0. 优化问题
线性
区分齐次和非齐次,齐次的用svd分解,非齐次的用伪逆求解
U, S, Vt = np.linalg.svd(A, full_matrices=True)
x = Vt[-1].T
print(x / -x[1])

非线性
一阶迭代

随机梯度下降/SGD variants: AdaGrad, RMSProp, Adam,
二阶迭代
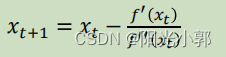
牛顿法


1. 一个例子直线拟合问题

2. CV3D中的优化问题
线性
仿射变换矩阵求解

def getAffineTransform(src, dst):
if len(src) == len(dst):
# Solve 'Ax = b'
A, b = [], []
for p, q in zip(src, dst):
A.append([p[0], p[1], 0, 0, 1, 0])
A.append([0, 0, p[0], p[1], 0, 1])
b.append(q[0])
b.append(q[1])
x = np.linalg.pinv(A) @ b
# Reorganize `x` as a matrix
H = np.array([[x[0], x[1], x[4]], [x[2], x[3], x[5]]])
return H
if __name__ == '__main__':
src = np.array([[115, 401], [776, 180], [330, 793]], dtype=np.float32)
dst = np.array([[0, 0], [900, 0], [0, 500]], dtype=np.float32)
my_H = getAffineTransform(src, dst)
cv_H = cv.getAffineTransform(src, dst) # Note) It accepts only 3 pairs of points.平面单应性求解

def getPerspectiveTransform(src, dst):
if len(src) == len(dst):
# Make homogeneous coordiates if necessary
if src.shape[1] == 2:
src = np.hstack((src, np.ones((len(src), 1), dtype=src.dtype)))
if dst.shape[1] == 2:
dst = np.hstack((dst, np.ones((len(dst), 1), dtype=dst.dtype)))
# Solve 'Ax = 0'
A = []
for p, q in zip(src, dst):
A.append([0, 0, 0, q[2]*p[0], q[2]*p[1], q[2]*p[2], -q[1]*p[0], -q[1]*p[1], -q[1]*p[2]])
A.append([q[2]*p[0], q[2]*p[1], q[2]*p[2], 0, 0, 0, -q[0]*p[0], -q[0]*p[1], -q[0]*p[2]])
_, _, Vt = np.linalg.svd(A, full_matrices=True)
x = Vt[-1]
# Reorganize `x` as a matrix
H = x.reshape(3, -1) / x[-1] # Normalize the last element as 1
return H基础矩阵求解

def findFundamentalMat(pts1, pts2):
if len(pts1) == len(pts2):
# Make homogeneous coordiates if necessary
if pts1.shape[1] == 2:
pts1 = np.hstack((pts1, np.ones((len(pts1), 1), dtype=pts1.dtype)))
if pts2.shape[1] == 2:
pts2 = np.hstack((pts2, np.ones((len(pts2), 1), dtype=pts2.dtype)))
# Solve 'Ax = 0'
A = []
for p, q in zip(pts1, pts2):
A.append([q[0]*p[0], q[0]*p[1], q[0]*p[2], q[1]*p[0], q[1]*p[1], q[1]*p[2], q[2]*p[0], q[2]*p[1], q[2]*p[
_, _, Vt = np.linalg.svd(A, full_matrices=True)
x = Vt[-1]
# Reorganize `x` as `F` and enforce 'rank(F) = 2'
F = x.reshape(3, -1)
U, S, Vt = np.linalg.svd(F)
S[-1] = 0
F = U @ np.diag(S) @ Vt
return F / F[-1,-1] # Normalize the last element as 1三角化求解

def triangulatePoints(P0, P1, pts0, pts1):
Xs = []
for (p, q) in zip(pts0.T, pts1.T):
# Solve 'AX = 0'
A = np.vstack((p[0] * P0[2] - P0[0],
p[1] * P0[2] - P0[1],
q[0] * P1[2] - P1[0],
q[1] * P1[2] - P1[1]))
_, _, Vt = np.linalg.svd(A, full_matrices=True)
Xs.append(Vt[-1])
return np.vstack(Xs).T非线性
绝对位姿估计

import numpy as np
from scipy.optimize import least_squares
from scipy.spatial.transform import Rotation
import cv2 as cv
def project_no_distort(X, rvec, t, K):
R = Rotation.from_rotvec(rvec.flatten()).as_matrix()
XT = X @ R.T + t # Transpose of 'X = R @ X + t'
xT = XT @ K.T # Transpose of 'x = KX'
xT = xT / xT[:,-1].reshape((-1, 1)) # Normalize
return xT[:,0:2]
def reproject_error_pnp(unknown, X, x, K):
rvec, tvec = unknown[:3], unknown[3:]
xp = project_no_distort(X, rvec, tvec, K)
err = x - xp
return err.ravel()
def solvePnP(obj_pts, img_pts, K):
unknown_init = np.array([0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1.]) # Sequence: rvec(3), tvec(3)
result = least_squares(reproject_error_pnp, unknown_init, args=(obj_pts, img_pts, K))
return result['success'], result['x'][:3], result['x'][3:]相机标定

def fcxcy_to_K(f, cx, cy):
return np.array([[f, 0, cx], [0, f, cy], [0, 0, 1]])
def reproject_error_calib(unknown, Xs, xs):
K = fcxcy_to_K(*unknown[0:3])
err = []
for j in range(len(xs)):
offset = 3 + 6 * j
rvec, tvec = unknown[offset:offset+3], unknown[offset+3:offset+6]
xp = project_no_distort(Xs[j], rvec, tvec, K)
err.append(xs[j] - xp)
return np.vstack(err).ravel()
def calibrateCamera(obj_pts, img_pts, img_size):
img_n = len(img_pts)
unknown_init = np.array([img_size[0], img_size[0]/2, img_size[1]/2] \
+ img_n * [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1.]) # Sequence: f, cx, cy, img_n * (rvec, tvec)
result = least_squares(reproject_error_calib, unknown_init, args=(obj_pts, img_pts))
K = fcxcy_to_K(*result['x'][0:3])
rvecs = [result['x'][(6*i+3):(6*i+6)] for i in range(img_n)]
tvecs = [result['x'][(6*i+6):(6*i+9)] for i in range(img_n)]
return result['cost'], K, np.zeros(5), rvecs, tvecs





















 220
220

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








