1,Android启动概述
Android系统启动基本可分为3个阶段:Bootloader启动,Linux启动,Android启动。
1.1,Bootloader启动
系统引导bootloader(bootable/bootloader/* u-boot/*),加电后,CPU先执行bootloader程序,正常启动系统,加载boot.img,中包含内核。
源码:bootable/bootloader/* , 说明:加电后,CPU将先执行bootloader程序,此处有三种选择:
a: 开机按Camera+Power启动到fastboot,即命令或SD卡烧写模式,不加载内核及文件系统,此处可以进行工厂模式的烧写
b: 开机按Home+Power启动到recovery模式,加载recovery.img,recovery.img包含内核,基本的文件系统,用于工程模式的烧写
c:开机按Power,正常启动系统,加载boot.img,boot.img包含内核,基本文件系统,用于正常启动手机(以下只分析正常启动的情况)
1.2,linux启动
由bootloader加载kernel,kernel经自解压,初始化,载入built-in驱动程序,完成启动。kernel启动后会创建若干内核线程,之后装入并执行程序/sbin/init/,载入init process,切换至user-space。
1.3,Android启动
1.3.1,init进程启动
源码:system/core/init/*
配置文件:system/rootdir/init.rc
说明:init是一个由内核启动的用户级进程,它按照init.rc中的设置执行:启动服务(这里的服务指linux底层服务,如adbd提供adb支持,vold提供SD卡挂载等),执行命令和按其中的配置语句执行相应功能。
1.3.2,zygote服务启动
源码:frameworks/base/cmds/app_main.cpp等。
说明:zygote是一个在init.rc中被指定启动的服务,该服务对应的命令是/system/bin/app_process。
作用:建立Java Runtime,建立虚拟机;建立Socket接收ActivityManangerService的请求,用于Fork应用程序;启动System Server。
1.3.3,systemserver服务启动
源码:frameworks/base/services/Java/com/android/server/SystemServer.java
说明:被zygote启动,通过System Manager管理android的服务(这里的服务指frameworks/base/services下的服务,如卫星定位服务,剪切板服务等)。
1.3.4,launcher桌面启动
源码:ActivityManagerService.java为入口,packages/apps/launcher*实现。
说明:系统启动成功后SystemServer使用xxx.systemReady()通知各个服务,系统已经就绪,桌面程序Home就是在ActivityManagerService.systemReady()通知的过程中建立的,最终调用startHomeActivityLocked()启launcher。
1.3.5,lockscreen启动
源码:frameworks/policies/base/phone/com/android/internal/policy/impl/*lock*
说明:系统启动成功后SystemServer调用wm.systemReady()通知WindowManagerService,进而调用PhoneWindowManager,最终通过LockPatternKeyguardView显示解锁界面,跟踪代码可以看到解锁界面并不是一个Activity,这是只是向特定层上绘图,其代码了存放在特殊的位置。
1.3.6,othersapp启动
源码:frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityManagerService.java
说明:系统启动成功后SystemServer调用ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().systemReady()通知ActivityManager启动成功,ActivityManager会通过置变量mBooting,通知它的另一线程,该线程会发送广播android.intent.action.BOOT_COMPLETED以告知已注册的第三方程序在开机时自动启动。
2,bootloader启动详细分析
2.1,Bootloader的定义和种类
简单地说,BootLoader是在操作系统运行之前运行的一段程序,它可以将系统的软硬件环境带到一个合适状态,为运行操作系统做好准备。这样描述是比较抽象的,但是它的任务确实不多,终极目标就是把OS拉起来运行。在嵌入式系统世界里存在各种各样的Bootloader,种类划分也有多种方式。除了按照处理器体系结构不同划分以外,还有功能复杂程度的不同。
先区分一下Bootloader和Monitor[l1] : 严格来说,Bootloader只是引导OS运行起来的代码;而Monitor另外还提供了很多的命令行接口,可以进行调试、读写内存、烧写Flash、配置环境变量等。在开发过程中Monitor提供了很好地调试功能,不过在开发结束之后,可以完全将其设置成一个Bootloader。所以习惯上将其叫做Bootloader。
| Bootloader | Monitor | 描述 | X86 | ARM | PowerPC |
| U-boot | 是 | 通用引导程序 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| RedBoot | 是 | 基于eCos的引导程序 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| BLOB | 否 | LART(主板)等硬件平台的引导程序 | 否 | 是 | 否 |
| LILO | 否 | Linux磁盘引导程序 | 是 | 否 | 否 |
| GRUB | 否 | GNU的LILO替代程序 | 是 | 否 | 否 |
| Loadlin | 否 | 从DOS引导Linux | 是 | 否 | 否 |
| Vivi | 是 | 韩国mizi 公司开发的bootloader | 否 | 是 | 否 |
更多bootloader还有:ROLO、Etherboot、ARMboot 、LinuxBIOS等。
对于每种体系结构,都有一系列开放源码Bootloader可以选用:
X86:X86的工作站和服务器上一般使用LILO和GRUB。
ARM:最早有为ARM720处理器开发板所做的固件,又有了armboot,StrongARM平台的blob,还有S3C2410处理器开发板上的vivi等。现在armboot已经并入了U-Boot,所以U-Boot也支持ARM/XSCALE平台。U-Boot已经成为ARM平台事实上的标准Bootloader。
PowerPC:最早使用于ppcboot,不过现在大多数直接使用U-boot。
MIPS:最早都是MIPS开发商自己写的bootloader,不过现在U-boot也支持MIPS架构。
M68K:Redboot能够支持m68k系列的系统。
2.2,Arm特定平台的bootloader
到目前为止,我们公司已经做过多个Arm平台的android方案,包括:marvell(pxa935)、informax(im9815)、mediatek(mt6516/6517)、broadcom(bcm2157)。由于不同处理器芯片厂商对arm core的封装差异比较大,所以不同的arm处理器,对于上电引导都是由特定处理器芯片厂商自己开发的程序,这个上电引导程序通常比较简单,会初始化硬件,提供下载模式等,然后才会加载通常的bootloader。
下面是几个arm平台的bootloader方案:
marvell(pxa935) : bootROM + OBM [l4] + BLOB
informax(im9815) : bootROM + barbox + U-boot
mediatek(mt6516/6517) : bootROM + pre-loader[l5] + U-boot
broadcom(bcm2157) : bootROM + boot1/boot2 + U-boot
为了明确U-boot之前的两个loader的作用,下面以broadcom平台为例,看下在上电之后到U-boot的流程,如图1.2.1:
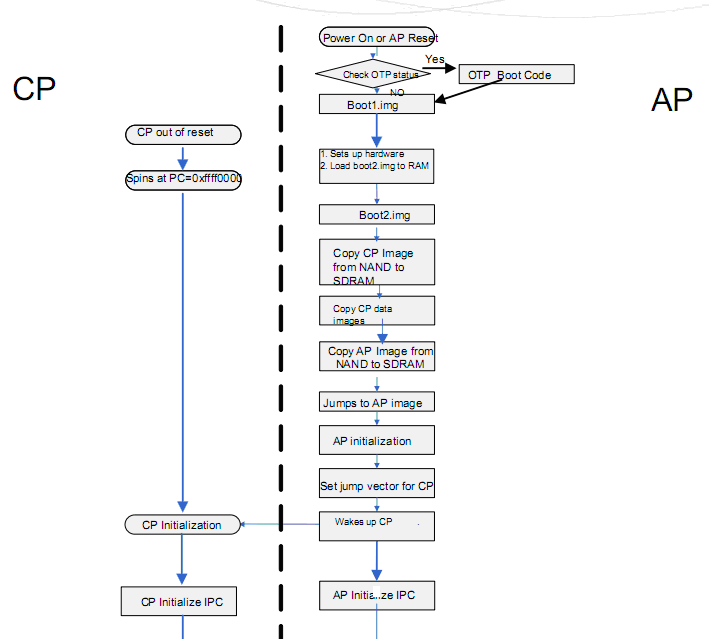
图1.2.1 broadcom平台上电流程
2.3,uboot启动流程详解
最常用的bootloader还是U-boot,可以引导多种操作系统,支持多种架构的CPU。它支持的操作系统有:Linux、NetBSD、VxWorks、QNX、RTEMS、ARTOS、LynxOS等,支持的CPU架构有:ARM、PowerPC、MISP、X86、NIOS、Xscale等。手机系统不像其他的嵌入式系统,它还需要在启动的过程中关心CP的启动,这个时候就涉及到CP的image和唤醒时刻,而一般的嵌入式系统的uboot只负责引导OS内核。所以这里我们也暂不关心CP的启动,而主要关心AP侧。
从上面第二小节中可以看出,bootloader通常都包含有处理器厂商开发的上电引导程序,不过也不是所有的处理都是这样,比如三星的S3C24X0系列,它的bootROM直接跳到U-boot中执行,首先由bootROM将U-boot的前4KB拷贝到处理器ISRAM,接着在U-boot的前4KB中必须保证要完成的两项主要工作:初始化DDR,nand和nand控制器,接着将U-boot剩余的code拷贝到SDRAM中,然后跳到SDRAM的对应地址上去继续跑U-boot。
所以U-boot的启动过程,大致上可以分成两个阶段:第一阶段,汇编代码;第二阶段,c代码。
2.3.1,汇编代码阶段
U-boot的启动由u-boot/arch/arm/cpu/xxx/u-boot.lds开始,其引导调用u-boot/arch/arm/cpu/xxx/start.S。u-boot.lds:
- OUTPUT_FORMAT("elf32-littlearm", "elf32-littlearm", "elf32-littlearm")
- OUTPUT_ARCH(arm)
- ENTRY(_start)
- SECTIONS
- {
- . = 0x00000000;
-
- . = ALIGN(4);
- .text :
- {
- arch/arm/cpu/arm920t/start.o (.text)
- *(.text)
- }
-
- . = ALIGN(4);
- .rodata : { *(SORT_BY_ALIGNMENT(SORT_BY_NAME(.rodata*))) }
-
- . = ALIGN(4);
- .data : {
- *(.data)
- }
-
- . = ALIGN(4);
-
- . = .;
- __u_boot_cmd_start = .;
- .u_boot_cmd : { *(.u_boot_cmd) }
- __u_boot_cmd_end = .;
-
- . = ALIGN(4);
-
- .rel.dyn : {
- __rel_dyn_start = .;
- *(.rel*)
- __rel_dyn_end = .;
- }
-
- .dynsym : {
- __dynsym_start = .;
- *(.dynsym)
- }
-
- .bss __rel_dyn_start (OVERLAY) : {
- __bss_start = .;
- *(.bss)
- . = ALIGN(4);
- _end = .;
- }
-
- /DISCARD/ : { *(.dynstr*) }
- /DISCARD/ : { *(.dynamic*) }
- /DISCARD/ : { *(.plt*) }
- /DISCARD/ : { *(.interp*) }
- /DISCARD/ : { *(.gnu*) }
- }
对应的Makefile文件如下:
- include $(TOPDIR)/config.mk
-
- LIB = $(obj)lib$(CPU).o
-
- START = start.o
-
- COBJS-y += cpu.o
- COBJS-$(CONFIG_USE_IRQ) += interrupts.o
-
- SRCS := $(START:.o=.S) $(SOBJS:.o=.S) $(COBJS-y:.o=.c)
- OBJS := $(addprefix $(obj),$(COBJS-y) $(SOBJS))
- START := $(addprefix $(obj),$(START))
-
- all: $(obj).depend $(START) $(LIB)
-
- $(LIB): $(OBJS)
- $(call cmd_link_o_target, $(OBJS))
-
- #########################################################################
-
- # defines $(obj).depend target
- include $(SRCTREE)/rules.mk
-
- sinclude $(obj).depend
所以U-boot的第一条指令从u-boot/arch/arm/cpu/xxx/start.S文件开始,第一阶段主要做了如下事情:
(1). 设置CPU进入SVC模式(系统管理模式),cpsr[4:0]=0xd3。
(2). 关中断,INTMSK=0xFFFFFFFF, INTSUBMSK=0x3FF。
(3). 关看门狗,WTCON=0x0。
(4). 调用s3c2410_cache_flush_all函数,使TLBS,I、D Cache,WB中数据失效。
(5). 时钟设置CLKDIVN=0x3 , FCLK:HCLK:PCLK = 1:2:4。
(6). 读取mp15的c1寄存器,将最高两位改成11,表示选择了异步时钟模型。
(7). 检查系统的复位状态,以确定是不是从睡眠唤醒。
- #include <asm-offsets.h>
- #include <common.h>
- #include <config.h>
-
- .globl _start
- _start: b start_code
- ldr pc, _undefined_instruction
- ldr pc, _software_interrupt
- ldr pc, _prefetch_abort
- ldr pc, _data_abort
- ldr pc, _not_used
- ldr pc, _irq
- ldr pc, _fiq
-
- ......
-
-
- start_code:
-
-
-
- mrs r0, cpsr
- bic r0, r0, #0x1f
- orr r0, r0, #0xd3
- msr cpsr, r0
-
- bl coloured_LED_init
- bl red_LED_on
-
- ......
-
-
-
-
-
- #ifndef CONFIG_SKIP_LOWLEVEL_INIT
- bl cpu_init_crit
- #endif
-
-
-
- call_board_init_f:
- ldr sp, =(CONFIG_SYS_INIT_SP_ADDR)
- bic sp, sp, #7
- ldr r0,=0x00000000
- bl board_init_f
-
-
- .globl relocate_code
- relocate_code:
- mov r4, r0
- mov r5, r1
- mov r6, r2
-
-
- stack_setup:
- mov sp, r4
-
- adr r0, _start
- cmp r0, r6
- beq clear_bss
- mov r1, r6
- ldr r2, _TEXT_BASE
- ldr r3, _bss_start_ofs
- add r2, r0, r3
-
- copy_loop:
- ldmia r0!, {r9-r10}
- stmia r1!, {r9-r10}
- cmp r0, r2
- blo copy_loop
-
- #ifndef CONFIG_PRELOADER
-
-
-
- ldr r0, _TEXT_BASE
- sub r9, r6, r0
- ldr r10, _dynsym_start_ofs
- add r10, r10, r0
- ldr r2, _rel_dyn_start_ofs
- add r2, r2, r0
- ldr r3, _rel_dyn_end_ofs
- add r3, r3, r0
- fixloop:
- ldr r0, [r2]
- add r0, r0, r9
- ldr r1, [r2, #4]
- and r7, r1, #0xff
- cmp r7, #23
- beq fixrel
- cmp r7, #2
- beq fixabs
-
- b fixnext
- fixabs:
-
- mov r1, r1, LSR #4
- add r1, r10, r1
- ldr r1, [r1, #4]
- add r1, r1, r9
- b fixnext
- fixrel:
-
- ldr r1, [r0]
- add r1, r1, r9
- fixnext:
- str r1, [r0]
- add r2, r2, #8
- cmp r2, r3
- blo fixloop
- #endif
-
- clear_bss:
- #ifndef CONFIG_PRELOADER
- ldr r0, _bss_start_ofs
- ldr r1, _bss_end_ofs
- ldr r3, _TEXT_BASE
- mov r4, r6
- add r0, r0, r4
- add r1, r1, r4
- mov r2, #0x00000000
-
- clbss_l:str r2, [r0]
- add r0, r0, #4
- cmp r0, r1
- bne clbss_l
-
- bl coloured_LED_init
- bl red_LED_on
- #endif
-
-
-
-
-
- #ifdef CONFIG_NAND_SPL
- ldr r0, _nand_boot_ofs
- mov pc, r0
-
- _nand_boot_ofs:
- .word nand_boot
- #else
- ldr r0, _board_init_r_ofs
- adr r1, _start
- add lr, r0, r1
- add lr, lr, r9
-
- mov r0, r5
- mov r1, r6
-
- mov pc, lr
-
- _board_init_r_ofs:
- .word board_init_r - _start
- #endif
-
- _rel_dyn_start_ofs:
- .word __rel_dyn_start - _start
- _rel_dyn_end_ofs:
- .word __rel_dyn_end - _start
- _dynsym_start_ofs:
- .word __dynsym_start - _start
-
- ......
-
- #endif
根据这几条语句来判断系统是从nand启动的还是直接将程序下载到SDRAM中运行的,这里涉及到运行时域 和位置无关代码的概念,ldr r0,_TEXT_BASE的作用是将config.mk文件中定义的TEXT_BASE值(0x33f80000)装载到r0中,adr r1,_start该指令是条伪指令,在编译的时候会被转换成ADD或SUB指令根据当前pc值计算出_start标号的地址,这样的话就可以知道当前程序在什么地址运行(位置无关代码:做成程序的所有指令都是相对寻址的指令,包括跳转指令等,这样代码就可以不在链接所指定的地址上运行)。在上电之后,系统从nand启动,这里得到r0和r1值是不一样的,r0=0x33f80000,而r1=0x00000000。所以接下来会执行cpu_init_crit函数。
cpu_init_crit函数,主要完成了两个工作:首先使ICache and Dcache,TLBs中早期内容失效,再设置p15 control register c1,关闭MMU,Dcache,但是打开了Icache和Fault checking,(要求mmu和Dcache是必须要关闭的,而Icache可以打开可以关闭);其次调用/board/nextdvr2410/memsetup.S文件中的memsetup函数来建立对SDRAM的访问时序。
Relocate函数,加载nand flash中的uboot到SDRAM中,代码会加载到0x33f80000开始的地址,空间大小是512。
//这里参考的是展讯平台7710的源代码,所以并无start_armboot函数,取而代之的是board_init_r函数。请知悉。
ldr pc, _start_armboot
_start_armboot: .word start_armboot
这里将会进入第二阶段的c代码部分:board_init_r()函数,/u-boot/arch/arm/lib/board.c。
2.3.2,C代码阶段
先看/u-boot/arch/arm/lib/board.c的board_init_r()函数:
- void board_init_r (gd_t *id, ulong dest_addr)
- {
- ......
-
- board_init();
-
- boot_pwr_check();
-
- #ifdef CONFIG_SERIAL_MULTI
- serial_initialize();
- #endif
-
- debug ("Now running in RAM - U-Boot at: %08lx\n", dest_addr);
-
- #ifdef CONFIG_LOGBUFFER
- logbuff_init_ptrs ();
- #endif
- #ifdef CONFIG_POST
- post_output_backlog ();
- #endif
-
-
- malloc_start = dest_addr - TOTAL_MALLOC_LEN;
- #ifdef SPRD_EVM_TAG_ON
- SPRD_EVM_TAG(4);
- #endif
- mem_malloc_init (malloc_start, TOTAL_MALLOC_LEN);
- #ifdef SPRD_EVM_TAG_ON
- SPRD_EVM_TAG(5);
- #endif
- boot_pwr_check();
-
- #if !defined(CONFIG_SYS_NO_FLASH)
- puts ("FLASH: ");
-
- if ((flash_size = flash_init ()) > 0) {
- # ifdef CONFIG_SYS_FLASH_CHECKSUM
- print_size (flash_size, "");
-
-
-
-
-
- s = getenv ("flashchecksum");
- if (s && (*s == 'y')) {
- printf (" CRC: %08X",
- crc32 (0, (const unsigned char *) CONFIG_SYS_FLASH_BASE, flash_size)
- );
- }
- putc ('\n');
- # else /* !CONFIG_SYS_FLASH_CHECKSUM */
- print_size (flash_size, "\n");
- # endif /* CONFIG_SYS_FLASH_CHECKSUM */
- } else {
- puts (failed);
- hang ();
- }
- #endif
- boot_pwr_check();
-
- #if !defined(CONFIG_EMMC_BOOT)
- #if defined(CONFIG_CMD_NAND)
- puts ("NAND: ");
- ret = nand_init();
- if (ret) {
- puts ("NAND init error ");
- while(1);
- }
- #endif
- #endif
-
- boot_pwr_check();
- #ifdef SPRD_EVM_TAG_ON
- SPRD_EVM_TAG(6);
- #endif
-
- #if defined(CONFIG_CMD_ONENAND)
- #if !(defined CONFIG_TIGER && defined CONFIG_EMMC_BOOT)
- onenand_init();
- #endif
- #endif
-
- #ifdef CONFIG_GENERIC_MMC
- puts("MMC: ");
- mmc_initialize(bd);
- #endif
-
- #ifdef CONFIG_HAS_DATAFLASH
- AT91F_DataflashInit();
- dataflash_print_info();
- #endif
-
- #ifdef CONFIG_EMMC_BOOT
- mmc_legacy_init(1);
- #endif
-
- env_relocate ();
- boot_pwr_check();
-
- #ifdef CONFIG_VFD
-
- drv_vfd_init();
- #endif /* CONFIG_VFD */
-
-
-
-
- gd->bd->bi_ip_addr = getenv_IPaddr ("ipaddr");
-
- stdio_init ();
- boot_pwr_check();
-
- jumptable_init ();
- boot_pwr_check();
-
- #if defined(CONFIG_API)
-
- api_init ();
- #endif
- char fake[4]="fak";
- setenv("splashimage", fake);
-
- console_init_r ();
- boot_pwr_check();
-
- #if defined(CONFIG_ARCH_MISC_INIT)
-
- arch_misc_init ();
- #endif
- #if defined(CONFIG_MISC_INIT_R)
-
- misc_init_r ();
- #endif
-
-
- interrupt_init ();
-
- enable_interrupts ();
- boot_pwr_check();
-
-
- #if defined(CONFIG_DRIVER_SMC91111) || defined (CONFIG_DRIVER_LAN91C96)
-
- if (getenv ("ethaddr")) {
- uchar enetaddr[6];
- eth_getenv_enetaddr("ethaddr", enetaddr);
- smc_set_mac_addr(enetaddr);
- }
- #endif /* CONFIG_DRIVER_SMC91111 || CONFIG_DRIVER_LAN91C96 */
-
-
- if ((s = getenv ("loadaddr")) != NULL) {
- load_addr = simple_strtoul (s, NULL, 16);
- }
- #if defined(CONFIG_CMD_NET)
- if ((s = getenv ("bootfile")) != NULL) {
- copy_filename (BootFile, s, sizeof (BootFile));
- }
- #endif
- boot_pwr_check();
-
- #ifdef BOARD_LATE_INIT
- board_late_init ();
- #endif
- ......
-
- #ifdef SPRD_EVM_TAG_ON
- SPRD_EVM_TAG(11);
- #endif
- extern int do_cboot(cmd_tbl_t *cmdtp, int flag, int argc, char *const argv[]);
- boot_pwr_check();
-
- do_cboot(NULL, 0, 1, NULL);
-
- for (;;) {
- main_loop ();
- }
-
-
- }
该段代码完成了一些设备的初始化do_cboot(NULL, 0, 1, NULL)和main_loop ()是此处重点函数,其中do_cboot(NULL, 0, 1, NULL)的实现在u-boot/property/cmd_cboot.c而main_loop()则是在u-boot/common/main.c中。先看u-boot/property/cmd_cboot.c。
- int boot_pwr_check(void)
- {
- static int total_cnt = 0;
- if(!power_button_pressed())
- total_cnt ++;
- return total_cnt;
- }
- #define mdelay(_ms) udelay(_ms*1000)
-
-
- int do_cboot(cmd_tbl_t *cmdtp, int flag, int argc, char *const argv[])
- {
- uint32_t key_mode = 0;
- uint32_t key_code = 0;
- volatile int i;
-
- if(argc > 2)
- goto usage;
-
- #ifdef CONFIG_SC8830
- if(cali_file_check())
- calibration_detect(2);
- #endif
- #ifdef CONFIG_SC7710G2
- {
- extern void set_cp_emc_pad(void);
- set_cp_emc_pad();
- }
- #endif
- CHG_Init();
-
- #ifdef CONFIG_SC8830
- DCDC_Cal_ArmCore();
-
- #endif
-
- #ifdef CONFIG_AUTOBOOT
- normal_mode();
- #endif
-
- #ifdef CONFIG_SC7710G2
- if(!pbint2_connected())
- normal_mode();
- #endif
-
- boot_pwr_check();
-
- #ifdef CONFIG_SC8800G
- CHG_ShutDown();
- if(charger_connected()){
- mdelay(10);
- CHG_TurnOn();
- }else{
-
- if(is_bat_low()){
- printf("shut down again for low battery\n");
- power_down_devices();
- while(1)
- ;
- }
- }
- #else
-
- #ifndef CONFIG_MACH_CORI
- if(is_bat_low()){
- printf("shut down again for low battery\n");
- mdelay(10000);
- power_down_devices();
- while(1)
- ;
- }
- #endif
- #endif
-
- boot_pwr_check();
- board_keypad_init();
- boot_pwr_check();
-
- #ifdef CONFIG_SPRD_SYSDUMP
- write_sysdump_before_boot();
- #endif
-
- int recovery_init(void);
- int ret =0;
- ret = recovery_init();
- if(ret == 1){
- DBG("func: %s line: %d\n", __func__, __LINE__);
- recovery_mode_without_update();
- }else if(ret == 2){
- #ifndef CONFIG_SC8830
- try_update_modem();
- #endif
- normal_mode();
- }
-
- unsigned check_reboot_mode(void);
-
-
- unsigned rst_mode= check_reboot_mode();
-
- if(rst_mode == RECOVERY_MODE){
- DBG("func: %s line: %d\n", __func__, __LINE__);
- recovery_mode();
- }
- else if(rst_mode == FASTBOOT_MODE){
- DBG("func: %s line: %d\n", __func__, __LINE__);
- fastboot_mode();
- }else if(rst_mode == NORMAL_MODE){
- normal_mode();
- }else if(rst_mode == WATCHDOG_REBOOT){
- watchdog_mode();
- }else if(rst_mode == UNKNOW_REBOOT_MODE){
- unknow_reboot_mode();
- }else if(rst_mode == PANIC_REBOOT){
- panic_reboot_mode();
- }else if(rst_mode == ALARM_MODE){
- int flag =alarm_flag_check();
- if(flag == 1)
- alarm_mode();
- else if(flag == 2)
- normal_mode();
- }else if(rst_mode == SLEEP_MODE){
- sleep_mode();
- }else if(rst_mode == SPECIAL_MODE){
- special_mode();
- }else if(rst_mode == CALIBRATION_MODE){
- calibration_detect(0);
- }
- #ifdef CONFIG_SC8810
-
- #endif
- DBG("func: %s line: %d\n", __func__, __LINE__);
-
- if(charger_connected()){
- DBG("%s: charger connected\n", __FUNCTION__);
- #if defined (CONFIG_SP8810W) || defined(CONFIG_SC7710G2)
- calibration_detect(1);
- #endif
- charge_mode();
- }
-
-
- else if(boot_pwr_check() >= get_pwr_key_cnt()){
- DBG("%s: power button press\n", __FUNCTION__);
- DBG("boot_pwr_check=%d,get_pwr_key_cnt=%d\n",boot_pwr_check(),get_pwr_key_cnt());
-
- mdelay(50);
- for(i=0; i<10;i++){
- key_code = board_key_scan();
- if(key_code != KEY_RESERVED)
- break;
- }
- DBG("key_code %d\n", key_code);
-
- key_mode = check_key_boot(key_code);
-
- switch(key_mode){
- case BOOT_FASTBOOT:
- fastboot_mode();
- break;
- case BOOT_RECOVERY:
- recovery_mode();
- break;
- case BOOT_CALIBRATE:
- engtest_mode();
- return 0;
- break;
- case BOOT_DLOADER:
- dloader_mode();
- break;
- default:
- break;
- }
- }
- else if(alarm_triggered() && alarm_flag_check()){
- DBG("%s: alarm triggered\n", __FUNCTION__);
- int flag =alarm_flag_check();
-
- if(flag == 1){
-
- alarm_mode();
- }
- else if(flag == 2){
- normal_mode();
- }
-
- }else{
- #if BOOT_NATIVE_LINUX_MODEM
- *(volatile u32*)CALIBRATION_FLAG = 0xca;
- #endif
- #if !defined (CONFIG_SC8830) && !defined(CONFIG_SC7710G2)
- calibration_detect(0);
- #endif
-
- DBG("%s: power done again\n", __FUNCTION__);
- power_down_devices();
- while(1)
- ;
- }
-
- if(argc == 1){
- DBG("func: %s line: %d\n", __func__, __LINE__);
- normal_mode();
- return 1;
- }
-
- if(argc == 2){
- DBG("func: %s line: %d\n", __func__, __LINE__);
-
- if(strcmp(argv[1],"normal") == 0){
- normal_mode();
- return 1;
- }
- DBG("func: %s line: %d\n", __func__, __LINE__);
-
- if(strcmp(argv[1],"recovery") == 0){
- recovery_mode();
- return 1;
- }
- DBG("func: %s line: %d\n", __func__, __LINE__);
-
- if(strcmp(argv[1],"fastboot") == 0){
- fastboot_mode();
- return 1;
- }
- DBG("func: %s line: %d\n", __func__, __LINE__);
-
- if(strcmp(argv[1],"dloader") == 0){
- dloader_mode();
- return 1;
- }
- DBG("func: %s line: %d\n", __func__, __LINE__);
-
- if(strcmp(argv[1],"charge") == 0){
-
- charge_mode();
- return 1;
- }
- DBG("func: %s line: %d\n", __func__, __LINE__);
-
- if(strcmp(argv[1],"caliberation") == 0){
- calibration_detect(1);
- return 1;
- }
- DBG("func: %s line: %d\n", __func__, __LINE__);
- }
- DBG("func: %s line: %d\n", __func__, __LINE__);
-
- usage:
- cmd_usage(cmdtp);
- return 1;
- }
接下来分析正常开机的流程也就是normal_mode(),其他几种开机流程与normal_mode()类似,不再一一分析。android共提供了多种mode:
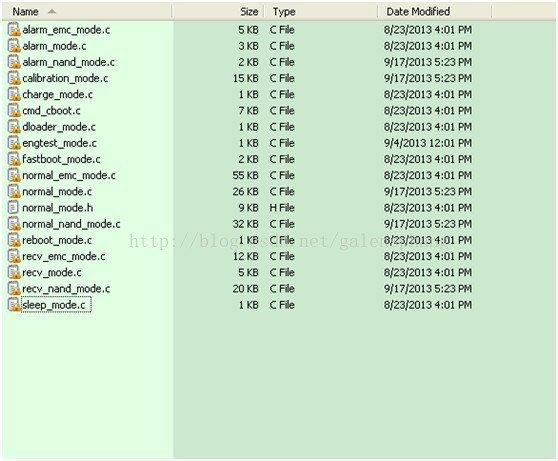
normal_mode()的实现在 u-boot/property/normal_mode.c:
- void normal_mode(void)
- {
- #if defined (CONFIG_SC8810) || defined (CONFIG_SC8825) || defined (CONFIG_SC8830)
-
- vibrator_hw_init();
- #endif
- set_vibrator(1);
-
- #ifndef UART_CONSOLE_SUPPORT
- #ifdef CONFIG_SC7710G2
- extern int serial1_SwitchToModem(void);
- serial1_SwitchToModem();
- #endif
- #endif
-
- #if BOOT_NATIVE_LINUX
- vlx_nand_boot(BOOT_PART, CONFIG_BOOTARGS, BACKLIGHT_ON);
- #else
- vlx_nand_boot(BOOT_PART, NULL, BACKLIGHT_ON);
- #endif
-
- }
最终将操作交给vlx_nand_boot(),其实现在u-boot/property/normal_nand_mode.c
- void vlx_nand_boot(char * kernel_pname, char * cmdline, int backlight_set)
- {
- ......
- char *fixnvpoint = "/fixnv";
- char *fixnvfilename = "/fixnv/fixnv.bin";
- char *fixnvfilename2 = "/fixnv/fixnvchange.bin";
- char *backupfixnvpoint = "/backupfixnv";
- char *backupfixnvfilename = "/backupfixnv/fixnv.bin";
-
- char *runtimenvpoint = "/runtimenv";
- char *runtimenvpoint2 = "/runtimenv";
- char *runtimenvfilename = "/runtimenv/runtimenv.bin";
- char *runtimenvfilename2 = "/runtimenv/runtimenvbkup.bin";
-
- char *productinfopoint = "/productinfo";
- char *productinfofilename = "/productinfo/productinfo.bin";
- char *productinfofilename2 = "/productinfo/productinfobkup.bin";
-
- int orginal_right, backupfile_right;
- unsigned long orginal_index, backupfile_index;
- nand_erase_options_t opts;
- char * mtdpart_def = NULL;
- #if (defined CONFIG_SC8810) || (defined CONFIG_SC8825)
- MMU_Init(CONFIG_MMU_TABLE_ADDR);
- #endif
- ret = mtdparts_init();
- if (ret != 0){
- printf("mtdparts init error %d\n", ret);
- return;
- }
-
- #ifdef CONFIG_SPLASH_SCREEN
- #define SPLASH_PART "boot_logo"
- ret = find_dev_and_part(SPLASH_PART, &dev, &pnum, &part);
- if(ret){
- printf("No partition named %s\n", SPLASH_PART);
- return;
- }else if(dev->id->type != MTD_DEV_TYPE_NAND){
- printf("Partition %s not a NAND device\n", SPLASH_PART);
- return;
- }
-
- off=part->offset;
- nand = &nand_info[dev->id->num];
-
- size = 1<<19;
- char * bmp_img = malloc(size);
- if(!bmp_img){
- printf("not enough memory for splash image\n");
- return;
- }
- ret = nand_read_offset_ret(nand, off, &size, (void *)bmp_img, &off);
- if(ret != 0){
- printf("function: %s nand read error %d\n", __FUNCTION__, ret);
- return;
- }
-
- lcd_display_logo(backlight_set,(ulong)bmp_img,size);
- #endif
- set_vibrator(0);
- {
- nand_block_info(nand, &good_blknum, &bad_blknum);
- printf("good is %d bad is %d\n", good_blknum, bad_blknum);
- }
-
- ret = load_sector_to_memory(fixnvpoint,
- fixnvfilename2,
- fixnvfilename,
- (unsigned char *)FIXNV_ADR,
- (unsigned char *)MODEM_ADR,
- FIXNV_SIZE + 4);
- ......
-
- #elif defined(CONFIG_CALIBRATION_MODE_NEW)
- #if defined(CONFIG_SP7702) || defined(CONFIG_SP8810W)
-
-
-
- extern void DSP_ForceSleep(void);
- DSP_ForceSleep();
- printf("dsp nand read ok1 %d\n", ret);
- #endif
-
- #ifdef CONFIG_SC7710G2
- ret = try_update_spl();
- if(ret == -1){
- printf("try update spl faild!\n");
- return -1;
- }
-
- ret = try_load_fixnv();
- if(ret == -1){
- printf("try load fixnv faild!\n");
- return -1;
- }
-
- ret = try_load_runtimenv();
- if(ret == -1){
- printf("try load runtimenv faild!\n");
- }
-
- ret = try_load_productinfo();
- if(ret == -1){
- printf("try load productinfo faild!\n");
- }
- #endif
- if(poweron_by_calibration())
- {
- #ifndef CONFIG_SC7710G2
-
-
- ......
-
-
- ......
-
- ......
-
- #endif
-
-
- printf("Reading kernel to 0x%08x\n", KERNEL_ADR);
-
- ret = find_dev_and_part(kernel_pname, &dev, &pnum, &part);
- if(ret){
- printf("No partition named %s\n", kernel_pname);
- return;
- }else if(dev->id->type != MTD_DEV_TYPE_NAND){
- printf("Partition %s not a NAND device\n", kernel_pname);
- return;
- }
-
- off=part->offset;
- nand = &nand_info[dev->id->num];
-
- #if 0
- size = nand->writesize;
- flash_page_size = nand->writesize;
- ret = nand_read_offset_ret(nand, off, &size, (void *)hdr, &off);
- if(ret != 0){
- printf("function: %s nand read error %d\n", __FUNCTION__, ret);
- return;
- }
- if(memcmp(hdr->magic, BOOT_MAGIC, BOOT_MAGIC_SIZE)){
- printf("bad boot image header, give up read!!!!\n");
- return;
- }
- else
- {
-
- size = (hdr->kernel_size+(flash_page_size - 1)) & (~(flash_page_size - 1));
- if(size <=0){
- printf("kernel image should not be zero\n");
- return;
- }
- ret = nand_read_offset_ret(nand, off, &size, (void *)KERNEL_ADR, &off);
- if(ret != 0){
- printf("kernel nand read error %d\n", ret);
- return;
- }
-
- size = (hdr->ramdisk_size+(flash_page_size - 1)) & (~(flash_page_size - 1));
- if(size<0){
- printf("ramdisk size error\n");
- return;
- }
- ret = nand_read_offset_ret(nand, off, &size, (void *)RAMDISK_ADR, &off);
- if(ret != 0){
- printf("ramdisk nand read error %d\n", ret);
- return;
- }
- }
- #else
-
- ret = load_kernel_and_layout(nand,
- (unsigned int)off,
- (char *)raw_header,
- (char *) KERNEL_ADR,
- (char *) RAMDISK_ADR,
- 2048,
- nand->writesize);
-
- if (ret != 0) {
- printf("ramdisk nand read error %d\n", ret);
- return;
- }
-
- #endif
-
- ......
-
- {
-
- good_blknum = 0;
- bad_blknum = 0;
- nand_block_info(nand, &good_blknum, &bad_blknum);
- printf("good is %d bad is %d\n", good_blknum, bad_blknum);
- }
- creat_cmdline(cmdline,hdr);
- vlx_entry();
- }
该函数的重点在开头和结尾的相关操作,开头部分见注释,重点分析vlx_entry()函数,其实现在normal_mode.c:
- void vlx_entry()
- {
- #if !(defined CONFIG_SC8810 || defined CONFIG_TIGER || defined CONFIG_SC8830)
- MMU_InvalideICACHEALL();
- #endif
-
- #if (defined CONFIG_SC8810) || (defined CONFIG_SC8825) || (defined CONFIG_SC8830)
- MMU_DisableIDCM();
- #endif
-
- #ifdef REBOOT_FUNCTION_INUBOOT
- reboot_func();
- #endif
-
- #if BOOT_NATIVE_LINUX
- start_linux();
- #else
- void (*entry)(void) = (void*) VMJALUNA_ADR;
- entry();
- #endif
- }
这里的entry()跳转到VM虚拟机的首地址,start_linux()则是进入kernel的方法,仍在normal_mode.c中实现:
- static int start_linux()
- {
- void (*theKernel)(int zero, int arch, u32 params);
- u32 exec_at = (u32)-1;
- u32 parm_at = (u32)-1;
- u32 machine_type;
-
- machine_type = machine_arch_type;
-
- theKernel = (void (*)(int, int, u32))KERNEL_ADR;
- #ifndef CONFIG_SC8830
- *(volatile u32*)0x84001000 = 'j';
- *(volatile u32*)0x84001000 = 'm';
- *(volatile u32*)0x84001000 = 'p';
- #endif
-
- theKernel(0, machine_type, VLX_TAG_ADDR);
- while(1);
- return 0;
- }
至此,已经到了Kernel\init\main.c的start_kernel(),即来到了linux的世界。
3,linux启动详细分析
Kernel\init\main.c的start_kernel()的kernel的起点,先看这个函数:
- asmlinkage void __init start_kernel(void)
- {
- char * command_line;
- extern const struct kernel_param __start___param[], __stop___param[];
-
- #ifdef CONFIG_NKERNEL
- jiffies_64 = INITIAL_JIFFIES;
- #endif
- smp_setup_processor_id();
-
-
-
-
-
- lockdep_init();
- debug_objects_early_init();
-
-
-
-
- boot_init_stack_canary();
-
- cgroup_init_early();
-
- local_irq_disable();
- early_boot_irqs_disabled = true;
-
-
-
-
-
- tick_init();
- boot_cpu_init();
- page_address_init();
- printk(KERN_NOTICE "%s", linux_banner);
- setup_arch(&command_line);
- mm_init_owner(&init_mm, &init_task);
- mm_init_cpumask(&init_mm);
- setup_command_line(command_line);
- setup_nr_cpu_ids();
- setup_per_cpu_areas();
- smp_prepare_boot_cpu();
-
- build_all_zonelists(NULL);
- page_alloc_init();
-
- printk(KERN_NOTICE "Kernel command line: %s\n", boot_command_line);
- parse_early_param();
- parse_args("Booting kernel", static_command_line, __start___param,
- __stop___param - __start___param,
- &unknown_bootoption);
-
-
-
-
- setup_log_buf(0);
- pidhash_init();
- vfs_caches_init_early();
- sort_main_extable();
- trap_init();
- mm_init();
-
-
-
-
-
-
- sched_init();
-
-
-
-
- preempt_disable();
- if (!irqs_disabled()) {
- printk(KERN_WARNING "start_kernel(): bug: interrupts were "
- "enabled *very* early, fixing it\n");
- local_irq_disable();
- }
- idr_init_cache();
- perf_event_init();
- rcu_init();
- radix_tree_init();
-
- early_irq_init();
- init_IRQ();
- prio_tree_init();
- init_timers();
- hrtimers_init();
- softirq_init();
- timekeeping_init();
- time_init();
- profile_init();
- call_function_init();
- if (!irqs_disabled())
- printk(KERN_CRIT "start_kernel(): bug: interrupts were "
- "enabled early\n");
- early_boot_irqs_disabled = false;
- local_irq_enable();
-
-
- gfp_allowed_mask = __GFP_BITS_MASK;
-
- kmem_cache_init_late();
-
-
-
-
-
-
- console_init();
- if (panic_later)
- panic(panic_later, panic_param);
-
- lockdep_info();
-
-
-
-
-
-
- locking_selftest();
-
- #ifdef CONFIG_BLK_DEV_INITRD
- if (initrd_start && !initrd_below_start_ok &&
- page_to_pfn(virt_to_page((void *)initrd_start)) < min_low_pfn) {
- printk(KERN_CRIT "initrd overwritten (0x%08lx < 0x%08lx) - "
- "disabling it.\n",
- page_to_pfn(virt_to_page((void *)initrd_start)),
- min_low_pfn);
- initrd_start = 0;
- }
- #endif
- page_cgroup_init();
- enable_debug_pagealloc();
- debug_objects_mem_init();
- kmemleak_init();
- setup_per_cpu_pageset();
- numa_policy_init();
- if (late_time_init)
- late_time_init();
- sched_clock_init();
- calibrate_delay();
- pidmap_init();
- anon_vma_init();
- #ifdef CONFIG_X86
- if (efi_enabled)
- efi_enter_virtual_mode();
- #endif
- thread_info_cache_init();
- cred_init();
- fork_init(totalram_pages);
- proc_caches_init();
- buffer_init();
- key_init();
- security_init();
- dbg_late_init();
- vfs_caches_init(totalram_pages);
- signals_init();
-
- page_writeback_init();
- #ifdef CONFIG_PROC_FS
- proc_root_init();
- #endif
- cgroup_init();
- cpuset_init();
- taskstats_init_early();
- delayacct_init();
-
- check_bugs();
-
- acpi_early_init();
- sfi_init_late();
-
- ftrace_init();
-
-
-
- rest_init();
- }
该函数所调用的大部分都是相关的初始化操作,而跟启动关联的是结尾的rest_init() ,该函数是第一个跟init进程相关的函数,看其实现:
- static noinline void __init_refok rest_init(void)
- {
- int pid;
-
- rcu_scheduler_starting();
-
-
-
-
-
-
- kernel_thread(kernel_init, NULL, CLONE_FS | CLONE_SIGHAND);
- numa_default_policy();
- pid = kernel_thread(kthreadd, NULL, CLONE_FS | CLONE_FILES);
- rcu_read_lock();
- kthreadd_task = find_task_by_pid_ns(pid, &init_pid_ns);
- rcu_read_unlock();
- complete(&kthreadd_done);
-
-
-
-
-
- init_idle_bootup_task(current);
- preempt_enable_no_resched();
- schedule();
- preempt_disable();
-
-
- cpu_idle();
- }
该函数启动了kernel_init来进行后续的初始化,进而看kernel_init(),这些函数任然在main.c中实现。
- static int __init kernel_init(void * unused)
- {
-
-
-
- wait_for_completion(&kthreadd_done);
-
-
-
- set_mems_allowed(node_states[N_HIGH_MEMORY]);
-
-
-
- set_cpus_allowed_ptr(current, cpu_all_mask);
-
- cad_pid = task_pid(current);
-
- smp_prepare_cpus(setup_max_cpus);
-
- do_pre_smp_initcalls();
- lockup_detector_init();
-
- smp_init();
- sched_init_smp();
-
- do_basic_setup();
-
-
- if (sys_open((const char __user *) "/dev/console", O_RDWR, 0) < 0)
- printk(KERN_WARNING "Warning: unable to open an initial console.\n");
-
- (void) sys_dup(0);
- (void) sys_dup(0);
-
-
-
-
-
- if (!ramdisk_execute_command)
- ramdisk_execute_command = "/init";
-
- if (sys_access((const char __user *) ramdisk_execute_command, 0) != 0) {
- ramdisk_execute_command = NULL;
- prepare_namespace();
- }
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- init_post();
- return 0;
- }
init进程由init_post()创建 即main.c 的init_post():
- static noinline int init_post(void)
- {
-
- async_synchronize_full();
- free_initmem();
- mark_rodata_ro();
- system_state = SYSTEM_RUNNING;
- numa_default_policy();
-
-
- current->signal->flags |= SIGNAL_UNKILLABLE;
-
- if (ramdisk_execute_command) {
- run_init_process(ramdisk_execute_command);
- printk(KERN_WARNING "Failed to execute %s\n",
- ramdisk_execute_command);
- }
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- if (execute_command) {
-
- run_init_process(execute_command);
- printk(KERN_WARNING "Failed to execute %s. Attempting "
- "defaults...\n", execute_command);
- }
- run_init_process("/sbin/init");
- run_init_process("/etc/init");
- run_init_process("/bin/init");
- run_init_process("/bin/sh");
-
- panic("No init found. Try passing init= option to kernel. "
- "See Linux Documentation/init.txt for guidance.");
- }
4,android启动详细分析
android部分的启动包括几个部分:init,zygote,systemserver,launcher,lockscreen,othersapps。
4.1,init启动
init是一个进程,确切的说,是linux系统用户空间的第一个进程,android是基于linux 的,所以init也是android用户空间的第一个进程,他的进程号是1,作为天字第一号进程,其有很多重要的职责。其最重要的职责是创建了Zygote以及提供了systemserver。system\core\init\init.c的入口函数是main()。
- int main(int argc, char **argv)
- {
- int fd_count = 0;
- struct pollfd ufds[4];
- char *tmpdev;
- char* debuggable;
- char tmp[32];
- int property_set_fd_init = 0;
- int signal_fd_init = 0;
- int keychord_fd_init = 0;
- bool is_charger = false;
-
- if (!strcmp(basename(argv[0]), "ueventd"))
- return ueventd_main(argc, argv);
-
-
- umask(0);
-
-
-
-
-
-
- mkdir("/dev", 0755);
- mkdir("/proc", 0755);
- mkdir("/sys", 0755);
-
- mount("tmpfs", "/dev", "tmpfs", MS_NOSUID, "mode=0755");
- mkdir("/dev/pts", 0755);
- mkdir("/dev/socket", 0755);
- mount("devpts", "/dev/pts", "devpts", 0, NULL);
- mount("proc", "/proc", "proc", 0, NULL);
- mount("sysfs", "/sys", "sysfs", 0, NULL);
-
-
- close(open("/dev/.booting", O_WRONLY | O_CREAT, 0000));
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- open_devnull_stdio();
-
-
- klog_init();
-
- property_init();
-
- get_hardware_name(hardware, &revision);
-
- process_kernel_cmdline();
-
- #ifdef HAVE_SELINUX
- INFO("loading selinux policy\n");
- selinux_load_policy();
- #endif
-
- is_charger = !strcmp(bootmode, "charger");
-
- INFO("property init\n");
- if (!is_charger)
- property_load_boot_defaults();
-
- INFO("reading config file\n");
-
-
- init_parse_config_file("/init.rc");
-
-
-
-
- action_for_each_trigger("early-init", action_add_queue_tail);
-
- queue_builtin_action(wait_for_coldboot_done_action, "wait_for_coldboot_done");
- queue_builtin_action(keychord_init_action, "keychord_init");
-
- queue_builtin_action(console_init_action, "console_init");
-
-
- action_for_each_trigger("init", action_add_queue_tail);
-
-
-
- action_for_each_trigger("early-fs", action_add_queue_tail);
-
- {
- bool has_3partions = false;
-
- has_3partions = (!access("/sys/block/mmcblk0/mmcblk0p3",R_OK))
- && (!access("/sys/block/mmcblk0/mmcblk0p2",R_OK))
- && (!access("/sys/block/mmcblk0/mmcblk0p1",R_OK));
-
- if (has_3partions) {
- action_for_each_trigger("fs-two", action_add_queue_tail);
- } else {
- action_for_each_trigger("fs", action_add_queue_tail);
- }
- }
- action_for_each_trigger("post-fs", action_add_queue_tail);
- if (!is_charger) {
-
- action_for_each_trigger("post-fs-data", action_add_queue_tail);
- }
-
- queue_builtin_action(property_service_init_action, "property_service_init");
- queue_builtin_action(signal_init_action, "signal_init");
- queue_builtin_action(check_startup_action, "check_startup");
-
- if (!strcmp(bootmode, "alarm")) {
- action_for_each_trigger("alarm", action_add_queue_tail);
- }
- if (is_charger) {
- action_for_each_trigger("charger", action_add_queue_tail);
- } else {
- action_for_each_trigger("early-boot", action_add_queue_tail);
- action_for_each_trigger("boot", action_add_queue_tail);
- }
-
-
- queue_builtin_action(queue_property_triggers_action, "queue_property_triggers");
-
-
- #if BOOTCHART
- queue_builtin_action(bootchart_init_action, "bootchart_init");
- #endif
-
- for(;;) {
- int nr, i, timeout = -1;
-
- execute_one_command();
- restart_processes();
-
- if (!property_set_fd_init && get_property_set_fd() > 0) {
- ufds[fd_count].fd = get_property_set_fd();
- ufds[fd_count].events = POLLIN;
- ufds[fd_count].revents = 0;
- fd_count++;
- property_set_fd_init = 1;
- }
- if (!signal_fd_init && get_signal_fd() > 0) {
- ufds[fd_count].fd = get_signal_fd();
- ufds[fd_count].events = POLLIN;
- ufds[fd_count].revents = 0;
- fd_count++;
- signal_fd_init = 1;
- }
- if (!keychord_fd_init && get_keychord_fd() > 0) {
- ufds[fd_count].fd = get_keychord_fd();
- ufds[fd_count].events = POLLIN;
- ufds[fd_count].revents = 0;
- fd_count++;
- keychord_fd_init = 1;
- }
-
- if (process_needs_restart) {
- timeout = (process_needs_restart - gettime()) * 1000;
- if (timeout < 0)
- timeout = 0;
- }
-
- if (!action_queue_empty() || cur_action)
- timeout = 0;
-
- #if BOOTCHART
- if (bootchart_count > 0) {
- if (timeout < 0 || timeout > BOOTCHART_POLLING_MS)
- timeout = BOOTCHART_POLLING_MS;
- if (bootchart_step() < 0 || --bootchart_count == 0) {
- bootchart_finish();
- bootchart_count = 0;
- }
- }
- #endif
-
- nr = poll(ufds, fd_count, timeout);
- if (nr <= 0)
- continue;
-
- for (i = 0; i < fd_count; i++) {
- if (ufds[i].revents == POLLIN) {
- if (ufds[i].fd == get_property_set_fd())
- handle_property_set_fd();
- else if (ufds[i].fd == get_keychord_fd())
- handle_keychord();
- else if (ufds[i].fd == get_signal_fd())
- handle_signal();
- }
- }
- }
-
- return 0;
- }
从以上代码可知,init的工作任务还是很重的,上面的代码已经省略的不少,但任然很多,不过分析两个知识点来看,可将init的工作流程精简为四点:1,解析配置文件重点是init.rc。2,执行各个阶段的动作,创建zygote的工作就在其中的某一个阶段完成。3,调用property_init()初始化属性相关的资源,并且通过property_load_boot_defaults()启动属性服务。4,init进入一个无限循环,并且等待一些事情的发生。接下来重点看下解析配置文件的init.rc。解析函数:
- int init_parse_config_file(const char *fn)
- {
- char *data;
- data = read_file(fn, 0);
- if (!data) return -1;
-
- parse_config(fn, data);
- DUMP();
- return 0;
- }
再看init.rc文件:
- ......
-
-
- service servicemanager /system/bin/servicemanager
- class core
- user system
- group system
- critical
- onrestart restart zygote ------ > 启动zygote进程
- onrestart restart media ------ > 启动media
- onrestart restart surfaceflinger------ > 启动surfaceflinger
- onrestart restart drm------ > 启动drm
-
- service vold /system/bin/vold
- class core
- socket vold stream 0660 root mount
- ioprio be 2
-
- service netd /system/bin/netd
- class main
- socket netd stream 0660 root system
- socket dnsproxyd stream 0660 root inet
-
- service debuggerd /system/bin/debuggerd
- class main
-
- service ril-daemon /system/bin/rild
- class main
- socket rild stream 660 root radio
- socket rild-debug stream 660 radio system
- user root
- group radio cache inet misc audio sdcard_rw log
-
-
- service surfaceflinger /system/bin/surfaceflinger
- class main
- user system
- group graphics
- onrestart restart zygote
-
-
-
- service zygote /system/bin/app_process -Xzygote /system/bin --zygote --start-system-server
- class main
- socket zygote stream 666
- onrestart write /sys/android_power/request_state wake
- onrestart write /sys/power/state on
- onrestart restart media
- onrestart restart netd
-
-
- service drm /system/bin/drmserver
- class main
- user drm
- group system inet drmrpc
-
-
-
- service media /system/bin/mediaserver
- class main
- user media
- group audio camera inet net_bt net_bt_admin net_bw_acct drmrpc
- ioprio rt 4
-
- service bootanim /system/bin/bootanimation
- class main
- user graphics
- group graphics
- disabled
- oneshot
- ......
在init.rc中完成了一系列的重要操作:文件系统权限及挂载,启动zygote,启动系统服务,播放开机动画。当然如何解析对应的代码,并完成对应的操作,如启动zygote、播放开机动画,可以参考相关资料或查看源码,此处不再详述。至此init已经将部分操作交给了zygote。
4.2,zygote启动
zygote的启动预示着真正的来到了java的世界。zygote这个词的中文意思的受精卵,他和android系统中的java世界有着重要关系。zygote本身是一个native的应用程序,与驱动,内核均无关系。根据对init的了解我们知道,zygote是有init进程根据init.rc文件中的配置项创建的。先分析其来历,zygote最初的名字叫app_process,这个名字是在android.mk文件中指定的。但在运行过程中,app_process通过linux下的pctrl系统调用将自己的名字换成了zygote,所以通过进程看到的名称是zygote。
Zygote进程中完成了java虚拟机的创建及初始化,以及准备了java运行时环境,还有jni的准备工作,所以zygote占据了整个android世界的半壁江山,另半壁江山则是system_server,后续会详细介绍。
Zygote---- >入口文件App_main.cpp ---- >main()
Zygote原意是受精卵的意思。
在linux中指app_process即:frameworks/base/cmds/app_process目录下的App_main.cpp
此处可发现main()
- int main(int argc, const char* const argv[])
- {
-
- mArgC = argc;
- mArgV = argv;
-
- mArgLen = 0;
- for (int i=0; i<argc; i++) {
- mArgLen += strlen(argv[i]) + 1;
- }
- mArgLen--;
-
- AppRuntime runtime;
- const char* argv0 = argv[0];
-
-
-
- argc--;
- argv++;
-
-
-
- int i = runtime.addVmArguments(argc, argv);
-
-
- bool zygote = false;
- bool startSystemServer = false;
- bool application = false;
- const char* parentDir = NULL;
- const char* niceName = NULL;
- const char* className = NULL;
- while (i < argc) {
- const char* arg = argv[i++];
- if (!parentDir) {
- parentDir = arg;
- } else if (strcmp(arg, "--zygote") == 0) {
- zygote = true;
- niceName = "zygote";
- } else if (strcmp(arg, "--start-system-server") == 0) {
- startSystemServer = true;
- } else if (strcmp(arg, "--application") == 0) {
- application = true;
- } else if (strncmp(arg, "--nice-name=", 12) == 0) {
- niceName = arg + 12;
- } else {
- className = arg;
- break;
- }
- }
-
- if (niceName && *niceName) {
- setArgv0(argv0, niceName);
- set_process_name(niceName);
- }
-
- runtime.mParentDir = parentDir;
-
- if (zygote) {
-
- ALOGV("doLastShutDownCheck");
- doLastShutDownCheck();
- runtime.start("com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit",
- startSystemServer ? "start-system-server" : "");
- } else if (className) {
-
- runtime.mClassName = className;
- runtime.mArgC = argc - i;
- runtime.mArgV = argv + i;
- runtime.start("com.android.internal.os.RuntimeInit",
- application ? "application" : "tool");
- } else {
- fprintf(stderr, "Error: no class name or --zygote supplied.\n");
- app_usage();
- LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL("app_process: no class name or --zygote supplied.");
- return 10;
- }
- }
该代码主要完成工作如下:
1,niceName = "zygote";---- >重命名,原进程名称为app_process
,2,setArgv0(argv0, niceName);
,3,set_process_name(niceName); ---- >完成重命名操作
,4,AppRuntime runtime;----- >App_main.cpp的一个内部类,其继承AndroidRuntime.cpp
,5,runtime.start("com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit",startSystemServer("startsystemserver"));
备注:AppRuntime 作为一个内部类,在main()里调用。其完成:
1, getClassName() ---- >运行时文件类名
2, onVmCreated()---- >java虚拟机创建
3, onStarted()---- >调用时加载
4, onZygoteInit()---- >初始化虚拟机
5, onExit()---- >退出时的操作 --------- > 上述函数基本自动调用
接着,走进runtime.start(com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit)。runtime来自AndroidRuntime.cpp。AndroidRuntime.cpp------ >AndroidRuntime::start(const char* className, const char* options)。frameworks\base\core\jni\AndroidRuntime.cpp。分析其start()函数:
- void AndroidRuntime::start(const char* className, const char* options)
- {
- ALOGD("\n>>>>>> AndroidRuntime START %s <<<<<<\n",
- className != NULL ? className : "(unknown)");
-
- blockSigpipe();
-
-
-
-
-
- if (strcmp(options, "start-system-server") == 0) {
-
- const int LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_START = 3000;
- LOG_EVENT_LONG(LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_START,
- ns2ms(systemTime(SYSTEM_TIME_MONOTONIC)));
- }
-
- const char* rootDir = getenv("ANDROID_ROOT");
- if (rootDir == NULL) {
- rootDir = "/system";
- if (!hasDir("/system")) {
- LOG_FATAL("No root directory specified, and /android does not exist.");
- return;
- }
- setenv("ANDROID_ROOT", rootDir, 1);
- }
-
-
-
-
-
- JNIEnv* env;
- if (startVm(&mJavaVM, &env) != 0) {
- return;
- }
- onVmCreated(env);
-
-
-
-
- if (startReg(env) < 0) {
- ALOGE("Unable to register all android natives\n");
- return;
- }
-
-
-
-
-
-
- jclass stringClass;
- jobjectArray strArray;
- jstring classNameStr;
- jstring optionsStr;
-
- stringClass = env->FindClass("java/lang/String");
- assert(stringClass != NULL);
- strArray = env->NewObjectArray(2, stringClass, NULL);
- assert(strArray != NULL);
- classNameStr = env->NewStringUTF(className);
- assert(classNameStr != NULL);
- env->SetObjectArrayElement(strArray, 0, classNameStr);
- optionsStr = env->NewStringUTF(options);
- env->SetObjectArrayElement(strArray, 1, optionsStr);
-
-
-
-
-
- char* slashClassName = toSlashClassName(className);
- jclass startClass = env->FindClass(slashClassName);
- if (startClass == NULL) {
- ALOGE("JavaVM unable to locate class '%s'\n", slashClassName);
-
- } else {
- jmethodID startMeth = env->GetStaticMethodID(startClass, "main",
- "([Ljava/lang/String;)V");
- if (startMeth == NULL) {
- ALOGE("JavaVM unable to find main() in '%s'\n", className);
-
- } else {
- env->CallStaticVoidMethod(startClass, startMeth, strArray);
-
- #if 0
- if (env->ExceptionCheck())
- threadExitUncaughtException(env);
- #endif
- }
- }
- free(slashClassName);
-
- ALOGD("Shutting down VM\n");
- if (mJavaVM->DetachCurrentThread() != JNI_OK)
- ALOGW("Warning: unable to detach main thread\n");
- if (mJavaVM->DestroyJavaVM() != 0)
- ALOGW("Warning: VM did not shut down cleanly\n");
- }
该函数完成操作:
1, onVmCreated(env);----- >创建虚拟机
2, JNIEnv* env; ---- > JNI环境的初始化
3, env->CallStaticVoidMethod(startClass, startMeth, strArray); ----- >最终函数与上述步骤中的runtime.start(com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit)对应。
4, 至此走到---- ZygoteInit.java----main()
ZygoteInit.java ---main()----- >java世界准备已经完成,欢迎来到java世界。
- public static void main(String argv[]) {
- try {
-
- SamplingProfilerIntegration.start();
-
- registerZygoteSocket();
- EventLog.writeEvent(LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_PRELOAD_START,
- SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
- preload();
- EventLog.writeEvent(LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_PRELOAD_END,
- SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
-
-
- SamplingProfilerIntegration.writeZygoteSnapshot();
-
-
- gc();
-
-
- if (argv.length != 2) {
- throw new RuntimeException(argv[0] + USAGE_STRING);
- }
-
- if (argv[1].equals("start-system-server")) {
- startSystemServer();
- } else if (!argv[1].equals("")) {
- throw new RuntimeException(argv[0] + USAGE_STRING);
- }
-
- Log.i(TAG, "Accepting command socket connections");
-
- if (ZYGOTE_FORK_MODE) {
- runForkMode();
- } else {
- runSelectLoopMode();
- }
-
- closeServerSocket();
- } catch (MethodAndArgsCaller caller) {
- caller.run();
- } catch (RuntimeException ex) {
- Log.e(TAG, "Zygote died with exception", ex);
- closeServerSocket();
- throw ex;
- }
- }
该函数重点完成如下3项工作:
1, registerZygoteSocket();
2, startSystemServer();----- > 核心方法,Zygote进程一分为二,此处分裂出一个system_server进程。
3, 至此system_server进程进入SystemServer.java---- >main()
先看下startSystemServer()方法:
- private static boolean startSystemServer()
- throws MethodAndArgsCaller, RuntimeException {
-
- String args[] = {
- "--setuid=1000",
- "--setgid=1000",
- "--setgroups=1001,1002,1003,1004,1005,1006,1007,1008,1009,1010,1018,3001,3002,3003,3006,3007",
- "--capabilities=130104352,130104352",
- "--runtime-init",
- "--nice-name=system_server",
- "com.android.server.SystemServer",
- };
- ZygoteConnection.Arguments parsedArgs = null;
-
- int pid;
-
- try {
- parsedArgs = new ZygoteConnection.Arguments(args);
- ZygoteConnection.applyDebuggerSystemProperty(parsedArgs);
- ZygoteConnection.applyInvokeWithSystemProperty(parsedArgs);
-
-
- pid = Zygote.forkSystemServer(
- parsedArgs.uid, parsedArgs.gid,
- parsedArgs.gids,
- parsedArgs.debugFlags,
- null,
- parsedArgs.permittedCapabilities,
- parsedArgs.effectiveCapabilities);
- } catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
- throw new RuntimeException(ex);
- }
-
-
- if (pid == 0) {
- handleSystemServerProcess(parsedArgs);
- }
-
- return true;
- }
com.android.server.SystemServer的创建,预示着SystemServer的的正式启动,自此Zygote一分为二。Zygote将系统服务交给SystemServer统一管理。而zygote则负责java运行时环境和Dalvik虚拟机的管理工作。
4.3,systemserver启动
system_server进程是android的第二大进程,其余zygote紧密联系,若其中任何一个进程死掉,就会导致系统死掉,其启动过程包含两个阶段Main()----- >init1()和init2()。
Init1(),为system_server的第一阶段SystemServer.java--- >Init1()的本地实现在com_android_server_SystemServer.cpp中。
先看frameworks\base\services\java\com\android\server\SystemServer.java的main()函数。
- native public static void init1(String[] args);
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- if (System.currentTimeMillis() < EARLIEST_SUPPORTED_TIME) {
-
-
-
-
-
- Slog.w(TAG, "System clock is before 1970; setting to 1970.");
- SystemClock.setCurrentTimeMillis(EARLIEST_SUPPORTED_TIME);
- }
-
- if (SamplingProfilerIntegration.isEnabled()) {
- SamplingProfilerIntegration.start();
- timer = new Timer();
- timer.schedule(new TimerTask() {
- @Override
- public void run() {
- SamplingProfilerIntegration.writeSnapshot("system_server", null);
- }
- }, SNAPSHOT_INTERVAL, SNAPSHOT_INTERVAL);
- }
-
-
- dalvik.system.VMRuntime.getRuntime().clearGrowthLimit();
-
-
-
- VMRuntime.getRuntime().setTargetHeapUtilization(0.8f);
-
- System.loadLibrary("android_servers");
- init1(args);
- }
-
- public static final void init2() {
- Slog.i(TAG, "Entered the Android system server!");
- Thread thr = new ServerThread();
- thr.setName("android.server.ServerThread");
- thr.start();
- }
其中init1()的本地实现在com_android_server_SystemServer.cpp中:
- static void android_server_SystemServer_init1(JNIEnv* env, jobject clazz)
- {
- system_init();
- }
system_init()在frameworks\base\cmds\system_server\library\system_init.cpp中:
- extern "C" status_t system_init()
- {
- ALOGI("Entered system_init()");
-
- sp<ProcessState> proc(ProcessState::self());
-
- sp<IServiceManager> sm = defaultServiceManager();
- ALOGI("ServiceManager: %p\n", sm.get());
-
- sp<GrimReaper> grim = new GrimReaper();
- sm->asBinder()->linkToDeath(grim, grim.get(), 0);
-
- char propBuf[PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX];
- property_get("system_init.startsurfaceflinger", propBuf, "1");
- if (strcmp(propBuf, "1") == 0) {
-
- SurfaceFlinger::instantiate();
- }
-
- property_get("system_init.startsensorservice", propBuf, "1");
- if (strcmp(propBuf, "1") == 0) {
-
- SensorService::instantiate();
- }
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- ALOGI("System server: starting Android runtime.\n");
- AndroidRuntime* runtime = AndroidRuntime::getRuntime();
-
- ALOGI("System server: starting Android services.\n");
- JNIEnv* env = runtime->getJNIEnv();
- if (env == NULL) {
- return UNKNOWN_ERROR;
- }
- jclass clazz = env->FindClass("com/android/server/SystemServer");
- if (clazz == NULL) {
- return UNKNOWN_ERROR;
- }
- jmethodID methodId = env->GetStaticMethodID(clazz, "init2", "()V");
- if (methodId == NULL) {
- return UNKNOWN_ERROR;
- }
- env->CallStaticVoidMethod(clazz, methodId);
-
- ALOGI("System server: entering thread pool.\n");
- ProcessState::self()->startThreadPool();
- IPCThreadState::self()->joinThreadPool();
- ALOGI("System server: exiting thread pool.\n");
-
- return NO_ERROR;
- }
再回到SystemServer.java的main()中的init2():init2()将操作交给了内部类ServerThread处理,看起run()函数:
- public void run() {
- EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.BOOT_PROGRESS_SYSTEM_RUN,
- SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
-
- Looper.prepare();
-
- android.os.Process.setThreadPriority(
- android.os.Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_FOREGROUND);
-
- .......
-
-
- AccountManagerService accountManager = null;
- ContentService contentService = null;
- LightsService lights = null;
- PowerManagerService power = null;
- BatteryService battery = null;
- VibratorService vibrator = null;
- AlarmManagerService alarm = null;
- NetworkManagementService networkManagement = null;
- NetworkStatsService networkStats = null;
- NetworkPolicyManagerService networkPolicy = null;
- ConnectivityService connectivity = null;
- WifiP2pService wifiP2p = null;
- WifiService wifi = null;
- NsdService serviceDiscovery= null;
- IPackageManager pm = null;
- Context context = null;
- WindowManagerService wm = null;
- BluetoothService bluetooth = null;
- BluetoothA2dpService bluetoothA2dp = null;
- DockObserver dock = null;
- UsbService usb = null;
- SerialService serial = null;
- UiModeManagerService uiMode = null;
- RecognitionManagerService recognition = null;
- ThrottleService throttle = null;
- NetworkTimeUpdateService networkTimeUpdater = null;
- CommonTimeManagementService commonTimeMgmtService = null;
- InputManagerService inputManager = null;
-
-
- DeviceStorageMonitorService.freeSpace();
-
- .......
- ServiceManager.addService("xxx",XXX);
- .......
-
- DevicePolicyManagerService devicePolicy = null;
- StatusBarManagerService statusBar = null;
- InputMethodManagerService imm = null;
- AppWidgetService appWidget = null;
- NotificationManagerService notification = null;
- WallpaperManagerService wallpaper = null;
- LocationManagerService location = null;
- CountryDetectorService countryDetector = null;
- TextServicesManagerService tsms = null;
- LockSettingsService lockSettings = null;
- DreamManagerService dreamy = null;
-
- ......
-
-
- final Context contextF = context;
- final BatteryService batteryF = battery;
- final NetworkManagementService networkManagementF = networkManagement;
- final NetworkStatsService networkStatsF = networkStats;
- final NetworkPolicyManagerService networkPolicyF = networkPolicy;
- final ConnectivityService connectivityF = connectivity;
- final DockObserver dockF = dock;
- final UsbService usbF = usb;
- final ThrottleService throttleF = throttle;
- final UiModeManagerService uiModeF = uiMode;
- final AppWidgetService appWidgetF = appWidget;
- final WallpaperManagerService wallpaperF = wallpaper;
- final InputMethodManagerService immF = imm;
- final RecognitionManagerService recognitionF = recognition;
- final LocationManagerService locationF = location;
- final CountryDetectorService countryDetectorF = countryDetector;
- final NetworkTimeUpdateService networkTimeUpdaterF = networkTimeUpdater;
- final CommonTimeManagementService commonTimeMgmtServiceF = commonTimeMgmtService;
- final TextServicesManagerService textServiceManagerServiceF = tsms;
- final StatusBarManagerService statusBarF = statusBar;
- final DreamManagerService dreamyF = dreamy;
- final InputManagerService inputManagerF = inputManager;
- final BluetoothService bluetoothF = bluetooth;
-
-
- ActivityManagerService.self().systemReady(new Runnable() {
- public void run() {
- Slog.i(TAG, "Making services ready");
-
- if (!headless) startSystemUi(contextF);
- try {
- if (batteryF != null) batteryF.systemReady();
- } catch (Throwable e) {
- reportWtf("making Battery Service ready", e);
- }
- try {
- if (networkManagementF != null) networkManagementF.systemReady();
- } catch (Throwable e) {
- reportWtf("making Network Managment Service ready", e);
- }
- try {
- if (networkStatsF != null) networkStatsF.systemReady();
- } catch (Throwable e) {
- reportWtf("making Network Stats Service ready", e);
- }
- try {
- if (networkPolicyF != null) networkPolicyF.systemReady();
- } catch (Throwable e) {
- reportWtf("making Network Policy Service ready", e);
- }
- try {
- if (connectivityF != null) connectivityF.systemReady();
- } catch (Throwable e) {
- reportWtf("making Connectivity Service ready", e);
- }
- try {
- if (dockF != null) dockF.systemReady();
- } catch (Throwable e) {
- reportWtf("making Dock Service ready", e);
- }
- try {
- if (usbF != null) usbF.systemReady();
- } catch (Throwable e) {
- reportWtf("making USB Service ready", e);
- }
- try {
- if (uiModeF != null) uiModeF.systemReady();
- } catch (Throwable e) {
- reportWtf("making UI Mode Service ready", e);
- }
- try {
- if (recognitionF != null) recognitionF.systemReady();
- } catch (Throwable e) {
- reportWtf("making Recognition Service ready", e);
- }
- Watchdog.getInstance().start();
-
-
-
-
- try {
- if (appWidgetF != null) appWidgetF.systemReady(safeMode);
- } catch (Throwable e) {
- reportWtf("making App Widget Service ready", e);
- }
- try {
- if (wallpaperF != null) wallpaperF.systemReady();
- } catch (Throwable e) {
- reportWtf("making Wallpaper Service ready", e);
- }
- try {
- if (immF != null) immF.systemReady(statusBarF);
- } catch (Throwable e) {
- reportWtf("making Input Method Service ready", e);
- }
- try {
- if (locationF != null) locationF.systemReady();
- } catch (Throwable e) {
- reportWtf("making Location Service ready", e);
- }
- try {
- if (countryDetectorF != null) countryDetectorF.systemReady();
- } catch (Throwable e) {
- reportWtf("making Country Detector Service ready", e);
- }
- try {
- if (throttleF != null) throttleF.systemReady();
- } catch (Throwable e) {
- reportWtf("making Throttle Service ready", e);
- }
- try {
- if (networkTimeUpdaterF != null) networkTimeUpdaterF.systemReady();
- } catch (Throwable e) {
- reportWtf("making Network Time Service ready", e);
- }
- try {
- if (commonTimeMgmtServiceF != null) commonTimeMgmtServiceF.systemReady();
- } catch (Throwable e) {
- reportWtf("making Common time management service ready", e);
- }
- try {
- if (textServiceManagerServiceF != null) textServiceManagerServiceF.systemReady();
- } catch (Throwable e) {
- reportWtf("making Text Services Manager Service ready", e);
- }
- try {
- if (dreamyF != null) dreamyF.systemReady();
- } catch (Throwable e) {
- reportWtf("making DreamManagerService ready", e);
- }
- try {
- if (inputManagerF != null) inputManagerF.systemReady(bluetoothF);
- } catch (Throwable e) {
- reportWtf("making InputManagerService ready", e);
- }
- }
- });
-
-
- (new Thread(new WakelockMonitor(power))).start();
-
- ......
-
- Looper.loop();
- Slog.d(TAG, "System ServerThread is exiting!");
- }
该函数有3个重要功能:
1,ServiceManager.addService("xxx",XXX),将系统服务注册进去。
2,systemReady(),告诉已经实现该接口servers,系统已经启动OK。
3,WakelockMonitor的启动。
至此,systemserver的启动工作已经完成。
4.4,launcher启动
桌面launcher即Home:
1)源码:ActivityManagerService.java为入口,packages/apps/launcher*实现
2)说明:系统启动成功后SystemServer使用xxx.systemReady()通知各个服务,系统已经就绪,桌面程序Home就是在ActivityManagerService.systemReady()通知的过程中建立的,最终调用startHomeActivityLocked()启动launcher。Home在((ActivityManagerService)ActivityManagerNative.getDefault()).systemReady(.)。函数调用的过程中启动,其中systemReady()的参数是一段callback代码,如上面灰色显示的部分。这个函数的实现部分在文件:ActivityManagerService.java中。
先看ActivityManagerService.java的systemReady():
- public void systemReady(final Runnable goingCallback) {
-
- ..
-
- retrieveSettings();
-
- if (goingCallback != null) goingCallback.run();
-
- synchronized (this) {
- if (mFactoryTest != SystemServer.FACTORY_TEST_LOW_LEVEL) {
- try {
- List apps = AppGlobals.getPackageManager().
- getPersistentApplications(STOCK_PM_FLAGS);
- if (apps != null) {
- int N = apps.size();
- int i;
- for (i=0; i<N; i++) {
- ApplicationInfo info
- = (ApplicationInfo)apps.get(i);
- if (info != null &&
- !info.packageName.equals("android")) {
- addAppLocked(info, false);
- }
- }
- }
- } catch (RemoteException ex) {
-
- }
- }
-
-
- mBooting = true;
-
- try {
- if (AppGlobals.getPackageManager().hasSystemUidErrors()) {
- Message msg = Message.obtain();
- msg.what = SHOW_UID_ERROR_MSG;
- mHandler.sendMessage(msg);
- }
- } catch (RemoteException e) {
- }
-
- mMainStack.resumeTopActivityLocked(null);
- }
- }
跳转至launcher的操作由resumeTopActivityLocked()完成,其实现在ActivityStack.java里的resumeTopActivityLocked()。
- final ActivityManagerService mService;
- final boolean resumeTopActivityLocked(ActivityRecord prev, Bundle options) {
-
- ActivityRecord next = topRunningActivityLocked(null);
-
-
-
- final boolean userLeaving = mUserLeaving;
- mUserLeaving = false;
-
- if (next == null) {
-
-
- if (mMainStack) {
- ActivityOptions.abort(options);
- return mService.startHomeActivityLocked(0);
- }
- }
从上述代码可以看出其实是走到了mService.startHomeActivityLocked(0),而这里的mService也就是ActivityManagerService.java,再次回到ActivityManagerService.java的startHomeActivityLocked(0),至此launcher启动完成。
4.5,lockscreen启动
源码:frameworks/policies/base/phone/com/android/internal/policy/impl/*lock*
说明:系统启动成功后SystemServer调用wm.systemReady()通知WindowManagerService,进而调用PhoneWindowManager,最终通过LockPatternKeyguardView显示解锁界面,跟踪代码可以看到解锁界面并不是一个Activity,这是只是向特定层上绘图,其代码了存放在特殊的位置。此处不再详细分析。
frameworks\base\policy\src\com\android\internal\policy\impl\PhoneWindowManager.java的systemReady()方法:
-
- public void systemReady() {
- if (mKeyguardMediator != null) {
-
- mKeyguardMediator.onSystemReady();
- }
- synchronized (mLock) {
- updateOrientationListenerLp();
- mSystemReady = true;
- mHandler.post(new Runnable() {
- public void run() {
- updateSettings();
- }
- });
- }
- }
第一步,告诉锁屏控制器,系统已经启动完成,接下来有锁屏处理。 frameworks\base\policy\src\com\android\internal\policy\impl\KeyguardViewMediator.java:
- public void onSystemReady() {
- synchronized (this) {
- if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "onSystemReady");
- mSystemReady = true;
- doKeyguardLocked();
- }
- }
再看其doKeyguardLocked()方法:
- private void doKeyguardLocked() {
-
-
- if(engModeFlag){
- Log.d(TAG, "show engmode!");
- engModeFlag = false;
- return ;
- }
-
-
- if (!mExternallyEnabled) {
- if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "doKeyguard: not showing because externally disabled");
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- return;
- }
-
-
- if (mKeyguardViewManager.isShowing()) {
- if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "doKeyguard: not showing because it is already showing");
- return;
- }
-
- final boolean provisioned = mUpdateMonitor.isDeviceProvisioned();
- final boolean lockedOrMissing = isSimLockedOrMissing();
-
- if (!lockedOrMissing && !provisioned) {
- if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "doKeyguard: not showing because device isn't provisioned"
- + " and the sim is not locked or missing");
- return;
- }
-
- if (mLockPatternUtils.isLockScreenDisabled() && !lockedOrMissing) {
- if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "doKeyguard: not showing because lockscreen is off");
- return;
- }
-
- if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "doKeyguard: showing the lock screen");
- showLocked();
- }
至此,锁屏启动完成。
4.6,othersapps启动
系统启动完成后,launcher会加载系统已经安装的apk,并显示在launcher上。
至此,android启动完成。
5,android启动动画效果剖析
在android启动的过程中我们通常可以看到若干个启动画面,均代表着不同的启动阶段,接下来根据启动阶段分析启动画面。
uboot启动:会有一帧 uboot logo。
kernel启动:会有一帧kernel logo。(默认不显示,其控制宏是默认关闭的)
android启动:会有一帧静态图片+一个闪动的图片序列(即开机动画)。
通常情况下,我们在分析android的开机动画效果时,很少去分析uboot logo和kernel logo,因为ubootlogo 属于uboot阶段,kernel logo 属于linux范围。正常情况下,我们在down版本,烧到手机里去时,会吧logo.bmp加进去,这是系统的处理是:uboot logo,kernel logo,android static logo是同一张图片,即我们加的logo.bmp。
双framebuffer显示logo机制分析:本来一直走的是一级logo显示,从uboot logo一直持续到系统动画,但考虑期间时间偏长,欲采用标准三级logo。1、uboot logo 2、kernle logo 3 initlogo.rle 最后动画bootanimation.zip。但是kernel 对framebuffer修改较大,故考虑在uboot开始和结束显示两张logo(第二幅logo显示调用在theKernel()跳入内核函数之前),kernel跳过。uboot 直接刷屏显示第二幅logo 动作过慢,效果不佳,经考虑采用双buffer策略。思路:
1.原来只要显示一张uboot logo :把nand 中boot.logo 拷贝至lcd_base+fbsize处,然后搬至lcd_base显示;
2.现在创建第二个framebuffer于lcd_base+2*fbsize处,在显示第二幅logo前把nand 中第二幅logo 仍然拷贝至lcd_base+fbsize处,然后搬至lcd_base+2*fbsize第二个framebuffer基地址;
3.把第二个framebuffer基地址告诉lcd 控制寄存器,更新framebuffer基地址;
4.但在kernel中,寄存器仍然会指向第一个framebuffer基地址,那么第二幅logo显示犹如昙花一现啊,不过这个问题好解决,既然第二幅logo已经搬进了第二个framebuffer那,那么只要在进入内核前做一个memcpy就好了。
注:logo是bmp格式,在拷贝前需要进行相应的解析,参考uboot给的解析代码,自定义函数。
5.1,uboot logo
以正常模式启动分析uboot logo。即normal_mode.c根据前部分的分析可知,流程会走至normal_nand_mode.c的vlx_nand_boot()函数。
-
- off=part->offset;
- nand = &nand_info[dev->id->num];
-
- size = 1<<19;
- char * bmp_img = malloc(size);
- if(!bmp_img){
- printf("not enough memory for splash image\n");
- return;
- }
- ret = nand_read_offset_ret(nand, off, &size, (void *)bmp_img, &off);
- if(ret != 0){
- printf("function: %s nand read error %d\n", __FUNCTION__, ret);
- return;
- }
-
- lcd_display_logo(backlight_set,(ulong)bmp_img,size);
即由lcd_display_logo()完成相关操作。该函数在normal_mode.c中定义。
- void lcd_display_logo(int backlight_set,ulong bmp_img,size_t size)
- {
- #ifdef CONFIG_SPLASH_SCREEN
- extern int lcd_display_bitmap(ulong bmp_image, int x, int y);
- extern void lcd_display(void);
- extern void *lcd_base;
- extern void Dcache_CleanRegion(unsigned int addr, unsigned int length);
- extern void set_backlight(uint32_t value);
- if(backlight_set == BACKLIGHT_ON){
- lcd_display_bitmap((ulong)bmp_img, 0, 0);
- #if defined(CONFIG_SC8810) || defined(CONFIG_SC8825) || defined(CONFIG_SC8830)
- Dcache_CleanRegion((unsigned int)(lcd_base), size);
- #endif
- lcd_display();
- set_backlight(255);
- }else{
- memset((unsigned int)lcd_base, 0, size);
- #if defined(CONFIG_SC8810) || defined(CONFIG_SC8825) || defined(CONFIG_SC8830)
- Dcache_CleanRegion((unsigned int)(lcd_base), size);
- #endif
- lcd_display();
- }
- #endif
- }
5.2,kernel logo
kernel logo 属于linux系统自带的logo机制,由于在android平台其显示默认是关闭的,此处不做多的分析,详细可参考博文:Android系统的开机画面显示过程分析 ,该博文只分析了启动过程的 kernel logo,android logo anim。
相关代码:
/kernel/drivers/video/fbmem.c
/kernel/drivers/video/logo/logo.c
/kernel/drivers/video/logo/Kconfig
/kernel/include/linux/linux_logo.h
- static int nologo;
- module_param(nologo, bool, 0);
- MODULE_PARM_DESC(nologo, "Disables startup logo");
-
-
-
-
- const struct linux_logo * __init_refok fb_find_logo(int depth)
- {
- const struct linux_logo *logo = NULL;
- if (nologo)
- return NULL;
- ......
- }
5.3,android logo anim
Android 系统启动后,init.c中main()调用queue_builtin_action(console_init_action, "console_init")时会根据console_init_action函数调用load_565rle_image()函数读取/initlogo.rle(一张565 rle压缩的位图),如果读取成功,则在/dev/graphics/fb0显示Logo图片;如果读取失败,则将/dev/tty0设为TEXT模式, 并打开/dev/tty0,输出文本“A N D R I O D”字样。
- static int console_init_action(int nargs, char **args)
- {
- int fd;
- char tmp[PROP_VALUE_MAX];
-
- if (console[0]) {
- snprintf(tmp, sizeof(tmp), "/dev/%s", console);
- console_name = strdup(tmp);
- }
-
- fd = open(console_name, O_RDWR);
- if (fd >= 0)
- have_console = 1;
- close(fd);
-
- if( load_565rle_image(INIT_IMAGE_FILE) ) {
- fd = open("/dev/tty0", O_WRONLY);
- if (fd >= 0) {
- const char *msg;
- msg = "\n"
- "\n"
- "\n"
- "\n"
- "\n"
- "\n"
- "\n"
- "\n"
- "\n"
- "\n"
- "\n"
- "\n"
- "\n"
- "\n"
- " A N D R O I D ";
- write(fd, msg, strlen(msg));
- close(fd);
- }
- }
- return 0;
- }
由此调用logo.c 的load_565rle_image()函数。
- int load_565rle_image(char *fn)
- {
- struct FB fb;
- struct stat s;
- unsigned short *data, *bits, *ptr;
- unsigned count, max;
- int fd;
-
- if (vt_set_mode(1))
- return -1;
-
- fd = open(fn, O_RDONLY);
- if (fd < 0) {
- ERROR("cannot open '%s'\n", fn);
- goto fail_restore_text;
- }
-
- if (fstat(fd, &s) < 0) {
- goto fail_close_file;
- }
-
- data = mmap(0, s.st_size, PROT_READ, MAP_SHARED, fd, 0);
- if (data == MAP_FAILED)
- goto fail_close_file;
-
- if (fb_open(&fb))
- goto fail_unmap_data;
-
- max = fb_width(&fb) * fb_height(&fb);
- ptr = data;
- count = s.st_size;
- bits = fb.bits;
- while (count > 3) {
- unsigned n = ptr[0];
- if (n > max)
- break;
- android_memset16(bits, ptr[1], n << 1);
- bits += n;
- max -= n;
- ptr += 2;
- count -= 4;
- }
-
- munmap(data, s.st_size);
- fb_update(&fb);
- fb_close(&fb);
- close(fd);
- unlink(fn);
- return 0;
-
- fail_unmap_data:
- munmap(data, s.st_size);
- fail_close_file:
- close(fd);
- fail_restore_text:
- vt_set_mode(0);
- return -1;
- }
该图片格式是565RLE image format格式的,可用工具将bmp格式转化为rle格式。之后会有init.rc 并发开机动画。
相关文件:
/frameworks/base/cmds/bootanimation/BootAnimation.h
/frameworks/base/cmds/bootanimation/BootAnimation.cpp
/frameworks/base/cmds/bootanimation/bootanimation_main.cpp
/system/core/init/init.c
/system/core/rootdir/init.rc
init.c解析init.rc(其中定义服务:“service bootanim /system/bin/bootanimation”),bootanim 服务由SurfaceFlinger.readyToRun()(property_set("ctl.start", "bootanim");)执行开机动画、bootFinished()(property_set("ctl.stop", "bootanim");)执行停止开机动画。 BootAnimation.h和BootAnimation.cpp文件放到了/frameworks/base/cmds /bootanimation目录下了,增加了一个入口文件bootanimation_main.cpp。Android.mk文件中可以看到,将开机 动画从原来的SurfaceFlinger里提取出来了,生成可执行文件:bootanimation。Android.mk代码如下:
-
- LOCAL_PATH:= $(call my-dir)
- include $(CLEAR_VARS)
- LOCAL_SRC_FILES:= \
- bootanimation_main.cpp \
- BootAnimation.cpp
- # need "-lrt" on Linux simulator to pick up clock_gettime
- ifeq ($(TARGET_SIMULATOR),true)
- ifeq ($(HOST_OS),linux)
- LOCAL_LDLIBS += -lrt
- endif
- endif
- LOCAL_SHARED_LIBRARIES := \
- libcutils \
- libutils \
- libui \
- libcorecg \
- libsgl \
- libEGL \
- libGLESv1_CM \
- libmedia
- LOCAL_C_INCLUDES := \
- $(call include-path-for, corecg graphics)
- LOCAL_MODULE:= bootanimation
- include $(BUILD_EXECUTABLE)
-
备注:
1,adb shell后,可以直接运行“bootanimation”来重新看开机动画,它会一直处于动画状态,而不会停止。
2,adb shell后,命令“setprop ctl.start bootanim”执行开机动画;命令“getprop ctl.start bootanim”停止开机动画。这两句命令分别对应SurfaceFlinger.cpp的两句语 句:property_set("ctl.start", "bootanim");和property_set("ctl.stop", "bootanim")。
至此android启动动画分析结束。








 本文详细剖析了Android系统的启动过程,从Bootloader启动、Linux启动到Android启动的各个阶段,包括init进程、zygote服务、systemserver服务、launcher桌面和lockscreen的启动。深入分析了Bootloader的定义、种类,特别是U-Boot的启动流程,以及在Android启动过程中的logo显示机制。
本文详细剖析了Android系统的启动过程,从Bootloader启动、Linux启动到Android启动的各个阶段,包括init进程、zygote服务、systemserver服务、launcher桌面和lockscreen的启动。深入分析了Bootloader的定义、种类,特别是U-Boot的启动流程,以及在Android启动过程中的logo显示机制。

















 7106
7106

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








