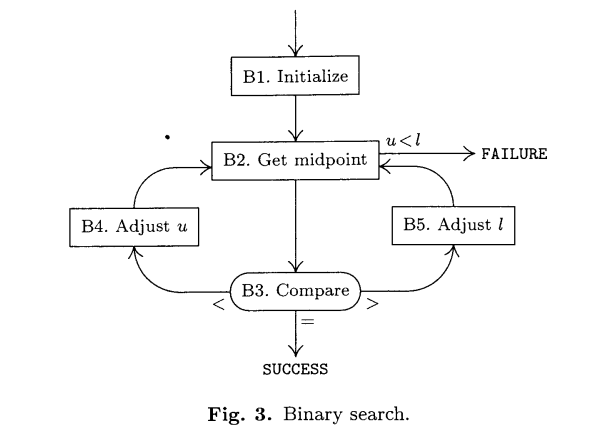
Algorithm B
Algorithm B (Binary search). Given a table of records R1R2 … RN whose
keys are in increasing order K1 < K2 < … < KN, this algorithm searches for a
given argument K.
B1. [Initialize.] Set I <– 1, u <– N.
B2. [Get midpoint.] (At this point we know that if K is in the table, it satisfies
Kl <= K <= Ku. A more precise statement of the situation appears in exer-
cise 1 below.) If u < I, the algorithm terminates unsuccessfully. Otherwise,
set i <– floor((I + u)/2), the approximate midpoint of the relevant table area.
B3. [Compare.] If K < Ki, go to B4; if K > Ki, go to B5; and if K = Ki, the
algorithm terminates successfully.
B4. [Adjust u.] Set u <– i-1 and return to B2.
B5. [Adjust I.] Set I <– i+1 and return to B2. |
Flow diagram
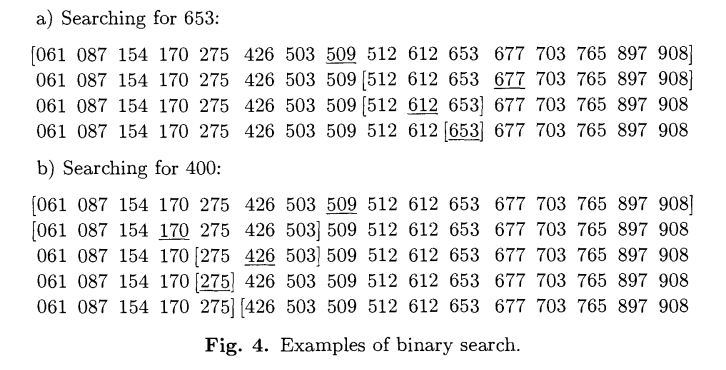
Data table
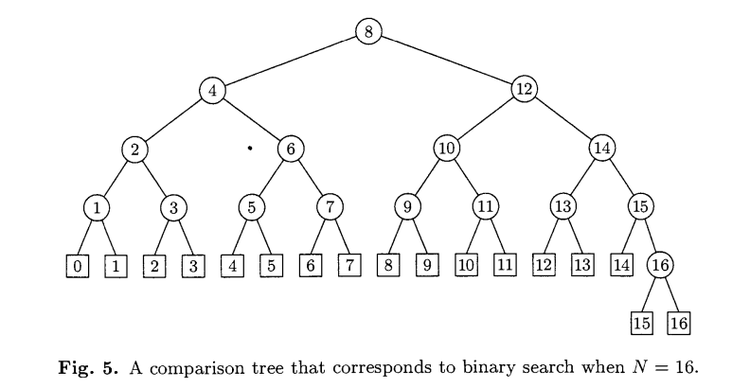
Comparison tree
Java program
In this program, R1,…,RN were simplified to K1,…,KN.
/**
* Created with IntelliJ IDEA.
* User: 1O1O
* Date: 12/10/13
* Time: 6:52 PM
* :)~
* Binary Search:Searching
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int N = 16;
int[] K = new int[17];
/*Prepare the ordered data table*/
K[1] = 61;
K[2] = 87;
K[3] = 154;
K[4] = 170;
K[5] = 275;
K[6] = 426;
K[7] = 503;
K[8] = 509;
K[9] = 512;
K[10] = 612;
K[11] = 653;
K[12] = 677;
K[13] = 703;
K[14] = 765;
K[15] = 897;
K[16] = 908;
/*Output sorted Ks*/
System.out.println("Sorted Ks:");
for(int i=1; i<=N; i++){
System.out.println(i+":"+K[i]);
}
System.out.println();
/*Kernel of the Algorithm!*/
int Key = 653; /*Key to be found*/
int i;
int l = 1;
int u = N;
do{
if(u < l){
System.out.println("Outputs: "+Key+" not found.");
break;
}else {
i = (int)Math.floor((double)(l+u)/2);
}
if(Key < K[i]){
u = i-1;
}else if(Key > K[i]){
l = i+1;
}else{
System.out.println("Outputs: "+Key+" in K["+i+"].");
break;
}
}while (true);
}
}Outputs
Sorted Ks:
1:61
2:87
3:154
4:170
5:275
6:426
7:503
8:509
9:512
10:612
11:653
12:677
13:703
14:765
15:897
16:908
Outputs: 653 in K[11].Reference
<< The art of computer programming: Sorting and Searching >> VOLUME 3, DONALD E. KNUTH























 1919
1919

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








