setContentView中的源码探索(未修订)
- PhoneWindow是window的子类
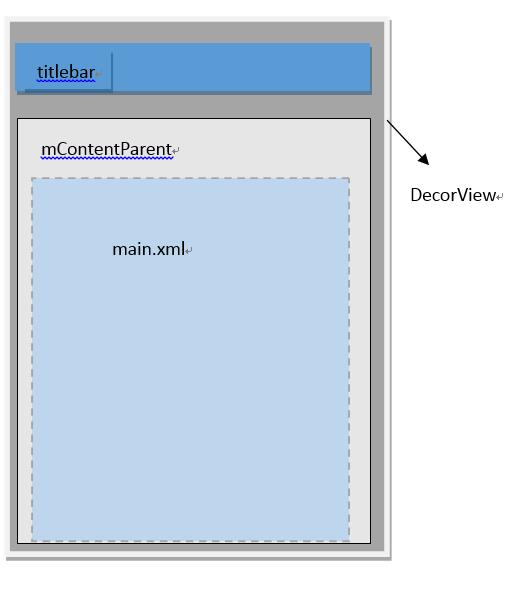
- DecorView是整个ViewTree的最顶层View
- DecorView和加载了我们提供的布局
- ViewRootImpl则负责渲染视图,WindowManager和DecorView的纽带
基于android 25源码进行探索,先从setContentView中进行探索
public void setContentView(@LayoutRes int layoutResID) {
getWindow().setContentView(layoutResID);
initWindowDecorActionBar();
}
public Window getWindow() {
return mWindow;
}
private Window mWindow;可以看到主要是从getwindow调用的方法,而getWindow就直接返回了一个window,可以看出window就是一个抽象类,我们的找出真正的实现类,用AS搜索了一下,看到在attach方法中找了实现类
final void attach(...) {
attachBaseContext(context);
mFragments.attachHost(null /*parent*/);
mWindow = new PhoneWindow(this, window);
mWindow.setWindowControllerCallback(this);
mWindow.setCallback(this);
mWindow.setOnWindowDismissedCallback(this);
mWindow.getLayoutInflater().setPrivateFactory(this);
...
mWindow.setWindowManager(
(WindowManager)context.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE),
mToken, mComponent.flattenToString(),
(info.flags & ActivityInfo.FLAG_HARDWARE_ACCELERATED) != 0);
if (mParent != null) {
mWindow.setContainer(mParent.getWindow());
}
mWindowManager = mWindow.getWindowManager();
}PhoneWindow就是window的实现类,接着我们就重点讲解这里,因为就是这里把我们的View给填充进入了
public PhoneWindow(Context context, Window preservedWindow) {
this(context);
...
if (preservedWindow != null) {
mDecor = (DecorView) preservedWindow.getDecorView();
mElevation = preservedWindow.getElevation();
...
}
...
}
public final View getDecorView() {
if (mDecor == null || mForceDecorInstall) {
installDecor();
}
return mDecor;
}
private void installDecor() {
if (mDecor == null) {
mDecor = generateDecor(-1);
} else {
mDecor.setWindow(this);
}
if (mContentParent == null) {
mContentParent = generateLayout(mDecor);
final DecorContentParent decorContentParent = (DecorContentParent) mDecor.findViewById(
R.id.decor_content_parent);
if (decorContentParent != null) {
mDecorContentParent = decorContentParent;
mDecorContentParent.setWindowCallback(getCallback());
if (mDecorContentParent.getTitle() == null) {
mDecorContentParent.setWindowTitle(mTitle);
}
} else {
mTitleView = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.title);
if (mTitleView != null) {
if ((getLocalFeatures() & (1 << FEATURE_NO_TITLE)) != 0) {
final View titleContainer = findViewById(R.id.title_container);
if (titleContainer != null) {
titleContainer.setVisibility(View.GONE);
} else {
mTitleView.setVisibility(View.GONE);
}
mContentParent.setForeground(null);
} else {
mTitleView.setText(mTitle);
}
}
}
if (mDecor.getBackground() == null && mBackgroundFallbackResource != 0) {
mDecor.setBackgroundFallback(mBackgroundFallbackResource);
}
}PhoneWindow构造方法创建了DecorView,而我前面所说DecorView是整个ViewTree的最顶层View,installDecor中也设置了标题栏和内容
generateDecor
protected DecorView generateDecor(int featureId) {
...
return new DecorView(context, featureId, this, getAttributes());
}我们在看看具体是怎么填充我们提供的View的
generateLayout
protected ViewGroup generateLayout(DecorView decor) {
...
mDecor.startChanging();
mDecor.onResourcesLoaded(mLayoutInflater, layoutResource);
...
}
void onResourcesLoaded(LayoutInflater inflater, int layoutResource) {
mDecorCaptionView = createDecorCaptionView(inflater);
//加载layoutResource
final View root = inflater.inflate(layoutResource, null);
if (mDecorCaptionView != null) {
if (mDecorCaptionView.getParent() == null) {
addView(mDecorCaptionView,
new ViewGroup.LayoutParams(MATCH_PARENT, MATCH_PARENT));
}
mDecorCaptionView.addView(root,
new ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams(MATCH_PARENT, MATCH_PARENT));
} else {
// Put it below the color views.
addView(root, 0, new ViewGroup.LayoutParams(MATCH_PARENT, MATCH_PARENT));
}
mContentRoot = (ViewGroup) root;
initializeElevation();
}
从generateLayout中的onResourcesLoaded方法中,终于看到了我们想看到的东西。
到目前为止,通过setContentView方法,创建了DecorView和加载了我们提供的布局,但是我们并没有被window添加
Window添加DecorView
每一个Activity组件都有一个关联的Window对象,用来描述一个应用程序窗口。每一个应用程序窗口内部又包含有一个View对象,用来描述应用程序窗口的视图。
首先,在ActivityThread#handleLaunchActivity中启动Activity,在这里面会调用到Activity#onCreate方法,从而完成上面所述的DecorView创建动作,当onCreate()方法执行完毕,在handleLaunchActivity方法会继续调用到ActivityThread#handleResumeActivity方法,我们看看这个方法的源码:
final void handleResumeActivity(...) {
...
//这里会调用到onResume()方法
r = performResumeActivity(token, clearHide, reason);
...
final Activity a = r.activity;
r.window = r.activity.getWindow();// 获得window对象
View decor = r.window.getDecorView();// 获得DecorView对象
decor.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE);
ViewManager wm = a.getWindowManager(); // 获得windowManager对象
WindowManager.LayoutParams l = r.window.getAttributes();
a.mDecor = decor;
l.type = WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_BASE_APPLICATION;
l.softInputMode |= forwardBit;
if (a.mVisibleFromClient && !a.mWindowAdded) {
a.mWindowAdded = true;
wm.addView(decor, l);// 调用addView方法
}
}
}就在这个方法里,终于看到windowManager将decorView添加进去了,当你准备点进去看addView 方法时,你没猜错它(ViewManager)又TM是抽象或者接口…windowManager都是抽象类,那到底谁实现了他呢…
还记得我为啥说每一个Activity组件都有一个关联的Window对象,请回到我上面说的activity->attach
//设置WindowManager
mWindow.setWindowManager(
(WindowManager)context.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE),
mToken, mComponent.flattenToString(),
(info.flags & ActivityInfo.FLAG_HARDWARE_ACCELERATED) != 0);
public void setWindowManager(WindowManager wm, IBinder appToken, String appName,
boolean hardwareAccelerated) {
...
if (wm == null) {
wm = (WindowManager)mContext.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE);
}
mWindowManager = ((WindowManagerImpl)wm).createLocalWindowManager(this);
}看到这里知道是谁了吧,就是他 WindowManagerImpl,赶紧看看他的addView方法中写了啥
WindowManagerImpl->addView
@Override
public void addView(@NonNull View view, @NonNull ViewGroup.LayoutParams params) {
applyDefaultToken(params);
mGlobal.addView(view, params, mContext.getDisplay(), mParentWindow);
}
public void addView(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params,
Display display, Window parentWindow) {
final WindowManager.LayoutParams wparams = (WindowManager.LayoutParams) params;
//创建ViewRootImpl
root = new ViewRootImpl(view.getContext(), display);
view.setLayoutParams(wparams);
mViews.add(view);
mRoots.add(root);
mParams.add(wparams);
//ViewRootImpl.setView
root.setView(view, wparams, panelParentView);
}
ViewRootImpl#setView方法,并把DecorView作为参数传递进去,在这个方法内部,会通过跨进程的方式向WMS(WindowManagerService)发起一个调用,从而将DecorView最终添加到Window上,在这个过程中,ViewRootImpl、DecorView和WMS会彼此关联,至于详细过程这里不展开来说了
ViewRootImpl对他不熟悉的可以看看 Android中的ViewRootImpl类源码解析






















 3303
3303

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








