入门-动态规划
- 1. [分梨](http://acm.zzu.edu.cn/problem.php?id=1163)
- 2. 最大公共子序列
- 3. [最大子段和](http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1003)
- 4. [最大子阵和](http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1081)
- 5. [母牛的故事](http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=2018)
- 6. [数塔](http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=2084)
- 7. [一只小蜜蜂](http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=2044)
- 8. [折线分割平面](http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=2050)
- 9. [献给杭电五十周年校庆的礼物](http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1290)
1. 分梨
题目描述
小明非常喜欢吃梨,有一天他得到了ACMCLUB送给他的一筐梨子。由于他比较仗义,就打算把梨子分给好朋友们吃。现在他要把M个梨子放到N个盘子里面(我们允许有的盘子为空),你能告诉小明有多少种分法吗?(请注意,例如有三个盘子,我们将5,1,1和1,1,5,视为同一种分法)
输入
输入包含多组测试样例。每组输入的第一行是一个整数t。
接下来t行,每行输入两个整数M和N,代表有M个梨和N个盘子。(M和N均大于等于0)
输出
对于每对输入的M和N,输出有多少种方法。
样例输入
1
7 3
样例输出
8
解析 递归分配
M个梨, N个盘子的分法
dp(m, n){
if (只有一个盘子 || 没有梨)
只有一种分法;
if (盘子N比梨M多)
则最多用M个盘子, dp(m,n) = dp(m,m);
else
如果每个至少一个梨, 则dp(m-n, n)
如果有一个盘子为空, 则dp(m, n-1)
dp(m, n) = dp(m, n-1) + dp(m-n, n)
}
AC
#include<stdio.h>
int c(int x,int y)
{
if(y == 1 || x == 0)
return 1;
if(x<y)
return c(x,x);
else
return c(x,y-1)+c(x-y,y);
}
int main()
{
int t,n,m;
while(scanf("%d",&t)!=EOF)
{
while(t--)
{
scanf("%d%d",&m,&n);
printf("%d\n",c(m,n));
}
}
return 0;
}
2. 最大公共子序列
3. 最大子段和
Problem Description
Given a sequence a[1],a[2],a[3]…a[n], your job is to calculate the max sum of a sub-sequence. For example, given (6,-1,5,4,-7), the max sum in this sequence is 6 + (-1) + 5 + 4 = 14.
Input
The first line of the input contains an integer T(1<=T<=20) which means the number of test cases. Then T lines follow, each line starts with a number N(1<=N<=100000), then N integers followed(all the integers are between -1000 and 1000).
Output
For each test case, you should output two lines. The first line is “Case #:”, # means the number of the test case. The second line contains three integers, the Max Sum in the sequence, the start position of the sub-sequence, the end position of the sub-sequence. If there are more than one result, output the first one. Output a blank line between two cases.
Sample Input
2
5 6 -1 5 4 -7
7 0 6 -1 1 -6 7 -5
Sample Output
Case 1:
14 1 4
Case 2:
7 1 6
解析
sum, maxsum = M[n-1]
for auto m : M[]:
sum = max(sum+m, m)
if sum >= maxsum:
maxsum = sum
AC
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
int M[100005], arr[100005];
int l, r;
int maxSubArr(int D[], int n){
int i, sum = 0, maxsum = D[n-1];
l = n-1;
for (i=n-1; i>=0; i--){
if (sum > 0){
sum = sum + D[i];
}else{
sum = D[i];
}
if (sum >= maxsum) { //If there are more than one result, output the first one.
maxsum = sum;
l = i;
}
}
return maxsum;
}
int main(){
int T, N;
cin>>T;
for (int t=1; t<=T; t++){
cin>>N;
for (int i=0; i<N; i++){
cin>>M[i];
}
int ans = maxSubArr(M, N);
cout<<"Case "<<t<<":"<<endl;
int s = 0;
for (int i = l; i<N; i++){
s += M[i];
if (s == ans){
r=i;
break;
}
}
cout<<ans<<" "<<l+1<<" "<<r+1<<endl;
if (t<T){
cout<<endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
4. 最大子阵和
Problem Description
Given a two-dimensional array of positive and negative integers, a sub-rectangle is any contiguous sub-array of size 1 x 1 or greater located within the whole array. The sum of a rectangle is the sum of all the elements in that rectangle. In this problem the sub-rectangle with the largest sum is referred to as the maximal sub-rectangle.
As an example, the maximal sub-rectangle of the array:
0 -2 -7 0
9 2 -6 2
-4 1 -4 1
-1 8 0 -2
is in the lower left corner:
9 2
-4 1
-1 8
and has a sum of 15.
Input
The input consists of an N x N array of integers. The input begins with a single positive integer N on a line by itself, indicating the size of the square two-dimensional array. This is followed by N 2 integers separated by whitespace (spaces and newlines). These are the N 2 integers of the array, presented in row-major order. That is, all numbers in the first row, left to right, then all numbers in the second row, left to right, etc. N may be as large as 100. The numbers in the array will be in the range [-127,127].
Output
Output the sum of the maximal sub-rectangle.
Sample Input
4
0 -2 -7 0
9 2 -6 2
-4 1 -4 1
-1 8 0 -2
Sample Output
15
解析
这一题可以借助上一题的思路,把求最大子阵转化为求最大子段和,也就是变成一维情况。
(以第一行最为开始)先求第一行的最大和;将第二行数据加到第一行,再求此时的最大值;再将下一行加上去,求最大值.....;
.最终得到第一列到最后一列的最大值;还要计算第二行到最后一行的最大和,第三行到最后一行的最大和;
fun(){
//求最大子段和
}
for i = 0 : N #第i行到j行最大子阵和
# 第一次循环结束,我们得到的是第一行到第N行的N x M的最大子阵和(N是行数,M是列数,M由fun()决定)
# 第二次循环结束,我们得到的是第二行到第N行的N-1 x M的最大子阵和
for j = i : N
把第j行加到array上:arry[k] = M[j][k]
计算array的最大子段和:fun(array)
AC
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
int M[105][105], arr[105];
int maxSubArr(int D[], int n){
int sum=0, maxsum=D[0];
for (int i=0; i<n; i++){
if (sum>0){
sum = sum + D[i];
}else{
sum = D[i];
}
if (sum > maxsum) maxsum = sum;
}
return maxsum;
}
int main(){
int N;
while(scanf("%d", &N) != EOF){//注意输入
for (int i=0; i<N; i++){
for (int j=0; j<N; j++){
cin>>M[i][j];
}
}
int maxsubrec = M[0][0];
for (int i=0; i<N; i++){
memset(arr, 0, sizeof(arr));
for (int j=i; j<N; j++){
for (int k=0; k<N; k++){
arr[k] += M[j][k];
}
int maxsubarr = maxSubArr(arr, N);
if (maxsubarr > maxsubrec) maxsubrec = maxsubarr;
}
}
cout<<maxsubrec<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
5. 母牛的故事
Problem Description
有一头母牛,它每年年初生一头小母牛。每头小母牛从第四个年头开始,每年年初也生一头小母牛。请编程实现在第n年的时候,共有多少头母牛?
Input
输入数据由多个测试实例组成,每个测试实例占一行,包括一个整数n(0<n<55),n的含义如题目中描述。
n=0表示输入数据的结束,不做处理。
Output
对于每个测试实例,输出在第n年的时候母牛的数量。
每个输出占一行。
Sample Input
2
4
5
0
Sample Output
2
4
6
解析
f(n) = f(n-1) + f(n-3)
AC
#include<stdio.h>
//递归
int sum(int n)
{
if (n <= 4) return n;
else return (sum(n-1) + sum(n - 3));
}
int main()
{
int n;
while (~scanf("%d", &n) != EOF&&n!=0)
printf("%d\n", sum(n));
getchar();
return 0;
}
6. 数塔
Problem Description
在讲述DP算法的时候,一个经典的例子就是数塔问题,它是这样描述的:
有如下所示的数塔,要求从顶层走到底层,若每一步只能走到相邻的结点,则经过的结点的数字之和最大是多少?
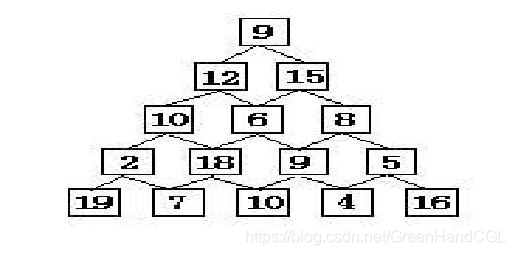
已经告诉你了,这是个DP的题目,你能AC吗?
Input
输入数据首先包括一个整数C,表示测试实例的个数,每个测试实例的第一行是一个整数N(1 <= N <= 100),表示数塔的高度,接下来用N行数字表示数塔,其中第i行有个i个整数,且所有的整数均在区间[0,99]内。
Output
对于每个测试实例,输出可能得到的最大和,每个实例的输出占一行。
Sample Input
1
5
7
3 8
8 1 0
2 7 4 4
4 5 2 6 5
Sample Output
30
解析
递推公式:DP[i][j] = M[i][j] + max(DP[i+1][j], DP[i+1][j+1])
自底向上计算到塔顶,得到的结果即为最大和
AC
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a[105][105];
int t, n, i, j;
while(cin>>t)
{
while(t--)
{
cin>>n;
memset(a,0,sizeof(a));
for(i=0; i<n; i++)
for(j=0; j<=i; j++)
cin>>a[i][j];
for(i=n-2; i>=0; i--)
for(j=0; j<=i; j++)
a[i][j] = a[i][j] + max(a[i+1][j], a[i+1][j+1]);
cout<<a[0][0]<<endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
7. 一只小蜜蜂
Problem Description
有一只经过训练的蜜蜂只能爬向右侧相邻的蜂房,不能反向爬行。请编程计算蜜蜂从蜂房a爬到蜂房b的可能路线数。
其中,蜂房的结构如下所示。
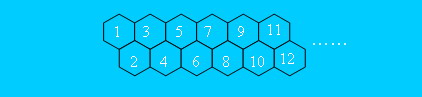
Input
输入数据的第一行是一个整数N,表示测试实例的个数,然后是N 行数据,每行包含两个整数a和b(0<a<b<50)。
Output
对于每个测试实例,请输出蜜蜂从蜂房a爬到蜂房b的可能路线数,每个实例的输出占一行。
Sample Input
2
1 2
3 6
Sample Output
1
3
解析
思路1:局部最优解得到全局最优解
蜂房5路线 = 蜂房3的路线 + 蜂房4的路线
蜂房6路线 = 蜂房4的路线 + 蜂房5的路线
。。。
蜂房n路线 = 蜂房n-2的路线 + 蜂房n-1的路线
斐波那契数列
思路2:枚举
1->2 (1种):1->2;
1->3 (2种): 1->2->3; 1->3;
1->4 (3种): 1->2->4; 1->2->3->4; 1->3->4;
1->5 (5种): 1->2->3->5; 1->3->5; 1->2->4->5; 1->2->3->4->5; 1->3->4->5;
1->6 (8种): 1->4(3种)->6; 1->5(5种)->6;
得斐波那契数列
唯一要注意的就是数比较大,得用long long类型
AC
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
long long ans = 0, pre = 0;
int T;
cin>>T;
while(T--){
int a, b;
cin>>a>>b;
for (int i=2; i <= b-a+1; i++){
if (i==2) {
pre = 0;
ans = 1;
}
else if (i==3) {
pre = 1;
ans = 2; continue;
}else{
ans = pre + ans;
pre = ans - pre;
}
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
return 0;
}
8. 折线分割平面
Problem Description
我们看到过很多直线分割平面的题目,今天的这个题目稍微有些变化,我们要求的是n条折线分割平面的最大数目。比如,一条折线可以将平面分成两部分,两条折线最多可以将平面分成7部分,具体如下所示。
Input
输入数据的第一行是一个整数C,表示测试实例的个数,然后是C 行数据,每行包含一个整数n(0<n<=10000),表示折线的数量。
Output
对于每个测试实例,请输出平面的最大分割数,每个实例的输出占一行。
Sample Input
2
1
2
Sample Output
2
7
解析
n条直线最多分平面问题
题目大致如:n条直线,最多可以把平面分为多少个区域。
析:可能你以前就见过这题目,这充其量是一道初中的思考题。但一个类型的题目还是从简单的入手,才容易发现规律。
当有n-1条直线时,平面最多被分成了f(n-1)个区域。
则第n条直线要是切成的区域数最多,就必须与每条直线相交且不能有同一交点。
这样就会得到n-1个交点。
这些交点将第n条直线分为2条射线和n-2条线段。
而每条射线和线断将已有的区域一分为二。这样就多出了2+(n-2)个区域。
故:f(n)=f(n-1)+n
=f(n-2)+(n-1)+n
……
=f(1)+1+2+……+n
=n(n+1)/2+1
根据直线分平面可知,由交点决定了射线和线段的条数,进而决定了新增的区域数。
当n-1条折线时,区域数为f(n-1)。
为了使增加的区域最多,则折线的两边的线段要和n-1条折线的边,即2*(n-1)条线段相交。
那么新增的线段数为4*(n-1),射线数为2。
但要注意的是,折线本身相邻的两线段只能增加一个区域。
故:f(n)=f(n-1)+4(n-1)+2-1
=f(n-1)+4(n-1)+1
=f(n-2)+4(n-2)+4(n-1)+2
……
=f(1)+4+4*2+……+4(n-1)+(n-1)
=2n^2-n+1
AC
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int num,k;
cin>>num;
while(num--)
{
cin>>k;
cout<<2*k*k-k+1<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
9. 献给杭电五十周年校庆的礼物
Problem Description
今年是我们杭电建校五十周年,这是一个值得祝福的日子。我们该送给母校一个怎样的礼物呢?对于目前的大家来说,最好的礼物当然是省赛中的好成绩,我不能参赛,就送给学校一个DOOM III球形大蛋糕吧,这可是名牌,估计要花掉我半年的银子呢。
想象着正式校庆那一天,校长亲自操刀,把这个大蛋糕分给各地赶来祝贺的校友们,大家一定很高兴,呵呵,流口水了吧…
等一等,吃蛋糕之前先考大家一个问题:如果校长大人在蛋糕上切了N刀(校长刀法极好,每一刀都是一个绝对的平面),最多可以把这个球形蛋糕切成几块呢?
做不出这个题目,没有蛋糕吃的!
为-了-母-校-,为-了-蛋-糕-(不是为了DGMM,枫之羽最会浮想联翩…),加-油-!
Input
输入数据包含多个测试实例,每个实例占一行,每行包含一个整数n(1<=n<=1000),表示切的刀数。
Output
对于每组输入数据,请输出对应的蛋糕块数,每个测试实例输出一行。
Sample Input
1
2
3
Sample Output
2
4
8
解析
平面分割空间问题
由二维的分割问题可知,平面分割与线之间的交点有关,即交点决定射线和线段的条数,从而决定新增的区域数。
试想在三维中则是否与平面的交线有关呢?
当有n-1个平面时,分割的空间数为f(n-1)。
要有最多的空间数,则第n个平面需与前n-1个平面相交,且不能有共同的交线。即最多有n-1 条交线。
而这n-1条交线把第n个平面最多分割成g(n-1)个区域。
(g(n)为(1)中的直线分平面的个数 )此平面将原有的空间一分为二,则最多增加g(n-1)个空间。
故:f=f(n-1)+g(n-1) ps:g(n)=n(n+1)/2+1
=f(n-2)+g(n-2)+g(n-1)
……
=f(1)+g(1)+g(2)+……+g(n-1)
=2+(1*2+2*3+3*4+……+(n-1)n)/2+(n-1)
=(1+2^2+3^2+4^2+……+n^2-1-2-3-……-n )/2+n+1
=(n^3+5n)/6+1
AC
#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
int n;
while(scanf("%d", &n)!=EOF){
printf("%d\n", (n*n*n+5*n)/6+1);
}
return 0;
}





















 1370
1370











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








