一.文件专属流
凡是类名带stream的都是字节流,带Reader和Writer的都是字符流
1.字节流
a:输入:FileInputStream:
负责将硬盘中的文件读取到内存之中,每次只读取一个字节,下面是具体的读取方法:
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileInputStream fis=null;
try {
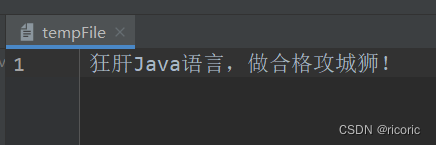
fis=new FileInputStream("tempFile") ;//""内为文件名
byte[] bytes=new byte[1024] ;//每次读取一个byte数组大小的内容
int count =0 ;//因为fis的read方法返回的是每次成功读取bytes的长度,
当返回-1时表示没有读取到任何字节,读取结束
while ((count=fis.read(bytes))!=-1){
System.out.println(new String(bytes,0,count)); //new 个String给他输出
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(fis!=null){
try {
fis.close();//所有流都要在最后关闭,try,catch这些编译器就可以解决啦
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
} 
D:\Java\jdk\bin\java.exe
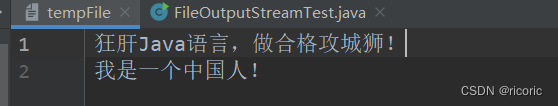
狂肝Java语言,做合格攻城狮!
Process finished with exit code 0
FileInputStream的常用方法:
int available() :返回该文件可读取的字节数,可以用在byte数组的初始化长度上,直接
byte[] bytes =new byte[ fis.available() ] ,
这样就用不到循环了,但是文件太大的时候不合适
long skip(long n) :读取时跳过n个长度的字节int count =0 ; fis=new FileInputStream("tempFile") ; fis.skip(13); byte[] bytes=new byte[fis.available()] ; count=fis.read(bytes) ; System.out.print(new String(bytes,0,count)); D:\Java\jdk\bin\java.exe 言,做合格攻城狮! Process finished with exit code 0
b:输出:FileOutputStream:
负责将内存中的内容一个字节一个字节的写入硬盘,一般用法
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileOutputStream fil =null ;
try {
//无参构造会将源文件内容清空
//fil=new FileOutputStream("file") ;
//以追加的方式写入文件的末尾
fil=new FileOutputStream("tempFile",true);
String s="\n我是一个中国人! " ;
byte[] bytes=s.getBytes();
fil.write(bytes);
//输出完成后要及时刷新
fil.flush();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(fil!=null){
try {
fil.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
字节的输出输入方式,几乎所有的文件都能复制,怎么复制呢?将两个结合一下就行
public static void copyDoc(File from, File to) {
FileInputStream fis = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream(from);
fos = new FileOutputStream(to, true);
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024 * 512];
int count = 0;
while ((count = fis.read(bytes)) != -1) {
fos.write(bytes, 0, count);
}
fos.flush();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (fis!=null) {
try {
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (fos != null) {
try {
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}2.字符流
a:输入:FileReader
负责从硬盘中一个字符一个字符的读取文件到内存中,一般用法和上面的字节输入流差不多,byte换成char
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileReader fir =null ;
try {
fir=new FileReader("tempFile") ;
char[] chars=new char[4] ;
int count=0;
while ((count=fir.read(chars))!=-1){
System.out.print(new String(chars,0,count));
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(fir!=null){
try {
fir.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}b:输出:FileWriter:
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileWriter fiw=null ;
try {
fiw=new FileWriter("file",true) ;
//直接写入字符串
char[] chars={'\n','我','是','一','名','J','a','v','a','攻','城','狮','!'};
fiw.write(chars);
//写入字符串的一部分
fiw.write(chars,5,8);
//直接写入字符串
String s="\n好好学软件,将来进鹅厂!" ;
fiw.write(s);
fiw.flush();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(fiw!=null){
try {
fiw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}二.转换流
a:输入:InputStreamReader,输出:OutputStreamWriter
分别实现将字节流转换为字符流, 一般建议定义在下面的缓冲流里面
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception {
FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("File") ;
FileReader fr=null ;
fr= (FileReader) new InputStreamReader(fis);
//FileReader fr =new InputStreamReader(New FileInoutStream("File"))
FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream("file") ;
FileWriter fw=null;
fw= (FileWriter) new OutputStreamWriter(fos);
//FileWriter fw=new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("File")) ;
}三.缓冲流
1.字符缓冲流
a:BufferedReader
BufferedReader(Reader in)创建使用默认大小的输入缓冲区的缓冲字符输入流。
BufferedReader(Reader in, int sz)创建使用指定大小的输入缓冲区的缓冲字符输入流。
构造方法中传入的是Reader的实现类,Reader接口是字符流专属,所以传入的参数要是字符流型,比如FileReader.
同时也可以将字节流转换成字符流当参数。
BufferedReader bfr= null;
try {
bfr = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("file")));
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
String readline=null ;
//一行一行的读,readline的返回类型是String,所以结束条件是返回NULL
try {
while ((readline = bfr.readLine()) !=null) {
System.out.println(readline);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(bfr!=null){
try {
bfr.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}b:BufferedWriter
BufferedWriter(Writer out)创建使用默认大小的输出缓冲区的缓冲字符输出流。
BufferedWriter(Writer out, int sz)创建一个新的缓冲字符输出流,使用给定大小的输出缓冲区。
public static void main(String[] args) {
BufferedWriter bfw= null;
try {
bfw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(new
FileOutputStream("file")));
String s="顶级套娃\n" ;
String s2="FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream();\n" +
"OutputStreamWriter osw=new OutStreamWriter(fos);\n" +
"BufferedWriter bfw=new BufferedWriter(osw);\n" ;
bfw.write(s);
bfw.write(s2);
bfw.flush();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(bfw!=null){
try {
bfw.close() ;
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}2.字节缓冲流
a:BufferedInputStream
b:BufferedOutStream
用法基本和字符缓冲流的一样,只不过传入的参数要是字节流类型的
BufferedInputStream(InputStream in)创建一个
BufferedInputStream并保存其参数,输入流in,供以后使用。
BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream out)创建一个新的缓冲输出流,以将数据写入指定的底层输出流。
四.标准输出流
1. printWriter
记得关闭文件,不然写的日志没得内容,它还不报错
printWriter
PrintWriter out=null ;
try {
//建立一个printStream指向文件logger
out =new PrintWriter(new FileOutputStream("logger",true)) ;
//改变输出方向
//System.setOut(out);
Date nowTime=new Date();
SimpleDateFormat sdf=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日 HH:mm:ss") ;
String strTime=sdf.format(nowTime);
out.write(strTime+":"+doSomething);
// System.out.println(strTime+":"+doSomething);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
out.close();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
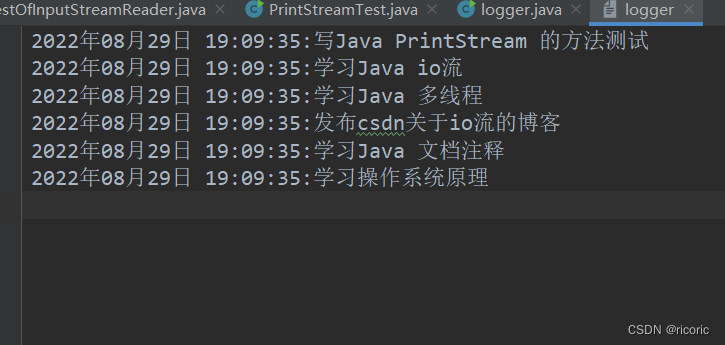
log("写Java PrintStream 的方法测试") ;
log("学习Java io流") ;
log("学习Java 多线程") ;
log("发布csdn关于io流的博客") ;
log("学习Java 文档注释") ;
log("学习操作系统原理") ;
System.out.println("----------------");
} 
2.printStream
默认输出到控制台,可以创建对象输出到指定文件,没有文件会创建文件
prtintStream
public class PrintStreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
PrintStream ps=System.out ;
ps.println("这就是流弊的标准输出流");
try {
PrintStream printStream=new PrintStream("file") ;
printStream.println("将输出流转入文件file,不向控制台输出");
String s="PrintString同时可以写入,相当于打印print" ;
byte[] bytes={'l','o','v','e','y','o','u'} ;
printStream.write(bytes);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("控制台我来喽@!");
}
}
五.序列化和反序列化
1.序列化:
ObjectOutputStream
可以序列化的类必须实现Serializable接口,这样jvm才会给该类生成serialVersionUID,即序列化版本号,jvm根据这个版本号序列化。版本号在后期修改类的代码时会发生变化,导致以前写的代码报错,所以建议对要进行序列化的类编写时,把版本号静态化,idea可以自动生成。
public class Dancer implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 5446290058445484067L;
public transient int age ;
public String name ;
public int no ;
public Dancer(int age, String name) {
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Dancer{" +
"age=" + age +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}创建对象来序列化,
ObjectOutputStream()为完全重新实现ObjectOutputStream的子类提供一种方法,不必分配刚刚被ObjectOutputStream实现使用的私有数据。
ObjectOutputStream(OutputStream out)创建一个写入指定的OutputStream的ObjectOutputStream。传入的参数要是字节流的
Dancer dancer=new Dancer(22,"dapiaoliang") ;
Dancer dancer1=new Dancer(29,"baihu");
ObjectOutputStream oos=null ;
try {
//写到文件file
oos=new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("file")) ;
oos.writeObject(dancer);
oos.writeObject(dancer1);
oos.flush();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
oos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}也可以序列化一组对象
Dancer dancer=new Dancer(22,"dapiaoliang") ;
Dancer dancer1=new Dancer(29,"baihu");
Dancer dancer2=new Dancer(18,"daxiong") ;
List<Dancer> l=new ArrayList<>() ;
l.add(dancer) ;
l.add(dancer1) ;
l.add(dancer2) ;
ObjectOutputStream Oos=null ;
try {
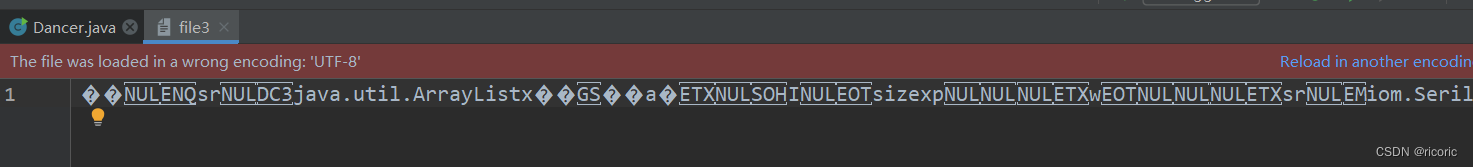
Oos=new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("file3")) ;
Oos.writeObject(l);
Oos.flush();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
try {
Oos.close() ;
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}序列化后的对象是无法正常读出来的,必须要反序列化才行
2.反序列化:
ObjectInputStream
ObjectInputStream ois=null;
try {
ois=new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("file3")) ;
List<Dancer> dancers=(List<Dancer>)ois.readObject();
for(Dancer d:dancers) {
System.out.println(d);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally{
try {
ois.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
D:\Java\jdk\bin\java.exe
Dancer{age=0, name='dapiaoliang'}
Dancer{age=0, name='baihu'}
Dancer{age=0, name='daxiong'}
Process finished with exit code 0





















 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








