2 {
//给你一个数组arr,和一个数num。[i]>num放数组右边,[i]<num放左边,等于放中间
public static void process(int[] arr,int num) {
int l = -1;
int r = arr.length;
int i = 0;
while(i!=r) {
if(arr[i] == num) i++;
else if(arr[i] > num) {
swap(arr,i,r-1);
r--;
}else if(arr[i] < num){
swap(arr,i,l+1);
l++;
i++;
}
}
}
static void swap(int[] arr,int i,int j) {
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
//数据生成器
public static int[] generator(int minValue,int maxValue,int length) {
int[] res = new int[length];
for(int i=0;i<length;i++) {
res[i] = (int)(Math.random() * (maxValue - minValue)) + minValue;
}
return res;
}
//判断器
public static boolean judge(int[] arr,int num) {
int i= 0;
for(;i<arr.length;i++) {
if(arr[i]>=num) break;
}
for(;i<arr.length;i++) {
if(arr[i]!=num) break;
}
for(;i<arr.length;i++) if(arr[i]<=num) return false;
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(int i=1;i<=10;i++) {
//数据生成
int minValue = (int)(Integer.MIN_VALUE * Math.random());
int maxValue = (int)(Integer.MAX_VALUE * Math.random());
int length = i*10;
int num = minValue + ((maxValue-minValue)>>1);
int[] arr = generator(minValue, maxValue, length);
process(arr,num);
if(judge(arr,num)) {
System.out.println("测试通过第"+i+"组数据");
}else {
System.out.println("测试失败");
System.out.println("处理后的数组:"+Arrays.toString(arr));
System.out.println("num: "+num);
break;
}
}
//特殊例子
int[] arr = {1,1,2,3,2};
process(arr, 2);
System.out.println(judge(arr, 2));
}
}
快排版本迭代
1.0版本
以最后一个元素为num的荷兰国旗问题1的划分
每次交换完之后,num和右划分第一个元素交换
下一个划分是:[l,i-1]、[i+1,r]
2.0版本
以最后一个元素为num的荷兰国旗问题2的划分
每次交换完之后,num和右划分第一个元素交换
[l,left]、[i+1,r]
3.0版本
- 1.0版本和2.0版本的时间复杂度都是O(N2),因为我们都可以找到一个例子使得它处理为O(N2)
划分值打得很偏,会导致该排序算法很差,怎么解决呢?
怎么解决
数学家为我们证明了,就是,我们随机从数组选一位数和最后一个数交换,然后再使用荷兰国旗问题2来处理,之后划分,这样算最后的数学期望得出:O(NlogN)
public class T3_quickSort {
public static void quickSort(int[] arr,int L,int R) {
if(L < R) {
//找到随机值
int idx = (int)(Math.random()*(R-L)) + L;
swap(arr,idx,R);
//荷兰国旗问题2
int[] p = partition(arr,L,R);
//划分
quickSort(arr, L, p[0]);
quickSort(arr, p[1], R);
}
}
private static int[] partition(int[] arr,int L,int R) {
int[] p = new int[2]; //分别记录左闭,右开
int num = arr[R];
int l = L - 1;
int r = R;
int i = L;
while(i!=r) {
if(arr[i] == num) {
i++;
}else if(arr[i] > num) {
swap(arr,i,r-1);
r--;
}else if(arr[i] < num) {
swap(arr,i,l+1);
l++;
i++;
}
}
swap(arr,r,R);
p[0] = l;
p[1] = r+1;
return p;
}
private static void swap(int[] arr,int i,int j) {
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
}
3.0版本的空间复杂度是多少呢?O(logN),这个的计算方法和时间复杂度计算是一样的,最好的情况O(LogN),最坏的情况O(N^2),最后通过1/N算数学期望可以得到空间复杂度收敛于O(logN)
堆排序
- 完全二叉树
- 数组从0开始
- i的左子树:2i+1;i的右子树:2i+2;i的父节点:(i-1)/2 (这个好理解,就是知道2i+1和2i+2求i嘛)
- 0的父节点是0,(0 - 1 )/ 2 = 0
大根堆
每课子树的最大值都是头节点的值
向上
//向上调整
private static void heapInsert(int[] arr,int idx) {
while(arr[idx] > arr[ (idx-1)/2 ]) {
swap(arr,idx,(idx-1)/2);
idx = (idx-1)/2;
}
}
向下
//向下调整
private static void heapify(int[] arr,int idx,int heapSize) {
int left = idx*2 + 1;
while(left < heapSize) {//是否存在孩子节点
int largest = left+1 < heapSize && arr[left+1] > arr[left] ? left+1 : left;
if(arr[largest]>arr[idx]) swap(arr,largest,idx);
else break;
idx = largest;
left = idx*2+1;
}
}
### 代码实现
public class T4_heapSort {
public static void heapSort(int[] arr) {
if(arr==null || arr.length < 2) return;
//O(NlogN)
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++) heapInsert(arr, i);
int heapSize = arr.length;
swap(arr,0,--heapSize);
//O(NlogN)
while(heapSize > 0) {
heapify(arr, 0, heapSize);
swap(arr,0,--heapSize);
}
}
//向上调整
private static void heapInsert(int[] arr,int idx) {
while(arr[idx] > arr[ (idx-1)/2 ]) {
swap(arr,idx,(idx-1)/2);
idx = (idx-1)/2;
}
}
//向下调整
private static void heapify(int[] arr,int idx,int heapSize) {
int left = idx*2 + 1;
while(left < heapSize) {//是否存在孩子节点
int largest = left+1 < heapSize && arr[left+1] > arr[left] ? left+1 : left;
if(arr[largest]>arr[idx]) swap(arr,largest,idx);
else break;
idx = largest;
left = idx*2+1;
}
}
private static void swap(int[] arr,int i,int j) {
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
}
复杂度分析
-
时间复杂度:O(NlogN)
-
空间复杂度:O(1)
堆排序的小小优化
我们假设一开始就有一棵完全二叉树,然后我们从N-1层最后一个元素开始向前向下调整。
我们就想想象成一个满二叉树,最后一层大概有N/2个元素
设有n层
第n层: 看一下就走:N/2
第n-1层:(N/2)/2 * 2{每个点,自己加向下判} =>N/4 * 2
第n-2层:N/8 * 3
.
.
.
.
最后一层,我们也可以不看,直接改变一下i就行了
//O(NlogN)
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++) heapInsert(arr, i);
//O(N)
for(int i=arr.length-1;i>=0;i--) heapify(arr,i,arr.length);
堆延申
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class T1_堆延深 {
//有一个数组,元素到数组排好序的位置距离不超过k,最后返回一个排好序的数组
public static void sortedArrDistanceLessK(int[] arr,int k) {
//小根堆走起
PriorityQueue<Integer> p = new PriorityQueue<>();
int idx = 0;
int i = 0;
for(;i<Math.min(k, arr.length);i++) p.add(arr[i]);
for(;i<arr.length;i++) {
p.add(arr[i]);
arr[idx++] = p.poll();
}
while(!p.isEmpty()) arr[idx++] = p.poll();
}
}
我先把前(k-1)个元素放到小根堆里面,然后我就在for的时候,先加一个元素再poll()出来了,这样就很nice了。
左神那里其实不用改了,左神草率了。
计数排序
计数排序的一个重要性质是它是稳定的:具有相同值的元素在输出数组中的相对次序与它们在输入数组中的相对次序是相同的。也就是说,对两个相同的数来说,在输入数组中先出现的数,在输出数组中也位于前面。
个人理解:我们可以根据范围,按照一个一个数来分片,就好像下面我们基数排序那样子,这样就可以实现稳定性了。dddd
基数排序
代码实现
public class T5_radixSort {
public static void radixSort(int[] arr) {
if(arr==null||arr.length<2) return;
radixSort(arr, 0, arr.length-1,maxBits(arr));
}
private static int maxBits(int[] arr) {
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++) max = Math.max(max, arr[i]);
int res = 0;
while(max != 0) {
res ++;
max /= 10;
}
return res;
}
private static void radixSort(int[] arr,int L,int R,int digit) {
final int radix = 10;
int[] bucket = new int[R-L+1];
for(int d=1;d<=digit;d++) {//有多少位,进多少次
int[] counts = new int[radix];
//找出该为数对应的
for(int i=L;i<=R;i++) counts[getDigit(arr[i], d)]++;
//求前缀和
for(int i=1;i<radix;i++) counts[i] += counts[i-1];
//放到对应里面
for(int i=R;i>=L;i--) bucket[ --counts[ getDigit(arr[i], d) ] ] = arr[i];
//把bucket的放到arr当中
for(int i=L,j=0;i<=R;i++,j++) arr[i] = bucket[j];
}
}
private static int getDigit(int x,int d) {
return ( (x / ( (int)Math.pow(10, d-1) ) ) % 10 );
}
}
左神的代码精髓
数找某十进制位的大小
private static int getDigit(int x,int d) {
return ( (x / ( (int)Math.pow(10, d-1) ) ) % 10 );
}
找数组最大值的位数
private static int maxBits(int[] arr) {
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++) max = Math.max(max, arr[i]);
int res = 0;
while(max != 0) {
res ++;
max /= 10;
}
return res;
}
桶的装入的拿出
一共进行10轮,然后每一轮过去,将某个数位出现的次数保存到counts数组中
然后对counts数组求前缀和
这样我们就知道某数位大于等于它的有多少个了,相当于给10个数位分片,前缀和之后知道分片终点的后一位是多少。
然后我们就可以从右到左依次放到分片当中,为什么是从右到左,因为后进桶的是右边的,左边的先进。
private static void radixSort(int[] arr,int L,int R,int digit) {
final int radix = 10;
int[] bucket = new int[R-L+1];
for(int d=1;d<=digit;d++) {//有多少位,进多少次
int[] counts = new int[radix];
//找出该为数对应的
for(int i=L;i<=R;i++) counts[getDigit(arr[i], d)]++;
//求前缀和
for(int i=1;i<radix;i++) counts[i] += counts[i-1];
//放到对应里面
for(int i=R;i>=L;i--) bucket[ --counts[ getDigit(arr[i], d) ] ] = arr[i];
//把bucket的放到arr当中
for(int i=L,j=0;i<=R;i++,j++) arr[i] = bucket[j];
}
}
稳定性分析
- 稳定性:就是在排序结束后,相同的元素排完序之后的相对位置不变。
- 优点:在基础数据的时候没什么卵用,但是在非基础的数据上由于,比如我排一次商品以价格最低,再排一次以物美,这样我们就可以达到物美价廉的效果了。
不稳定的:选择(3 3 3 3 1 3 3 3),快速排序[随机](6 7 6 6 3),堆排序(5 4 4 6)
稳定:冒泡、插入、归并、基排、计排
速度分析
- 经过实验表明,常数项时间,快速排序是最快的,但是不稳定
- 归并排序稳定,但是空间开销O(N)
- 堆虽然不稳定,但是空间复杂度O(1),也有它的优点
至今为止,时间复杂度为O(NlogN)的,想要保持稳定,空间最优O(N)
时间复杂度低于O(NlogN),空间为O(1)的,还没有出现。
快排加速,我们可以在小规模的时候不分了,直接使用插入排序来搞。例如:(l>r-60) 插入排序;结束。
面试说
系统库给我们提高的排序,基本类型使用快速排序,非基本类型使用归并排序,可以保持稳定性。
面试官叫你将一个数组奇左,偶右,时间复杂度为O(N),空间复杂度为O(1),直接怼它,但是这个是可以实现了01 stable sort这篇论文就有说,只是实现比较困难。
归并可以将空间复杂度降到O(1),但是这会失去稳定性这个点,实现还困难,所以没什么卵用。
快排可以实现稳定性,只是空间复杂度为O(N),实现起来非常困难,所以没什么卵用,0 1 stable sort
桶排序
希尔排序
二分查找
简单二分
public static void binarySearch(int[] arr,int target) {
int l = 0;
int r = arr.length;
while(l < r) {
int mid = l + (r - l)/2;
if(arr[mid]>target) {
r = mid;
}else if(arr[mid]<target) {
l = mid + 1;
}else {
System.out.println("目标数下标:"+mid);
break;
}
}
}
找最右端二分
最右端二分//小于等于target的最右边
public static void rightFix1(int[] arr,int target) {
int l = 0;
int r = arr.length;
int ans = -1;
while(l < r) {
int mid = l + (r-l)/2;
if(arr[mid]>target) {
r = mid;
}else {
l = mid + 1;
ans = mid;
}
}
System.out.println("目标数的下标:"+ans);
}
//等于target的最右边
public static void rightFix2(int[] arr,int target) {
int l = 0;
int r = arr.length;
int ans = -1;
while(l < r) {
int mid = l + (r-l)/2;
if(arr[mid]>target) {
r = mid;
}else if(arr[mid]<target) {
l = mid + 1;
}else {
l = mid+1;
ans = mid;
}
}
System.out.println("目标数的下标:"+ans);
}
找最左端二分
//找大于等于target的最左边
public static void leftFit1(int[] arr,int target) {
int ans = -1;
int l = 0;
int r = arr.length;
while(l < r) {
int mid = l + (r - l)/2;
if(target > arr[mid]) {
l = mid + 1;
}else {
r = mid;
ans = mid;
}
}
System.out.println("目标数下标:"+ans);
}
//找等于target的最左边
public static void leftFit2(int[] arr,int target) {
int ans = -1;
int l = 0;
int r = arr.length;
while(l<r) {
int mid = l + (r - l)/2;
if(arr[mid]>target) {
r = mid;
}else if(arr[mid]<target) {
l = mid+1;
}else {
r = mid;
ans = mid;
}
}
System.out.println("目标数下标:"+ans);
}
局部最小问题
import java.util.Scanner;
public class T4_局部最小 {
//在数组中找到一个局部最小的"位置"
public static void partialMinNum(int[] arr) {
if(arr.length == 1) {
System.out.println(0);
return;
}
if(arr[0] < arr[1]) {
System.out.println(0);
return;
}
if(arr[arr.length-1] < arr[arr.length-2]) {
System.out.println(arr.length-1);
return;
}
//开始二分,元素个数一定大于2个
int l = 1;
int r = arr.length-1;
while(l < r) {
int mid = l + (r-l)/2;
if(arr[mid]<arr[mid+1]&&arr[mid]<arr[mid-1]) {
System.out.println(mid);
return;
}else if(arr[mid]>arr[mid-1]) {
r = mid;
}else {
l = mid + 1;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
int[] nums = new int[n];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) {
nums[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
partialMinNum(nums);
}
}
对数器
实现步骤
- 有一个你想要测的方法a
- 实现复杂度不好但容易实现的方法b(方法b也可以是标准答案)
- 实现一个随机样本产生器
- 吧方法a和方法b跑相同的随机样本,看看得到的结果是否一样
- 不一样,我们就打印不一致的结果,随机产生的数据
- 当样本数量很多时对比测试依然正确,可以确定方法a已经正确
例子
对数器测试自己写的冒泡排序
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Random;
public class T1_冒泡排序 {
//要测试的方法
public static void bubbleSort(int[] arr) {
if(arr==null||arr.length<2) return;
//冒泡,就是不断往最后一个地方冒泡
for(int i=arr.length-1;i>0;i--) {
for(int j=0;j<i;j++) {
if(arr[j]>arr[j+1]) swap(arr,j,j+1);
}
}
}
public static void swap(int[] arr,int i,int j) {
if(i == j) return;
arr[i] ^= arr[j];
arr[j] ^= arr[i];
arr[i] ^= arr[j];
}
//完全正确的方法
public static void myComparator(int[] arr) {
Arrays.sort(arr);
}
//数据生成器
public static int[] generator(int minValue,int maxValue,int length) {
int[] res = new int[length];
for(int i=0;i<length;i++) {
res[i] = (int)(Math.random() * (maxValue - minValue)) + minValue;
}
return res;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
boolean pass = true;
for(int i=1;i<=1000;i++) {
//数据生成
int minValue = (int)(Integer.MIN_VALUE * Math.random());
int maxValue = (int)(Integer.MAX_VALUE * Math.random());
int length = i*10;
int[] arr = generator(minValue, maxValue, length);
int[] arr01 = Arrays.copyOf(arr, arr.length);
int[] arr02 = Arrays.copyOf(arr, arr.length);
//测试
bubbleSort(arr01);
myComparator(arr02);
//判断
if(!Arrays.equals(arr01, arr02)) {
pass = false;
System.out.println("原数据:");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
System.out.println("错误结果:");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr01));
System.out.println("正确结果:");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr02));
break;
}else {
System.out.println("测试成功第"+i+"次");
}
}
if(pass) System.out.println("恭喜你测试通过全部用例");
}
}
比较器
作为一个学了一年半Java的人了,别告诉我你不懂啊!
^ & |
int rightOne = eor & (~eor + 1);//提取出最右边的1
出现奇数次只有一个数
//出现奇数次只有一个数
public static void printOddTimesNum1(int[] arr) {
if(arr == null||arr.length == 0) throw new RuntimeException("传入数组元素个数少于1");
int eor = 0;
for(int num : arr) eor ^= num;
System.out.print(eor);
}
出现奇数次只有两个个数
//出现奇数次的个数有两个
public static void printOddTimesNum2(int[] arr) {
if(arr == null||arr.length<2) throw new RuntimeException("传入数组元素个数少于2");
int eor = 0;
for(int num : arr) eor ^= num;
int rightOne = eor & (~eor + 1);//提取出最右边的1
int onlyOne = 0;
for(int num : arr) if( (rightOne & num) == 0 ) onlyOne ^= num;
System.out.println("第一个数:"+onlyOne);
System.out.println("第二个数:"+(onlyOne^eor));
}
递归
master公式
例子代码
public static int getMaxInArr(int[] arr,int l,int r) {
if(l == r) return arr[l];
int mid = l + ((r-l)>>1);
int maxLeft = getMaxInArr(arr, l, mid);
int maxRight = getMaxInArr(arr, mid+1, r);
return Math.max(maxLeft, maxRight);
}
master公式应用
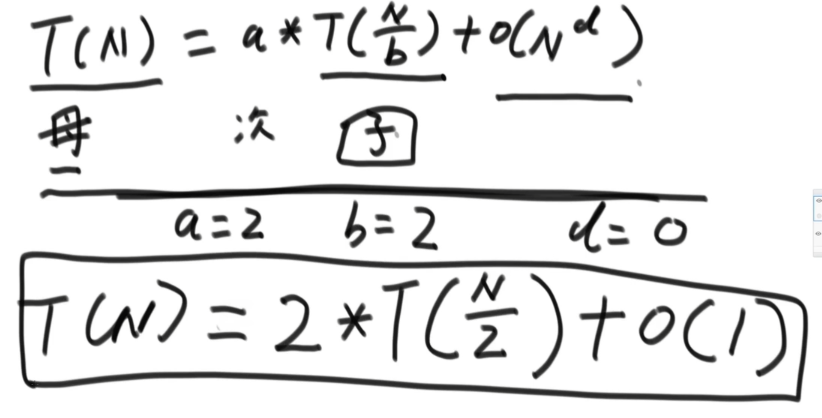
我们由此就可以知道我们这个代码所对应的:a = 2,b = 2,d = 0
查看对应的时间复杂度

log(b,a):表示以b为底,a为对数
该递归函数时间复杂度
log(2,2) = 1 > d = 0
所以该算法的时间复杂度是:O(N^log(2,2)) = O(N)
暴力递归
汉诺塔问题
1,2,3,…n
讲(1,…,n-1)搬到辅助柱子上,
然后将n搬到目标柱子
重复这个过程。
public class T4_汉诺塔 {
// static int sum = 0;
public static void hanoi(int n) {
if( n > 0) {
func(n,"左","右","中");
}
}
public static void func(int i,String from ,String to, String help) {
if( i == 1) {
// sum++;
System.out.println("Move 1 from "+from+" to "+to);
return;
}
func(i-1,from,help,to);
// sum ++;
System.out.println("Move "+i+" from "+from+" to "+to);
func(i-1,help,to,from);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
hanoi(22);
// System.out.println(sum);
}
}
打印字符串全部子序列
public class T5_字符串子序列 {
//字符串不包含空
public static void printAllSubsquence(String str) {
process(str.toCharArray(),0);
}
public static void process(char[] chs, int i) {
if(chs.length == i) {
System.out.println("字串:"+new String(chs).replaceAll(" ", ""));
return ;
}
process(chs,i+1);//要第i位
char c = chs[i];
chs[i] = ' ';
process(chs,i+1);
chs[i] = c;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
printAllSubsquence("12");
}
}
import java.util.*;
public class T6_字符串全排列 {
//字符串全是小写字母
public static ArrayList<String> Permutation(String str) {
ArrayList<String> res = new ArrayList<>();
int[] counts = new int[26];
for(int i=0;i<str.length();i++) ++counts[str.charAt(i)-'a'];
process(counts,new char[str.length()],0,res);
return res;
}
private static void process(int[] counts,char[] chs,int idx,ArrayList<String> res) {
if(idx == chs.length) {
res.add(String.valueOf(chs));
return ;
}
for(int i=0;i<26;i++) {
if(counts[i] != 0) {
-- counts[i];
chs[idx] = (char)(i+'a');
process(counts,chs,idx+1,res);
++ counts[i];
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> res = Permutation("abcddx");
res.toArray(new String[res.size()]);
for(String s : res) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
}
纸牌博弈
public class T7_抽牌游戏 {
/*
给定一个整型数组arr,代表数值不同的纸牌排成一条线。玩家A和玩家B依次拿走每张纸 牌,
规定玩家A先拿,玩家B后拿,但是每个玩家每次只能拿走最左或最右的纸牌,
玩家A 和玩家B都绝顶聪明。请返回最后获胜者的分数。
*/
public static int win(int[] arr) {
if(arr == null || arr.length == 0) return 0;
int a = first(arr,0,arr.length-1);//先手的人
int b = second(arr,0,arr.length-1);//后手的人
return Math.max(a, b);
}
public static int first(int[] arr, int i, int j) {
if(i == j) return arr[i];
int a = arr[i] + second(arr,i+1,j);
int b = arr[j] + second(arr,i,j-1);
return Math.max(a, b);
}
public static int second(int[] arr, int i, int j) {
if(i == j) return 0;
int a = first(arr,i+1,j);
int b = first(arr,i,j-1);
return Math.min(a, b);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = { 1, 9, 1 };
System.out.println(win(arr));
}
}
递归逆序栈
import java.util.Stack;
public class T8_递归逆序栈 {
//给你一个栈,请你逆序这个栈,不能申请额外的数据结构,只能使用递归函数。 如何实现?
public static void reverse(Stack<Integer> stack) {
if(stack == null || stack.isEmpty()) return ;
Integer last = f(stack);
reverse(stack);
stack.push(last);
}
public static Integer f(Stack<Integer> stack) {
Integer res = stack.pop();
if(stack.isEmpty()) return res;
Integer last = f(stack);
stack.push(res);
return last;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(1);
stack.push(2);
stack.push(3);
stack.push(4);
while(!stack.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println(stack.pop());
}
}
}
数字字符串转字符字符串
public class T9_数字转换字符串 {
/*
规定1和A对应、2和B对应、3和C对应...
那么一个数字字符串比如"111",就可以转化为"AAA"、"KA"和"AK"。
给定一个只有数字字符组成的字符串str,返回有多少种转化结果。
----------------------------------------------
全部数字都是要转成字符串的
如果出现了0做决择,直接放弃
*/
public static int number(String str) {
if(str == null || str.length() == 0) return 0;
return process(str.toCharArray(),0);
}
//从idx开始,有多少种结果
public static int process(char[] chs,int idx) {
if(idx == chs.length) return 1;
int res = 0;
if(chs[idx] == '0') return 0;
else if(chs[idx] == '1') {
res += process(chs,idx+1);
if(idx+1<chs.length) res += process(chs,idx+2);
return res;
}else if(chs[idx] == '2') {
res += process(chs,idx+1);
if(idx+1<chs.length && chs[idx+1]>='0' && chs[idx+1] <= '6') res += process(chs,idx+2);
return res;
}else {
return process(chs,idx+1);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(number("11111"));
}
}
01背包暴力解
public static int maxValue(int[] weights,int[] vals,int bag) {
if(bag == 0 || weights.length == 0 || vals.length == 0) return 0;
return process(weights,vals,bag,0,0);
}
public static int process(int[] ws,int[] vs,int bag,int idx,int sum) {
if(idx == ws.length) return 0;
if(sum > bag) return 0;
int a = process(ws,vs,bag,idx+1,sum);//没选
int b = 0;
//要的时候要判断一下是否满足要求
if(sum + ws[idx] <= bag) b = process(ws,vs,bag,idx+1,sum+ws[idx]) + vs[idx];//选了
return Math.max(a, b);
}
N皇后问题
public static int num1(int n) {
if(n < 1) return 0;
//[i] = num:i表示在第i层的,num:表示在第i层的第num位置
int[] record = new int[n];
return process1(0, record, n);
}
public static int process1(int i, int[] record, int n) {
if(i == n) return 1;
int res = 0;
for(int j=0;j<n;j++) {
if(isValid(record,i,j)) {
record[i] = j;
res += process1(i+1,record,n);
}
}
return res;
}
public static boolean isValid(int[] record, int i, int j) {
for(int k = 0; k < i; k++) {
//第二个条件:相当于斜率绝对值为1
if(record[k] == j || Math.abs(j-record[k]) == Math.abs(i-k)) return false;
}
return true;
}
public static int num2(int n) {
if(n < 1 || n > 32) return 0;
int limit = (1<<n) - 1;
//一个皇后都没有的时候,限制是无
return process2(limit,0,0,0);
}
public static int process2(int limit, int colLimit, int leftLimit, int rightLimit) {
if( limit == colLimit) return 1;
int res = 0;
int pos = limit & (~(colLimit | leftLimit | rightLimit));
while( pos != 0) {
//提取最右边第一个1
int mostRight = pos & (~pos + 1);
pos = pos - mostRight;//去掉
//这个是不对的
// res += process2( limit,colLimit | mostRight, leftLimit | (mostRight<<1), rightLimit | (mostRight>>1) );
res += process2( limit,colLimit | mostRight, (leftLimit | mostRight )<<1, (rightLimit | mostRight)>>>1 );
}
return res;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(int i=1;i<=14;i++) {
int n1 = num1(i);
int n2 = num2(i);
if(n1 == n2) {
System.out.println("pass: 第"+i+"层,sum = "+n1);
}else {
System.out.println("error: 第"+i+"层,n1 = "+n1+",n2 = "+n2);
break;
}
}
}
表
哈希表
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<Integer, String> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
//增删改查都是常数时间的,只是会比较大而已。
hashMap.put(1, "我是1");
hashMap.remove(1);
hashMap.put(1, "我是11");
hashMap.containsKey(1);
//没有value的HashMap
HashSet<Integer> hashSet = new HashSet<>();
hashSet.add(1);
hashSet.remove(1);
hashSet.contains(1);
}
基础数据类型(String、Integer、Long、Character…)使用值传递
- 就是在放的时候,复制一份,你改变原来的值不会影响放进去的值
自定义数据类型,传递时地址传递(8字节不会变),这里应该包含Key和Value的。
有序表
比较重要的点:
- 它是对Key进行排序的
- 基础数据类型可以不需要比较器,但是自定义类型一定要加比较器。
import java.util.TreeMap;
import java.util.TreeSet;
public class T2_有序表 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeMap<Integer, String> treeMap = new TreeMap<>();
//增删改查 -> 复杂度O(logN)
treeMap.put(1, "我是1");
treeMap.remove(1);
treeMap.put(1, "我是11");
treeMap.containsKey(1);
treeMap.firstKey();
treeMap.lastKey();
treeMap.floorKey(8);//小于等于8,最靠近8的元素
treeMap.ceilingKey(8);//大于等于8,最靠近8的元素
TreeSet<Student> treeSet = new TreeSet<>((s1,s2)->s1.age - s2.age);
}
class Student {
public int age;
}
}
链表
面试:拿出时间最好,空间最省的
笔试:能做出来就行
重要技巧:快慢指针、额外数据结构记录(数组,哈希表)
单链表
- dddd
双链表
- dddd
反转单链表
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null) return head;
ListNode p1 = head;
ListNode p2 = head.next;
p1.next = null;
while(p2 != null) {
ListNode temp = p2.next;
p2.next = p1;
p1 = p2;
p2 = temp;
}
return p1;
}
}
有序链表公共部分
import java.util.*;
public class T1_有序链表公共部分 {
public static List<Integer> publicPart1(ListNode head1,ListNode head2) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
if(head1==null||head2==null) return list;
ListNode p1 = head1;
ListNode p2 = head2;
while(p1!=null && p2!=null) {
if(p1.val == p2.val) {
list.add(p1.val);
p1 = p1.next;
p2 = p2.next;
}else if(p1.val > p2.val) {
p2 = p2.next;
}else if(p1.val < p2.val) {
p1 = p1.next;
}
}
return list;
}
class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode() {}
ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
}
}
判断回文链表
使用一个栈
- 笔试的时候使用
使用快慢指针
- 面试的时候使用
- 不破环链表结构
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null) return true;
//快慢指针
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
//找到反转链表开始位置
while(fast.next!=null && fast.next.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
//反转链表
ListNode t1 = slow;
ListNode t2 = reverseList(slow.next);
//开始判别
ListNode begin = head;
ListNode end = t2;
boolean flag = true;
do {
if(begin.val != end.val) {
flag = false;
break;
}
begin = begin.next;
end = end.next;
}while(end!=null);
//复原
ListNode t3 = reverseList(t2);
t1.next = t3;
//返回结果
return flag;
}
ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode p1 = null;
ListNode p2 = head;
while(p2 != null) {
ListNode temp = p2.next;
p2.next = p1;
p1 = p2;
p2 = temp;
}
return p1;
}
}
链表类型的荷兰国旗问题2
使用一个数组
- 笔试的时候使用
使用六个指针
- 面试的时候使用
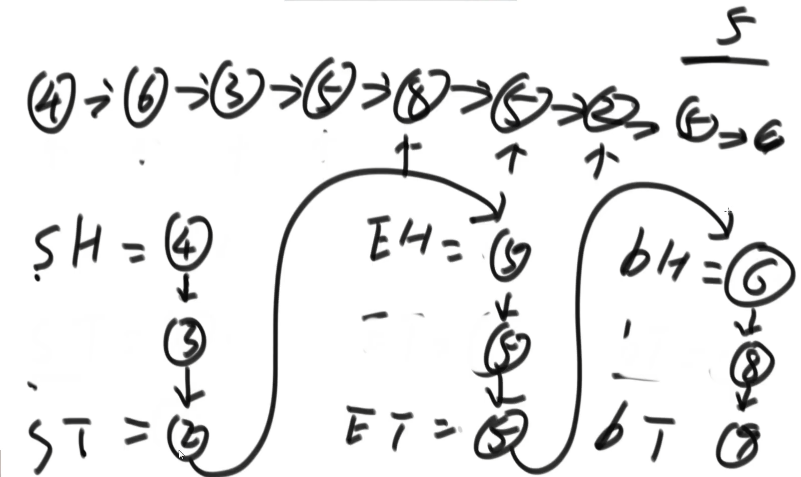
public class T2_链表的荷兰国旗问题2 {
public static void partition(ListNode head,int target) {
if(head==null||head.next==null) return;
ListNode lf = null;
ListNode le = null;
ListNode mf = null;
ListNode me = null;
ListNode rf = null;
ListNode re = null;
ListNode p = head;
while(p != null) {
ListNode temp = p.next;
if(p.val == target) {
ListNode[] fe = add(mf,me,p);
mf = fe[0];
me = fe[1];
}else if(p.val > target) {
ListNode[] fe = add(rf,re,p);
rf = fe[0];
re = fe[1];
}else if(p.val < target) {
ListNode[] fe = add(lf,le,p);
lf = fe[0];
le = fe[1];
}
p = temp;
}
p = null;
//合并
if(lf != null) {
head = lf;
p = le;
le.next = null;
}
if(p != null && mf != null) {
p.next = mf;
me.next = null;
p = me;
}
if(p != null) {
p.next = rf;
if(re !=null) re.next = null;
}else {
head = rf;
re.next = null;
}
}
private static ListNode[] add(ListNode f,ListNode e,ListNode p) {
if(f==null&&e==null) {
f = p;
e = p;
}else {
e.next = p;
e = p;
}
return new ListNode[] {f,e};
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ListNode head = new ListNode(1);
head.next = new ListNode(3);
head.next.next = new ListNode(100);
head.next.next.next = new ListNode(10);
head.next.next.next.next = new ListNode(3);
partition(head, 3);
while(head!=null) {
System.out.println(head.val);
head = head.next;
}
}
}
class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode() {}
ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
}
复制链表
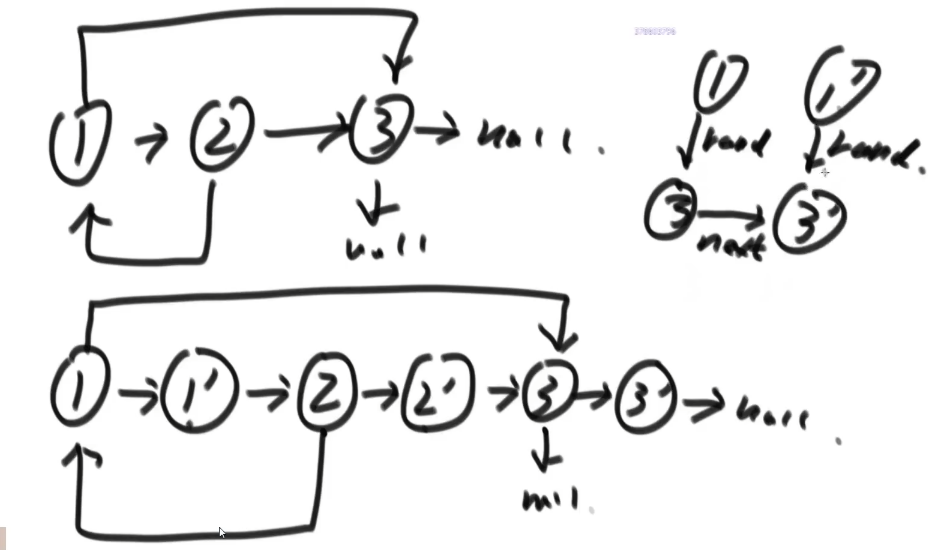
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
int val;
Node next;
Node random;
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
this.random = null;
}
}
*/
class Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
return copyListNode(head);
}
//方法1:Map,old Node : new Node
//方法2:1->2->3 1->1(new)->2->2(new)->3->3(new)
public static Node copyListNode(Node head) {
if(head==null) return null;
Node rt = new Node(1);
Node p = head;
//复制主体形成相邻
while(p != null) {
Node newNode = new Node(p.val);
Node temp = p;
p = p.next;
temp.next = newNode;
newNode.next = p;
}
//复制random
p = head;
while(p!=null) {
Node t1 = p;
Node t2 = p.next;
p = t2.next;
t2.random = (t1.random==null?null:t1.random.next);
}
//分离开来
p = head;
Node ans = rt;
while(p!=null) {
Node t1 = p;
Node t2 = p.next;
p = t2.next;
rt.next = t2;
rt = t2;
t2.next = null;
t1.next = p;
}
return ans.next;
}
}
环形链表
链表交点
- 有两个链表可能有环,两链表可能相较,相交返回第一个交点,不相交返回null
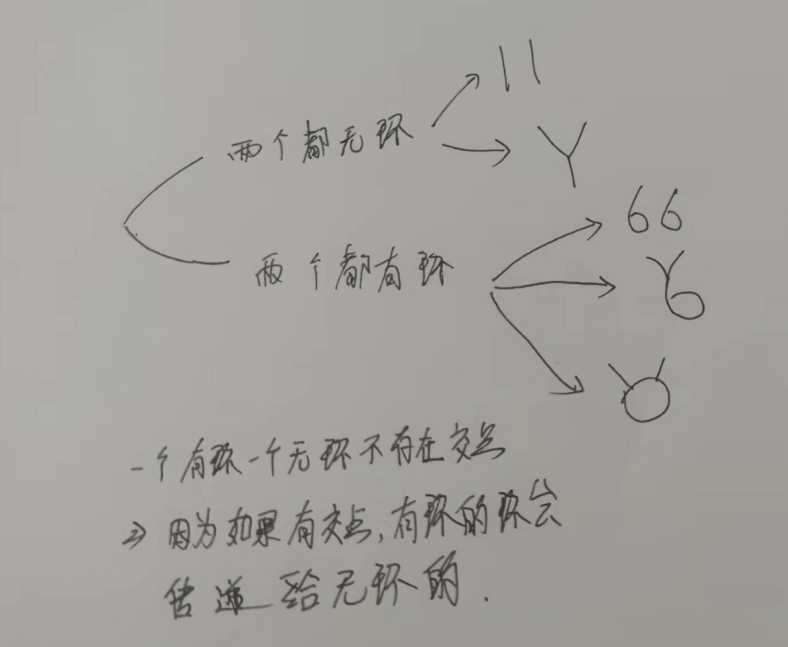
public class T4_链表究极题 {
//有两个链表可能有环,两链表可能相较,相交返回第一个交点,不相交返回null
public static Node getIntersectNode(Node head1, Node head2) {
if(head1==null||head2==null) return null;
Node loop1 = getLoopNode(head1);
Node loop2 = getLoopNode(head2);
if(loop1==null&&loop2==null) return noLoop(head1, head2);
return bothLoop(head1, loop1, head2, loop2);
}
public static Node getLoopNode(Node head) {
if(head==null||head.next==null||head.next==null) return null;
Node n1 = head.next;
Node n2 = head.next.next;
while(n1!=n2) {
if(n2.next==null||n2.next.next==null) return null;
n1 = n1.next;
n2 = n2.next.next;
}
n2 = head;
while(n1!=n2) {
n1 = n1.next;
n2 = n2.next;
}
return n1;
}
public static Node noLoop(Node head1, Node head2) {
if(head1==null||head2==null) return null;
Node cur1 = head1;
Node cur2 = head2;
int n = 0;
while(cur1.next!=null) {
cur1 = cur1.next;
++n;
}
// --n;//或者n直接等于0
while(cur2.next!=null) {
cur2 = cur2.next;
--n;
}
if(cur1 != cur2) return null;
cur1 = n > 0 ? head1 : head2;
cur2 = cur1 == head1 ? head2 : head1;
n = Math.abs(n);
while(n!=0) {
cur1 = cur1.next;
--n;
}
while( cur1 != cur2) {
cur1 = cur1.next;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
return cur1;
}
public static Node bothLoop(Node head1, Node loop1, Node head2, Node loop2) {
if(loop1 == loop2) {
//复用上面的方法
Node t1 = loop1;
Node t2 = loop1.next;
loop1.next = null;
Node rtNode = noLoop(head1, head2);
//复原
t1.next = t2;
return rtNode;
}
Node cur = loop1.next;
while(loop1 != cur) {
if(cur == loop2) return loop1;//loop1,loop2随便返回一个就行
cur = cur.next;
}
return null;
}
public static class Node {
public int value;
public Node next;
public Node(int data) {
this.value = data;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1->2->3->4->5->6->7->null
Node head1 = new Node(1);
head1.next = new Node(2);
head1.next.next = new Node(3);
head1.next.next.next = new Node(4);
head1.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);
head1.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(6);
head1.next.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(7);
// 0->9->8->6->7->null
Node head2 = new Node(0);
head2.next = new Node(9);
head2.next.next = new Node(8);
head2.next.next.next = head1.next.next.next.next.next; // 8->6
System.out.println(getIntersectNode(head1, head2).value);
// 1->2->3->4->5->6->7->4...
head1 = new Node(1);
head1.next = new Node(2);
head1.next.next = new Node(3);
head1.next.next.next = new Node(4);
head1.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);
head1.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(6);
head1.next.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(7);
head1.next.next.next.next.next.next = head1.next.next.next; // 7->4
// 0->9->8->2...
head2 = new Node(0);
head2.next = new Node(9);
head2.next.next = new Node(8);
head2.next.next.next = head1.next; // 8->2
System.out.println(getIntersectNode(head1, head2).value);
// 0->9->8->6->4->5->6..
head2 = new Node(0);
head2.next = new Node(9);
head2.next.next = new Node(8);
head2.next.next.next = head1.next.next.next.next.next; // 8->6
System.out.println(getIntersectNode(head1, head2).value);
}
// public static void main(String[] args) {
// Node n1 = new Node(1);
// Node n2 = new Node(2);
// Node n3 = new Node(3);
// n1.next = n2;
// n2.next = n3;
// n3.next = n2;
// System.out.println(getLoopNode(n1).value);
// }
}
二叉树
先序遍历
递归
非递归
- 进去顺序是:右左头,弹出就相反:头左右
- 弹出一个节点cur
- 打印
- cur的右节点先进(如果存在的话),在左节点进(如果存在的话)
import java.util.Stack;
public class T1_先序遍历 {
public static void preOrderRecur(Node root) {
if(root == null) return;
System.out.println(root.value+" ");
preOrderRecur(root.left);
preOrderRecur(root.right);
}
public static void preOrderUnRecur(Node root) {
/**
1. 弹出一个节点cur
2. 打印
3. cur的右节点先进(如果存在的话),在左节点进(如果存在的话)
*/
if(root == null) return;
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(root);
while(!stack.isEmpty()) {
Node cur = stack.pop();
System.out.printl(cur.value+" ");
if(cur.right != null) stack.push(cur.right);
if(cur.left != null) stack.push(cur.left);
}
}
}
class Node {
public int value;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node(int data) {
this.value = data;
}
}
中序遍历
递归
非递归
- 左边全进
- 弹出一个节点cur,打印
- 右边继续重复左边全进
import java.util.Stack;
public class T2_中序遍历 {
public static void inOrderRecur(Node root) {
if(root == null) return;
inOrderRecur(root.left);
System.out.print(root.value+" ");
inOrderRecur(root.right);
}
public static void inOrderUnRecur(Node root) {
if(root == null) return;
//1. 左边全进
//2. 弹出一个节点cur,打印
//3. 右边继续重复左边全进
Node cur = root;
Stack<Node> s = new Stack<>();
while(!s.isEmpty() || cur != null) {
if(cur != null) {
s.push(cur);
cur = cur.left;
}else {
cur = s.pop();
System.out.print(cur.value+" ");
cur = cur.right;
}
}
}
}
后序遍历
递归
非递归
- s1进入顺序:左右头
- s2进入顺序:头右左
- 最后弹出顺序就成了:左右头
import java.util.Stack;
public class T3_后序遍历 {
public static void posOrderRecur1(Node root) {
if(root == null) return;
posOrderRecur1(root.left);
posOrderRecur1(root.right);
System.out.print(root.value+" ");
}
public static void posOrderUnRecur1(Node root) {
if(root == null) return;
Stack<Node> s1 = new Stack<>();
Stack<Node> s2 = new Stack<>();//收集栈
s1.push(root);
while(!s1.isEmpty()) {
Node cur = s1.pop();
s2.push(cur);
if(cur.left!=null) s1.push(cur.left);
if(cur.right!=null) s2.push(cur.right);
}
while(!s2.isEmpty()) {
Node cur = s2.pop();
System.out.print(cur.value+" ");
}
}
}
二叉树深度
private static int treeDepth(Node root) {
if(root == null) return 0;
return Math.max( treeDepth(root.left), treeDepth(root.right) )+1;
}
public satic void depth(Node root) {
System.out.println(treeDepth(root));
}
二叉树宽度
import java.util.*;
public class T4_二叉树宽度 {
public static void treeWidth(Node root) {
if(root == null) {
System.out.println("The Tree Width is 0");
return;
}
Queue<Node> q = new LinkedList<>();
int maxWidth = 0;
q.add(root);
while(!q.isEmpty()) {
int n = q.size();
maxWidth = Math.max(n, maxWidth);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) {
Node cur = q.poll();
if(cur.left!=null) q.add(cur.left);
if(cur.right!=null) q.add(cur.right);
}
}
System.out.println("The Tree Width is "+maxWidth);
}
}
打印一颗二叉树
package class05;
public class Code02_PrintBinaryTree {
public static class Node {
public int value;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node(int data) {
this.value = data;
}
}
public static void printTree(Node head) {
System.out.println("Binary Tree:");
printInOrder(head, 0, "H", 17);
System.out.println();
}
public static void printInOrder(Node head, int height, String to, int len) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
printInOrder(head.right, height + 1, "v", len);
String val = to + head.value + to;
int lenM = val.length();
int lenL = (len - lenM) / 2;
int lenR = len - lenM - lenL;
val = getSpace(lenL) + val + getSpace(lenR);
System.out.println(getSpace(height * len) + val);
printInOrder(head.left, height + 1, "^", len);
}
public static String getSpace(int num) {
String space = " ";
StringBuffer buf = new StringBuffer("");
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
buf.append(space);
}
return buf.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node head = new Node(1);
head.left = new Node(-222222222);
head.right = new Node(3);
head.left.left = new Node(Integer.MIN_VALUE);
head.right.left = new Node(55555555);
head.right.right = new Node(66);
head.left.left.right = new Node(777);
printTree(head);
head = new Node(1);
head.left = new Node(2);
head.right = new Node(3);
head.left.left = new Node(4);
head.right.left = new Node(5);
head.right.right = new Node(6);
head.left.left.right = new Node(7);
printTree(head);
head = new Node(1);
head.left = new Node(1);
head.right = new Node(1);
head.left.left = new Node(1);
head.right.left = new Node(1);
head.right.right = new Node(1);
head.left.left.right = new Node(1);
printTree(head);
}
}
判断二叉搜索树
public class T5_判断搜索二叉树 {
private static int preVal = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
public static boolean isBST(Node root) {
if(root == null) return true;
boolean left = isBST(root.left);
if(!left) return false;
if(root.value > preVal) return false;
else preVal = root.value;
return isBST(root.right);
}
}
判断完全二叉树
- 条件1:左边为空,右边非空
- 条件2:出现了少又子树的节点之后后面全是叶子节点
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class T6_判断完全二叉树 {
public static boolean isCBT(Node root) {
if(root == null) return true;
boolean leaf = false;
Queue<Node> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.add(root);
while(!q.isEmpty()) {
Node cur = q.poll();
Node l = cur.left;
Node r = cur.right;
if(l==null && r != null) return false;
if(leaf && (l!=null || r!=null)) return false;
if(l != null) q.add(l);
if(r != null) q.add(r);
//肯能重复多次,不过问题不大
if(r==null) leaf = true;
}
return true;
}
}
二叉树套路
套路做法:
- 思考左右子树需要给我们什么数据,然后定义一个这种返回值类型,可以叫做ReturnData
- 然后就。。。。。。。
树型DP都可以使用这个套路来解题
判断平衡二叉树
public class T7_判断平衡二叉树 {
//判断是不是平衡二叉树
//它的左子树和右子树的深度之差(平衡因子)的绝对值不超过1,且它的左子树和右子树都是一颗平衡二叉树。
public static class ReturnData {
boolean isBBT;
int height;
public ReturnData(boolean is,int h) {
isBBT = is;
height = h;
}
}
public static boolean isBBT(Node root) {
return process(root).isBBT;
}
public static ReturnData process(Node root) {
if(root == null) return new ReturnData(true,0);
ReturnData l = process(root.left);
ReturnData r = process(root.right);
int hegiht = Math.max(l.height, r.height)+1;
boolean isBBT = l.isBBT && r.isBBT && Math.abs(l.height-r.height)<2;
return new ReturnData(isBBT,hegiht);
}
}
判断满二叉树
public class T8_判断满二叉树 {
public static class ReturnData {
boolean isFull;
int height;
public ReturnData(boolean b,int h) {
isFull = b;
height = h;
}
}
public static boolean isFBT(Node root) {
if(root == null) return true;
return process(root).isFull;
}
private static ReturnData process(Node root) {
if(root == null) return new ReturnData(true,0);
ReturnData l = process(root.left);
ReturnData r = process(root.right);
return new ReturnData(l.isFull && r.isFull && l.height == r.height,Math.max(l.height, r.height)+1);
}
}
判断二叉搜索树
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
return isBST(root);
}
public static class R {
boolean is;
int min;
int max;
public R(boolean b,int mi,int ma) {
is = b;
min = mi;
max = ma;
}
}
public static boolean isBST(TreeNode node) {
if(node == null) return true;
return process(node).is;
}
private static R process(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return null;
R l = process(root.left);
R r = process(root.right);
boolean b = false;
if(l!=null && r != null) {
b = l.is && r.is && root.val > l.max && root.val < r.min;
}else if( l==null && r == null) {
b = true;
}else {
b = l==null?r.is && r.min > root.val:l.is && l.max < root.val;
}
int min = l==null?root.val:l.min;
int max = r==null?root.val:r.max;
return new R(b,min,max);
}
}
祖先节点
public class T10_祖先节点 {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(root == null || root == p || root == q) return root;
TreeNode l = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q);
TreeNode r = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q);
if(l!=null && r!=null) return root;
return l==null?r:l;
}
class TreeNode {
public int val;
public TreeNode left;
public TreeNode right;
public TreeNode(int data) {
this.val = data;
}
}
}
后继节点
- 有右子树:右子树最左
- 无右子树:是否为父亲的左孩子
- 左右:最后一个中序遍历的节点无后继节点
public class T11_后继节点 {
//寻找node的后继节点
public static Node getSuccessorNode(Node node) {
if(node == null) return null;
if(node.right != null) {
return getNodeMaxLeft(node.right);
}else {
Node parent = node.parent;
while(parent != null && parent.left != node) {
node = parent;
parent = parent.parent;
}
return parent;
}
}
public static Node getNodeMaxLeft(Node node) {
while(node.left != null) {
node = node.left;
}
return node;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node head = new Node(6);
head.parent = null;
head.left = new Node(3);
head.left.parent = head;
head.left.left = new Node(1);
head.left.left.parent = head.left;
head.left.left.right = new Node(2);
head.left.left.right.parent = head.left.left;
head.left.right = new Node(4);
head.left.right.parent = head.left;
head.left.right.right = new Node(5);
head.left.right.right.parent = head.left.right;
head.right = new Node(9);
head.right.parent = head;
head.right.left = new Node(8);
head.right.left.parent = head.right;
head.right.left.left = new Node(7);
head.right.left.left.parent = head.right.left;
head.right.right = new Node(10);
head.right.right.parent = head.right;
Node test = head.left.left;
System.out.println(test.value + " next: " + getSuccessorNode(test).value);
test = head.left.left.right;
System.out.println(test.value + " next: " + getSuccessorNode(test).value);
test = head.left;
System.out.println(test.value + " next: " + getSuccessorNode(test).value);
test = head.left.right;
System.out.println(test.value + " next: " + getSuccessorNode(test).value);
test = head.left.right.right;
System.out.println(test.value + " next: " + getSuccessorNode(test).value);
test = head;
System.out.println(test.value + " next: " + getSuccessorNode(test).value);
test = head.right.left.left;
System.out.println(test.value + " next: " + getSuccessorNode(test).value);
test = head.right.left;
System.out.println(test.value + " next: " + getSuccessorNode(test).value);
test = head.right;
System.out.println(test.value + " next: " + getSuccessorNode(test).value);
test = head.right.right; // 10's next is null
System.out.println(test.value + " next: " + getSuccessorNode(test));
}
public static class Node {
public int value;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node parent;
public Node(int data) {
this.value = data;
}
}
}
序列化&反序列化
- 这个dddd
- 先序、中序、后序、层次
Trie树实现
public class T07_前缀树 {
//合适全是小写字母的字符串
public static class TrieNode {
public int pass;
public int end;
//我们遇到不同的情况可以使用HashMap或者TreeMap
public TrieNode[] nexts;
public TrieNode() {
nexts = new TrieNode[26];
}
}
public static class Trie {
private static TrieNode root;
static {
root = new TrieNode();
}
public static void add(String s) {
char[] chs = s.toCharArray();
TrieNode node = root;
++ node.pass;
for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++) {
int idx = chs[i] - 'a';
if(node.nexts[idx] == null) {
node.nexts[idx] = new TrieNode();
}
node = node.nexts[idx];
++node.pass;
}
++node.end;
}
public static boolean delete(String s) {
//没有得删
if(!search(s)) return false;
char[] chs = s.toCharArray();
TrieNode node = root;
//特殊情况,这个根节点不能删
if(root.pass == 1) {
root.end = 0;
root.pass = 0;
root.nexts = new TrieNode[26];
return true;
}
--node.pass;
for(char ch : chs) {
int idx = ch - 'a';
if(--node.nexts[idx].pass == 0) {
node.nexts[idx] = null;
return true;
}
node = node.nexts[idx];
}
--node.end;
return true;
}
public static boolean search(String s) {
char[] chs = s.toCharArray();
TrieNode node = root;
for(char ch : chs) {
int idx = ch - 'a';
if(node.nexts[idx] == null) return false;
node = node.nexts[idx];
}
return node.end != 0;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Trie.add("lin");
Trie.add("ye");
Trie.add("run");
System.out.println(Trie.delete("suifeng"));
System.out.println(Trie.delete("ye"));
System.out.println(Trie.search("ye"));
System.out.println(Trie.search("run"));
System.out.println(Trie.search("lin"));
}
}
中位数
大根堆小根堆应用
public class MedianUtil {
public PriorityQueue<Integer> pb;//大根堆
public PriorityQueue<Integer> ps;//小根堆
public MedianUtil() {
pb = new PriorityQueue<Integer>((o1,o2)->o2.compareTo(o1));
ps = new PriorityQueue<Integer>();
}
public void add(int num) {
if(pb.size() == 0 && ps.size() == 0) {
pb.add(num);
return ;
}
//加
if(pb.peek().compareTo(num) < 0) {
ps.add(num);
}else {
pb.add(num);
}
if(pb.size() > ps.size() + 1) {
ps.add(pb.poll());
}else if(pb.size()+1 < ps.size()) {
pb.add(ps.poll());
}
}
public double getMediun() {
if(pb.size() > ps.size()) return pb.peek();
else if(pb.size() < ps.size()) return ps.peek();
return pb.peek() + ( ps.peek()-pb.peek() ) / 2.0;
}
public void init(int[] arr) {
for(int num : arr) add(num);
}
}
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class T1_中位数 {
public static class medianUtil {
public static PriorityQueue<Integer> pb;//大根堆
public static PriorityQueue<Integer> ps;//小根堆
static {
pb = new PriorityQueue<Integer>((o1,o2)->o2.compareTo(o1));
ps = new PriorityQueue<Integer>();
}
public static void add(int num) {
if(pb.size() == 0 && ps.size() == 0) {
pb.add(num);
return ;
}
//加
if(pb.peek().compareTo(num) < 0) {
ps.add(num);
}else {
pb.add(num);
}
if(pb.size() > ps.size() + 1) {
ps.add(pb.poll());
}else if(pb.size()+1 < ps.size()) {
pb.add(ps.poll());
}
}
public static double getMediun() {
if(pb.size() > ps.size()) return pb.peek();
else if(pb.size() < ps.size()) return ps.peek();
return pb.peek() + ( ps.peek()-pb.peek() ) / 2.0;
}
public static void init(int[] arr) {
for(int num : arr) add(num);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
medianUtil.add(1);
System.out.println(medianUtil.getMediun());
medianUtil.add(3);
medianUtil.add(4);
medianUtil.add(15);
System.out.println(medianUtil.getMediun());
medianUtil.add(9);
System.out.println(medianUtil.getMediun());
}
}
微软面试题
- 拿纸叠一下
public class T12_微软面试题 {
//规律是:一颗满二叉树,第一层节点:凹,节点的左节点:凹、右节点:凸
public static void printAllFolds(int N) {
printProcess(1, N, true);
}
public static void printProcess(int i,int N,boolean down) {
if(i > N) return;
printProcess(i+1, N, true);
System.out.println(down?"凹":"凸");
printProcess(i+1, N, false);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int N = 3;
printAllFolds(N);
}
}
图
宽搜
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class T01_宽搜图 {
public static void bfs(Node node) {
if(node == null) return;
HashSet<Node> s = new HashSet<>();
Queue<Node> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.add(node);
s.add(node);
while(!q.isEmpty()) {
Node cur = q.poll();
System.out.print(cur.value+" ");
for(Node next : cur.nexts) {
if(!s.contains(next)) {
q.add(next);
s.add(next);
}
}
}
System.out.println();
}
}
深搜
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Stack;
public class T02_深搜图 {
public static void dfs(Node node) {
if(node == null) return;
HashSet<Node> m = new HashSet<>();
Stack<Node> s = new Stack<>();
m.add(node);
s.push(node);
System.out.print(node.value+" ");
while(!s.isEmpty()) {
Node cur = s.pop();
for(Node next : cur.nexts) {
if(!m.contains(next)) {
s.push(cur);
s.push(next);
m.add(next);
System.out.print(next.value+" ");
break;
}
}
}
System.out.println();
}
}
拓扑排序算法
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Queue;
public class T03_拓扑排序算法 {
public static List<Node> sortedTopology(Graph graph) {
List<Node> res = new ArrayList<>();
HashMap<Node,Integer> m = new HashMap<>();
Queue<Node> q = new LinkedList<>();
for(Node cur : graph.nodes.values()) {
m.put(cur, cur.in);
//入度为0
if(cur.in == 0) q.add(cur);
}
while(!q.isEmpty()) {
Node cur = q.poll();
res.add(cur);
for(Node next : cur.nexts) {
//会出现已经为0的继续被减,但是不影响我们最后的结果
m.put(next, m.get(next)-1);
if(m.get(next).equals(0)) q.add(next);
}
}
return res;
}
}
最小生成树kruskal算法
- 适用于无向图
也是可以解决最小生成森林问题的
思路:一开始所有点在各自的集合里面,然后开始从最小边到最大边遍历
如果边两个点不在一个集合里面就将他们合并到一个集合里面
循环这个操作就可以得到最小生成树了
import java.util.*;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class T04_最小生成树K算法 {
public static class MySet {
public HashMap<Node, List<Node>> setMap;
public MySet(List<Node> nodes) {
for(Node cur : nodes) {
List<Node> set = new ArrayList<>();
set.add(cur);
setMap.put(cur, set);
}
}
public boolean isSameSet(Node from,Node to) {
List<Node> fromSet = setMap.get(from);
List<Node> toSet = setMap.get(to);
return fromSet == toSet;
}
public void union(Node from,Node to) {
List<Node> fromSet = setMap.get(from);
List<Node> toSet = setMap.get(to);
for(Node toNode : toSet) {
fromSet.add(toNode);
setMap.put(toNode, fromSet);
}
}
}
public static Set<Edge> kruskalMST(Graph graph) {
Set<Edge> s = new HashSet<>();
List<Node> list = graph
.nodes
.values()
.stream()
.collect(Collectors.toList());
//创建垃圾版并查集
MySet mySet = new MySet(list);
PriorityQueue<Edge> p = new PriorityQueue<>((o1,o2)->o1.weight - o2.weight);
//加到优先队列里面
for(Edge e : graph.edges) p.add(e);
while(!p.isEmpty()) {
Edge edge = p.poll();
Node fromNode = graph.nodes.get(edge.from);
Node toNode = graph.nodes.get(edge.to);
//如果两个点不在一个集合里面我们就要了
if(!mySet.isSameSet(fromNode, toNode)) {
s.add(edge);
mySet.union(fromNode, toNode);
}
}
return s;
}
}
最小生成树Prime算法
- 适用于无向图
创建一个最小堆:存储边
创建一个点集合
创建一个边集合
然后从任意一个节点出发,该点加入集合里面,它的边加入最小堆里面
没错从最小堆里面弹出一个元素,将元素加入边集合里面,边的to点的边加入最小堆里面
循环上面的过程。
import java.util.*;
public class T05_最小生成树P算法 {
public static Set<Edge> primeMTS(Graph graph) {
Set<Edge> res = new HashSet<>();//返回最小生成树的边
Set<Node> nodes = new HashSet<>();//加入集合的点
//未加入结果集合的边
PriorityQueue<Edge> p = new PriorityQueue<>((o1,o2)->o1.weight-o2.weight);
//加入过优先队列的边
Set<Edge> edges = new HashSet<>();
for(Node node : graph.nodes.values()) {
if(!nodes.contains(node)) {
//将点加入到集合里面
nodes.add(node);
for(Edge e : node.edges) {
p.add(e);
edges.add(e);
}
while(!p.isEmpty()) {
//集合里面最短的边
Edge edge = p.poll();
//将边加入我们的边结果集合里面
res.add(edge);
//将边的末位点加进来
nodes.add(graph.nodes.get(edge.to));
//然后将to的点的边加到堆里面(边不能样它加已经用过的加进来了)
for(Edge e : graph.nodes.get(edge.to).edges) {
//这样会将其他重复的边加进来,但是加进来的重复的边不会
if(!edges.contains(e)) {
p.add(e);
edges.add(e);
}
}
}
}
}
return res;
}
}
一开始我想在直接判断边有没有加入结果集就可以了,其他边是否重复我不管,但是这会违背我们堆的边不重复的前提,所以还是要开一个边集合
dijkstra算法
- 不适合负权图
- 思路:找到距离最小的点,然后一它为中介更新别的没加入集合的点,然后该点加入集合里面。
左神表示:图的边是可以是负数的,但是不能形成环为负数
import java.util.*;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
public class T06_Dijkstra {
public static HashMap<Node, Integer> dijkstra1(Node head,Graph graph) {
HashMap<Node,Integer> disMap = new HashMap<>();//key:点, value: head=>点的最小距离
//初始化一下我们这个map
for(Node node : graph.nodes.values()) disMap.put(node, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
Set<Node> s = new HashSet<>();//确定最短距离的点
disMap.put(head, 0);
s.add(head);
Node minDisNode = getMinDis(disMap,s);
while(minDisNode != null) {
//最小点就是我们想要的
s.add(minDisNode);
//开始更新以最小点为起点的边到其他点的值
for(Edge edge : minDisNode.edges) {
int to = edge.to;
//以from作为中转点让其点到to点的距离
int dis = disMap.get(minDisNode) + edge.weight;
//如果当前起点到node距离大于dis我们就更新值
if(disMap.get(graph.nodes.get(to)).compareTo(dis) > 0) {
disMap.put(minDisNode, dis);
}
}
minDisNode = getMinDis(disMap, s);
}
return disMap;
}
public static Node getMinDis(HashMap<Node,Integer> disMap,Set<Node> s) {
Node rtNode = null;
int minDis = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for(Entry<Node, Integer> e: disMap.entrySet() ) {
if( !s.contains(e.getKey()) && e.getValue().compareTo(minDis) < 0) {
rtNode = e.getKey();
minDis = e.getValue();
}
}
return rtNode;
}
}
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
// no negative weight
public class Code06_Dijkstra {
public static HashMap<Node, Integer> dijkstra1(Node head) {
HashMap<Node, Integer> distanceMap = new HashMap<>();
distanceMap.put(head, 0);
HashSet<Node> selectedNodes = new HashSet<>();
Node minNode = getMinDistanceAndUnselectedNode(distanceMap, selectedNodes);
while (minNode != null) {
int distance = distanceMap.get(minNode);
for (Edge edge : minNode.edges) {
Node toNode = edge.to;
if (!distanceMap.containsKey(toNode)) {
distanceMap.put(toNode, distance + edge.weight);
}
distanceMap.put(edge.to, Math.min(distanceMap.get(toNode), distance + edge.weight));
}
selectedNodes.add(minNode);
minNode = getMinDistanceAndUnselectedNode(distanceMap, selectedNodes);
}
return distanceMap;
}
public static Node getMinDistanceAndUnselectedNode(HashMap<Node, Integer> distanceMap,
HashSet<Node> touchedNodes) {
Node minNode = null;
int minDistance = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (Entry<Node, Integer> entry : distanceMap.entrySet()) {
Node node = entry.getKey();
int distance = entry.getValue();
if (!touchedNodes.contains(node) && distance < minDistance) {
minNode = node;
minDistance = distance;
}
}
return minNode;
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
public static class NodeRecord {
public Node node;
public int distance;
public NodeRecord(Node node, int distance) {
this.node = node;
this.distance = distance;
}
}
public static class NodeHeap {
private Node[] nodes;
private HashMap<Node, Integer> heapIndexMap;
private HashMap<Node, Integer> distanceMap;
private int size;
public NodeHeap(int size) {
nodes = new Node[size];
heapIndexMap = new HashMap<>();
distanceMap = new HashMap<>();
this.size = 0;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
public void addOrUpdateOrIgnore(Node node, int distance) {
if (inHeap(node)) {
distanceMap.put(node, Math.min(distanceMap.get(node), distance));
insertHeapify(node, heapIndexMap.get(node));
}
if (!isEntered(node)) {
nodes[size] = node;
heapIndexMap.put(node, size);
distanceMap.put(node, distance);
insertHeapify(node, size++);
}
}
public NodeRecord pop() {
NodeRecord nodeRecord = new NodeRecord(nodes[0], distanceMap.get(nodes[0]));
swap(0, size - 1);
heapIndexMap.put(nodes[size - 1], -1);
distanceMap.remove(nodes[size - 1]);
nodes[size - 1] = null;
heapify(0, --size);
return nodeRecord;
}
private void insertHeapify(Node node, int index) {
while (distanceMap.get(nodes[index]) < distanceMap.get(nodes[(index - 1) / 2])) {
swap(index, (index - 1) / 2);
index = (index - 1) / 2;
}
}
private void heapify(int index, int size) {
int left = index * 2 + 1;
while (left < size) {
int smallest = left + 1 < size && distanceMap.get(nodes[left + 1]) < distanceMap.get(nodes[left])
? left + 1 : left;
smallest = distanceMap.get(nodes[smallest]) < distanceMap.get(nodes[index]) ? smallest : index;
if (smallest == index) {
break;
}
swap(smallest, index);
index = smallest;
left = index * 2 + 1;
}
}
private boolean isEntered(Node node) {
return heapIndexMap.containsKey(node);
}
private boolean inHeap(Node node) {
return isEntered(node) && heapIndexMap.get(node) != -1;
}
private void swap(int index1, int index2) {
heapIndexMap.put(nodes[index1], index2);
heapIndexMap.put(nodes[index2], index1);
Node tmp = nodes[index1];
nodes[index1] = nodes[index2];
nodes[index2] = tmp;
}
}
public static HashMap<Node, Integer> dijkstra2(Node head, int size) {
NodeHeap nodeHeap = new NodeHeap(size);
nodeHeap.addOrUpdateOrIgnore(head, 0);
HashMap<Node, Integer> result = new HashMap<>();
while (!nodeHeap.isEmpty()) {
NodeRecord record = nodeHeap.pop();
Node cur = record.node;
int distance = record.distance;
for (Edge edge : cur.edges) {
nodeHeap.addOrUpdateOrIgnore(edge.to, edge.weight + distance);
}
result.put(cur, distance);
}
return result;
}
}
public class T08_Dijkstra优化 {
public static class Node {
int value;
int in;
int out;
List<Node> nexts;
List<Edge> edges;
public Node(int val) {
value = val;
}
public int hashCode() {
return value;
}
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if(o == this) return true;
if(!(o instanceof Node)) return false;
Node node = (Node)o;
return node.value == value;
}
}
public static class Edge {
int weight;
Node from;
Node to;
public Edge(int w,Node f,Node t) {
weight = w;
from = f;
to = t;
}
public int hashCode() {
int res = weight;
res = 31*res + from.hashCode();
res = 31*res + to.hashCode();
return res;
}
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if(o == this) return true;
if(!(o instanceof Edge)) return false;
return from.equals(o) && to.equals(o);
}
}
public static class Graph {
HashMap<Integer,Node> nodes;
HashSet<Edge> edges;
}
public static class NodeRecord {
Node node;
int weight;
public NodeRecord(Node n,int w) {
node = n;
weight = w;
}
}
public static class NodeHeap {
private Node[] nodes;
private HashMap<Node,Integer> heapIndexMap;//不存在的元素下标为 -1
private HashMap<Node,Integer> distanceMap;
private int size;
public NodeHeap(int size) {
nodes = new Node[size];
heapIndexMap = new HashMap<>();
distanceMap = new HashMap<>();
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
public void addOrUpdateOrIgnore(Node node, int distance) {
if(inHeap(node)) {
distanceMap.put(node, Math.min(distance, distanceMap.get(node)));
insertHeapify(heapIndexMap.get(node));
}else if(!isEntered(node)) {
nodes[size++] = node;
distanceMap.put(node, distance);
heapIndexMap.put(node, size-1);
insertHeapify(size-1);
}
}
public NodeRecord pop() {
NodeRecord res = new NodeRecord(nodes[0],distanceMap.get(nodes[0]));
swap(0,size-1);
heapIndexMap.put(nodes[size-1], -1);
distanceMap.remove(nodes[size-1]);
nodes[size-1] = null;
heapify(0, --size);
return res;
}
private void insertHeapify(int index) {
while(distanceMap.get(nodes[index]).compareTo(distanceMap.get(nodes[ (index-1)/2 ])) < 0) {
swap(index,(index-1)/2);
index = (index-1)/2;
}
}
private void heapify(int index, int size) {
int left = index*2 + 1;
while(left < size) {
int smallest = left+1<size &&
distanceMap.get(nodes[left+1]).compareTo(distanceMap.get(nodes[left]))<0?
left+1:left;
smallest =
distanceMap.get(nodes[index])>distanceMap.get(nodes[smallest])?
smallest:index;
if(smallest == index) return;
swap(smallest,index);
index = smallest;
left = index*2+1;
}
}
private boolean isEntered(Node node) {
return heapIndexMap.containsKey(node);
}
private boolean inHeap(Node node) {
return isEntered(node) && distanceMap.get(node) != -1;
}
private void swap(int index1, int index2) {
heapIndexMap.put(nodes[index1], index2);
heapIndexMap.put(nodes[index2], index1);
Node t = nodes[index1];
nodes[index1] = nodes[index2];
nodes[index2] = t;
}
}
public static HashMap<Node,Integer> dijkstra(Graph graph,Node head) {
HashMap<Node,Integer> res = new HashMap<>();
NodeHeap nodeHeap = new NodeHeap(graph.nodes.size());
nodeHeap.addOrUpdateOrIgnore(head, 0);
while(!nodeHeap.isEmpty()) {
NodeRecord node = nodeHeap.pop();
res.put(node.node, node.weight);
for(Edge edge : node.node.edges) {
nodeHeap.addOrUpdateOrIgnore(edge.to, node.weight+edge.weight);
}
}
return res;
}
public static Graph createGraph(Integer[][] matrix) {
Graph graph = new Graph();
for (int i = 0; i < matrix.length; i++) {
Integer weight = matrix[i][0];
Integer from = matrix[i][1];
Integer to = matrix[i][2];
if (!graph.nodes.containsKey(from)) {
graph.nodes.put(from, new Node(from));
}
if (!graph.nodes.containsKey(to)) {
graph.nodes.put(to, new Node(to));
}
Node fromNode = graph.nodes.get(from);
Node toNode = graph.nodes.get(to);
Edge newEdge = new Edge(weight, fromNode, toNode);
fromNode.nexts.add(toNode);
fromNode.out++;
toNode.in++;
fromNode.edges.add(newEdge);
graph.edges.add(newEdge);
}
return graph;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
int m = sc.nextInt();
Integer[][] mat = new Integer[m][3];
for(int i=0;i<m;i++) {
mat[i][1] = sc.nextInt();
mat[i][2] = sc.nextInt();
mat[i][0] = sc.nextInt();
}
Graph g = createGraph(mat);
System.out.println(dijkstra(g,g.nodes.get(1)));
}
}
贪心算法
- 贪心策略,最常用的就是堆和排序
会议选择
- 给你一个时间二维数组(只有两列,0开始,1结束),里面有一个会议的开始时间和结束时间,请返回这一天最多能开多少个会议
- 会议开始时间和结束时间合法
public static int meetings(int[][] meetingTimes) {
if(meetingTimes == null || meetingTimes.length == 0) return 0;
Arrays.sort(meetingTimes,(o1,o2)->o1[1]-o2[1]);
int count = 0;
int preEnd = 0;
for(int[] m : meetingTimes) {
if(m[0]>=preEnd) {
++count;
preEnd = m[1];
}
}
return count;
}
字符串拼接
import java.util.Arrays;
public class T2_字符串拼接 {
public static String strSplit(String[] strs) {
if(strs == null || strs.length == 0) return null;
Arrays.sort(strs,(o1,o2) -> (o1+o2).compareTo(o2+o1));
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
for(String str : strs) res.append(str);
return res.toString();
}
}
投资选择
一开始不太理解为什么可以贪心,因为:
我们可以投资的,找出最大能投资的加到我们的账户里面是最好的。
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
/*
输入: 正数数组costs 正数数组profits 正数k 正数m 含义:
costs[i]表示i号项目的花费
profits[i]表示i号项目在扣除花费之后还能挣到的钱(利润)
k表示你只能串行的最多做k个项目 m表示你初始的资金
说明: 你每做完一个项目,马上获得的收益,可以支持你去做下一个项目。 输出: 你最后获得的最大钱数
*/
public class T4_赚钱问题 {
public static class Node {
public int p;//得到利润
public int c;//需要资本
public Node(int p, int c) {
this.p = p;
this.c = c;
}
}
public static int findMaximizedCapital(int k, int w, int[] Profits, int[] Capital) {
PriorityQueue<Node> pb = new PriorityQueue<>((o1,o2)->o2.p - o1.p);//利润小根堆
PriorityQueue<Node> ps = new PriorityQueue<>((o1,o2)->o1.c - o2.c);//资本小根堆
//将所有项目加到小根堆里面,按照投资花费投入
for(int i=0;i<Profits.length;i++) ps.add(new Node(Profits[i],Capital[i]));
//核心逻辑
for(int i=0;i<k;i++) {
//将可以做的生意加到利润大根堆里面
while(!ps.isEmpty() && ps.peek().c <= w) pb.add(ps.poll());
//如果利润大根堆为空,说明没有得选择了,退出
if(pb.isEmpty()) return w;
//将大根堆里面最大的弹出
w += pb.poll().p;
}
return w;
}
}























 178
178

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










