要求:
- (1)用递归代码实现斐波那契数列求解;
- (2)利用转换规则(goto) 将代码(1)转换为非递归代码;
- (3)简化并梳理代码(2);
- (4)递归斐波那契数列最优解;
分析:
- 利用递归求出前两项求和得到第三项,依次递增求解;
- 利用goto实现强跳转,转到程序的某个片段中,用栈记录参数和返回的位置,利用栈的特性依次出栈实现递归的思想,将新元素入栈实现新数据的连续计算;
- 在判断时,使用 ? : 语句简化代码;
首先自定义栈类:
Stack.h
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
template<typename T>
class Stack
{
public:
Stack() { count =0; };
bool isEmpty()const;
bool isFull()const;
T top();
void push(const T x);
void pop();
void pop(T& x);
int getCount();
private:
int count;
T data[100] = { 0 };
};
Stack.cpp
#include "Stack.h"
template<typename T>
bool Stack<T>::isEmpty()const
{
if (count == 0) {
return 1;
}
else return 0;
}
template<typename T>
bool Stack<T>::isFull()const
{
return count == 100;
}
template<typename T>
T Stack<T>::top()
{
if (isEmpty())
{
cout << "栈是空的" << endl;
}
else
{
return data[count - 1];
}
}
template<typename T>
void Stack<T>::push(const T x)
{
if (isFull())
{
cout << "栈满了" << endl;
}
else
data[count] = x;
count++;
}
template<typename T>
void Stack<T>::pop()
{
if (isEmpty())
{
cout << "栈是空的" << endl;
}
else
{
count--;
}
}
template<typename T>
int Stack<T>::getCount()
{
return count;
}
template<typename T>
void Stack<T>::pop(T& x)
{
if (isEmpty())
{
cout << "栈是空的" << endl;
}
else
{
x = data[count - 1];
count--;
}
}
fbnq_num4挑战最优解:
Main.cpp
#include<iostream>
#include"Stack.cpp"
using namespace std;
struct data
{
int n;
int fun_n;
int fun_n_1;
int fun_n_2;
int index;
};
int fbnq_num1(int n) //(1)用递归代码实现斐波那契数列求解
{
if (n==1)
{
return 1;
}
else if(n==2)
{
return 1;
}
else
{
return fbnq_num1(n - 2) + fbnq_num1(n - 1);
}
}
int fbnq_num2(int N) //(2)利用转换规则(不简化) 将代码(1)转换为非递归代码
{
struct data cur, temp;
cur.n = N;
cur.fun_n = 0;
cur.fun_n_1 = 0;
cur.fun_n_2 = 0;
cur.index = 3;
int result = 0;
Stack<struct data> s;
s.push(cur);
L0:
temp = s.top();
if (cur.n<=1)
{
s.pop();
temp.fun_n = cur.n;
s.push(temp);
goto L3;
}
cur.n--;
cur.fun_n = 0;
cur.fun_n_1 = 0;
cur.fun_n_2 = 0;
cur.index = 1;
s.push(cur);
goto L0;
L1:
temp = s.top();
s.pop();
cur = s.top();
s.pop();
cur.fun_n_1 = temp.fun_n;
s.push(cur);
cur.n -= 2;
cur.index = 2;
s.push(cur);
goto L0;
L2:
temp = s.top();
s.pop();
cur = s.top();
s.pop();
cur.fun_n_2 = temp.fun_n;
cur.fun_n = cur.fun_n_1 + cur.fun_n_2;
s.push(cur);
goto L3;
L3:
temp = s.top();
switch (temp.index)
{
case 1:
goto L1;
break;
case 2:
goto L2;
break;
case 3:
s.pop();
result = temp.fun_n;
break;
}
return result;
}
int fbnq_num3(int n) //(3)简化并梳理代码(2)的流程。
{
if (n<3)
{
return 1;
}
int temp1 = 1;
int temp2 = 1;
int a = n - 2;
while (a--)
{
temp2 = temp1 + temp2;
temp1 = temp2 - temp1;
}
return temp2;
}
int fbnq_num4(int n) //(4)优化递归斐波那契数列求解
{
return (n==1||n==2)?1: fbnq_num4(n - 2) + fbnq_num4(n - 1);
}
int main()
{
int n;
cout << "请输入n:" ;
cin >> n;
cout << "斐波那契数列第" << n << "个数为:" << fbnq_num4(n) << endl;
return 0;
}测试数据:3 5 8 10 15 20 25 30
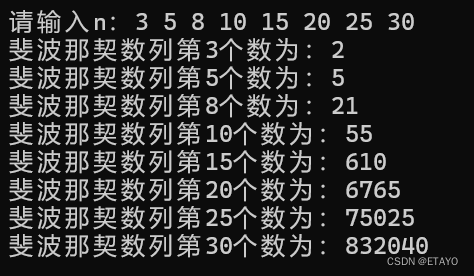
大一萌新努力学习ing,一点算法总结,仅供学习参考,如有不足欢迎指正!






















 922
922











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








