一.分治思想
缺点:容易找不到全局最优点
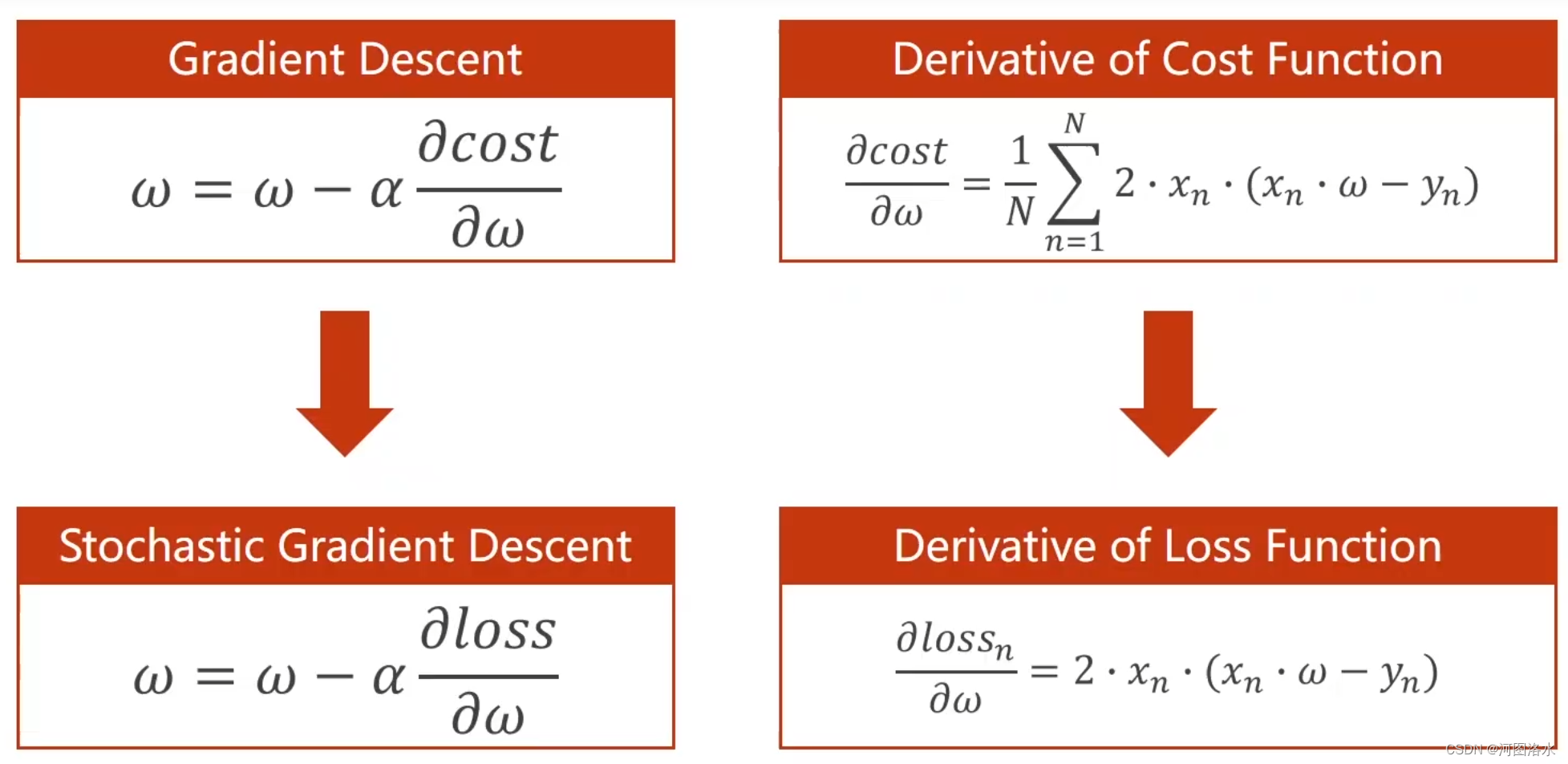
二.贪心思想(Gradient Descent)
2.1斜率:
2.2 更新:
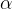 是学习率(步长):
是学习率(步长):
- 过大无法收敛
- 过小,找到局部最优,找不到全局最优
深度学习算法中,并没有过多的局部最优的点,如何解决鞍点是最大的难题
2.3 鞍点:
梯度为0
导致
无法继续更新迭代
2.4 Derivation步骤:
updates:
2.5Codes:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# prepare the training set
x_data = [1.0, 2.0, 3.0]
y_data = [2.0, 4.0, 6.0]
# initial guess of weight
w = 1.0
# define the model linear model y = w*x
def forward(x):
return x*w
#define the cost function MSE
def cost(xs, ys):
cost = 0
for x, y in zip(xs,ys):
y_pred = forward(x)
cost += (y_pred - y)**2
return cost / len(xs)
# define the gradient function gd
def gradient(xs,ys):
grad = 0
for x, y in zip(xs,ys):
grad += 2*x*(x*w - y)
return grad / len(xs)
epoch_list = []
cost_list = []
print('predict (before training)', 4, forward(4))
for epoch in range(100):
cost_val = cost(x_data, y_data)
grad_val = gradient(x_data, y_data)
w-= 0.01 * grad_val # 0.01 learning rate
print('epoch:', epoch, 'w=', w, 'loss=', cost_val)
epoch_list.append(epoch)
cost_list.append(cost_val)
print('predict (after training)', 4, forward(4))
plt.plot(epoch_list,cost_list)
plt.ylabel('cost')
plt.xlabel('epoch')
plt.show() 
P.S最 后结果是收敛的 指数加权均值会更平滑
如果最后是发散的说明训练失败,学习率太大
三.随机梯度下降(Stochastic Gradient Descent)
3.1比较
| 梯度下降 | 随机梯度下降 | |
|---|---|---|
| 性能 | 低 | 高 |
| 时间复杂度 | 并行效率高 低 | 不并行 高 |
3.2公式
N个随机样本选一个loss的梯度,作为梯度下降的依据,而不用总体所有点的梯度和,作为梯度下降的依据。cost function 所有样本 而一个样本有随机噪声, 使得可以跨越鞍点 cost->loss
3.3Codes
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x_data = [1.0, 2.0, 3.0]
y_data = [2.0, 4.0, 6.0]
w = 1.0
def forward(x):
return x*w
# calculate loss function
def loss(x, y):
y_pred = forward(x)
return (y_pred - y)**2
# define the gradient function sgd
def gradient(x, y):
return 2*x*(x*w - y)
epoch_list = []
loss_list = []
print('predict (before training)', 4, forward(4))
for epoch in range(100):
for x,y in zip(x_data, y_data):
grad = gradient(x,y)
w = w - 0.01*grad # update weight by every grad of sample of training set
print("\tgrad:", x, y,grad)
l = loss(x,y)
print("progress:",epoch,"w=",w,"loss=",l)
epoch_list.append(epoch)
loss_list.append(l)
print('predict (after training)', 4, forward(4))
plt.plot(epoch_list,loss_list)
plt.ylabel('loss')
plt.xlabel('epoch')
plt.show() 3.4批量随机梯度下降(Batch)
多个loss作为一组























 1066
1066











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








