使用类型萃取的原因
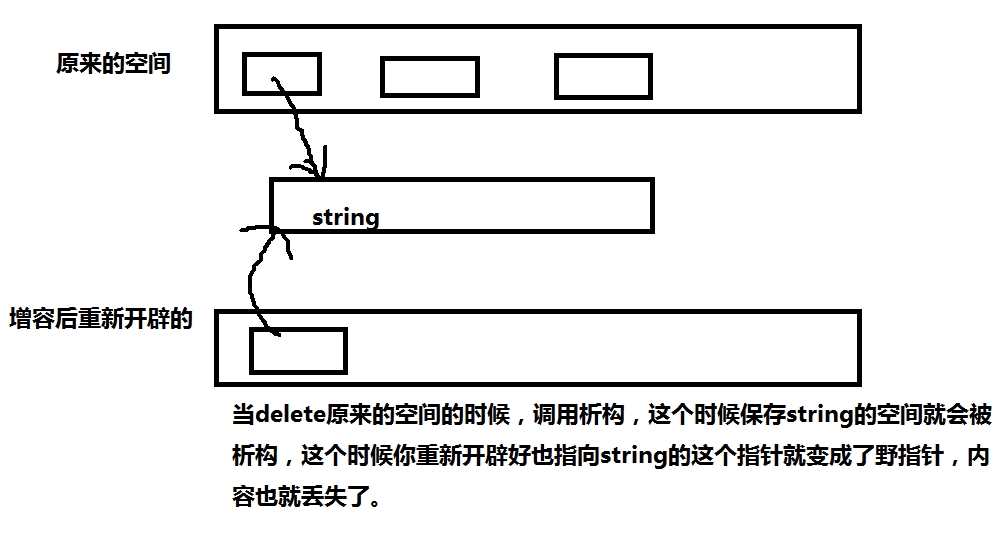
就是当你的顺序表是自定义类型,我们进行顺序表增容的时候,这个时候会出现一个问题,比如string类型,这个类型中有一个_buf与_ptr,当储存少于16个的时候这时会储存在_buf当中的,如果多于16个,那个会单独开辟空间,进行储存,这时拷贝的时候就是拷贝过去这个储存的地址而已,所以这样调用析构函数的时候,当增加容量的时候,这个时候会把储存string的那块空间进行释放。会造成数据丢失的问题。
所以,在这里面我们提到一个类型萃取的技巧,可以把自定义类型和内置类型的区分开,然后对自定义类型的使用for循环拷贝,对于内置类型的,采用memcpy的方式进行拷贝
#include<iostream>
#include<stdlib.h>
using namespace std;
//类型萃取
struct __truetype
{
bool get()
{
return true;
}
};
struct __falsetype
{
bool get()
{
return false;
}
};
template<typename T>
struct typetraits
{
typedef __falsetype __ispodtype;
};
template<>
struct typetraits<int >
{
typedef __truetype __ispodtype;
};
template<>
struct typetraits<char >
{
typedef __truetype __ispodtype;
};
template<>
struct typetraits<short >
{
typedef __truetype __ispodtype;
};
template<>
struct typetraits<bool >
{
typedef __truetype __ispodtype;
};
template<>
struct typetraits<unsigned int >
{
typedef __truetype __ispodtype;
};
template<>
struct typetraits<unsigned short >
{
typedef __truetype __ispodtype;
};
template<>
struct typetraits<unsigned long >
{
typedef __truetype __ispodtype;
};
template<>
struct typetraits<long >
{
typedef __truetype __ispodtype;
};
template<>
struct typetraits<long long >
{
typedef __truetype __ispodtype;
};
template<>
struct typetraits<unsigned long long >
{
typedef __truetype __ispodtype;
};
template<>
struct typetraits<long double >
{
typedef __truetype __ispodtype;
};
template<>
struct typetraits<double >
{
typedef __truetype __ispodtype;
};
template<>
struct typetraits<float >
{
typedef __truetype __ispodtype;
};
template<typename T>
void Copy(const T*src, T* dst, size_t size)
{
if (typetraits<T>::__ispodtype().get())
{
cout << "__truetype:" << typeid(T).name() << endl;
memcpy(dst, src, size*sizeof(T));
}
else
{
cout << "__falsetype:" << typeid(T).name() << endl;
for (size_t i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
dst[i] = src[i];
}
}
}
void test()
{
int a1[8] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 };
int a2[8] = { 9, 5, 6, 7, 8, 2, 2 };
Copy(a1, a2, 3);
cout << a2<<endl;
string c1[10] = {"123","7989465","456321","4561","4563"};
string c2[5] = {"654","312","a"};
Copy(c1, c2, 3);
}
int main()
{
test();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
在这里我们采用了模板的特化,这里使用了全特化,直接给int,double等内置类型做特化。
在这里我们设定内置类型是truetype,设置自定义类型是falsetype,然后我们通过不同的类型利用get()函数返回不同的布尔值,这样对内置类型采用memcp拷贝,对于非内置类型,采用for循环拷贝,这样就能实现我们想要的结果了。





















 1041
1041











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








