1527. Tiling a Grid With Dominoes
Description
We wish to tile a grid 4 units high and N units long with rectangles (dominoes) 2 units by one unit (in either orientation). For example, the figure shows the five different ways that a grid 4 units high and 2 units wide may be tiled.
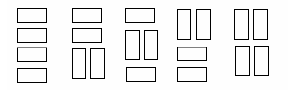
Write a program that takes as input the width, W , of the grid and outputs the number of different ways to tile a 4-by-W grid.
Input
The first line of input contains a single integer N , (1<=N<=1000) which is the number of datasets that follow.
Each dataset contains a single decimal integer, the width, W , of the grid for this problem instance.
Output
For each problem instance, there is one line of output: The problem instance number as a decimal integer (start counting at one), a single space and the number of tilings of a 4-by-W grid. The values of W will be chosen so the count will fit in a 32-bit integer.
Sample Input
3
2
3
7
Sample Output
1 5
2 11
3 781
一. 题意理解
现有长为 2,宽为 1 的多米诺骨牌,给定一个长为 n,宽为 4 的矩形区域,要求使用多米诺骨牌完美覆盖这个区域,并且算出覆盖的方法数。
二. 解题思路
对于这种完美覆盖问题,有一种比较通用的方法:列出所有的基本状态,再考虑状态之间的转换关系。在列举的时候,我们的思考要有方向性,要有一个特定的规则。如若我们想到什么列什么,很容易漏掉一些情况。我们不妨用如下的规则列举:用二维数组 f[i][j]表示前 i 列已经完美覆盖,第 i+1列的状态为 j,j一共有如下5中情况:


解释:我们用4位数表示每个状态,第一行有突出,则为1;没有突出,则为0。比如,j=4的情况,第一、第四行没有突出,二、三行有突出,它的状态就是0110。至于j等于几对应什么状态则无所谓。接下来我们来找状态转移方程。
以 f[i][0]为例。它的前 i 列铺满了,第 j+1 列没有突出。它可以由 f[i-1][0]得出(补上两块构成的 4×1 区域);可以由 f[i-1][1]得出(右下角补上一块) ;可以由 f[i-1][2]得出(右上角补上一块);可以由 f[i-1][3]
得出(中间补上一块) ;无法由 f[i-1][4]得出。注意特殊情况:可以直接由 f[n-2]得出(补上 4 块构成的 4×4 区域)。其他状态也是如此递推。注意f[0][0]为1!状态转移方程如下:
• f[i][0] = f[i-1][0] + f[i-1][1] + f[i-1][2] + f[i-1][3] + f[i-2][0]
• f[i][1] = f[i-1][0] + f[i-1][2]
• f[i][2] = f[i-1][0] + f[i-1][1]
• f[i][3] = f[i-1][0] + f[i-1][4]
• f[i][4] = f[i-1][3]
三. 代码实现
#include<iostream>
#include<string.h>
using namespace std;
int f[1005][5];
int Domi(int n) {
f[0][0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
f[i][0] = f[i - 1][0] + f[i - 1][1] + f[i - 1][2] + f[i - 1][3];
if (i > 1) f[i][0] += f[i - 2][0];
f[i][1] = f[i - 1][0] + f[i - 1][2];
f[i][2] = f[i - 1][0] + f[i - 1][1];
f[i][3] = f[i - 1][0] + f[i - 1][4];
f[i][4] = f[i - 1][3];
}
return f[n][0];
}
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
int counter = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
int num;
cin >> num;
memset(f, 0, sizeof(f));
cout << counter << " " << Domi(num) << endl;
counter++;
}
return 0;
}
四. 时间复杂度分析:算法的时间复杂度为O(n)。






















 687
687











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








