5.1盒模型的定义
Web页面上大部分的元素(特别是块状元素)都可以看作是一个盒子,W3C组织建议把所有网页上的对象都放在一个盒子(box)中,设计者可以通过创建定义来控制这个盒子的各种属性,这些对象包括段落、列表、标题、图片及层。
盒子的结构可以看作一个矩形框,包括边框(border)、外边距(margin)、内边距(padding),以及元素内容(content),元素会在指定的高度和宽度范围内在页面上显示出来。它们之间的关系,如图所示。

5.2 CSS元素的高度和宽度
当设计者布局一个网页时,网页最终的宽度和高度会超出预计的数值,这是因为盒模型的宽度或高度计算误差造成的。指定一个CSS元素的宽度和高度属性时,只是设置内容区域的宽度和高度。而浏览器实际大小的元素,还必须添加内边距、外边距和边框。而增加或减少内边距、外边距和边框,不会影响内容区域的尺寸,只会增加盒模型的总尺寸。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
<style>
<!--5.1盒模型的定义-->
*{
margin: 0px;
padding: 0px;
}
div{
width: 40px;
height: 30px;
border: 10px solid #ff0000;
margin: 20px;
padding: 20px;
}
img{
height: 30px;
weight:40px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div><img src="../img/山水.jpg"/></div>
<div><img src="../img/山水.jpg"/></div>
</body>
</html>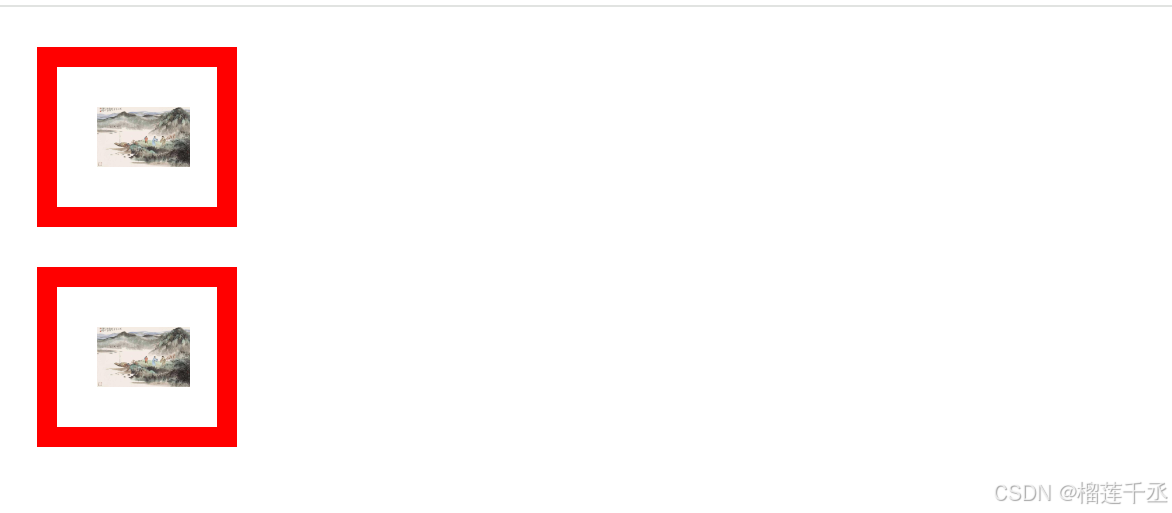
5.2.1 盒模型的宽度
盒模型的宽度=左外边距(margin-left)+左边框(border-let)+左内边距(padding-left)+内容宽度(width)+右内边距(padding-right)+右边框(borler-right)+右外边距(margin-right)。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>示例5.2</title>
<style type="text/css">
.ap{
width:200px;
height:100px;
border:2px solid #ff0000;
margin: 10px;
background-color:lightblue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="ap">这是div 块级元素,可设置宽度和高度</div>
<span class ="ap">这是span行级元素,不能设置宽度和高度</span>
</body>
</html>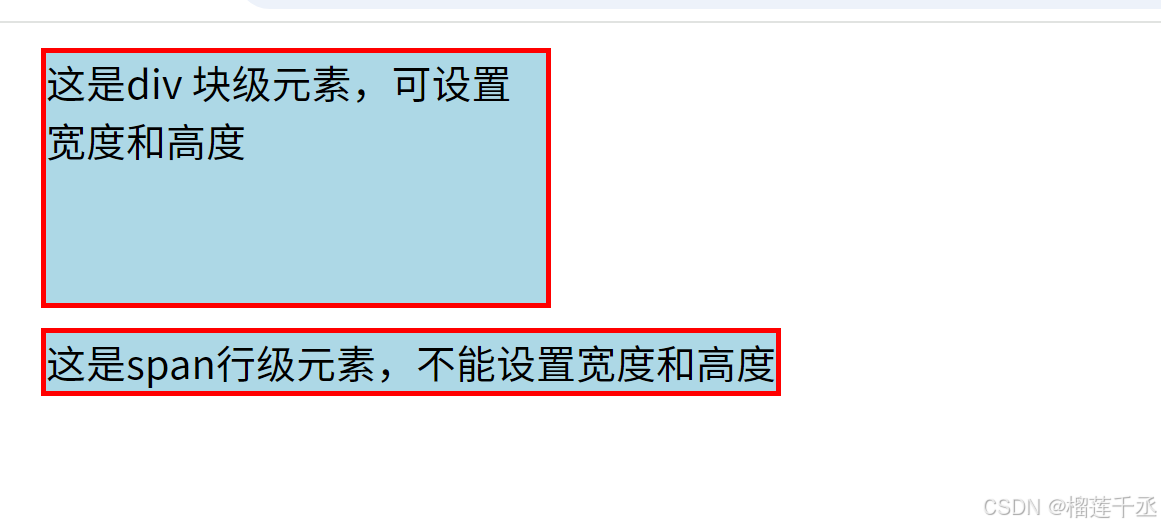
5.1.2 盒模型的高度
盒模型的高度=上外边距(margin-top)+上边框(border-top)+上内边距(paddling-top )+内容高度(height)+下内边距(padding-bottom)+下边框(border-bottom)+下外边距(margin-bottom)。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>示例5.2</title>
<style type="text/css">
.ap{
width:200px;
height:100px;
border:2px solid #ff0000;
margin: 10px;
background-color:#00ff00;
display: block;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="ap">这是div 块级元素,可设置宽度和高度</div>
<span class ="ap">这是span行级元素,不能设置宽度和高度</span>
</body>
</html>
5.3 边距设置和边框设置
5.3.1 外边距设置
外边距是指元素与元素之间的距离,外边距设置属性,可分别设置margin-lop、margin-right、margin-bottom、margin-left,也可以用 margin 属性一次性设置所有外边距。
5.3.1.1 上外边距
语法: margin-top:length | percent | auto
参数: lengh 包括长度值和长度单位,包括绝对单位和相对单位。percent 是基于父对象的高度。auto 值为自动提取边距值,是默认值。
说明: 设置对象上外边距,外边距始终透明。内联元素要使用该属性,必须先设定元素的 height 属性或 width 属性,或者设定 position 属性为 absolute。
5.3.1.2 右外边距
语法:margin-right:length | percent | auto
参数:同 margin-top。
说明:同 margin-top。
5.3.1.3 下外边距
语法:margin-bottom:length | percent | auto
参数:同 margin-top。
说明:同 margin-top。
5.3.1.4 左外边距
语法:margin-left:length |percent | auto
参数:同 margin-top。
说明:同 margin-top。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
<style type="text/css">
#big{
width:450px;
height:200px;
margin:0;
background-color: #ff0;
}
#small1,#small2,#small3,#small4{
width:200px;
height:50px;
text-align:center;
background-color:#0ff;
}
#small1{
margin-left:20px;
margin-bottom:30px;
}
#small2{
margin-right : 20px ;
margin-top : 10px ;
float:right;
}
#small3{
margin-bottom :5px ;
}
#small4{
margin-left :10px ;
margin-top:15px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id= "big" >
<div id="small1">A:左外边距 20 像素,下外边距 30 像素</div>
<div id="small2">B:右外边距20像素,上外边距10像素,右浮动</div>
<div id="small3">C:下外边距5 像素</div>
<div id="small4">D:左外边距 10 像素,上外边距 15 像素</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>5.3.1.5 外边距
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
<style type="text/css">
div{
border:solid #0000FF 1px;
width:auto;
margin:5px;
float:left;
}
.margin1{
background-color:#9F6;
border:none; /*无边框*/
width:200px:
height:80px;
margin:0px 15px 5px 30px;
}
.margin2{
background-color:yellow;
border : none ;
width :200px ;
height : 80px ;margin :5px 30px 15px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<div class="margin1"> 上、右、下、左外边距分别为:0px、15px、5px、30px </div>
</div>
<div>
<div class="margin2">上外边距为:5px,下外边距为:15px,左右外边距为:30px</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
5.3.2 外边距的合并
通常,盒子与盒子之间的外边距相遇会互相影响,必须对margin 属性深入了解,才能精确地控制盒子的位置。
5.3.2.1 行级元素外边距合并
行级元素的盒子相遇,盒子与盒子之间的距离等于两个盒子外边距的总和。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
<style type="text/css">
*{
margin: 50px;
}
.margin1{
background-color:#9F6;
margin: 20px;
padding: 30px;
}
.margin2{
background-color:yellow;
margin-left: 30px;
padding: 30px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<span class="margin1"> 绿色 span </span><span class="margin2">黄色 span </span>
</body>
</html>
5.3.2.2 块级元素外边距合并
块级元素的盒子相遇,盒子与盒子之间的距离等于两盒子中外边距的较大者。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
<style type="text/css">
*{
margin: 50px;
}
.div1{
background-color:#9F6;
margin-bottom: 30px;
padding: 30px;
}
.div2{
background-color:yellow;
margin-top: 30px;
padding: 30px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="div1"> 绿色margin </div>
<div class="div2">黄色 margin </div>
</body>
</html>
5.3.3 内边距设置
元素的内边距用来控制边框和内容区之间的空白距离,并非实体,用padding属性表示,类似于HTML中表格单元格的填充属性。内边距(padding)和外边距(margin)很相似,都是透明不可见的,只是内边距和外边距之间还有边框。从语法和用法上来说,内边距的属性与外边距的属性也是类似的,既可以使用复合属性,也可以使用单边属性,属性接受 length 值或 percent值,区别于外边距,内边距不可以使用负值。padding。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
<style type="text/css">
span{
background-color: #ffff99;
}
div{
border: solid #000000 1px;
width : auto ;
height : auto ;
margin : 15px ;
float : left ;
}
.paddingl {
padding-top:30px ;
padding-left : 15px ;
}
.padding2 {
padding-bottom : 30px ;
padding-right : 30px ;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class = "paddingl">
<span>文字元素的上内边距为 30p,左内边距为 15px</span>
</div>
<div class = "padding2" >
<span>文字元素的下内边距为 30px,右内边距为 30px</span>
</div>
</body>
</html>
5.3.4 边框设置
元素外边距内就是元素的边框(border),它是围绕内边距和元素内容的一条或多条线在内边距和外边距之间。边框的四条边分别用border-top、border-right、border-bottomborder-let 表示,它们的属性与内外边距的属性也是类似的,既可以使用复合属性,也可以使用单边属性。
5.3.4.1上边框
语法:border-top:border-style | border-width | border-color
参数:该属性是复合属性。需要通过参数设置来实现。
5.3.4.2右边框
语法:border-right:border-style | border-width | border-color
参数:该属性是复合属性。需要通过参数设置来实现。
5.3.4.3下边框
语法:border-bottom:border-style | border-width | border-color
参数:该属性是复合属性。需要通过参数设置来实现。
5.3.4.4 左边框
语法:border-left:border-style | border-width | border-color
参数:该属性是复合属性。需要通过参数设置来实现
5.3.4.5 边框样式
在CSS中,样式是边框最重要的一个设置,因为如果没有样式,在Web页面中边框就不会显示。
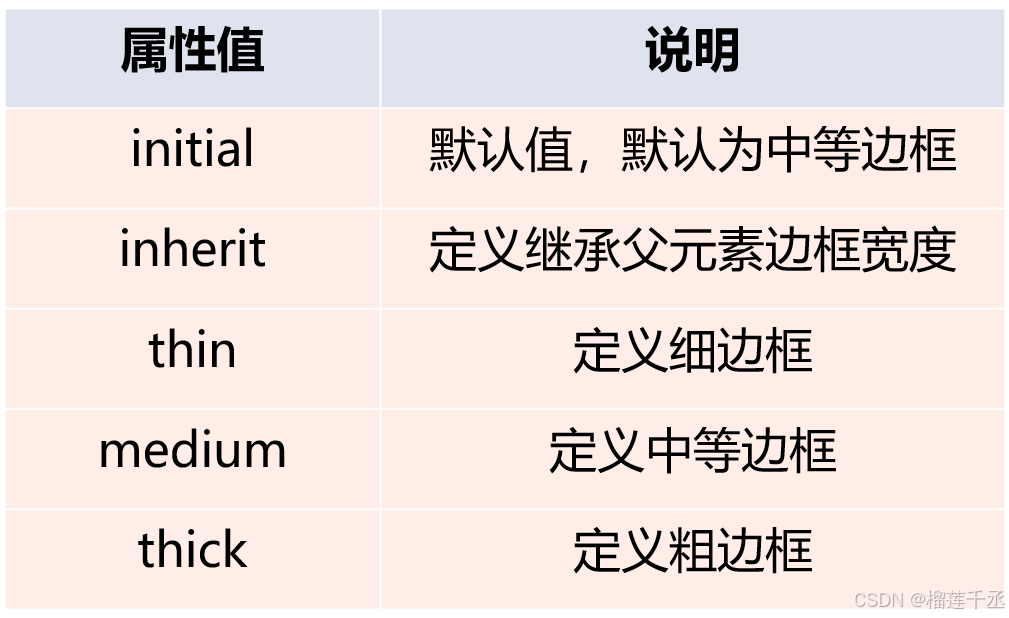
border-style 是一个复合属性,可以同时取1~4个值,取值方法与外边距相似。边框属性有 12个值可选,包括默认(imnital)和无边框(none)。属性值说明见表。

5.3.4.6 边框宽度
在CSS中,宽度是通过border-width属性来设置边框粗细的。
与border-slyle属性相同,border-width也是一个复合属性。设置边框宽度时,可以直接输入leng 确定长度值,如5px或2cm,但不可以为负值;或者选择系统预设属性值。属性值说明见表。
5.3.4.7 边框颜色
在CSS中,边框颜色是通过border-color 属性来设置的,该属性可以使用任何类型的颜色值,包括用颜色命名的值、十六进制参数或RGB值。但是如果对象的border-style 设置为none或者border-width设置为0,本属性将失去作用。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
<style>
<!--5.1盒模型的定义-->
*{
margin: 0px;
padding: 0px;
}
div{
width: 40px;
height: 30px;
border-top:10px #ff0000 solid;
border-bottom:10px #000000 dashed;
border-right :10px #ccf0ff dotted;
border-left :10px #ffff00 double;
margin: 20px;
display: inline;
padding: 20px;
}
img{
height: 30px;
weight:40px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div><img src="../img/山水.jpg"/></div>
<div><img src="../img/山水.jpg"/></div>
</body>
</html>
5.3.5 新增边框属性
5.3.5.1圆角边框
border-radius:设置边框四个角有弧度成为圆角,需要设置相关参数。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
<style>
<!--5.1盒模型的定义-->
*{
margin: 0px;
padding: 0px;
}
div{
width: 40px;
height: 30px;
border-top:10px #ff0000 solid;
border-bottom:10px #000000 dashed;
border-right :10px #ccf0ff dotted;
border-left :10px #ffff00 double;
border-radius: 25px;
margin: 20px;
padding: 20px;
}
img{
height: 30px;
weight:40px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div><img src="../img/山水.jpg"/></div>
<div><img src="../img/山水.jpg"/></div>
</body>
</html>
5.3.5.2阴影边框
box-shadow :向四个边框添加一到多个阴影,需要设置相关参数。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
<style>
<!--5.1盒模型的定义-->
*{
margin: 0px;
padding: 0px;
}
div{
width: 40px;
height: 30px;
border-top:10px #ff0000 solid;
border-bottom:10px #000000 dashed;
border-right :10px #ccf0ff dotted;
border-left :10px #ffff00 double;
border-radius: 25px;
box-shadow: -15px 20px 50px #acacff;/*右,下,模糊距离,颜色 */
margin: 20px;
padding: 20px;
}
img{
height: 30px;
weight:40px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div><img src="../img/山水.jpg"/></div>
<div><img src="../img/山水.jpg"/></div>
</body>
</html>
5.3.5.3图片绘制边框
border-image:设置所有边框用图片显示,需要嵌人相关图片,但是部分浏览器不支持此属性。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
<style>
<!--5.1盒模型的定义-->
*{
margin: 0px;
padding: 0px;
}
div{
width: 40px;
height: 30px;
border-top:10px #ff0000 solid;
border-bottom:10px #000000 dashed;
border-right :10px #ccf0ff dotted;
border-left :10px #ffff00 double;
border-radius: 25px;
box-shadow: -15px 20px 50px #acacff;/*右,下,模糊距离,颜色 */
margin: 20px;
padding: 20px;
border-image: url(../img/边框.jpg)5 10 round;
}
img{
height: 30px;
weight:40px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div><img src="../img/山水.jpg"/></div>
<div><img src="../img/山水.jpg"/></div>
<div>利用图片</div>
</body>
</html>
5.4 CSS元素的定位
前面所讲的盒模型都是标准流情况下可用的,但是盒模型仅有的几种排版对布局有很大的限制,导致元素无法在页面中随意地摆放,因此,我们需要使用盒子的定位(position)来增加排版的灵活性和适应性,
定位(position)的思想是,它允许你定义元素框相对于其正常位置应该出现的位置或者相对于父元素、另一个元素甚至浏览器窗口本身的位置。position 属性值有4个。
语法:position:static | relative | absolute l fixed
参数:static是默认值,默认没有定位,或者用于取消特殊定位的继承,恢复默认,又称静态定位。relatives是相对定位,生成相对定位的元素,相对于其正常位置进行定位。ab-solute 是绝对定位,相对于父元素或者浏览器窗口进行定位,需要 top、right、bottom 和 left属性辅助完成。fxed是固定定位,相对于浏览器窗口进行定位,需要top、right、bottom 和left 属性辅助完成。
5.4.1 static 定位
slatc 是 HTML 元素的默认值,不受 top、right、boom 和let 属性影响,元素出现在正常的文档流中。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
<style type="text/css">
.father{
border: 2px solid red;
width: 300px;
height: 250px;
}
.son1{
border: 2px double red;
background-color: yellow;
width: 200px;
height: 80px;
}
.son2{
border: 20 double red;
width: 200px;
height: 25px;
margin-top: 50px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="father">父盒子,无定位
<div class="son1">子盒子1,无定位
<h2>静态定位的盒子</h2>
</div>
<div class="son2">子盒子2,无定位</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
5.4.2 relative定位
relative 不脱离文档流的布局,需要参照父元素的四条边(不是浏览器)oP、right、bottom 和left属性的参数,从盒子中独立出来浮在上面。相对定位只改变自身的位置,在文档流原先的位置留出空白区域。定位的起始位置为此元素原先在文档流的位置。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
<style type="text/css">
.father{
border: 2px solid red;
width: 300px;
height: 250px;
}
.son1{
border: 2px double red;
background-color: yellow;
width: 200px;
height: 80px;
position: relative;
top: 10px;
left: 30px;
}
.son2{
border: 20 double red;
width: 200px;
height: 25px;
margin-top: 50px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="father">父盒子,无定位
<div class="son1">子盒子1,相对于父盒子在左水平偏移30px,上边垂直偏移10px。
<h2>静态定位的盒子</h2>
</div>
<div class="son2">子盒子2,无定位
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
5.4.3 absolute定位
absolute 脱离原来文档流的布局,浮在其他盒子上面,独立出来。子盒子原来位置的空间由后面的盒子填充。绝对定位的起始位置为最近已定位的父盒子,如果父盒子没有定位那么子盒子的起始位置为浏览器,并随着滚动条的移动而改变位置。
5.4.3.1 相对浏览器绝对定位
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
<style type="text/css">
.father{
border: 2px solid red;
width: 300px;
height: 250px;
}
.son1{
border: 2px double red;
background-color: yellow;
width: 200px;
height: 80px;
/* position: relative;
top: 10px;
left: 30px; */
position: absolute;
top: 10px;
left: 30px;
}
.son2{
border: 20 double red;
width: 200px;
height: 25px;
margin-top: 50px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="father">父盒子,无定位
<div class="son1">子盒子1,相对于浏览器绝对定位
</div>
<div class="son2">子盒子2,无定位
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
5.4.3.2 相对父盒子绝对定位
只需要在例5.14示例程序中把father和sonl的CSS 修改 position、top和ripu属性即可。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
<style type="text/css">
.father{
border: 2px solid red;
width: 300px;
height: 250px;
position: relative;
}
.son1{
border: 2px double red;
background-color: yellow;
width: 200px;
height: 80px;
/* position: relative;
top: 10px;
left: 30px; */
position: absolute;
bottom: 10px;
right: 30px;
}
.son2{
border: 20 double red;
width: 200px;
height: 25px;
margin-top: 50px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="father">父盒子,无定位
<div class="son1">子盒子1,相对于父盒子的绝对定位
</div>
<div class="son2">子盒子2,无定位
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
5.4.4 fixed定位
fixed 类似于absolute,但在固定定位中,盒子的位置不随着滚动条的移动而改变位置相对于浏览器窗口是固定不变的。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
<style type="text/css">
.father{
border: 2px solid red;
width: 300px;
height: 250px;
}
.son1{
border: 2px double red;
background-color: yellow;
width: 200px;
height: 80px;
/* position: relative;
top: 10px;
left: 30px; */
position: fixed;
bottom: 10px;
right: 30px;
}
.son2{
border: 20 double red;
width: 200px;
height: 25px;
margin-top: 50px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="father">父盒子,无定位
<div class="son1">子盒子1,运用fixed定位
</div>
<div class="son2">子盒子2,无定位
</div>
</div>
<br/><br/><br/><br/><br/><br/><br/><br/><br/><br/><br/><br/><br/><br/><br/><br/><br/><br/><br/><br/>
<br/><br/><br/><br/><br/><br/><br/><br/><br/><br/><br/><br/><br/><br/><br/><br/><br/><br/><br/><br/>
</body>
</html>
5.5 CSS元素的浮动
在CSS的盒模型布局上,除了使用定位避免按照标准流的方式进行排版的限制性问题还可以使用浮动来避免。而使用浮动(loat)和清除(clear)属性设置,可以解决各种页面错位的现象。
5.5.1 盒子的浮动添加
一般情况下,页面中的块状元素在水平方向上宽度会自动延伸,直到父元素的边界;而在垂直方向上会按照元素在页面中出现的先后次序依次排列,即所说的标准流排列,如5-19 所示。
任何元素都可以浮动,浮动元素会变成一个块状元素,元素的水平浮动就是通过其 hoat属性的设置,使元素向其父元素的左侧或右侧靠拢,间接设置一个元素的文本环绕方式,从而改变原来的竖直排列方式。此时元素的宽度不再延伸,大小将由其内容的宽度而定。
语法:float:left | right | none
参数:let 元素浮动到左边,即向左侧靠拢,则右边可以有文字环绕;ight元素浮动到右边,即向右侧靠拢,左边可以有文字环绕;默认值none 就是标准流通常的显示状态。
Html代码为:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>示例5.17</title>
<style type="text/css">
@import url("../css/course3.css");
</style>
<!-- <link type="text/css" rel="stylesheet" href="../css/course3.css"/> -->
</head>
<body>
<div class="father">
<h2>父盒子</h2>
<div style="float: right;">右浮动盒子</div>
<div>标准流盒子2</div>
<div>标准流盒子3</div>
<p>css中,有一个float属性,默认为none,也就是标准流通常的情况。
如果将float属性的值设置为left或right,元素就会向其父级元素的左
侧或右侧靠近,同时默认情况下,盒子的宽度不再伸展,而是根据盒子里面的内容的宽度确定</p >
</div>
</body>
</html>CSS代码为:
.father{
background-color: #ffccff;
border: 2px solid red;
padding: 5px;
}
.father div{
width: 100px;
height: 20px;
padding: 10px;
margin: 10px;
border: 2px dashed blue;
background-color: #ccffff;
}
.father p{
border: 2px dotted green;
background-color: #ffff99;
}
5.5.2 盒子的浮动清除
元素浮动后,下面的元素内容会自动上移,结果就会受到上面浮动元素的影响,如果想要清除这种影响,需要使用clear 属性完成。
由于浮动元素可以清除,是相对定位属性的优势,因而浮动属性成为控制分栏布局的最好工具。
语法:clear:left | right | both | none
参数:lett清除左边浮动元素,即不允许左边有浮动对象;ght清除右边浮动元素,即不允许右边有浮动对象;Both同时清除左右两边的浮动元素,即不允许左右两边有浮动对象;默认值 none。
Html代码为:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>示例5.17</title>
<style type="text/css">
@import url("../css/course3.css");
</style>
<!-- <link type="text/css" rel="stylesheet" href="../css/course3.css"/> -->
</head>
<body>
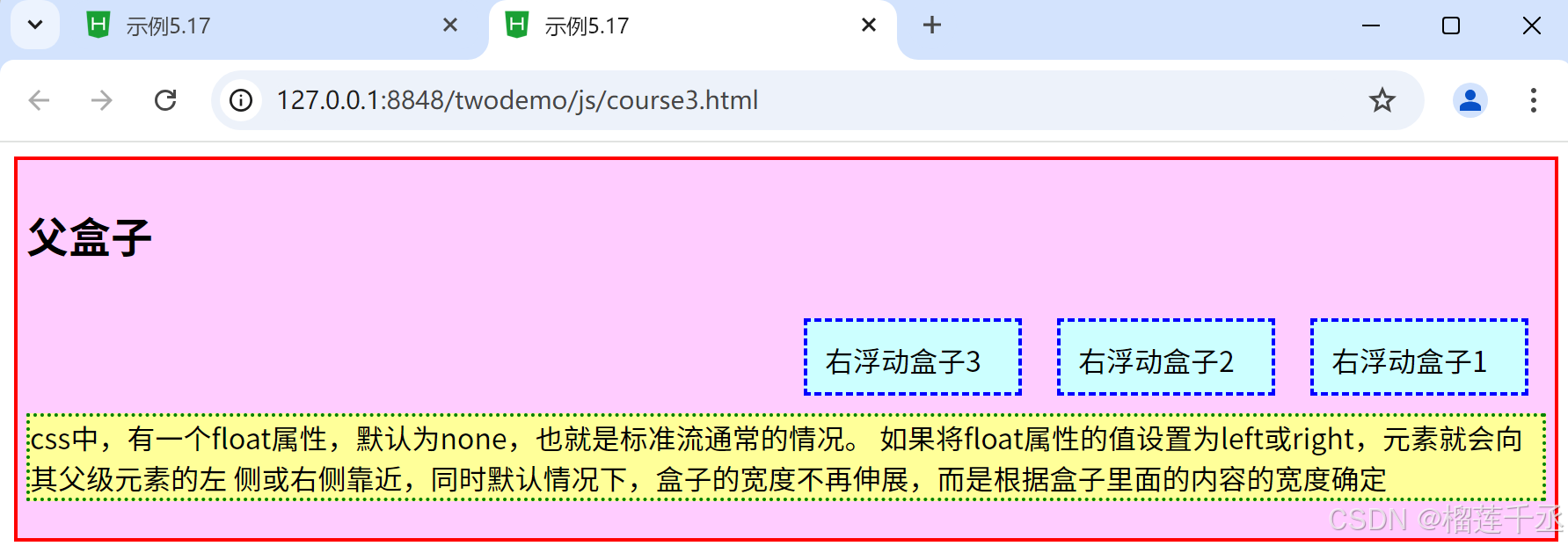
<div class="father">
<h2>父盒子</h2>
<div style="float: right;">右浮动盒子1</div>
<!-- <div>标准流盒子1</div> -->
<div style="float: right;">右浮动盒子2</div>
<div style="float: right;">右浮动盒子3</div>
<p style="clear: both;">css中,有一个float属性,默认为none,也就是标准流通常的情况。
如果将float属性的值设置为left或right,元素就会向其父级元素的左
侧或右侧靠近,同时默认情况下,盒子的宽度不再伸展,而是根据盒子里面的内容的宽度确定</p >
</div>
</body>
</html>CSS代码为:
.father{
background-color: #ffccff;
border: 2px solid red;
padding: 5px;
}
.father div{
width: 100px;
height: 20px;
padding: 10px;
margin: 10px;
border: 2px dashed blue;
background-color: #ccffff;
}
.father p{
border: 2px dotted green;
background-color: #ffff99;
}
5.6 综合案例——昵心美食空间
效果图如下:

Html代码为:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>昵心美食空间</title>
<style type="text/css">
@import url("../js/anli5.css");
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="all">
<div class="banner">
<img src="../img/banner.jpg" width="700px" height="70px" />
</div>
<div class="menu">
<img src="../img/menu.jpg" width="690px" height="40px" />
</div>
<div class="main">
<div class ="left">
<marquee direction="up">
<img src="../img/mm_1.jpg" width="150px" height="140px" />
<img src="../img/mm_2.jpg" width="150px" height="140px" />
<img src="../img/mm_3.jpg" width="150px" height="140px" />
</marquee>
</div>
<div class="middle">
<div class="one">
<img src="../img/font.jpg" width="25px" height="25px"/>为您推荐
<br><br>
<img src="../img/x_1.jpg" width="80px" height="40px" />
<img src="../img/x_2.jpg" width="80px" height="40px" />
<img src="../img/x_3.jpg" width="80px" height="40px" />
<img src="../img/x_4.jpg" width="80px" height="40px" />
<img src="../img/x_5.jpg" width="80px" height="40px" />
<img src="../img/x_6.jpg" width="80px" height="40px" />
</div>
<center>
<div class="two">
<h1>昵心美食空间</h1>
</div>
</center>
<div class="three">
<img src="../img/font.jpg" width="25px" height="25px" />团购信息
<br>
<a href="#">1.火锅团购</a><br>
<a href="#">2.烧烤团购</a><br>
<a href="#">3.自助餐团购</a><br>
<a href="#">4.新春特惠</a>
</div>
</div>
<div class ="right" >
<marquee direction="up" >
<img src="../img/good_1.jpg" width="150px" height="140px" />
<img src="../img/good_2.jpg" width="148px" height="140px" />
<img src="../img/good_3.jpg" width="148px" height="140px" />
</marquee>
</div>
</div>
<div class="bottom">
<hr color="#0000FF">
<center style="font-family: '楷体';"> 版权所有©昵心美食空间<br />
地址:江门市大学路XXX号邮编:500000 电话:0750-9999999</center>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>CSS代码为:
*{
background-color:#FFFF99;
}
a{
color: red;
}
.all{
width: 700px;
height: 650px;
margin: 10px auto;
padding: 5px;
background-image:url("../img/bg1.JPG");
}
.banner{
width: 700px;
height: 70px;
}
.menu{
width: 690px;
height: 40px;
padding: 5px;
}
.main{
width: 700px;
height: 450px;
margin: 5px Opx;
position: relative;
}
.left,.right{
width: 150px;
height: 440px;
border: 1px solid #999;
float: left;
}
.middle{
width: 384px;
height: 450px;
margin: 0px 5px;
float: left;
font-size: 20px;
font-family: "楷体";
font-weight: 700;
color: #0000FF;
}
.one{
width: 380px;
height: 155px;
border: 1px solid #999;
}
.two{
width: 255px;
height: 100px;
border: 5px double red;
margin-top: 20px;
margin-bottom: 20px;
border-radius: 25px;
}
.three{
width: 380px;
height: 135px;
border: 1px solid #999;
}
.bottom{
width: 700px;
height: 70px;
}






















 2068
2068

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








