
目录
1、二叉树搜索模型实现及应用场景
1. 二叉搜索树Key模型及其应用
K模型:K模型即只有key作为关键码,结构中只需要存储Key即可,关键码即为需要搜索到的值。
比如:给一个单词word,判断该单词是否拼写正确,具体方式如下: 以词库中所有单词集合中的每个单词作为key,构建一棵二叉搜索树 在二叉搜索树中检索该单词是否存在,存在则拼写正确,不存在则拼写错误。
Key模型的实现(普通二叉搜索数的实现):
template<class K> class BSTreeNode { public: BSTreeNode(const K& key) :_key(key) , _left(nullptr) , _right(nullptr) { } BSTreeNode<K>* _left; BSTreeNode<K>* _right; K _key; }; //key template<class K> class BinarySearchTree { typedef BSTreeNode<K> Node; int _depth(Node* root) const { if (root == nullptr) { return 0; } int leftDepth = _depth(root->_left) + 1; int rightDepth = _depth(root->_right) + 1; return leftDepth > rightDepth ? leftDepth : rightDepth; } int _nodeCount(Node* root) const { if (root == nullptr) { return 0; } int leftCount = _nodeCount(root->_left) + 1; int rightCount = _nodeCount(root->_right) + 1; return leftCount + rightCount - 1; } int _leafSize(Node* root) const { if (root == nullptr) { return 0; } if (root->_left == nullptr && root->_right == nullptr) { return 1; } int leftSize = _leafSize(root->_left); int rightSize = _leafSize(root->_right); return leftSize + rightSize; } void _destory(Node*& root) { if (root == nullptr) { return; } _destory(root->_left); _destory(root->_right); delete root; root = nullptr; } Node* _copy(Node* root) { if (root == nullptr) { return nullptr; } Node* copyRoot = new Node(root->_key); copyRoot->_left = _copy(root->_left); copyRoot->_right = _copy(root->_right); return copyRoot; } public: /*BinarySearchTree() :_root(nullptr) { }*/ //拷贝构造也是构造,写了,编译器不在生成默认构造 //强制编译器生成默认构造 —— c++11用法,default BinarySearchTree() = default; BinarySearchTree(const BinarySearchTree<K>& bst) { _root = _copy(bst._root); } ~BinarySearchTree() { _destory(_root); } BinarySearchTree<K>& operator=(BinarySearchTree<K> bst) { std::swap(_root, bst._root); return *this; } int depth() const { return _depth(_root); } int nodeCount() const { return _nodeCount(_root); } int leafSize() const { return _leafSize(_root); } bool Insert(const K& key) { if (_root == nullptr) { _root = new Node(key); return true; } Node* cur = _root; Node* parent = nullptr; while (cur) { parent = cur; if (cur->_key > key) { cur = cur->_left; } else if (cur->_key < key) { cur = cur->_right; } else { return false; } } if (parent->_key > key) { parent->_left = new Node(key); return true; } else { parent->_right = new Node(key); return true; } } bool Find(const K& key) const { if (_root == nullptr) { return false; } Node* cur = _root; while (cur) { if (cur->_key > key) { cur = cur->_left; } else if (cur->_key < key) { cur = cur->_right; } else { return true; } } return false; } bool Erase(const K& key) { if (_root == nullptr) { return false; } Node* cur = _root; Node* parent = nullptr; while (cur) { if (cur->_key > key) { parent = cur; cur = cur->_left; } else if (cur->_key < key) { parent = cur; cur = cur->_right; } else { if (cur->_left == nullptr) { if (cur == _root) { _root = cur->_right; } else { if (cur == parent->_left) { parent->_left = cur->_right; } else { parent->_right = cur->_right; } } delete cur; cur = nullptr; return true; } else if (cur->_right == nullptr) { if (cur == _root) { _root = cur->_left; } else { if (cur == parent->_left) { parent->_left = cur->_left; } else { parent->_right = cur->_left; } } delete cur; cur = nullptr; return true; } else { //替换法删除 -- 右数最小节点 Node* replace = cur->_right; Node* replaceParent = cur; while (replace->_left != nullptr) { replaceParent = replace; replace = replace->_left; } std::swap(cur->_key, replace->_key); if (replaceParent->_left == replace) { replaceParent->_left = replace->_right; } else { replaceParent->_right = replace->_right; } delete replace; return true; } } } return false; } void InOrder() { _InOrder(_root); cout << endl; } bool FindR(const K& key) const { return _FindR(_root, key); } bool InsertR(const K& key) { if (_root == nullptr) { _root = new Node(key); return true; } else { return _InsertR(_root, key); } } bool EraseR(const K& key) { return _EraseR(_root, key); } private: bool _EraseR(Node*& root, const K& key) { if (root == nullptr) { return false; } if (key > root->_key) { return _EraseR(root->_right, key); } else if (key < root->_key) { return _EraseR(root->_left, key); } else { //删除数据 Node* del = root; if (root->_left == nullptr) { root = root->_right; } else if (root->_right == nullptr) { root = root->_left; } else { Node* replace = root->_right; while (replace->_left != nullptr) { replace = replace->_left; } std::swap(root->_key, replace->_key); return _EraseR(root->_right, key); } delete del; return true; } } bool _InsertR(Node*& root, const K& key) { if (root == nullptr) { root = new Node(key); return true; } if (key > root->_key) { return _InsertR(root->_right, key); } else if (key < root->_key) { return _InsertR(root->_left, key); } else { return false; } } bool _FindR(Node* root, const K& key) const { if (root == nullptr) { return false; } if (key > root->_key) { return _FindR(root->_right, key); } else if (key < root->_key) { return _FindR(root->_left, key); } else { return true; } } void _InOrder(Node* root) { if (root == nullptr) { return; } _InOrder(root->_left); cout << root->_key << " "; _InOrder(root->_right); } public: Node* GetRoot() { return _root; } void SetRoot(Node* root) { _root = root; } private: Node* _root = nullptr; }; class Solution { public: void InOrder(BSTreeNode<int>* root, vector<BSTreeNode<int>*>& vt) { if (root == nullptr) { return; } InOrder(root->_left, vt); vt.push_back(root); InOrder(root->_right, vt); } BSTreeNode<int>* Convert(BSTreeNode<int>* pRootOfTree) { vector<BSTreeNode<int>*> vt; vt.push_back(nullptr); InOrder(pRootOfTree, vt); vt.push_back(nullptr); for (size_t i = 1; i < vt.size() - 1; ++i) { vt[i]->_left = vt[i - 1]; vt[i]->_right = vt[i + 1]; } return vt[1]; } };
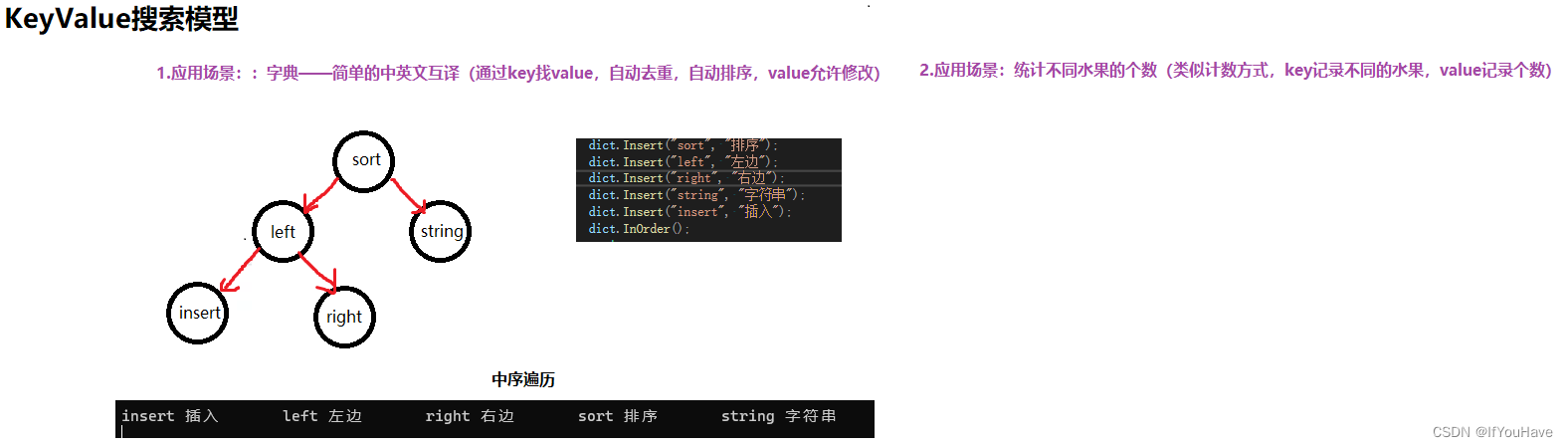
2. 二叉搜索树Key-Value模型及其应用
KV模型:每一个关键码key,都有与之对应的值Value,即的键值对。
该种方式在现实生活中非常常见: 比如英汉词典就是英文与中文的对应关系,通过英文可以快速找到与其对应的中文,英 文单词与其对应的中文就构成一种键值对; 再比如统计单词次数,统计成功后,给定单词就可快速找到其出现的次数,单词与其出 现次数就是就构成一种键值对。
template<class K,class V> class BSTreeNode { public: BSTreeNode(const K& key,const V& value) :_key(key) ,_value(value) , _left(nullptr) , _right(nullptr) { } BSTreeNode<K,V>* _left; BSTreeNode<K,V>* _right; K _key; V _value; }; //key template<class K, class V> class BinarySearchTree { typedef BSTreeNode<K,V> Node; void _destory(Node*& root) { if (root == nullptr) { return; } _destory(root->_left); _destory(root->_right); delete root; root = nullptr; } Node* _copy(Node* root) { if (root == nullptr) { return nullptr; } Node* copyRoot = new Node(root->_key); copyRoot->_left = _copy(root->_left); copyRoot->_right = _copy(root->_right); return copyRoot; } public: /*BinarySearchTree() :_root(nullptr) { }*/ //拷贝构造也是构造,写了,编译器不在生成默认构造 //强制编译器生成默认构造 —— c++11用法,default BinarySearchTree() = default; BinarySearchTree(const BinarySearchTree<K,V>& bst) { _root = _copy(bst._root); } ~BinarySearchTree() { _destory(_root); } BinarySearchTree<K,V>& operator=(BinarySearchTree<K,V> bst) { std::swap(_root, bst._root); return *this; } bool Insert(const K& key,const V& value) { if (_root == nullptr) { _root = new Node(key,value); return true; } Node* cur = _root; Node* parent = nullptr; while (cur) { parent = cur; if (cur->_key > key) { cur = cur->_left; } else if (cur->_key < key) { cur = cur->_right; } else { return false; } } if (parent->_key > key) { parent->_left = new Node(key, value); return true; } else { parent->_right = new Node(key, value); return true; } } Node* Find(const K& key) const { if (_root == nullptr) { return nullptr; } Node* cur = _root; while (cur) { if (cur->_key > key) { cur = cur->_left; } else if (cur->_key < key) { cur = cur->_right; } else { return cur; } } return nullptr; } bool Erase(const K& key) { if (_root == nullptr) { return false; } Node* cur = _root; Node* parent = nullptr; while (cur) { if (cur->_key > key) { parent = cur; cur = cur->_left; } else if (cur->_key < key) { parent = cur; cur = cur->_right; } else { if (cur->_left == nullptr) { if (cur == _root) { _root = cur->_right; } else { if (cur == parent->_left) { parent->_left = cur->_right; } else { parent->_right = cur->_right; } } delete cur; cur = nullptr; return true; } else if (cur->_right == nullptr) { if (cur == _root) { _root = cur->_left; } else { if (cur == parent->_left) { parent->_left = cur->_left; } else { parent->_right = cur->_left; } } delete cur; cur = nullptr; return true; } else { //替换法删除 -- 右数最小节点 Node* replace = cur->_right; Node* replaceParent = cur; while (replace->_left != nullptr) { replaceParent = replace; replace = replace->_left; } std::swap(cur->_key, replace->_key); if (replaceParent->_left == replace) { replaceParent->_left = replace->_right; } else { replaceParent->_right = replace->_right; } delete replace; return true; } } } return false; } void InOrder() { _InOrder(_root); cout << endl; } private: void _InOrder(Node* root) { if (root == nullptr) { return; } _InOrder(root->_left); cout << root->_key << " " << root->_value << " "; _InOrder(root->_right); } private: Node* _root = nullptr; }; void test() { BinarySearchTree<string, string> dict; dict.Insert("sort", "排序"); dict.Insert("left", "左边"); dict.Insert("right", "右边"); dict.Insert("string", "字符串"); dict.Insert("insert", "插入"); dict.InOrder(); string str; while (cin >> str) { BSTreeNode<string,string>* ret = dict.Find(str); if (ret != nullptr) { cout << "Find it :: " << str << "\t\tmean :: " << ret->_value << endl; } else { cout << "Not find it!!!" << endl; } } } void test1() { string arr[] = { "苹果", "苹果","香蕉","香蕉","梨" ,"西瓜","香蕉"}; BinarySearchTree<string, int> statCount; int value = 0; for (auto& e : arr) { auto ret = statCount.Find(e); if (ret) { ++ret->_value; } else { statCount.Insert(e, 1); } } statCount.InOrder(); }
2、二叉树OJ
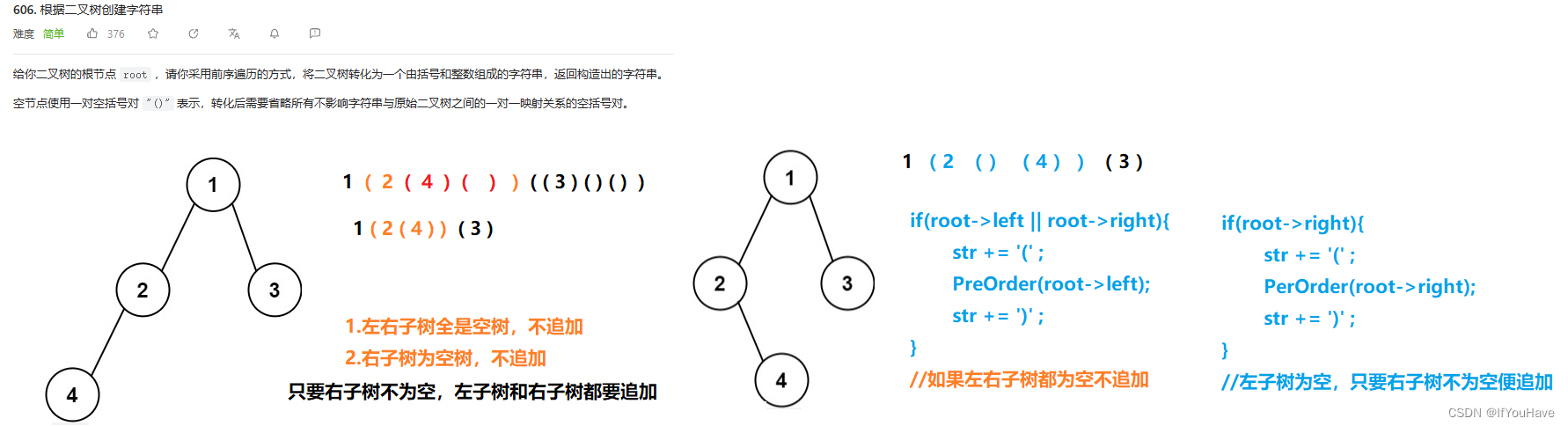
2.1 根据二叉树创建字符串
题目分析:
代码:
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: void PerOrder(TreeNode* root,string& str){ if(root == nullptr){ return; } str += to_string(root->val); if(root->left || root->right){ str += '('; PerOrder(root->left,str); str += ')'; } if(root->right){ str += '('; PerOrder(root->right,str); str += ')'; } } string tree2str(TreeNode* root) { string str; PerOrder(root,str); return str; } };
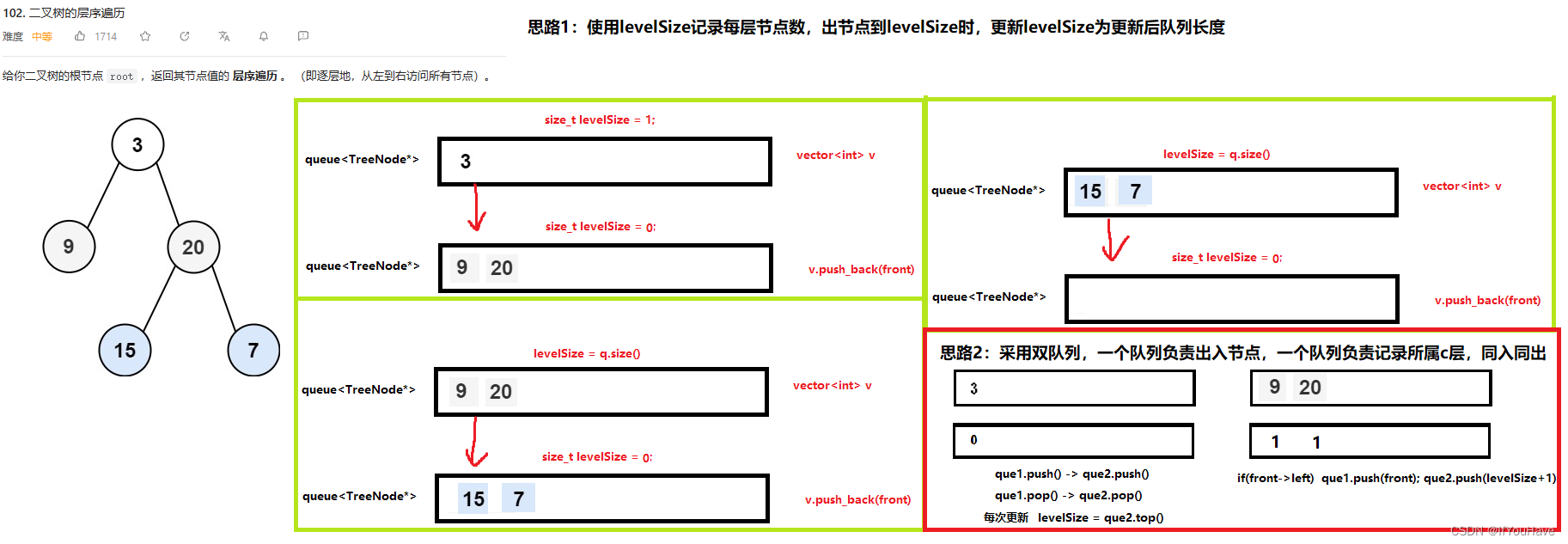
2.2 二叉树的层序遍历I
题目分析:
思路一代码:
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) { vector<vector<int>> vv; if (root == nullptr) return vv; queue<TreeNode*> q; q.push(root); while (!q.empty()) { vector<int> v; int sz = q.size(); while (sz--) { TreeNode* front = q.front(); v.push_back(front->val); q.pop(); if (front->left) q.push(front->left); if (front->right) q.push(front->right); } vv.push_back(v); } return vv; } };思路二代码:
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) { vector<vector<int>> vv; queue<TreeNode*> que1; queue<int> que2; size_t levelSize = 0; size_t newLevel = 0; if(root){ que1.push(root); que2.push(levelSize); } vector<int> v; while(!que1.empty()){ TreeNode* front = que1.front();que1.pop();// 15 17 newLevel = que2.front();que2.pop();// 2 if(levelSize != newLevel){ vv.push_back(v); v.clear(); levelSize = newLevel; } v.push_back(front->val);// [3] [9,20] if(front->left){ que1.push(front->left);// 15 17 que2.push(newLevel + 1);// 2 2 } if(front->right){ que1.push(front->right);// 20 que2.push(newLevel + 1);// 1 } } if(!v.empty()){ vv.push_back(v); } return vv; } };
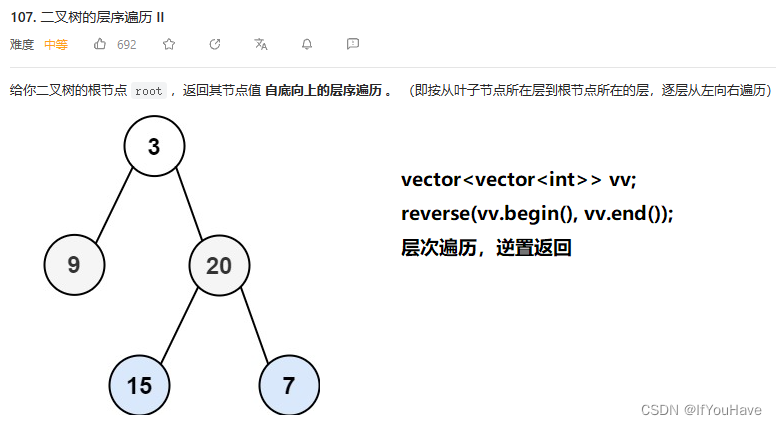
2.3 二叉树的层序遍历II
题目分析:
代码:
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: vector<vector<int>> levelOrderBottom(TreeNode* root) { vector<vector<int>> vv; if (root == nullptr) return vv; queue<TreeNode*> q; q.push(root); while (!q.empty()) { vector<int> v; int sz = q.size(); while (sz--) { TreeNode* front = q.front(); v.push_back(front->val); q.pop(); if (front->left) q.push(front->left); if (front->right) q.push(front->right); } vv.push_back(v); } reverse(vv.begin(),vv.end()); return vv; } };
2.4 二叉树的最近公共祖先
题目分析:
思路一使用Find代码:
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: bool Find(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* x){ if(root == nullptr){ return false; } return root == x || Find(root->left,x) || Find(root->right,x); } TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) { if(root == nullptr){ return nullptr; } if(root == p || root == q){ return root; } bool pInLeft, pInRight, qInLeft, qInRight; pInLeft = Find(root->left, p); pInRight = !pInLeft; qInLeft = Find(root->left, q); qInRight = !qInLeft; if((pInLeft && qInRight) || (pInRight && qInLeft)){ return root; }else if(pInLeft && qInLeft){ return lowestCommonAncestor(root->left, p, q); }else{ return lowestCommonAncestor(root->right, p, q); } } };思路二使用FindWay代码:
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: bool FindWay(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* x, stack<TreeNode*>& st){ if(root == nullptr){ return false; } st.push(root); if(root == x){ return true; } if(FindWay(root->left, x, st)){ return true; } if(FindWay(root->right, x, st)){ return true; } st.pop(); return false; } TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) { stack<TreeNode*> pPath; stack<TreeNode*> qPath; FindWay(root, p, pPath); FindWay(root, q, qPath); while(pPath.size() != qPath.size()){ if(pPath.size() > qPath.size()){ pPath.pop(); } else{ qPath.pop(); } } while(pPath.top() != qPath.top()){ pPath.pop(); qPath.pop(); } return pPath.top(); } };
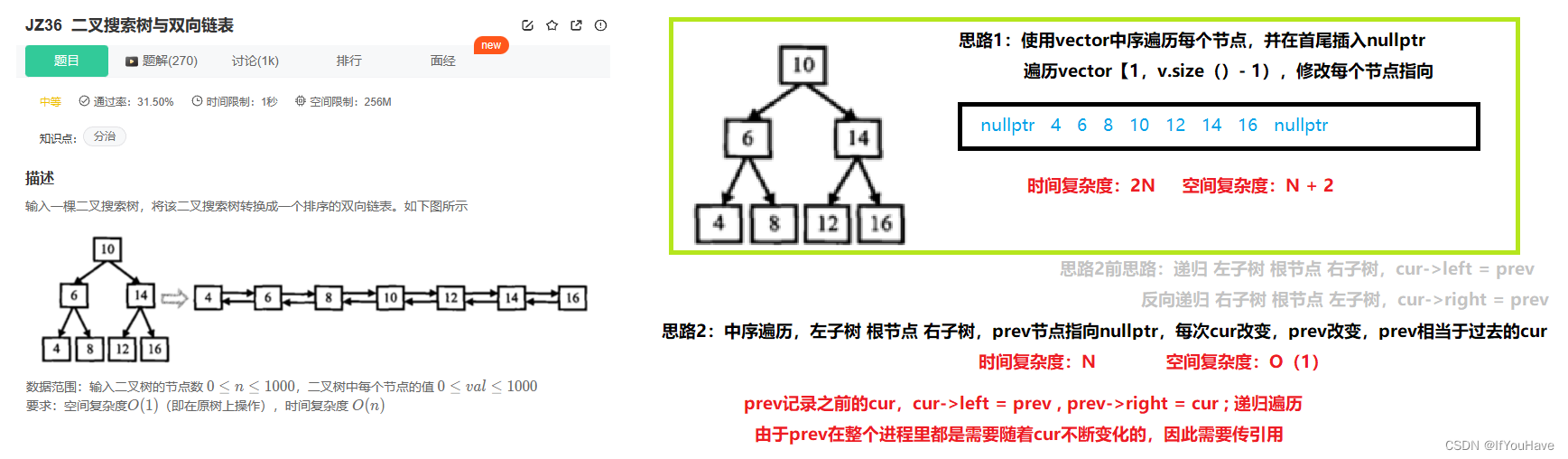
2.5 二叉搜索树及双向链表
题目分析:
思路一代码:
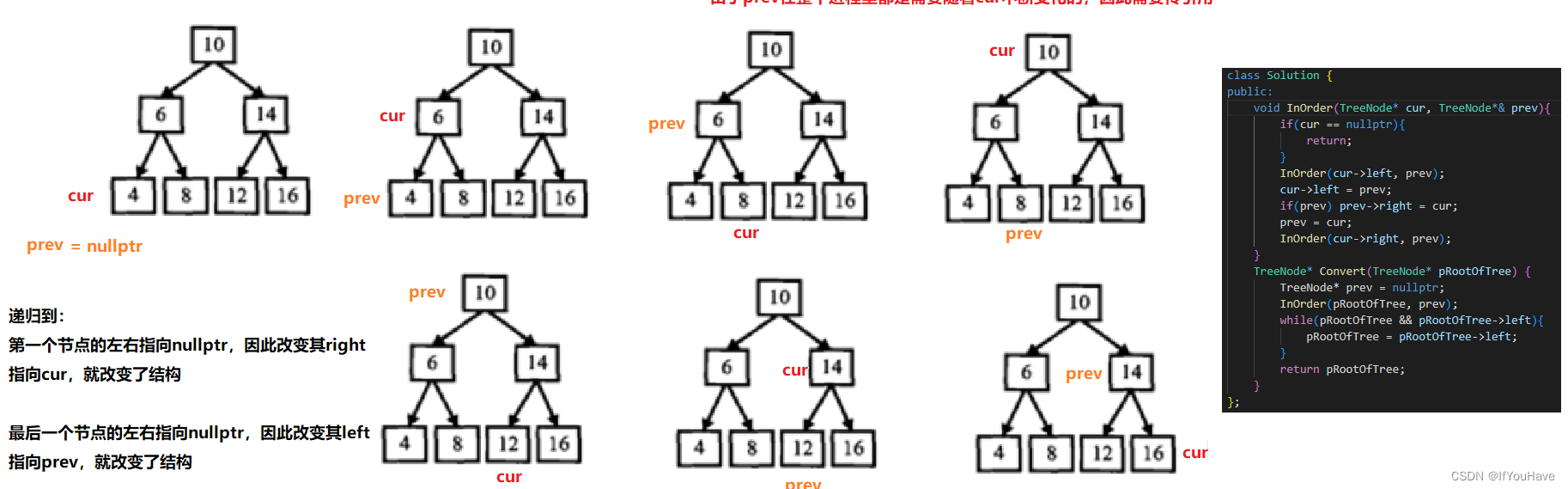
/* struct TreeNode { int val; struct TreeNode *left; struct TreeNode *right; TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) { } };*/ /* #include <vector> class Solution { public: void InOrder(TreeNode* root,vector<TreeNode*>& vt){ if(root == nullptr){ return; } InOrder(root->left,vt); vt.push_back(root); InOrder(root->right,vt); } TreeNode* Convert(TreeNode* pRootOfTree) { vector<TreeNode*> vt; vt.push_back(nullptr); InOrder(pRootOfTree,vt); vt.push_back(nullptr); for(size_t i = 1; i < vt.size() - 1; ++i){ vt[i]->left = vt[i-1]; vt[i]->right = vt[i+1]; } return vt[1]; } };思路二代码:
/* struct TreeNode { int val; struct TreeNode *left; struct TreeNode *right; TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) { } };*/ #include <vector> class Solution { public: void InOrder(TreeNode* cur,TreeNode*& prev){ if(cur == nullptr){ return; } InOrder(cur->left,prev); cur->left = prev; if(prev) prev->right = cur; prev = cur; InOrder(cur->right,prev); } TreeNode* Convert(TreeNode* pRootOfTree) { TreeNode* prev = nullptr; InOrder(pRootOfTree, prev); while(pRootOfTree && pRootOfTree->left){ pRootOfTree = pRootOfTree->left; } return pRootOfTree; } };
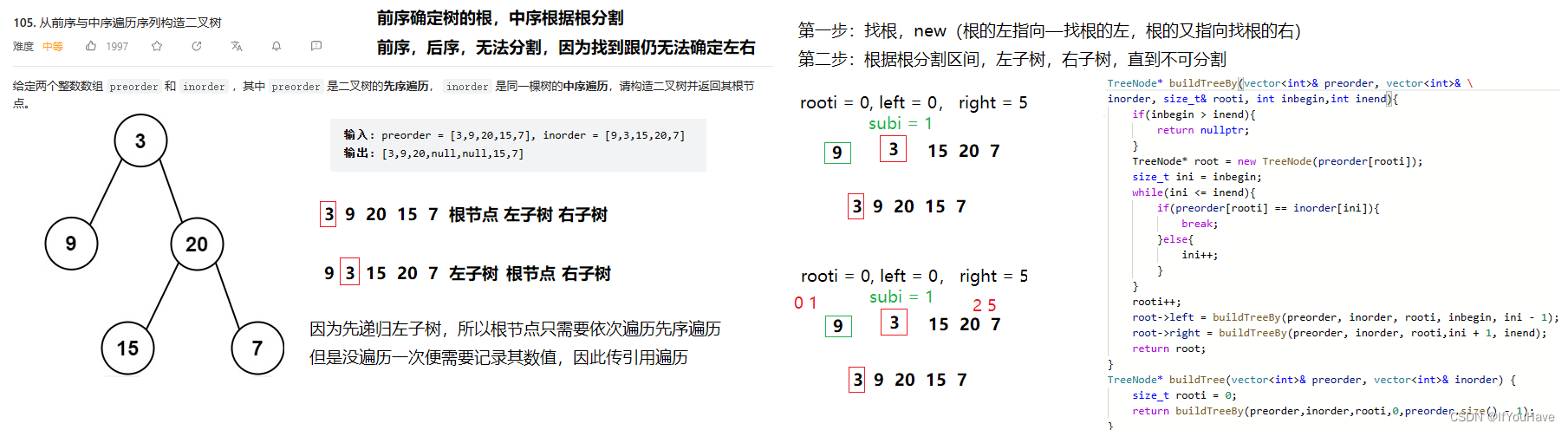
2.6 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
题目分析:
代码:
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: TreeNode* buildTreeBy(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder, size_t& rooti, int inbegin,int inend){ if(inbegin > inend){ return nullptr; } TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(preorder[rooti]); size_t ini = inbegin; while(ini <= inend){ if(preorder[rooti] == inorder[ini]){ break; }else{ ini++; } } rooti++; root->left = buildTreeBy(preorder, inorder, rooti, inbegin, ini - 1); root->right = buildTreeBy(preorder, inorder, rooti,ini + 1, inend); return root; } TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder) { size_t rooti = 0; return buildTreeBy(preorder,inorder,rooti,0,preorder.size() - 1); } };
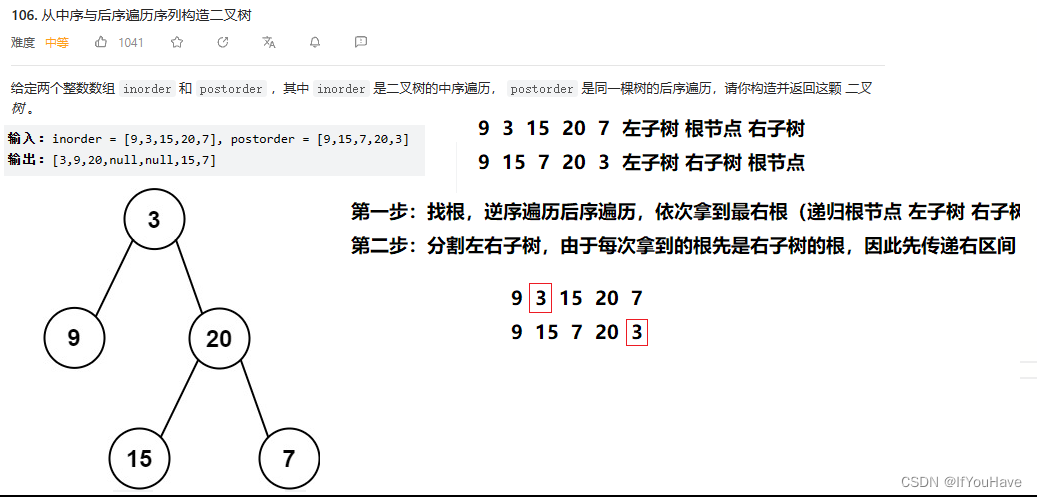
2.7 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
题目分析:
代码:
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: TreeNode* buildTreeBy(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder, size_t& rooti, int inbegin, int inend){ if(inbegin > inend){ return nullptr; } TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(postorder[rooti--]); int ini = inbegin; while(ini <= inend){ if(inorder[ini] == root->val){ break; } ++ini; } root->right = buildTreeBy(inorder,postorder,rooti,ini + 1,inend); root->left = buildTreeBy(inorder,postorder,rooti,inbegin,ini-1); return root; } TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder) { size_t rooti = postorder.size() - 1; return buildTreeBy(inorder,postorder,rooti,0,inorder.size() - 1); } };
3、非递归实现二叉树遍历
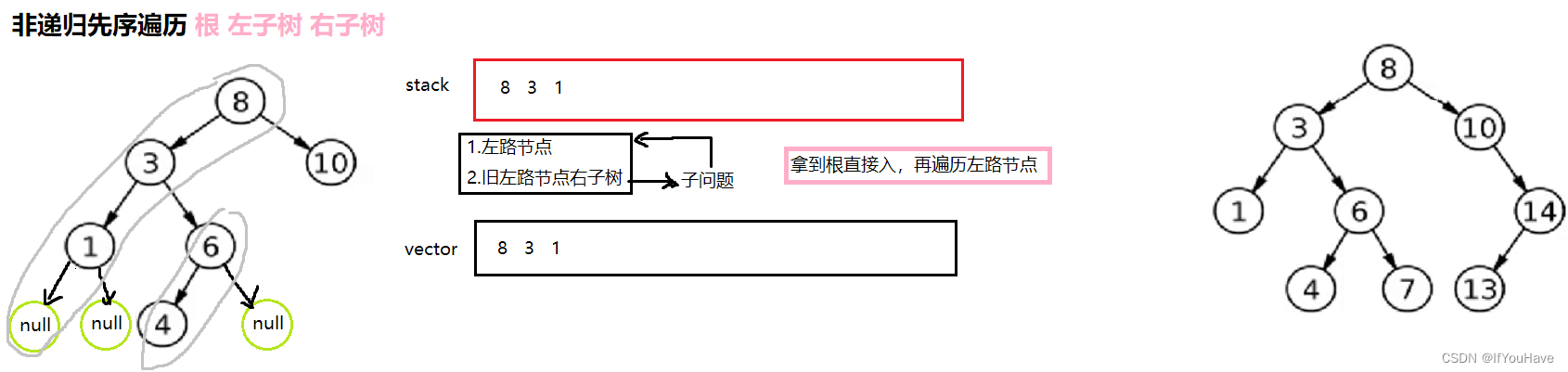
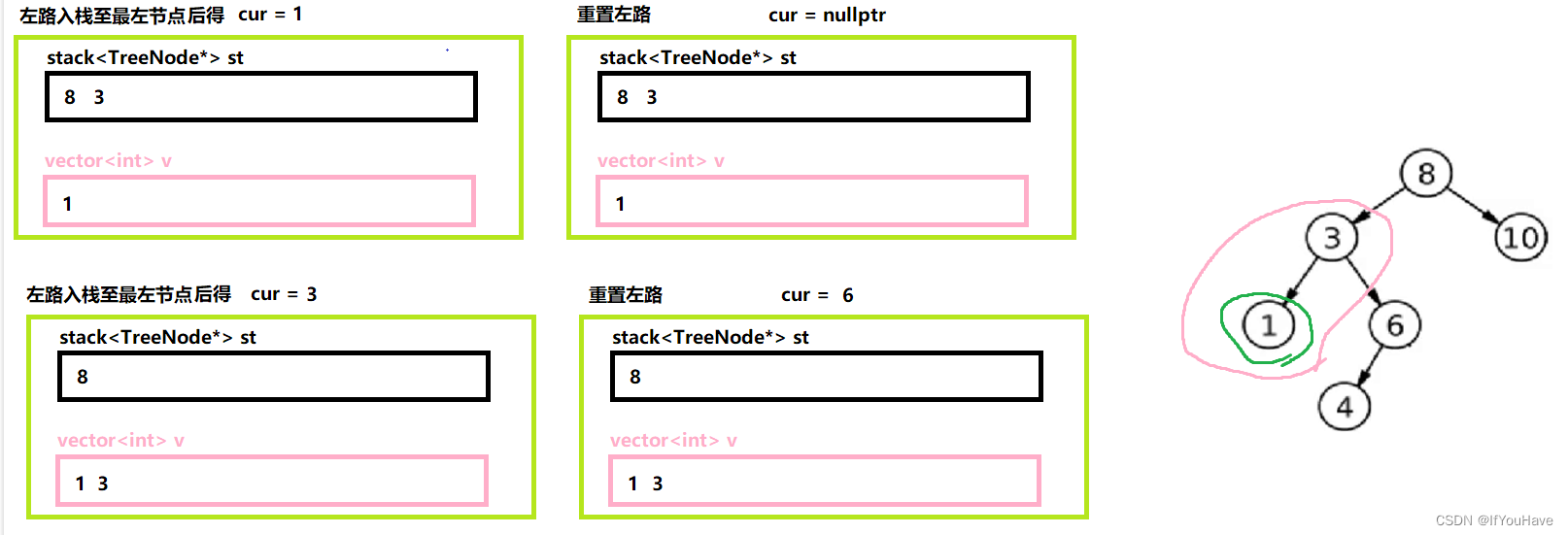
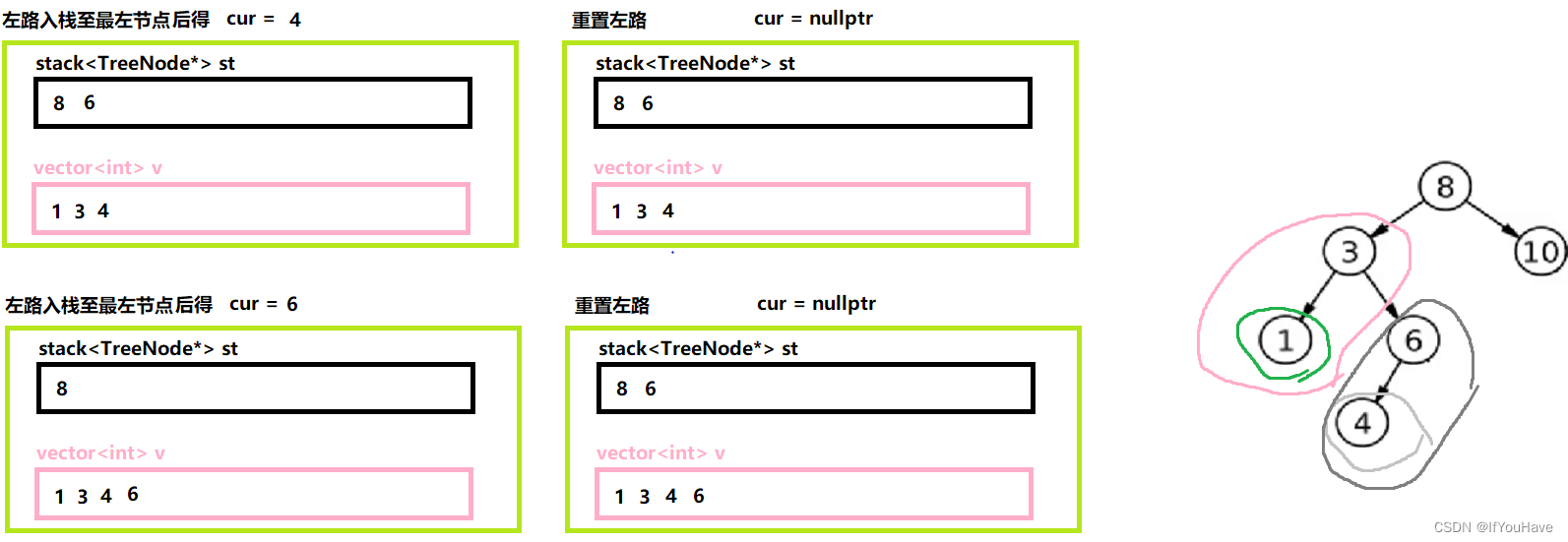
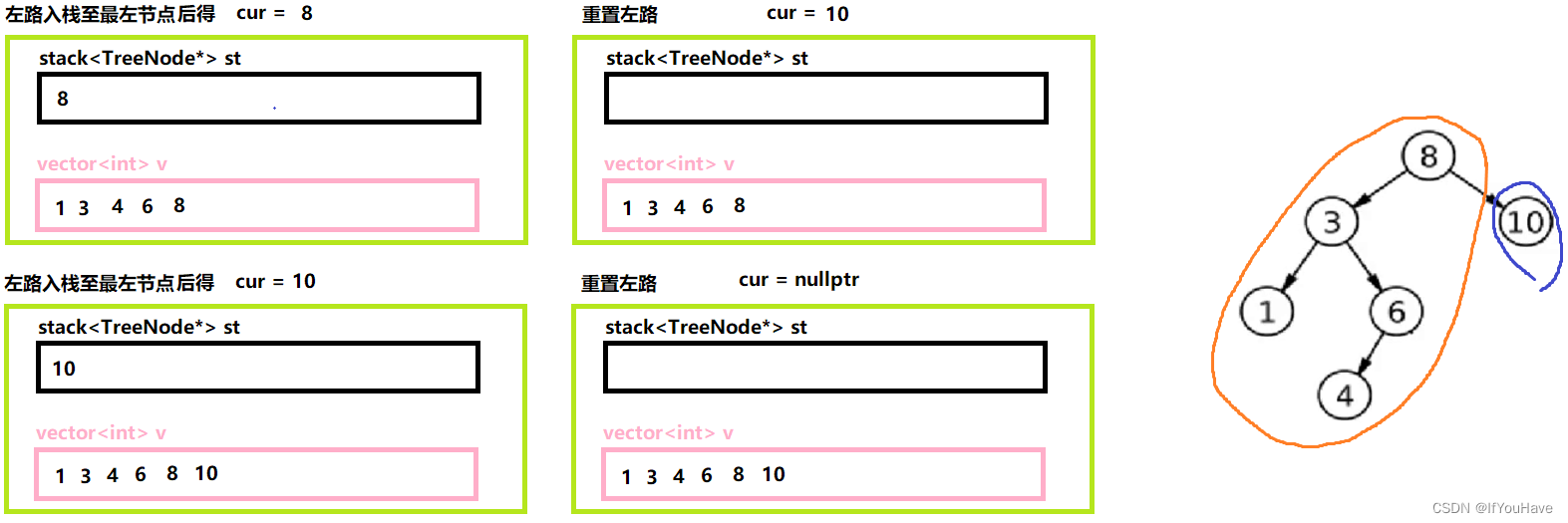
3.1 非递归前序遍历
图解分析:
代码:
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} * }; */ #include<vector> class Solution { public: vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) { vector<int> v; stack<TreeNode*> st; TreeNode* cur = root; while(cur || !st.empty()){ //左路节点 while(cur){ v.push_back(cur->val); st.push(cur); cur = cur->left; } //重置左路节点,为其原左路节点的右子树 cur = st.top(); st.pop(); cur = cur->right; } return v; } };
3.2 非递归实现中序遍历
图解分析:
代码:
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) { vector<int> v; stack<TreeNode*> st; TreeNode* cur = root; while(cur || !st.empty()){ while(cur){ st.push(cur); cur = cur->left; } cur = st.top(); st.pop(); v.push_back(cur->val); cur = cur->right; } return v; } };
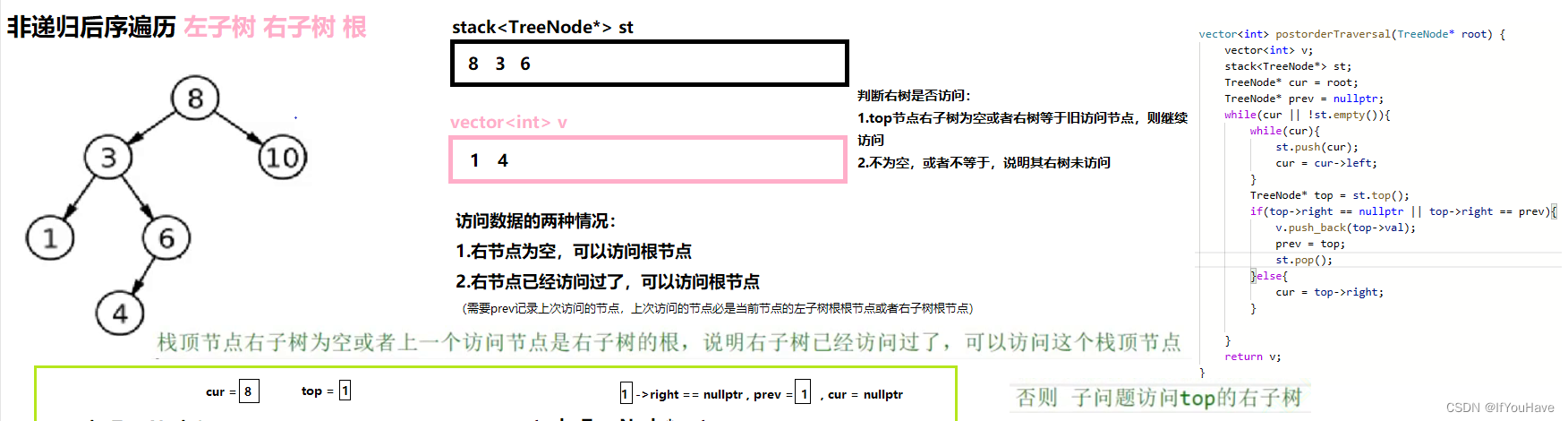
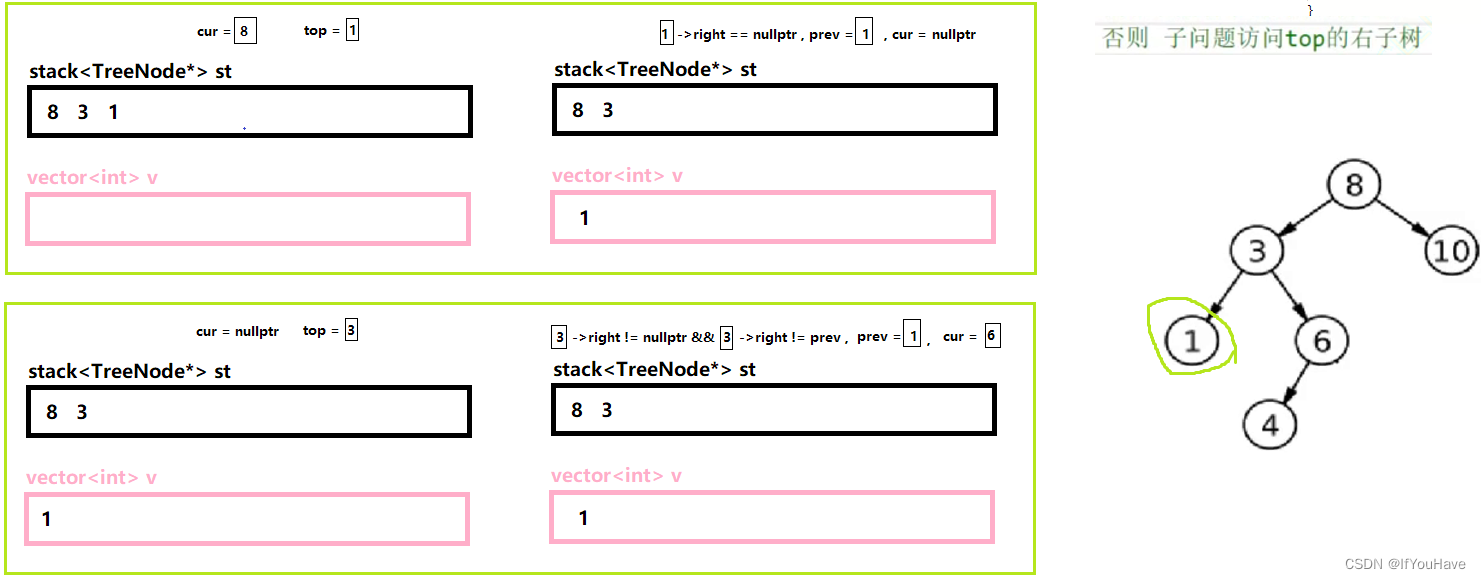
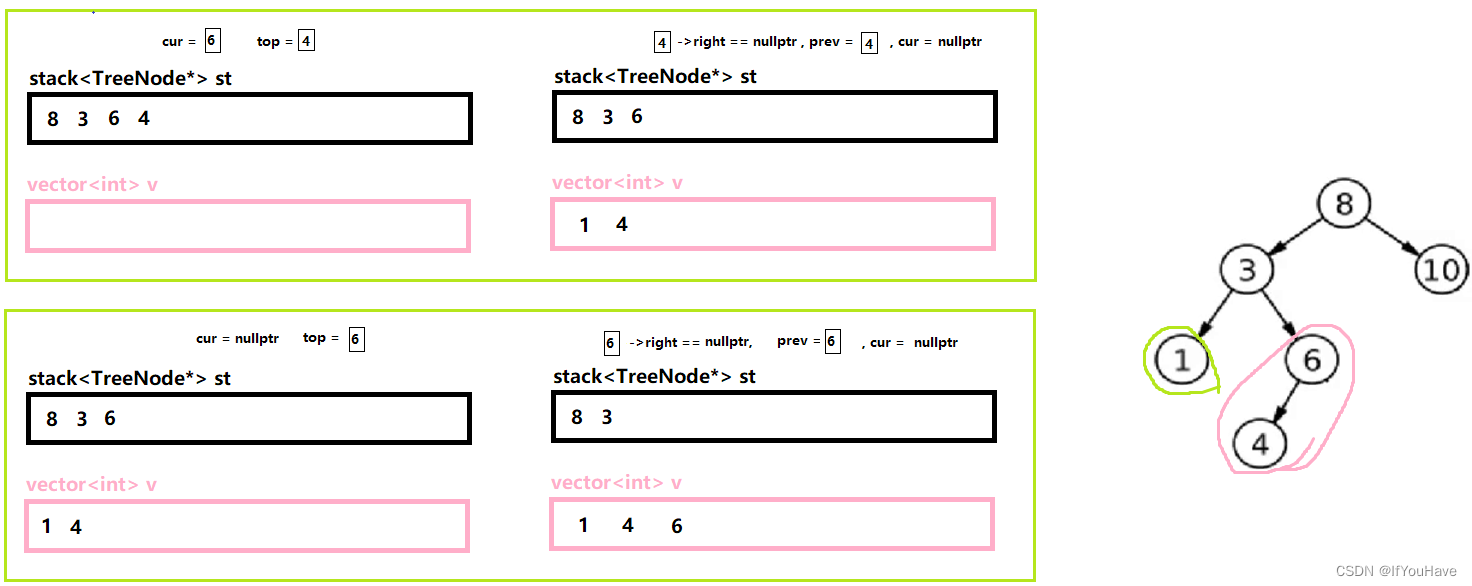
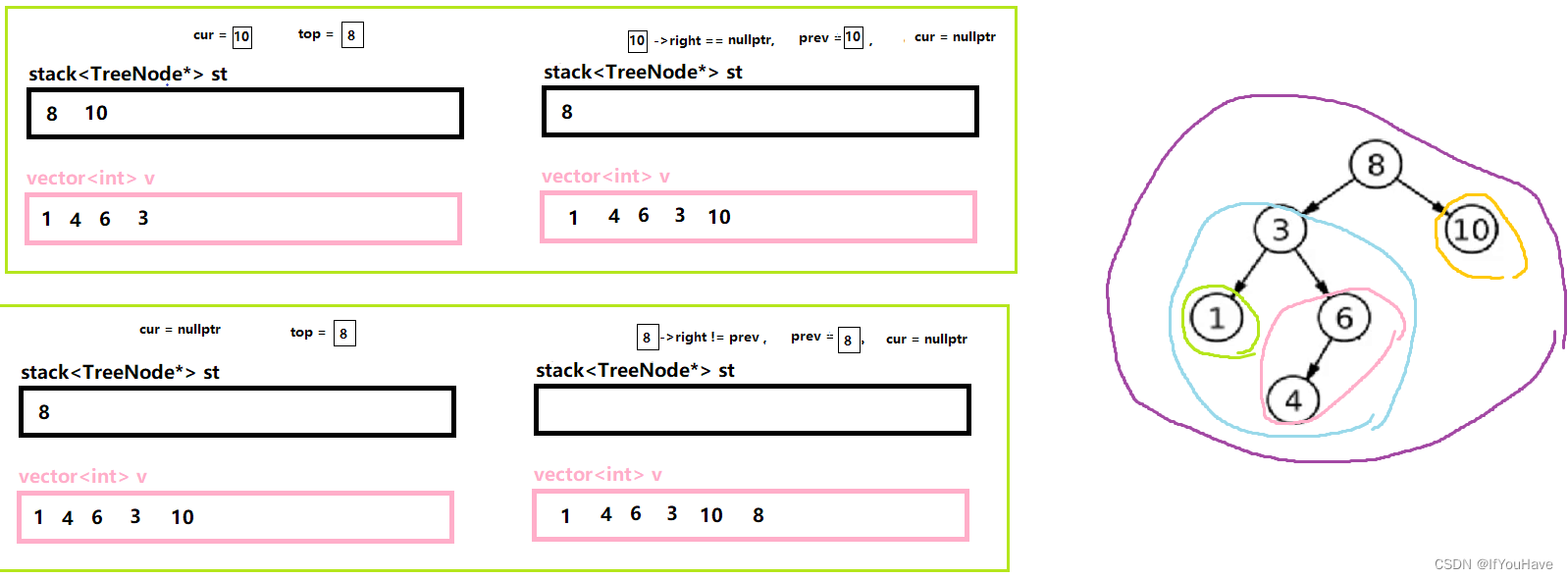
3.3 非递归实现后序遍历
图解分析:
代码:
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) { vector<int> v; stack<TreeNode*> st; TreeNode* cur = root; TreeNode* prev = nullptr; while(cur || !st.empty()){ while(cur){ st.push(cur); cur = cur->left; } TreeNode* top = st.top(); if(top->right == nullptr || top->right == prev){ v.push_back(top->val); prev = top; st.pop(); }else{ cur = top->right; } } return v; } };





























 1994
1994











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








