老铁们是不是经常为写一些实体转换的原始代码感到头疼,尤其是实体字段特别多的时候。介绍一个开源项目 mapstruct ,可以轻松优雅的进行转换,简化你的代码。当然有的人喜欢写get set,或者用BeanUtils 进行复制,代码只是工具,本文只是提供一种思路。
先贴下官网地址吧:https://mapstruct.org/
废话不多说,上代码:
pom 配置:
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<maven.compiler.source>1.8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.8</maven.compiler.target>
<org.mapstruct.version>1.4.1.Final</org.mapstruct.version>
<org.projectlombok.version>1.18.12</org.projectlombok.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mapstruct</groupId>
<artifactId>mapstruct</artifactId>
<version>${org.mapstruct.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- lombok dependencies should not end up on classpath -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>${org.projectlombok.version}</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- idea 2018.1.1 之前的版本需要添加下面的配置,后期的版本就不需要了,可以注释掉,
我自己用的2019.3 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mapstruct</groupId>
<artifactId>mapstruct-processor</artifactId>
<version>${org.mapstruct.version}</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.8.1</version>
<configuration>
<source>1.8</source>
<target>1.8</target>
<annotationProcessorPaths>
<path>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>${org.projectlombok.version}</version>
</path>
<path>
<groupId>org.mapstruct</groupId>
<artifactId>mapstruct-processor</artifactId>
<version>${org.mapstruct.version}</version>
</path>
</annotationProcessorPaths>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
关于lombok和mapstruct的版本兼容问题多说几句,maven插件要使用3.6.0版本以上、lombok使用1.16.16版本以上,另外编译的lombok mapstruct的插件不要忘了加上。否则会出现下面的错误:No property named "aaa" exists in source parameter(s). Did you mean "null"?
这种异常就是lombok编译异常导致缺少get setter方法造成的。还有就是缺少构造函数也会抛异常。
@Data
@Builder
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
private GenderEnum gender;
private Double height;
private Date birthday;
}
public enum GenderEnum {
Male("1", "男"),
Female("0", "女");
private String code;
private String name;
public String getCode() {
return this.code;
}
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
GenderEnum(String code, String name) {
this.code = code;
this.name = name;
}
}
@Data
@Builder
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class StudentVO {
private String name;
private int age;
private String gender;
private Double height;
private String birthday;
}
@Mapper
public interface StudentMapper {
StudentMapper INSTANCE = Mappers.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
@Mapping(source = "gender.name", target = "gender")
@Mapping(source = "birthday", target = "birthday", dateFormat = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")
StudentVO student2StudentVO(Student student);
}
实体类是开发过程少不了的,就算是用工具生成肯定也是要有的,需要手写的部分就是这个Mapper的接口,编译完成后会自动生成相应的实现类
然后就可以直接用mapper进行实体的转换了
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student student = Student.builder().name("小明").age(6).gender(GenderEnum.Male).height(121.1).birthday(new Date()).build();
System.out.println(student);
//这行代码便是实际要用的代码
StudentVO studentVO = StudentMapper.INSTANCE.student2StudentVO(student);
System.out.println(studentVO);
}
}
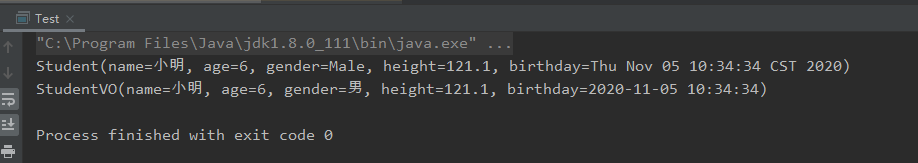
mapper可以进行字段映射,改变字段类型,指定格式化的方式,包括一些日期的默认处理。
可以手动指定格式化的方法:
@Mapper
public interface StudentMapper {
StudentMapper INSTANCE = Mappers.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
@Mapping(source = "gender", target = "gender")
@Mapping(source = "birthday", target = "birthday", dateFormat = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")
StudentVO student2StudentVO(Student student);
default String getGenderName(GenderEnum gender) {
return gender.getName();
}
}
上面只是最简单的实体映射处理,下面介绍一些高级用法
1、List 转换
属性映射基于上面的mapping配置
@Mapper
public interface StudentMapper {
StudentMapper INSTANCE = Mappers.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
@Mapping(source = "gender.name", target = "gender")
@Mapping(source = "birthday", target = "birthday", dateFormat = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")
StudentVO student2StudentVO(Student student);
List<StudentVO> students2StudentVOs(List<Student> studentList);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student student = Student.builder().name("小明").age(6).gender(GenderEnum.Male).height(121.1).birthday(new Date()).build();
List<Student> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(student);
List<StudentVO> result = StudentMapper.INSTANCE.students2StudentVOs(list);
System.out.println(result);
}
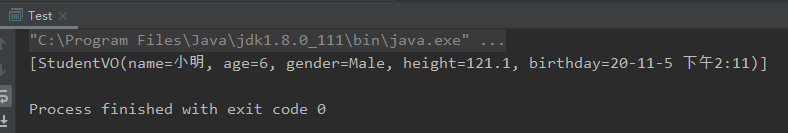
2、多对象转换到一个对象
@Data
@Builder
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
private GenderEnum gender;
private Double height;
private Date birthday;
}
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@Builder
@NoArgsConstructor
public class Course {
private String courseName;
private int sortNo;
private long id;
}
@Data
@Builder
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class StudentVO {
private String name;
private int age;
private String gender;
private Double height;
private String birthday;
private String course;
}
@Mapper
public interface StudentMapper {
StudentMapper INSTANCE = Mappers.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
@Mapping(source = "student.gender.name", target = "gender")
@Mapping(source = "student.birthday", target = "birthday", dateFormat = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")
@Mapping(source = "course.courseName", target = "course")
StudentVO studentAndCourse2StudentVO(Student student, Course course);
}
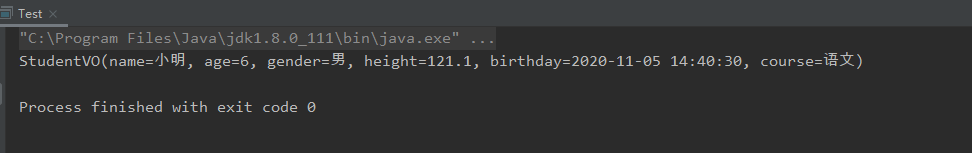
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student student = Student.builder().name("小明").age(6).gender(GenderEnum.Male).height(121.1).birthday(new Date()).build();
Course course = Course.builder().id(1L).courseName("语文").build();
StudentVO studentVO = StudentMapper.INSTANCE.studentAndCourse2StudentVO(student, course);
System.out.println(studentVO);
}
}
3、默认值
@Mapper
public interface StudentMapper {
StudentMapper INSTANCE = Mappers.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
@Mapping(source = "student.gender.name", target = "gender")
@Mapping(source = "student.birthday", target = "birthday", dateFormat = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")
@Mapping(source = "course.courseName", target = "course")
@Mapping(target = "name", source = "student.name", defaultValue = "张三")
StudentVO studentAndCourse2StudentVO(Student student, Course course);
}





















 4万+
4万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










