虽然有了现成的凸包
算法,但是还有一些求得凸点前期或后期类问题需要自己解决。在这里来个小小的总结。
SPOJ MTRIAREA - Maximum Triangle Area
hdu 5251 矩形面积
UVA 10652 Board Wrapping
计算多边形面积,使用叉积来个顶点循环即可
先贴出求凸包的算法:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N=5e4+10;
struct point{
int x,y;
}p[N];
int dis(point a,point b){
return (a.x-b.x)*(a.x-b.x)+(a.y-b.y)*(a.y-b.y);
}
int cross(point p0,point p1,point p2){
return (p1.x-p0.x)*(p2.y-p0.y)-(p2.x-p0.x)*(p1.y-p0.y);
}
int cmp1(point p1,point p2){
return p1.x<p2.x||(p1.x==p2.x&&p1.y<p2.y);
}
int cmp2(point p1,point p2){
int c=cross(p[0],p1,p2);
if(c==0) return dis(p[0],p1)<dis(p[0],p2);
return c>0;
}
point sta[N];
int top;
void convex(int n){
top=0;
sort(p,p+n,cmp1);
sort(p+1,p+n,cmp2);
sta[top++]=p[0];
sta[top++]=p[1];
for(int i=2;i<n;i++){
if(cross(sta[top-2],sta[top-1],p[i])>0) sta[top++]=p[i];
else {
top--;
while(top>=2&&cross(sta[top-2],sta[top-1],p[i])<=0) top--;
sta[top++]=p[i];
}
}
}
int rotating() //旋转卡壳
{
int q=1,ans=0;
sta[top]=sta[0];
for(int i=0;i<top;i++)
{
while(cross(sta[i],sta[i+1],sta[q+1])>cross(sta[i],sta[i+1],sta[q]))
q=(q+1)%top;
ans=max(ans,max(dis(sta[i],sta[q]),dis(sta[i+1],sta[q+1])));
}
return ans;
}SPOJ MTRIAREA - Maximum Triangle Area
题目:Given n distinct points on a plane, your task is to find the triangle that have the maximum area, whose vertices are from the given points.
分析:用凸包算法求得所有的凸点后直接寻找可以构成最大三角形的三个点。所以重点在于怎么找那三个点。
求最远点对算法带来灵感,由两个固定的点可以求出第三个离这条边最远的点,那么我们求出第三个点后再更新第二个点,最后更新第一个点。恩,就这样找那三个点。(较高效的三重循环)
寻找最大的面积:
double area(){
double res=0;
for(int i=0;i<top;i++){
int j=(i+1)%top;
int k=(j+1)%top;
while(i!=j && k!=j){
while(k!=i && cross(ans[i],ans[j],ans[k+1])>cross(ans[i],ans[j],ans[k])) k=(k+1)%top;
double temp=fabs(cross(ans[i],ans[j],ans[k]))/2;
res=max(res,temp);
j=(j+1)%top;
}
}
return res;
}hdu 5251 矩形面积
大意:给出n个矩形,求最小的矩形盖住所有的矩形其面积。
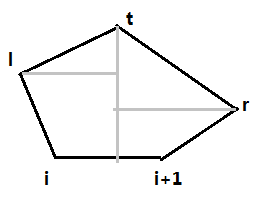
分析:先求出凸包,然后寻找相应的最小(最大)矩形。核心代码需结合上图理解:
已知相邻两点由旋转卡壳求出最远点,令len表示相邻点的距离,t和i、i+1的叉积除以len就是高度。设p离那个高最远,那么即是点积最大,同样用类似于求最远点的方法求得宽度。不过这次使用点积而不是叉积。就这样不断更新最大值——高×宽。
double work()
{
int t,r,l;
double res=999999999;
t=r=1;
if(top<3)
return 0;
for(int i=0; i<top; i++)
{
while(xmul(ans[i],ans[i+1],ans[t+1])>eps+xmul(ans[i],ans[i+1],ans[t]))
t=(t+1)%top;
while(dmul(ans[i],ans[i+1],ans[r+1])>eps+dmul(ans[i],ans[i+1],ans[r]))
r=(r+1)%top;
if(!i) l=r;
while(dmul(ans[i],ans[i+1],ans[l+1])<=eps+dmul(ans[i],ans[i+1],ans[l]))
l=(l+1)%top;
double d=dis(ans[i],ans[i+1]);
double tmp=xmul(ans[i],ans[i+1],ans[t])*
( dmul(ans[i],ans[i+1],ans[r])-
dmul(ans[i],ans[i+1],ans[l]) )/d;
res=min(res,tmp);
}
return res;
}UVA 10652 Board Wrapping
大意:给出n个矩形的中心坐标、宽、高和旋转角度(宽轴和x轴的夹角),求解所有的矩形的面积的和与最小包含他们的多边形的面积比,以百分数表示。
分析:由x,y,w,h,angle可以推算出所有的顶点坐标。即由坐标旋转的知识
推得所有的四个顶点。
Vector Rotate(Vector A, double rad) {
return Vector(A.x*cos(rad)-A.y*sin(rad), A.x*sin(rad)+A.y*cos(rad));
}
p[pc++] = o + Rotate(Vector(-w/2, -h/2), ang);
p[pc++] = o + Rotate(Vector(w/2, -h/2), ang);
p[pc++] = o + Rotate(Vector(-w/2, h/2), ang);
p[pc++] = o + Rotate(Vector(w/2, h/2), ang);计算多边形面积,使用叉积来个顶点循环即可
double area(point* p, int n) {
double area = 0;
for(int i = 1; i < n-1; i++) {
area += cross(p[i]-p[0], p[i+1]-p[0]);
}
return area / 2;
}恩,剩下的就是套模板了。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
const double eps=1e-7;
struct point {
double x,y;
point(){};
point(double _x,double _y) { x=_x; y=_y; }
void show(){
printf("%.2lf %.2lf\n",x,y);
}
};
double xmul(point p0,point p1,point p2){
return (p1.x-p0.x)*(p2.y-p0.y)-(p2.x-p0.x)*(p1.y-p0.y);
}
point intersec(point A,point B,point C,point D){
double md=xmul(A,B,D), mc=xmul(A,B,C);
double x=(D.x*mc-C.x*md)/(mc-md);
double y=(D.y*mc-C.y*md)/(mc-md);
return point(x,y);
}
int main()
{
freopen("cin1.txt","r",stdin);
int n;
cin>>n;
while(n--){
point A,B,C,D;
scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf",&A.x,&A.y,&B.x,&B.y);
scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf",&C.x,&C.y,&D.x,&D.y);
intersec(A,B,C,D).show();
}
return 0;
}






















 931
931

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








