Part.I Introduction
递归算法是一种直接或者间接调用自身函数或者方法的算法。说简单了就是程序自身的调用。它的实质就是将原问题不断分解为规模缩小的子问题,然后递归调用方法来表示问题的解。
递归递归,顾名思义,分为两个阶段:递(递去)和归(归来)
- 递去:将递归问题分解为若干个规模较小,与原问题形式相同的子问题,这些子问题可以用相同的解题思路来解决
- 归来:当你将问题不断缩小规模递去的时候,必须有一个明确的结束递去的临界点(递归出口),一旦达到这个临界点即就从该点原路返回到原点,最终问题得到解决。
下面是它的图解:
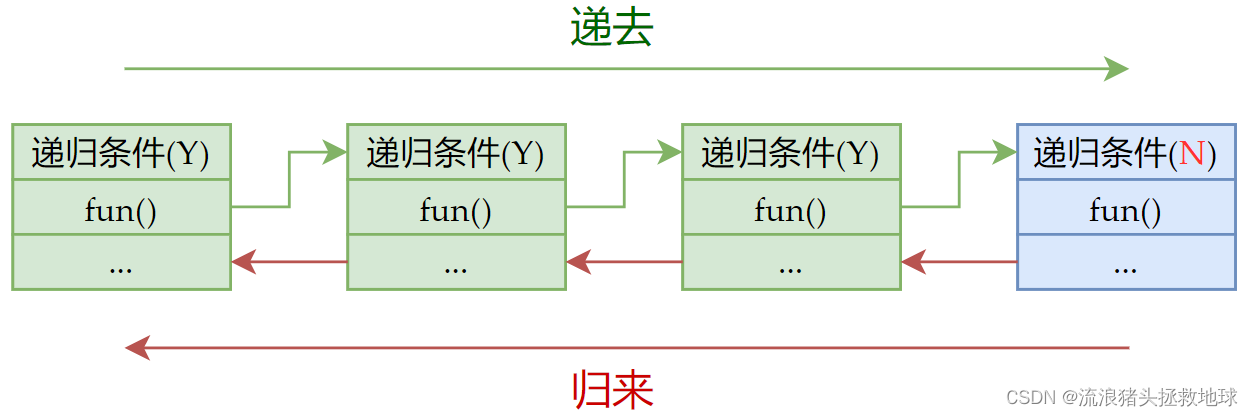
递归思维是一种从下向上的思维方式,使用递归算法往往可以简化我们的代码,而且还帮我们解决了很复杂的问题。递归算法的难点就在于它的逻辑性,一般设计递归算法需要考虑以下几点:
- 提取重复的逻辑,缩小问题的规模不断递去
- 明确递归的终止条件
- 给出递归终止时的处理方法
Part.II 算例分析
有一些经典的算法就可以用递归思想来解决,比如:
- 问题定义即为递归定义:阶乘、斐波那契数列、杨辉三角的取值
- 问题可以应用递归算法来解决:汉诺(hanoi)塔
- 递归思想来定义数据结构:树
Chap.I 杨辉三角问题
下面以杨辉三角为例来进行一下实际操作。
杨辉三角问题描述
杨辉三角形又称Pascal三角形,它的第i+1行是(a+b)i的展开式的系数。它的一个重要性质是:三角形中的每个数字等于它两肩上的数字相加。
下面给出了杨辉三角形的前4行:
1
1 1
1 2 1
1 3 3 1
给出n,要求输出它的前n行。
问题解决
int getValue(int x, int y)
{
if(y<=x&&y>=0)
{
if(y==1||x==y) // end condition
return 1;
else if(y<1 || x<1)
return 0;
else
return getValue(x-1,y-1)+getValue(x-1,y); // deescalate
}
return 0;
}
void printPascal(int n)
{
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
for(int j=1;j<=i;j++)
cout << getValue(i,j)<< " ";
cout<<'\n';
}
}
调用示例与输出
int main()
{
printPascal(8);
getchar();
}
---------------- output ---------------
1
1 1
1 2 1
1 3 3 1
1 4 6 4 1
1 5 10 10 5 1
1 6 15 20 15 6 1
1 7 21 35 35 21 7 1
Chap.II 其他问题
除了上面经典的问题,还有许多问题都可以用递归思维来解决,比如Leetcode 2022-10-30日的每日打卡
下面是笔者用递归思维的解题方法:
class Solution
{
public:
vector<string> letterCasePermutation(string s)
{
int n = s.length();
vector<string> result;
vector<int> index_str;
string tem_str = s;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (isalpha(s[i]))
{
index_str.push_back(i); // get the index of alpha in string-s
tem_str[i] = tolower(s[i]);
}
}
string low_str = tem_str;
result.push_back(low_str);
func(low_str, index_str, result);
return result;
}
void func(string s, vector<int> index_str, vector<string> &result)
{ // recursion
string s1 = s;
string s2 = s;
if (index_str.size() == 0)
{
return;
}
int ind = index_str[0];
vector<int>::iterator k = index_str.begin();
index_str.erase(k); // remove the first element
s2[ind] = toupper(s[ind]);
result.push_back(s2);
func(s1, index_str, result);
func(s2, index_str, result);
}
};
调用示例:
void printVec(vector<string> result)
{
int nSize = result.size();
for (int i = 0; i < nSize; i++)
{
cout << result[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
string st = "1a2bcd";
Solution *solu = new Solution();
vector<string> result = solu->letterCasePermutation(st);
printVec(result);
getchar();
return 0;
}
--------------------- output -------------------
1a2bcd 1A2bcd 1a2Bcd 1a2bCd 1a2bcD 1a2bCD
1a2BCd 1a2BcD 1a2BCD 1A2Bcd 1A2bCd 1A2bcD
1A2bCD 1A2BCd 1A2BcD 1A2BCD
ps:这个应该不是最优解决方案,但是这个解决方案用到了迭代思想,所以可以参考一下。























 2007
2007











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










