1、
93. Restore IP Addresses
其实只要意识到这是切割问题,切割问题就可以使用回溯搜索法把所有可能性搜出来,和刚做过的131.分割回文串 (opens new window)就十分类似了。
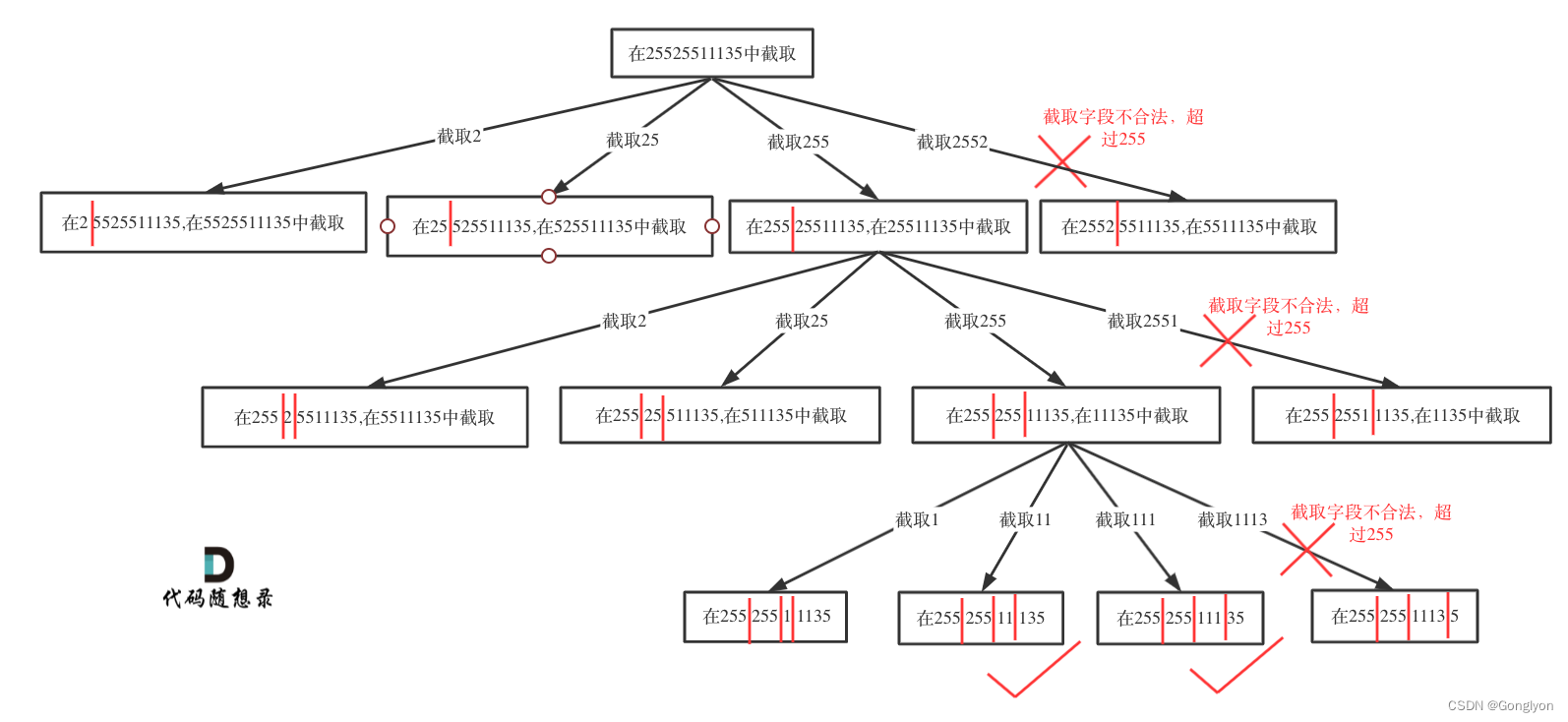
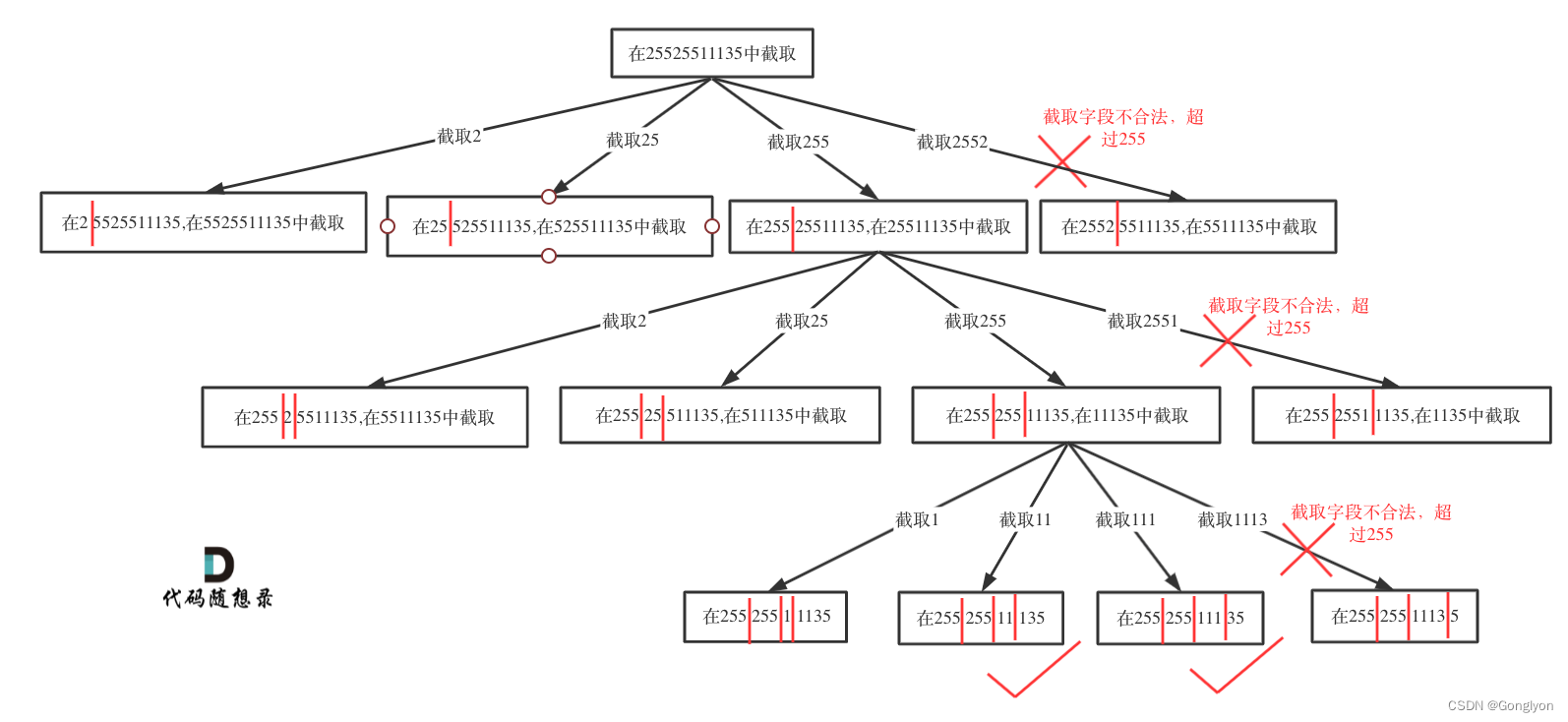
1)Determining Recursive Function Arguments
result, path, s, startIndex
2)Determination of termination conditions
点达到了四个就是终止条件
Four points is the termination condition.
3)single-level search process
if is a valid IP address,
then add point
push path
delete point
pop path
valid IP address:
1、0-255
2、开头没有0
3、不能有非法字符
class Solution(object):
def restoreIpAddresses(self, s):
"""
:type s: str
:rtype: List[str]
"""
result = []
self.backtracking(s, 0, 0, "", result)
return result
def backtracking(self, s, startIndex, pointNum, current, result):
if pointNum == 3:
# 点数量为3屎,分隔结束
if self.isValid(s, startIndex, len(s) - 1):
current += s[startIndex:]
# 添加最后一段子字符串
result.append(current)
return
for i in range(startIndex, len(s)):
if self.isValid (s, startIndex, i):
sub = s[startIndex: i + 1]
self.backtracking(s, i + 1, pointNum + 1, current + sub + '.', result)
else:
break
#这段还不是很明白
def isValid(self, s, start, end):
if start > end:
return False
# 0开头的数字不合法
if s[start] == '0' and start != end:
return False
num = 0
for i in range(start, end): #这里是end+1 why?
if not s[i].isdigit(): # 遇到非数字字符不合法
return False
#if s[i] > '9' or s[i] < '0':
# return False
#num = num * 10 + (s[i] - '0') #why?
num = num * 10 + int(s[i])
if num > 255:
return False
return True
2、
如果把 子集问题、组合问题、分割问题都抽象为一棵树的话,那么组合问题和分割问题都是收集树的叶子节点,而子集问题是找树的所有节点!
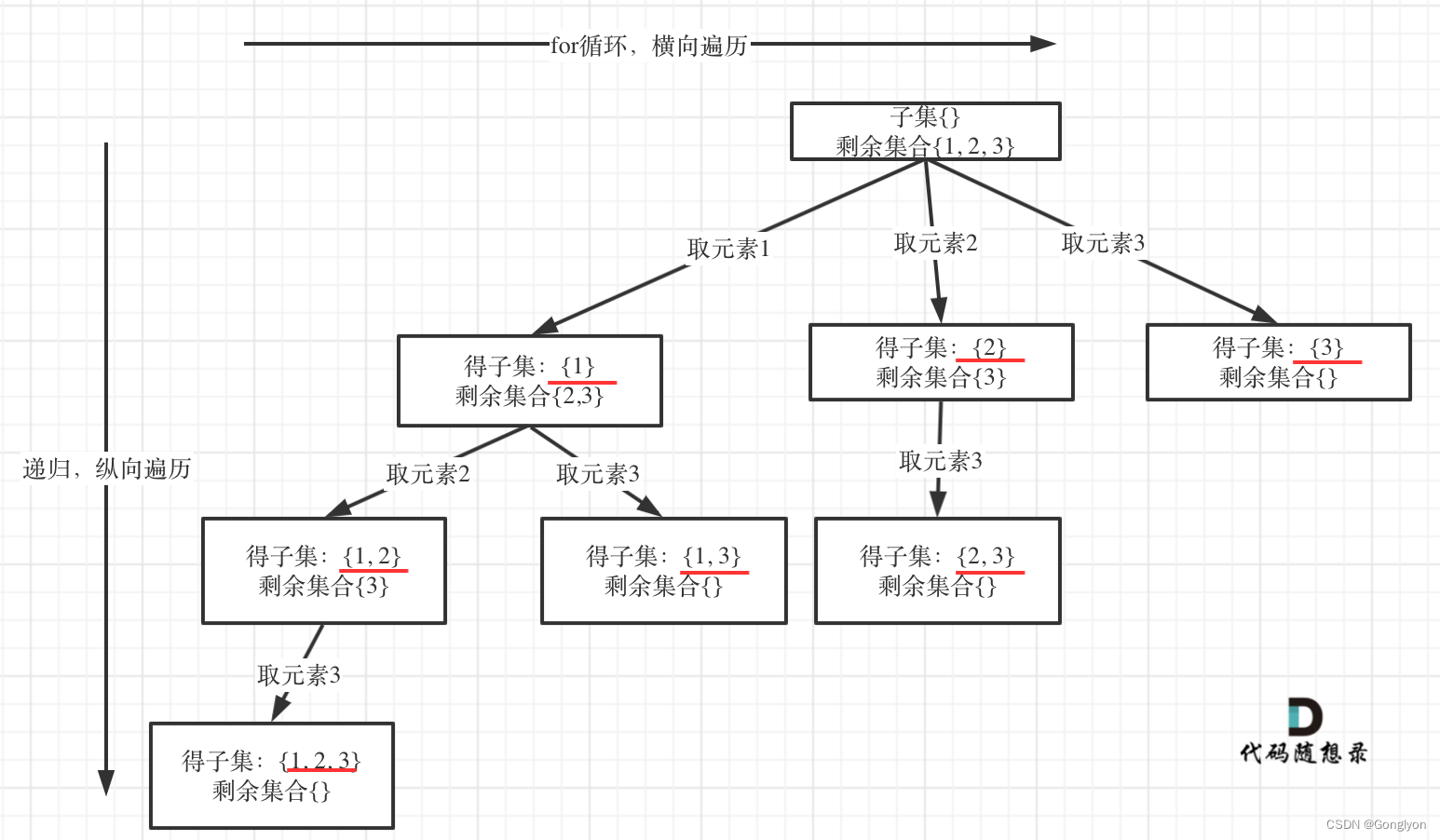
模板如上
自己写的时候很多时候忘记加self
class Solution(object):
def subsets(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
result = []
path = []
self.backtracking(nums, 0, path, result)
return result
def backtracking(self, nums, startIndex, path, result):
#result.append(path) # 这里不是直接path
result.append(path[:])
if startIndex >= len(nums):
return
for i in range(startIndex, len(nums)):
path.append(nums[i])
self.backtracking(nums, i + 1, path, result)
path.pop()
3、
LeetCode - The World's Leading Online Programming Learning Platform
跟组合总和2很像,也是通用可以用used数组,如果直接用startIndex会比较抽象。
3.1 用used数组
关键:if i > 0 and nums[i] == nums[i - 1] and not used [i - 1]
class Solution(object):
def subsetsWithDup(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
result = []
path = []
# 忘记了 初始化 used
used = [False] * len(nums)
nums.sort()
# 记得startIndex = 0
self.backtracking(nums, 0, used, path, result)
return result
# 忘记加了used,记得去重要加used
def backtracking(self, nums, startIndex, used ,path, result):
result.append(path[:])
for i in range(startIndex, len(nums)):
if i > 0 and nums[i] == nums[i - 1] and not used[i - 1]:
continue
path.append(nums[i])
used[i] = True
self.backtracking(nums, i + 1, used, path, result)
used[i] = False
path.pop()
3.2 startIndex
class Solution(object):
def subsetsWithDup(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
nums.sort()
result = []
path = []
self.backtracking(nums, 0, path, result)
return result
def backtracking(self, nums, startIndex, path, result):
#why startIndex?
result.append(path[:])
for i in range(startIndex, len(nums)):
if i > startIndex and nums[i] == nums[i - 1]:
continue
if startIndex >= len(nums):
return
path.append(nums[i])
self.backtracking(nums, i + 1, path, result)
path.pop()





















 1046
1046











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








